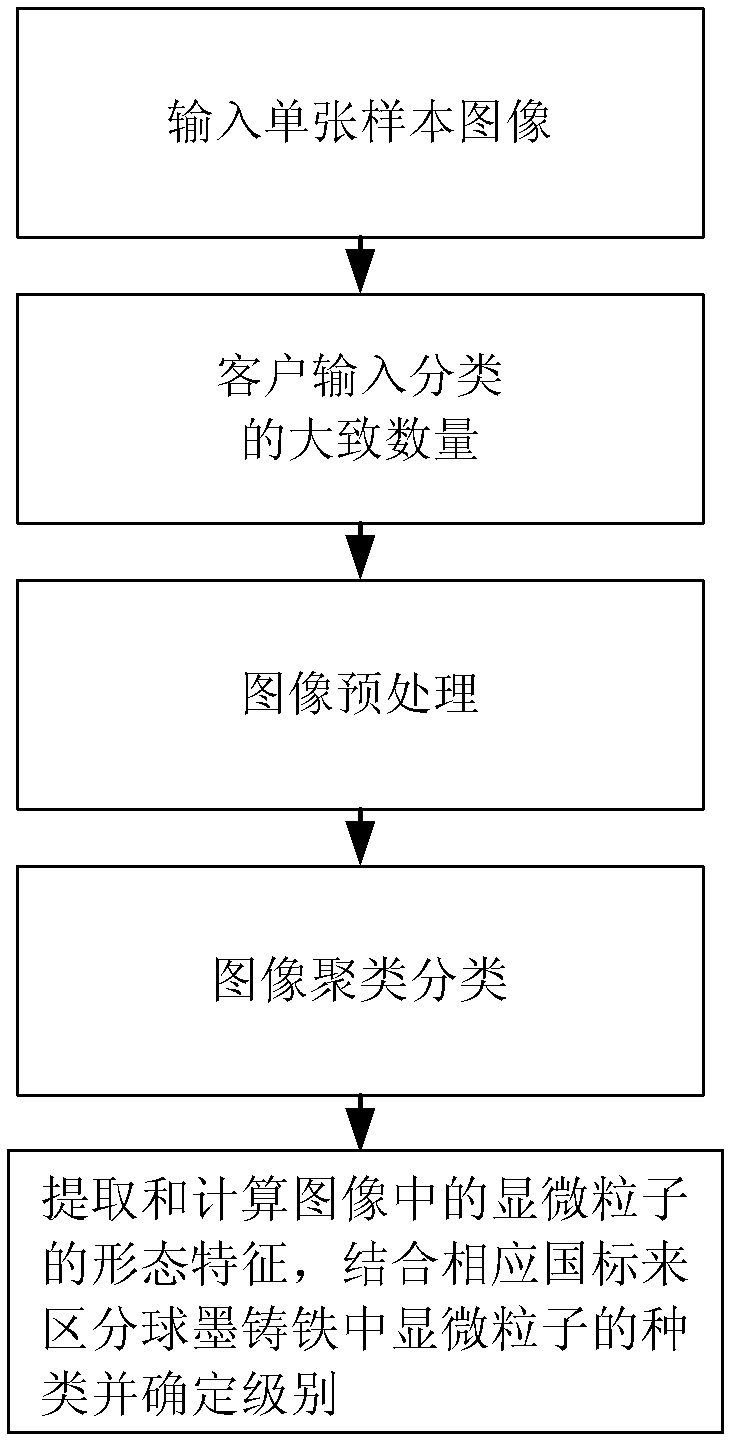
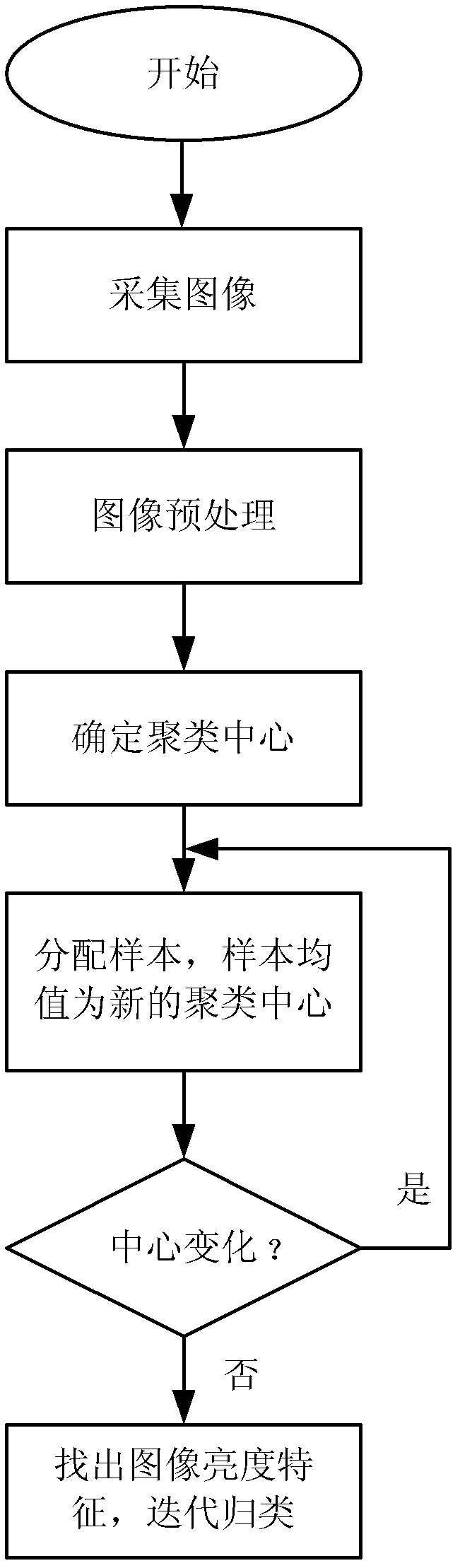
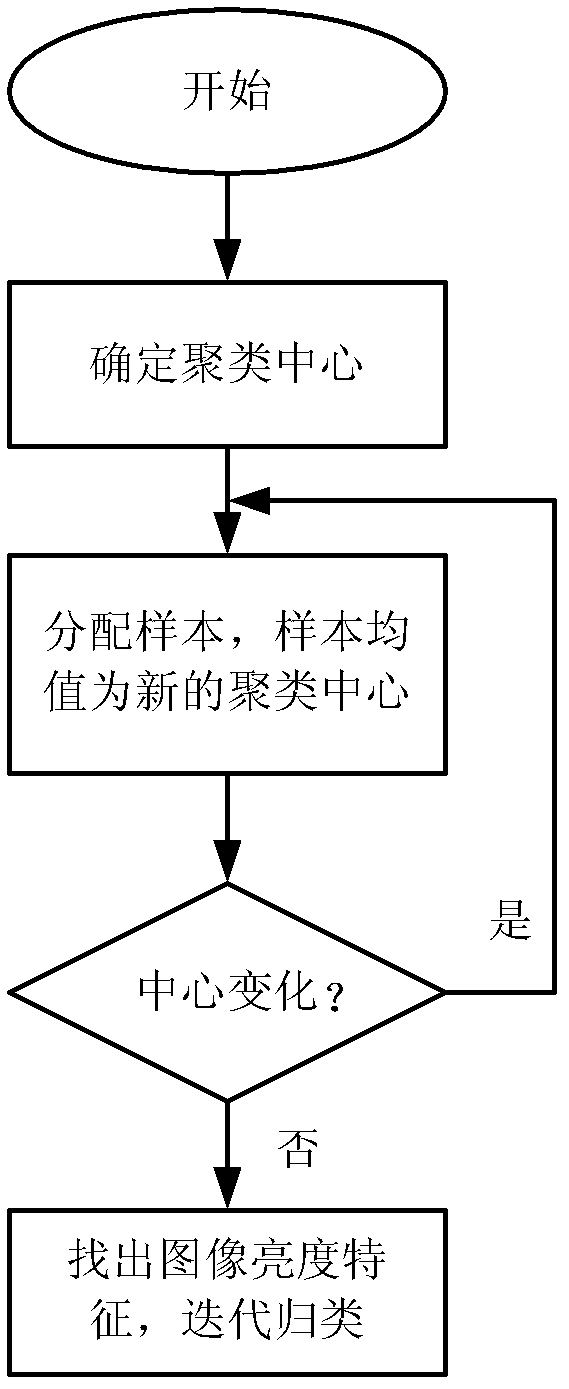
Automatic category rating method for microscopic particles in nodular cast iron
A nodular cast iron, automatic classification technology, applied in the direction of individual particle analysis, particle and sedimentation analysis, image data processing, etc., can solve the problems of inability to accurately identify and judge the name of the organization, lack of adaptability and accuracy, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] Automatic Classification and Grading of Microscopic Particles in Ductile Iron Sample 1
[0071] The first step is to collect images
[0072] The metallographic image of the tested nodular cast iron is collected through an optical microscope and a CCD camera. The resolution of the CCD camera used is 2 million pixels, and the USB interface is used for communication. Frames are saved as images in BMP format.
[0073] In the second step, the customer enters the estimated number of microparticle categories for classification
[0074] Considering the quantification of the metallographic structure rating of nodular cast iron, the estimated value of the microscopic particle cluster number for the classification input by the customer is K=2.
[0075] The third step, image preprocessing
[0076] The image collected in the first step is subjected to image preprocessing. The operation process is to grayscale the image first, then convert the three-channel image into a single-cha...
Embodiment 2
[0118] Automatic Classification and Grading of Microscopic Particles in Ductile Iron Sample 2
[0119] The first step is to collect images
[0120] Collect the metallographic image of the tested nodular cast iron sample 2 through an optical microscope and a CCD camera. The resolution of the CCD camera used is 3 million pixels, and the USB interface is used for communication. The frame rate of video collection is 31 frames per second, and the capture effect is better. A frame is saved as an image in JPG format.
[0121] In the second step, the customer enters the estimated number of microparticle categories for classification
[0122] Considering the quantification of metallographic structure rating of nodular cast iron, the estimated value of microscopic particle cluster number for customer input classification is K=3.
[0123] The third step, image preprocessing
[0124] The image collected in the first step is subjected to image preprocessing. The operation process is to ...
Embodiment 3
[0166] Automatic Classification and Grading of Microscopic Particles in Ductile Iron Sample 3
[0167] The first step is to collect images
[0168] Collect the metallographic image of the tested nodular cast iron sample 3 through an optical microscope and a CCD camera. The resolution of the CCD camera used is 1.3 million pixels, and the USB interface is used for communication. The frame rate of the video collection is 11 frames per second, and the capture effect is better. A frame is saved as an image in BMP format.
[0169] In the second step, the customer enters the estimated number of microparticle categories for classification
[0170] Considering the quantification of metallographic structure rating of nodular cast iron, the estimated value of microscopic particle cluster number for customer input classification is K=3.
[0171] The third step, image preprocessing
[0172] The image collected in the first step is subjected to image preprocessing. The operation process ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com