Thin ply laminates
A thin-layer, composite material technology, applied in the field of fiber composite materials, can solve problems such as high cost, unreliability, and reduced in-plane characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
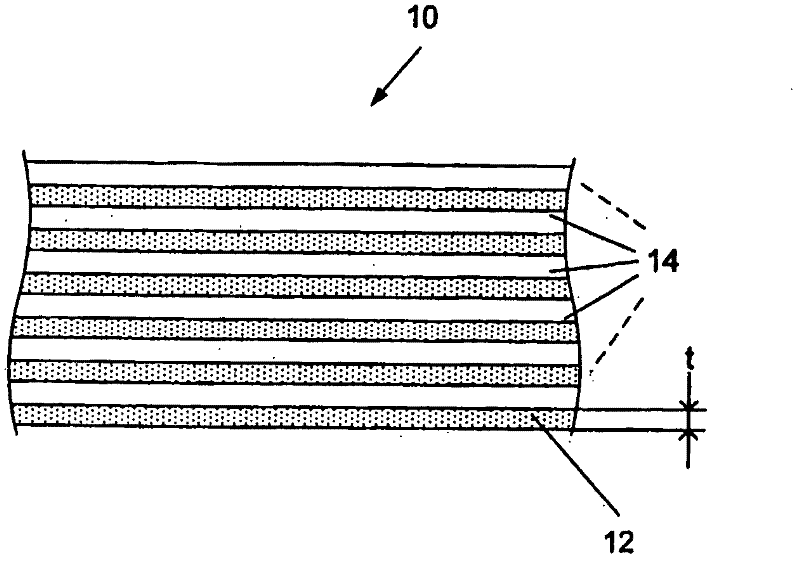
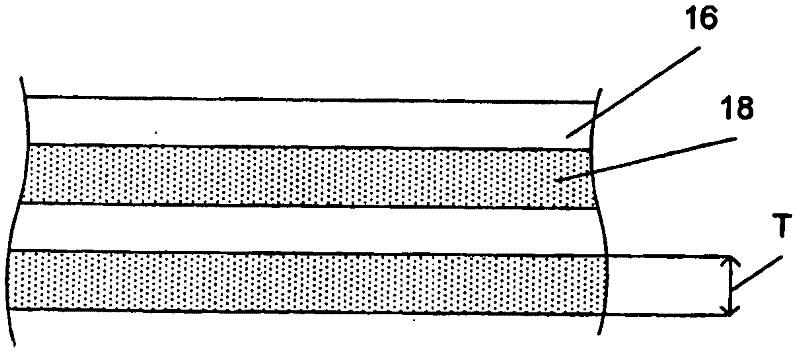
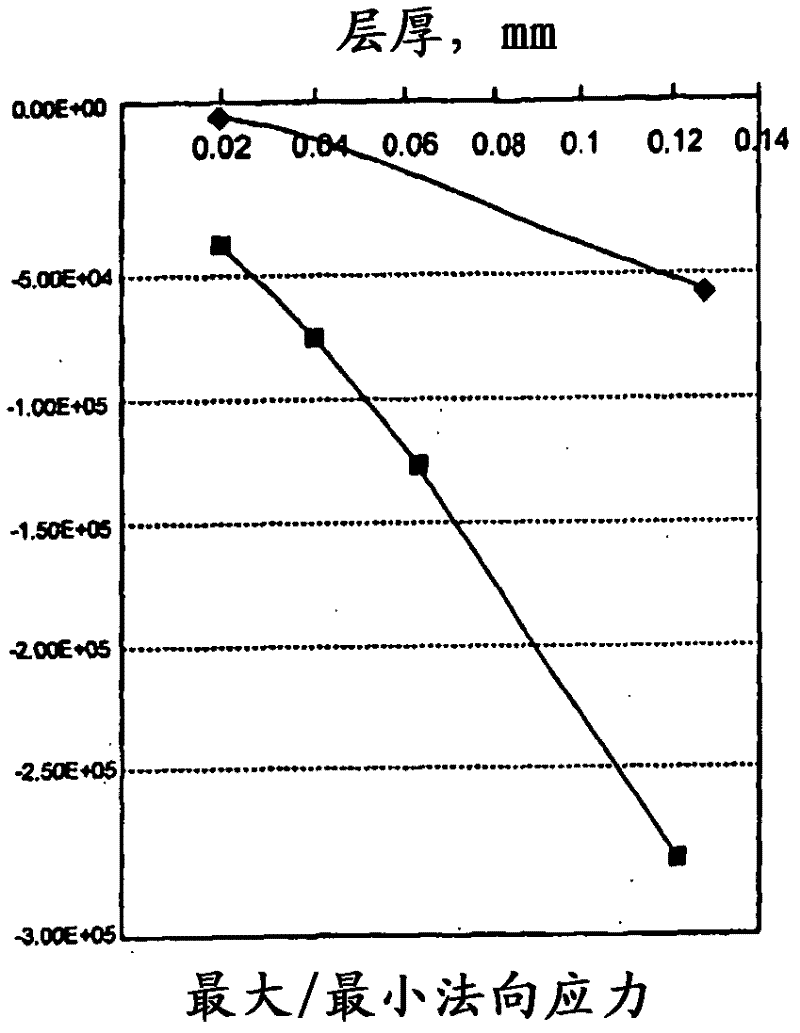
[0038] Example 1: An example of the invention comprising a combination of a thick layer with a thickness of 0.12 mm and a thin layer with a thickness of 0.02 mm. this is in Figure 6A is shown as having a thin layer 21 and a thick layer 23 . and, Figure 6B The sublaminate 25 in can be a mix of thick and thin, with one thick layer [0] 27 and one thin layer [90] 29 . The total thickness of the sub-laminate module can be 0.12mm+0.02mm=0.14mm, then the percentage of [0] should be 0.12 / 0.14=86%. The use of such sub-laminates in the construction of masts or booms will provide a highly anisotropic structure with a rigidity not achievable using only thick layers of ordinary laminates. For common laminates, repeating modules for thick layers must have 9 layers [0] and 1 layer [90]. The thickness of the total sub-laminate module will be 1.20mm, where the percentage of [0] is equal to 90%. The design stacks 9 layers of [0] together, which is a poor design from a rigid standpoint. ...
example 2
[0039] Example 2: When a higher percentage of [0] is desired, there can be two thick layers of [0] followed by a thin layer of [90]. At this time, the percentage of [0] should be 0.24 / 0.26=92%. In a three-directional sub-laminate module with two [0] and one [+ / -45], the [0] percentage is 0.24 / 0.28 = 86%. These two examples would allow a more rigid laminate for the mast or boom. This hybrid structure is also used in drive shafts, reeds and sporting goods (eg pole vault poles, hockey sticks, golf clubs, etc.).
example 3
[0040] Example 3: Another example of a thick and thin ply laminate is a three-way sub-laminate with one 0.12mm thick ply [0] and two 0.02mm angled plies [+ / -30] or [+ / - 45], such as [+30 / 0 / -30] or [+45 / 0 / -45] modules. The total sub-laminate has a thickness of 0.16mm and it can be done as a single step in the descent of the plies. Three-directional modules of any combination of thick and thin layers can be fabricated. This design flexibility enables products with significantly improved laminate properties and significant cost savings in manufacture.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com