Laminating manufacture method for symmetric laminated plate
A manufacturing method and laminated board technology, which is applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of few layup forms, no consideration of asymmetric deformation, and failure to meet the requirements for active control of CFPR mirrors, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
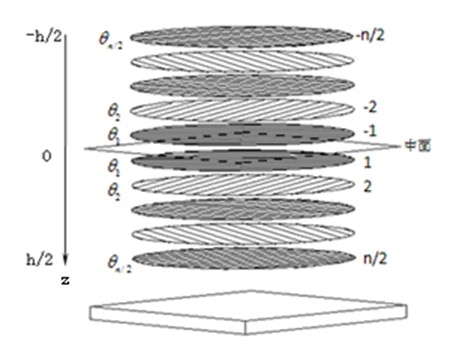
[0072] 1. In this embodiment, the carbon fiber reinforced polymer composite material adopts M40 / epoxy 648, and the engineering elastic constant of the one-way plate of this material is: E 1 =206GPa,E 2 =9.02GPa, v 1 =0.3, G 12 = 4.7 GPa. In addition, the fiber volume content v f =0.578, the total number of layers of the laminated board is 24 layers, the total thickness is 3mm, and the thickness of the single layer is the same; the laminated board adopts the form of symmetrical lay-up.
[0073] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0074] (1) On the premise that the number of single-layer groups is the largest, according to the total number of layers, determine the lay-up structure of several directional single-layers.
[0075]In order to verify the regularized stiffness coefficient method for the design of quasi-uniform laminates with bending stiffness, the following is a specific example to compare the uniformity of bending stiffness of symmetrical laminate...
Embodiment 2
[0113] Select the same carbon fiber reinforced polymer composite material as in Example 1, the same single-layer engineering elastic constant, the same lay-up form, and the same single-layer thickness, and set a 0° in the lay-up angle. For a symmetrical laminate with a total number of 30 layers, the number of single-layer groups m should be 15, and the number of oriented single layers p can be 3, 5, or 15. The quasi-isotropic and quasi-uniform symmetrical laminates are calculated using the regularized stiffness coefficient method The best ply sequence of p = 3 and 5, the exhaustive method is used, and the random sampling calculation method is used when p = 15. The calculation results are shown in Table 8.
[0114] Table 8 The optimal layup sequence under different directional single-ply numbers p
[0115] p
[0116] It can be seen from Table 8 that the target value Δ of the optimal ply sequence when p=15 is smaller than the target value of p=12 ply in Table 1, indi...
Embodiment 4
[0118] With reference to the conditions of Example 2, the optimal ply sequence of quasi-isotropic and quasi-uniform symmetrical laminates with a total number of layers of 36 layers of symmetrical laminates was calculated with the regularized stiffness coefficient method. For a symmetrical laminate with a total number of 36 layers, the number of single-layer groups m should be 18, and the number of directional single-layer p can be 3, 6, 9, 18, where p = 3, 6 and 9 use the exhaustive method, p =18, the random sampling calculation method is adopted, and the calculation results are shown in Table 9.
[0119] Table 9 The optimal layup sequence under different directional single-layer numbers p
[0120] p
[0121] It can be seen from Table 9 that the target value Δ of the optimal ply sequence when p=18 is smaller than the target value of p=15 ply in Table 8, indicating that when p increases, after the optimization calculation of the regularized stiffness coefficient met...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com