Sectional rotor structure for permanent magnet synchronous motor
A permanent magnet synchronous motor, rotor structure technology, applied in the magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuit and other directions, can solve the problem of unsuitable motors, bending of positioning tension bolts, occupying the effective length of the rotor and other problems, to achieve the effect of not easy to break, avoid magnetic leakage, and long service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
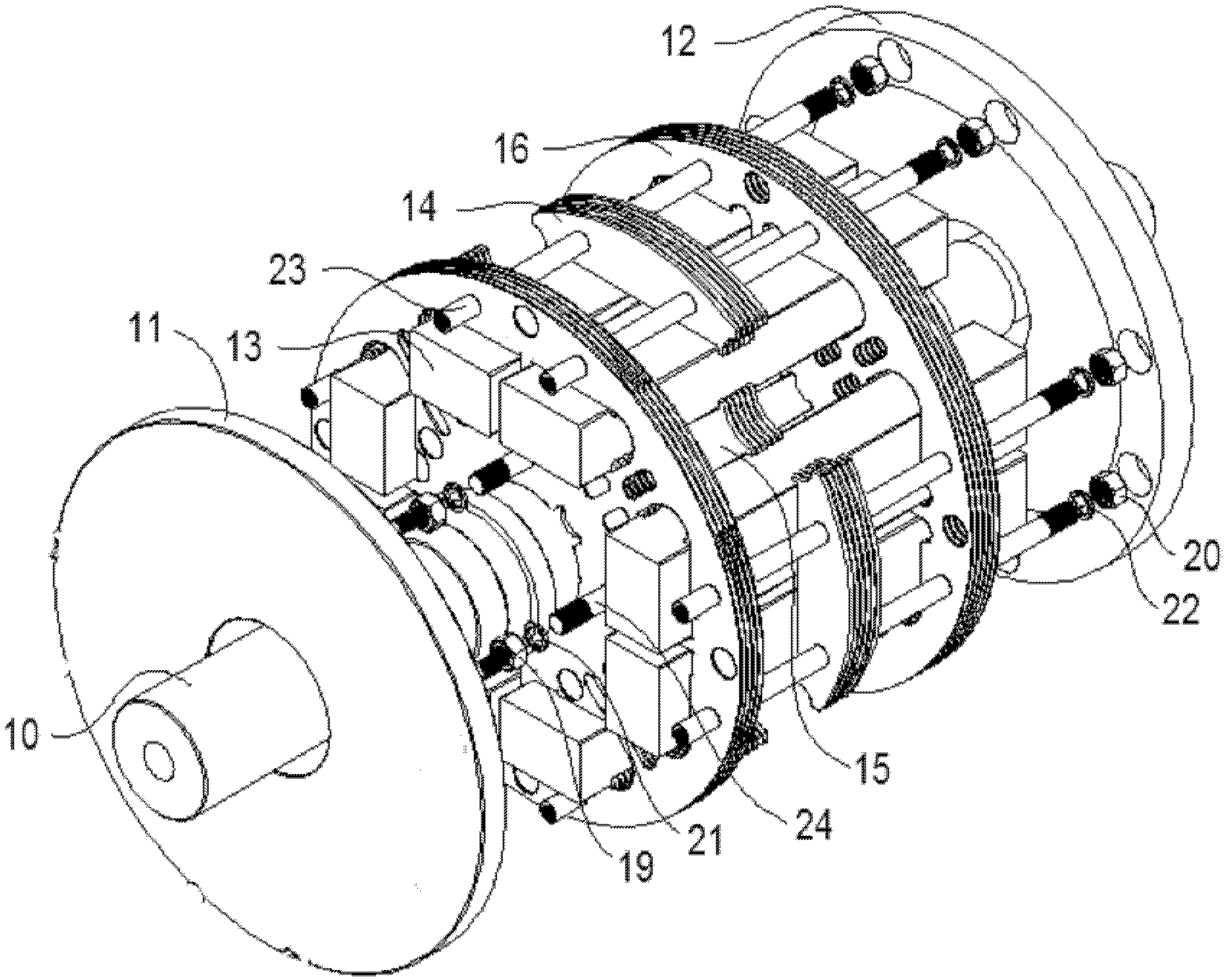
[0035] refer to Figure 1-5
[0036] like figure 1As shown, the rotor structure of the segmented permanent magnet synchronous motor includes a rotating shaft 10, a rotor core 15 fixed on the rotating shaft 10, a permanent magnet 13 sleeved outside the rotor core 15, and located outside the permanent magnet 13 for reasonable distribution of the magnetic field and permanent magnetism. The rotor pole piece 14 for protection by the magnet 13, and the front end plate 11 and the rear end plate 12 respectively located at both ends of the rotor core 15;
[0037] A plurality of rotor diaphragms 16 made of non-magnetic conductive materials are arranged between the two end plates 11 and 12, the rotor pole pieces 14 are independent of each other, and the rotor pole pieces 14 and the rotor diaphragm 16 are distributed at intervals in the axial direction. The rotor diaphragm 16 divides the rotor into a plurality of rotor units in the axial direction. The two end faces of the rotor pole pi...
Embodiment 2
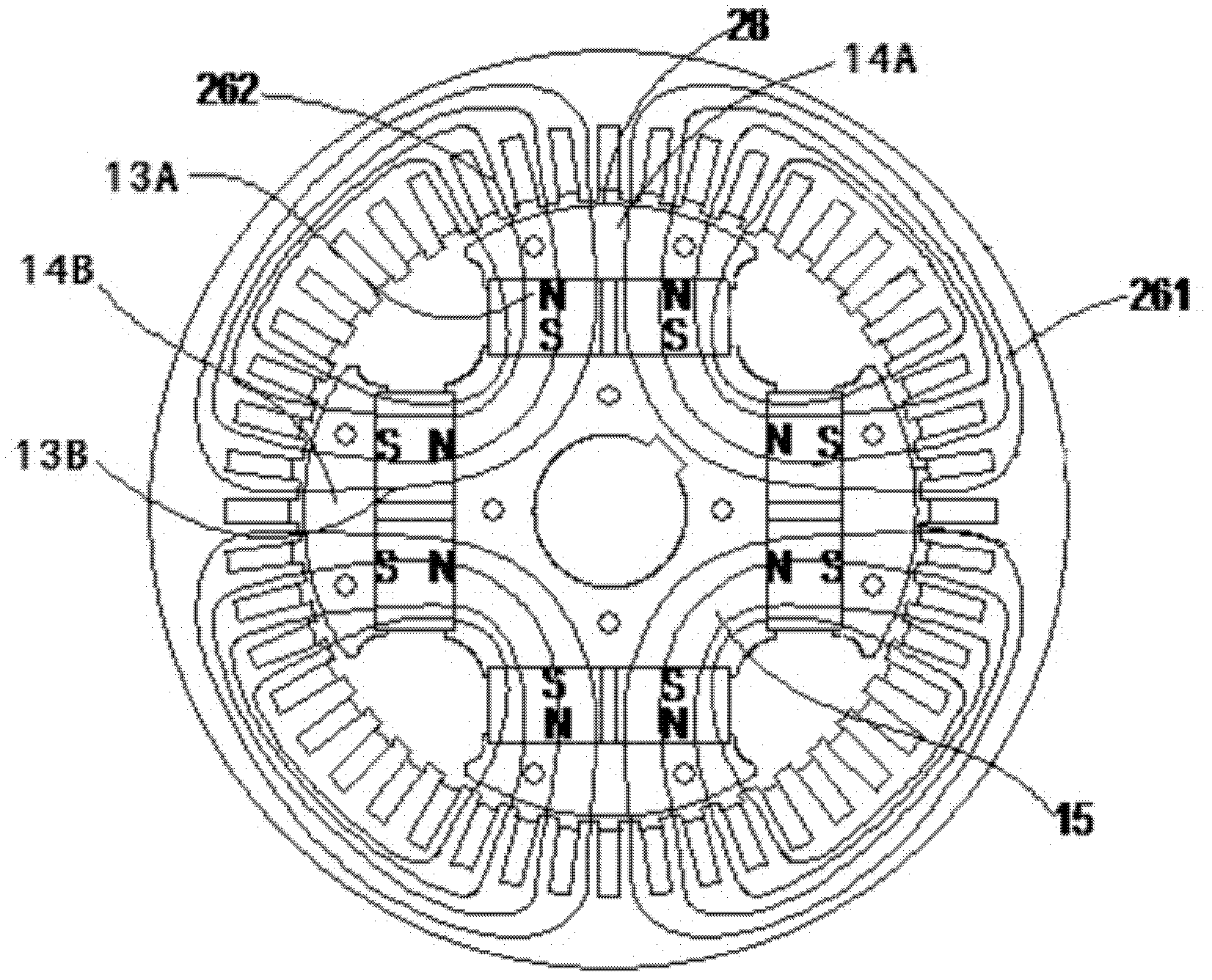
[0049] refer to Figure 6-12
[0050] The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the rotor diaphragm 16 is provided with a weight-reducing hole. The rotor diaphragm 16 is provided with weight reduction holes 166 for reducing the weight of the diaphragm and reducing stress concentration. A plurality of weight reduction holes 166 are distributed around each permanent magnet through hole 165, and a plurality of weight reduction holes 166 around the same permanent magnet 13 The holes 166 form a group of weight-reduction holes, which are symmetrically distributed among the groups of weight-reduction holes. The weight-reducing holes 166 are circular holes or waist-shaped holes or polygonal holes whose corners are arc transitions, and the weight-reducing holes 166 are mainly concentrated at the corners of the permanent magnet through holes.
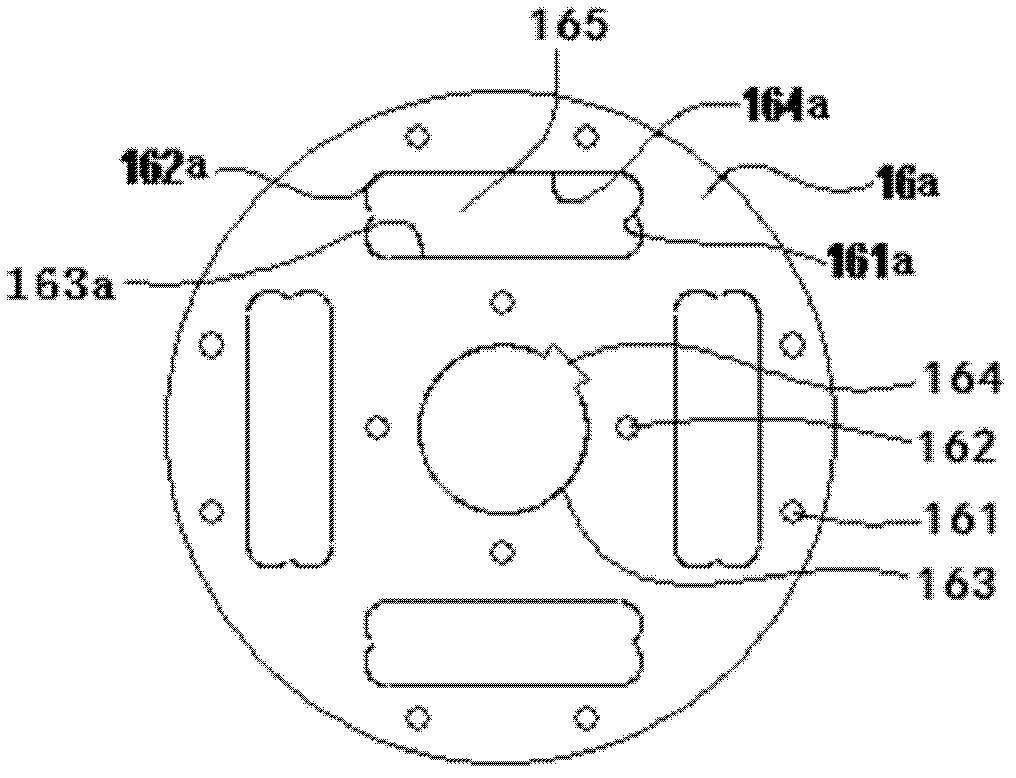
[0051] The structure of the third rotor diaphragm 16c is as follows Image 6 As shown, the inner sides 163c and...
Embodiment 3
[0058] refer to Figure 13
[0059] The difference between this embodiment and the second embodiment is that pole shoe tightening nuts 20 are respectively provided at both ends of the pole shoe tightening bolt 23, and the pole shoe tightening nuts 20 are in close contact with the rotor pole shoes 14 at both ends; The two ends of the tightening bolt 20 are respectively provided with fixed screw holes. The front end plate 11 and the rear end plate 12 are respectively connected to the pole shoe tightening bolts 23 through screws 18 which engage with the fixed screw holes. The rest of the structure is the same.
[0060] The front end plate 11 and the rear end plate 12 of the rotor are made of thicker non-magnetically conductive material (such as high-strength aluminum alloy) or low-permeability material (such as high-strength austenitic stainless steel), which not only affects the rotor pole piece 14, The rotor diaphragm 16 and the permanent magnets 13 have a stabilizing effect,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com