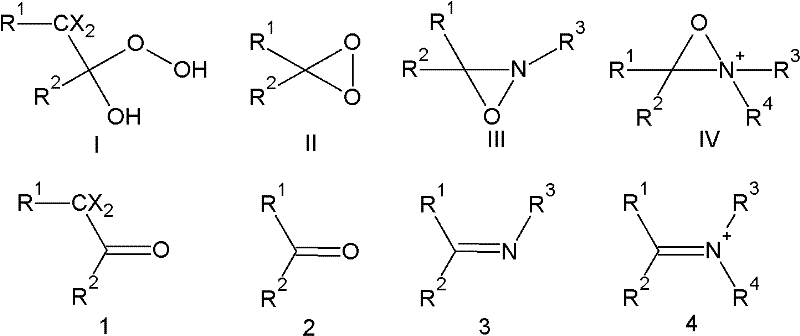
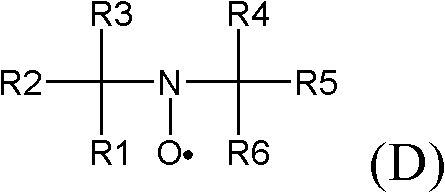
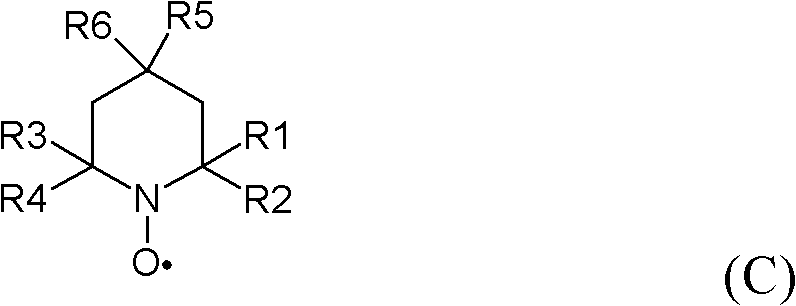Methods of preparing fluorinated carboxylic acids and their salts
A technology for fluorinating carboxylic acids and carboxylic acids, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of carboxylate salts, preparation of organic compounds, etc., and can solve problems such as low yield and expensive reagents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0122] The following is a summary of specific embodiments of the invention:
[0123] 1. A method for the preparation of highly fluorinated carboxylic acids and salts thereof, which comprises making a highly fluorinated alcohol of general formula (A):
[0124] A-CH 2 -OH
[0125] contacting at least one first oxidizing agent and at least one second oxidizing agent to generate a highly fluorinated carboxylic acid or salt thereof of general formula (A1):
[0126] A-COO - m +
[0127] where M + Represents a cation and wherein A in formulas (A) and (A1) is the same and represents a residue:
[0128] Rf-[O] p -CX"Y" -[O] m -CX'Y'-[O] n -CXY-
[0129] wherein Rf represents a fluorinated alkyl residue which may or may not contain one or more catenary oxygen atoms, p, m and n are 1 or 0 independently of each other, X, X', X", Y, Y' and Y" independently of each other is H, F, CF 3 or C 2 f 5 , with the proviso that X, X', X", Y, Y', and Y" are not all H, and wherein said a...
example
[0194] The following examples further describe the preparation of compositions of the present invention. The particular materials and amounts thereof, as well as other conditions and details, recited in these examples should not be construed to unduly limit this invention. All materials are commercially available, for example, from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Company (Milwaukee, Wisconsin) or are known to those skilled in the art unless otherwise stated or apparent.
[0195] These abbreviations are used in the following examples: eq = equivalent, g = gram, M = mole, min = minute, mol = mole; mmol = millimole, hr = hour, mL = milliliter, mmHg = millimeter of mercury, L = liter , wt = weight, FTIR = Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, NMR = nuclear magnetic resonance and GC-MS = gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
[0196] The resulting samples were analyzed by proton or fluorine NMR as follows unless otherwise stated. Peaks in NMR were integrated. The peak areas believed t...
example 1
[0218] To a mixture of 92.8 g of 5.25 wt % sodium hypochlorite solution (65.4 mmol, 2.5 eq) and 2.09 g (52.3 mmol, 2 eq) of sodium hydroxide was added 10.0 g (26.2 mmol, 1 eq) of 2,2,3-trifluoro-3 -(1,1,2,2,3,3-hexafluoro-3-trifluoromethoxypropoxy)propan-1-ol, 0.0573g (0.366mmol, 0.014eq) TEMPO and 0.716g (1.30 mmol, 0.05eq) a mixture of tetra-n-octylammonium bromide. The mixture was stirred and heated to 40°C for about 2 hours. In an attempt to extract the fluorinated carboxylic acids while retaining tetra-n-octylammonium bromide, the following procedure was performed. The reaction mixture was cooled and washed with a 50:50 methyl tert-butyl ether / hexane mixture. The organic phase was acidified with 8.0 mL of 12M hydrochloric acid solution. The mixture was extracted with methyl tert-butyl ether, the organic phase was washed with water, filtered and concentrated to give 8.5 g of crude product.
[0219] pass 1 H NMR and 19 As determined by F NMR, the crude product contain...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com