Manufacturing process of shaft bodies of carbon-fiber arrow shafts
A manufacturing process, carbon fiber technology, applied in the direction of layered products, glass/slag layered products, synthetic resin layered products, etc., can solve problems such as poor deflection, affecting flight trajectory, arrow shaft breakage, etc., and achieve easy production and operation Sexuality, reduction of production process, and improvement of production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] The production specifications are: ID6.2*OD7.5*L762, the deflection is 300Spine, and the straightness is ≤0.004";
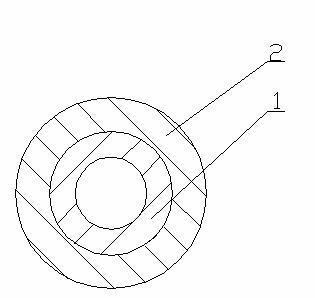
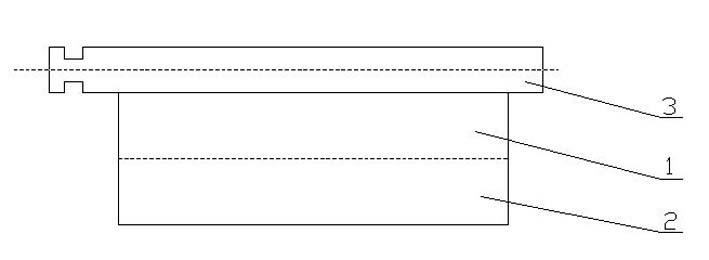
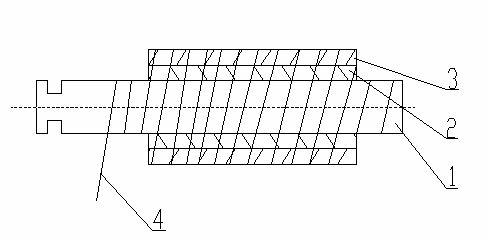
[0030] Arrow shaft structure of present embodiment is as figure 1 As shown: the rod body is made of a bottom layer 1 and a coating layer 2, two layers of fabric impregnated with resin and epoxy resin are laminated and wound, and made into a hollow tubular structure with a constant inner and outer diameter. In this embodiment, the inner diameter of the finished product is 6.2 mm, and the outer diameter is 7.5 mm.
[0031] The fabric of the bottom layer 1 is a whole block with the warp and weft yarns as coordinates, and is cut into rectangular and sheet-like pre-impregnated resin plain weave fabrics at 40-60°, and the weight of the resin is 55% of the weight of the glass fiber; the bottom layer 1 is a rectangle, sheet Shaped pre-impregnated resin plain fabric is wound with the long side as the length of the rod body to form a hollow tubular laminate. After ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com