FCM (flow cytometry) based method for quickly and quantitatively detecting total viruses in freshwater environment
A flow cytometry and quantitative detection technology, which is applied in the field of rapid quantitative detection of total virus in freshwater environment based on flow cytometry, can solve the problems of time-consuming and laborious, achieve short detection time, broad application prospects, and simple operation steps. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
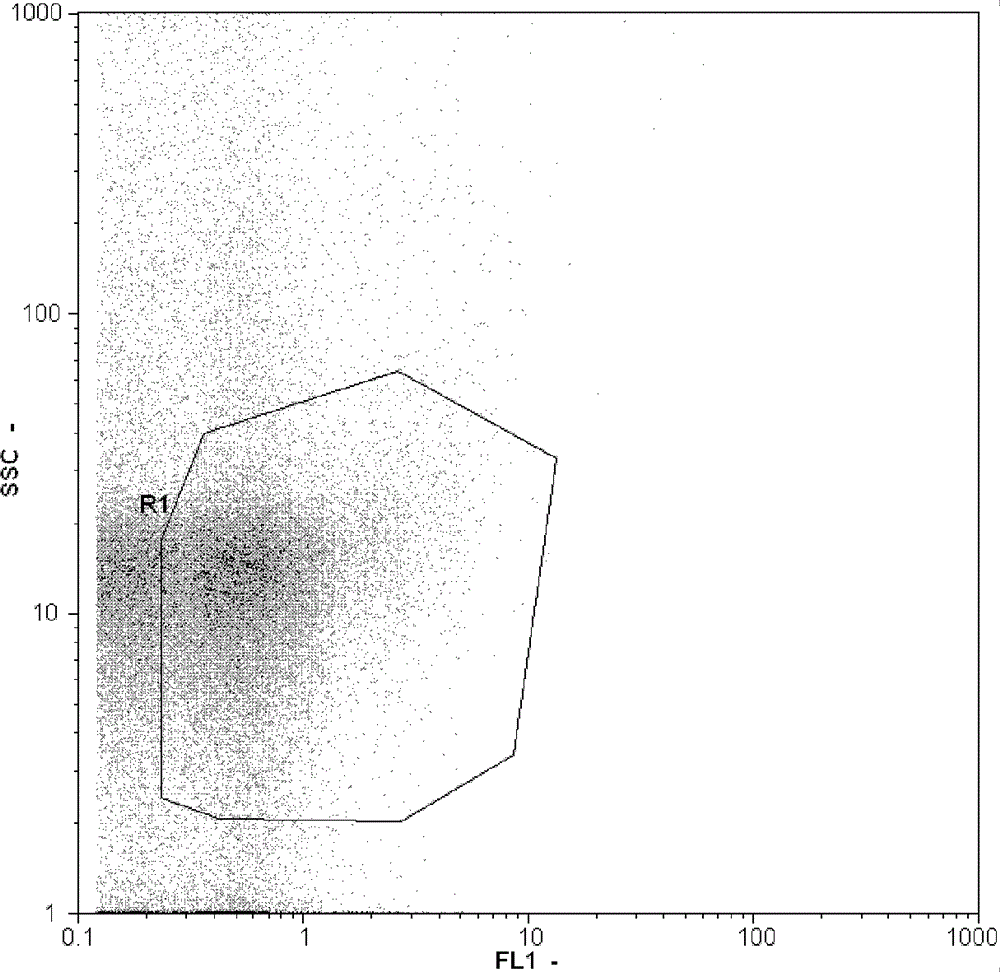
[0019] Example 1 Detection of virus total amount in a certain fresh water sample in Tianjin
[0020] 1. Pass the collected fresh water sample through a 0.22 μm filter membrane, add an appropriate amount of glutaraldehyde to fix it, so that the final mass concentration of glutaraldehyde is 0.25%, and immediately put it in a 4°C refrigerator; after 15 minutes, use liquid nitrogen Freeze and store in a -80°C freezer.
[0021] 2. Take out the sample frozen in the previous step and thaw it at room temperature, take 1ml into a sterilized centrifuge tube, add 10μl of Na with a concentration of 0.5mol / l 2 EDTA solution (final concentration up to 5mmol / l), then add 5 μl of SYBR Green I stock solution (dilute 100-fold SYBR Green I stock solution with dimethyl sulfoxide passing through a filter membrane with a pore size of 0.22 μm as the stock solution).
[0022] 3. After shaking and mixing, stain in the dark at 80°C for 10 minutes. After cooling to room temperature, dilute with Milli-Q...
Embodiment 2
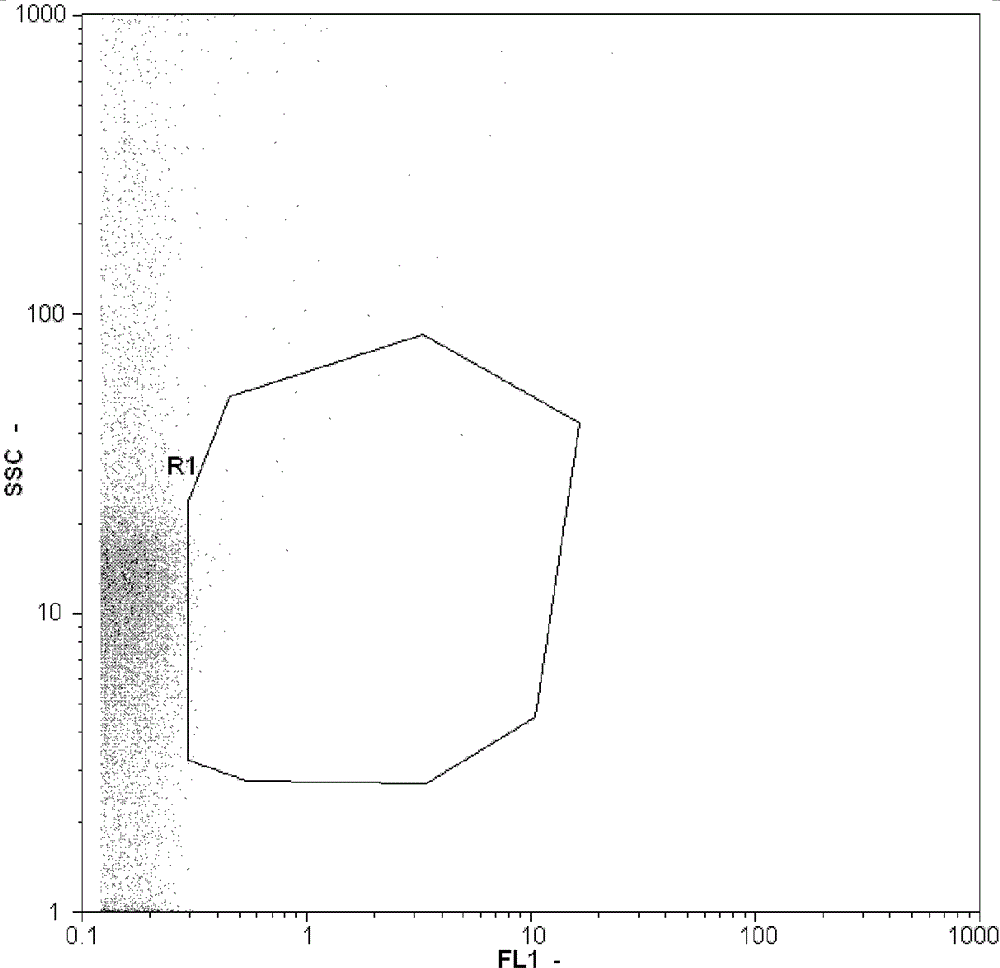
[0025] The detection of virus total amount in embodiment 2 blank water samples
[0026] Milli-Q water was used as the water sample to be tested, and the method steps in Example 1 were used for detection. Since Milli-Q water does not contain viruses, bacteria, etc., the test results are as follows: figure 2 As shown, only the background part can be seen, and no virus colonies appear. This sample can be used as a negative control sample.
Embodiment 3
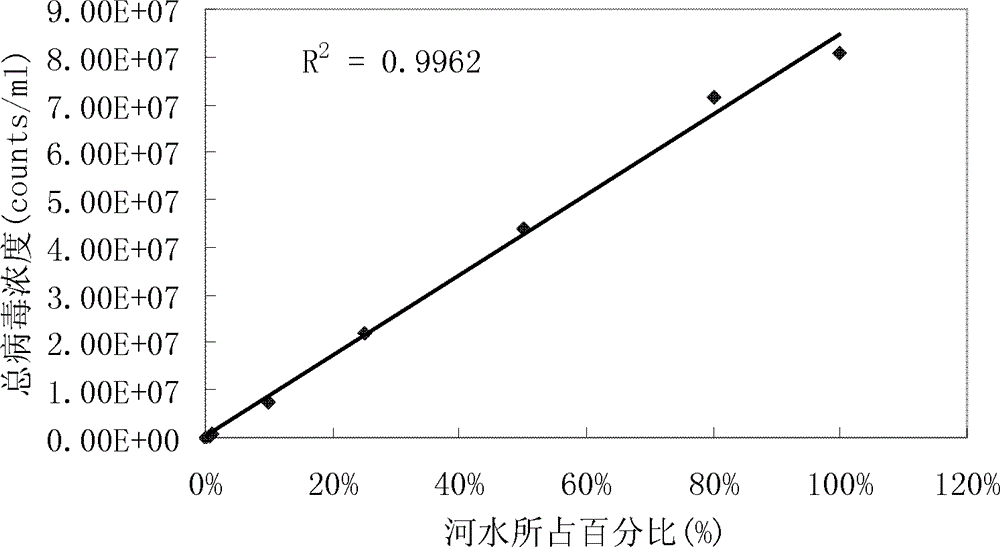
[0027] The detection limit of embodiment 3 method
[0028] Dilute a certain river water sample with Milli-Q water, and the diluted river water in each sample accounts for 0.05%, 0.1%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 10%, 25%, 50%, 80%, and 100% respectively .
[0029] After the above samples were processed according to the method in Example 1, they were detected by flow cytometry. The test results showed that ( image 3 ), the method among the present invention can detect the minimum concentration of virus in fresh water to be 4.04 * 10 4 counts / ml, the correlation of the method is very good, the correlation coefficient R 2 >0.99 (n=9), the repeatability of the method is very good, and the average error of the detected samples (n=9) is less than 10%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com