Method for erasing single-transistor memory array
A memory array and target memory technology, applied in the field of single-tube memory array erasure, can solve problems such as increased reliability failure risk, lack of monitoring and adjustment means, and low memory cell erasure window.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
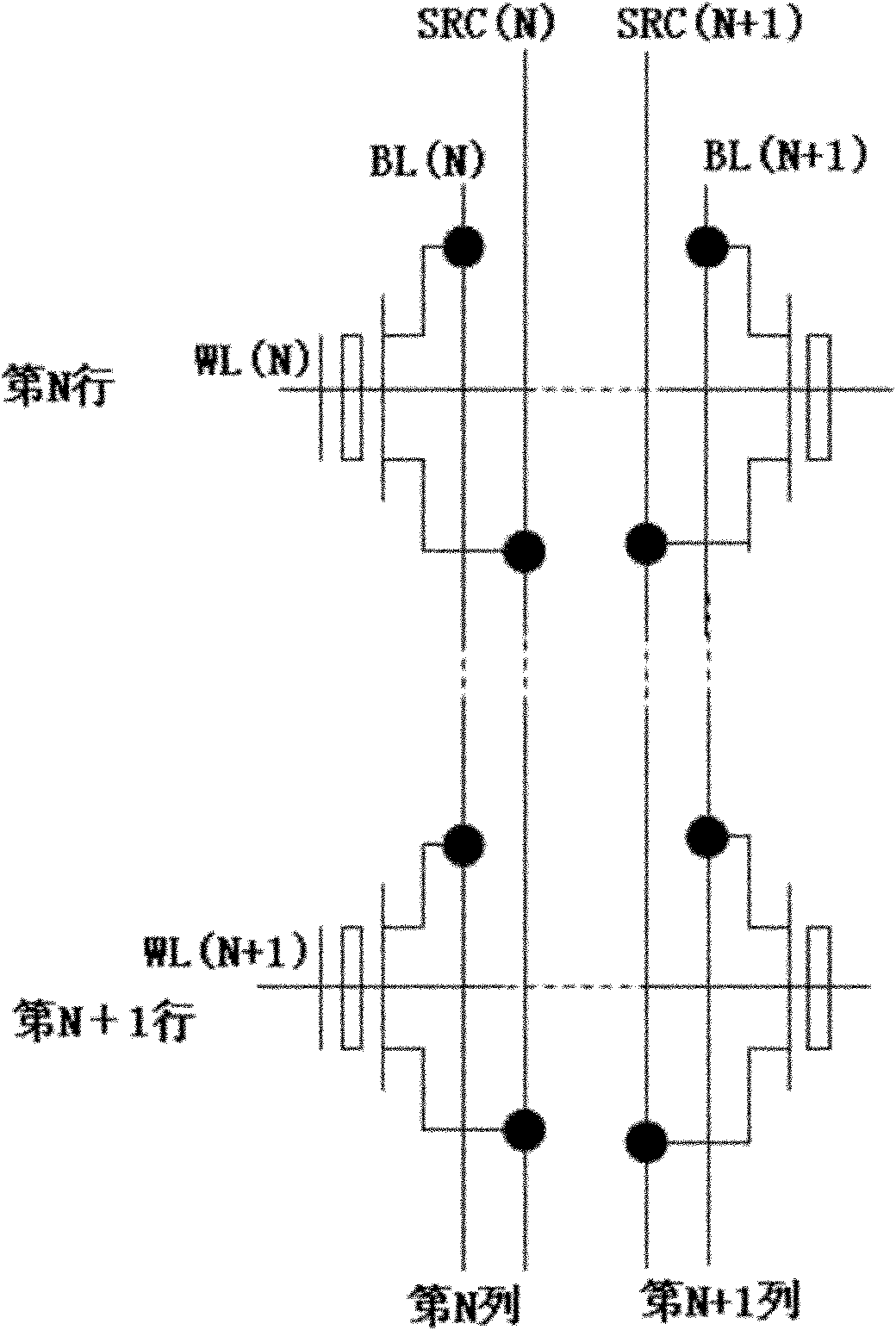
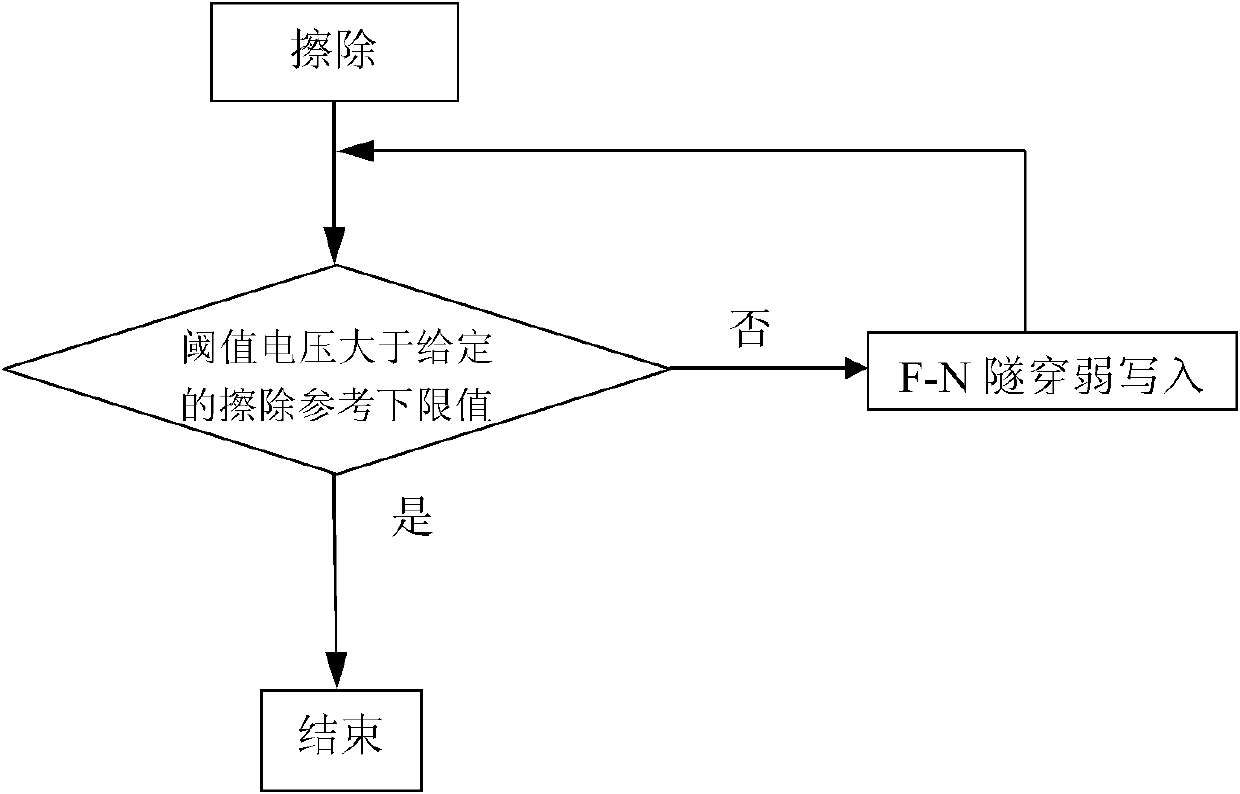
[0029] One embodiment of the method for erasing a single-pipe memory array of the present invention is as follows: Figure 6 shown, including the following steps:
[0030] 1. Erase each target memory unit;
[0031] 2. Read the threshold voltage of each target memory cell, compare the current threshold voltage of each target memory cell with the same threshold voltage upper limit, if the current threshold voltage of a target memory cell is greater than the threshold voltage upper limit value, proceed to step 1, otherwise proceed to step 3;
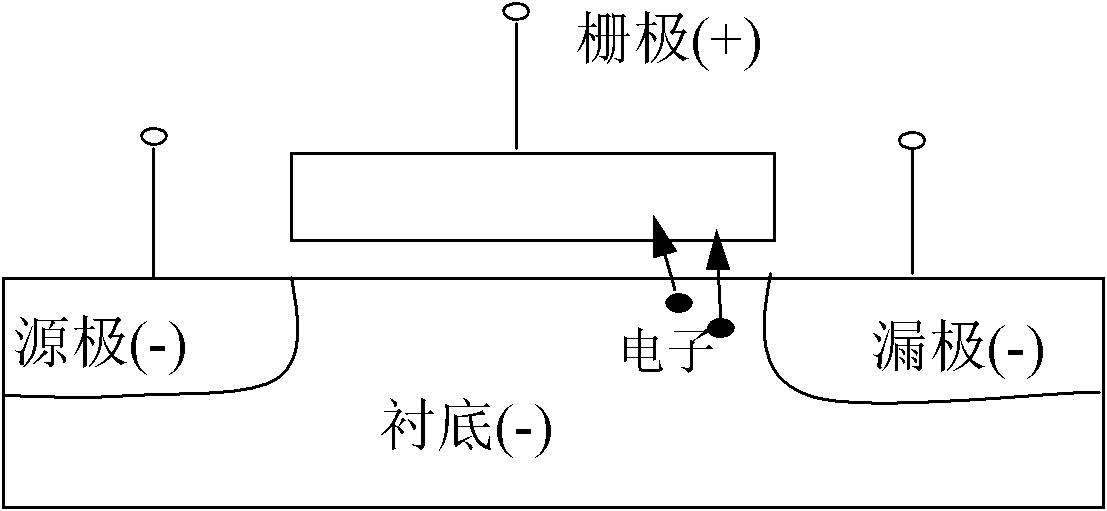
[0032] 3. Ground the substrate and the source of each target memory cell, and connect the gate and the drain to the pulse voltage respectively;
[0033] Four. The current threshold voltage of each target memory cell is compared with the same threshold voltage lower limit, if the current threshold voltage of each target memory cell is greater than the threshold voltage lower limit, then proceed to step 7, otherwise Carry out step five; in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com