Solar cell component structure
A solar cell and component technology, applied in electrical components, circuits, photovoltaic power generation, etc., can solve problems such as deepening health, human health hazards, environmental pollution, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing waste liquid and avoiding cadmium pollution of the environment.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The making and use of the presently preferred embodiments of the present invention are discussed in detail below. However, it should be understood that the present invention provides many applicable devices, which can be implemented in a variety of specific situations. The specific examples discussed only illustrate specific ways to make and use the invention, and do not limit the scope of the invention.
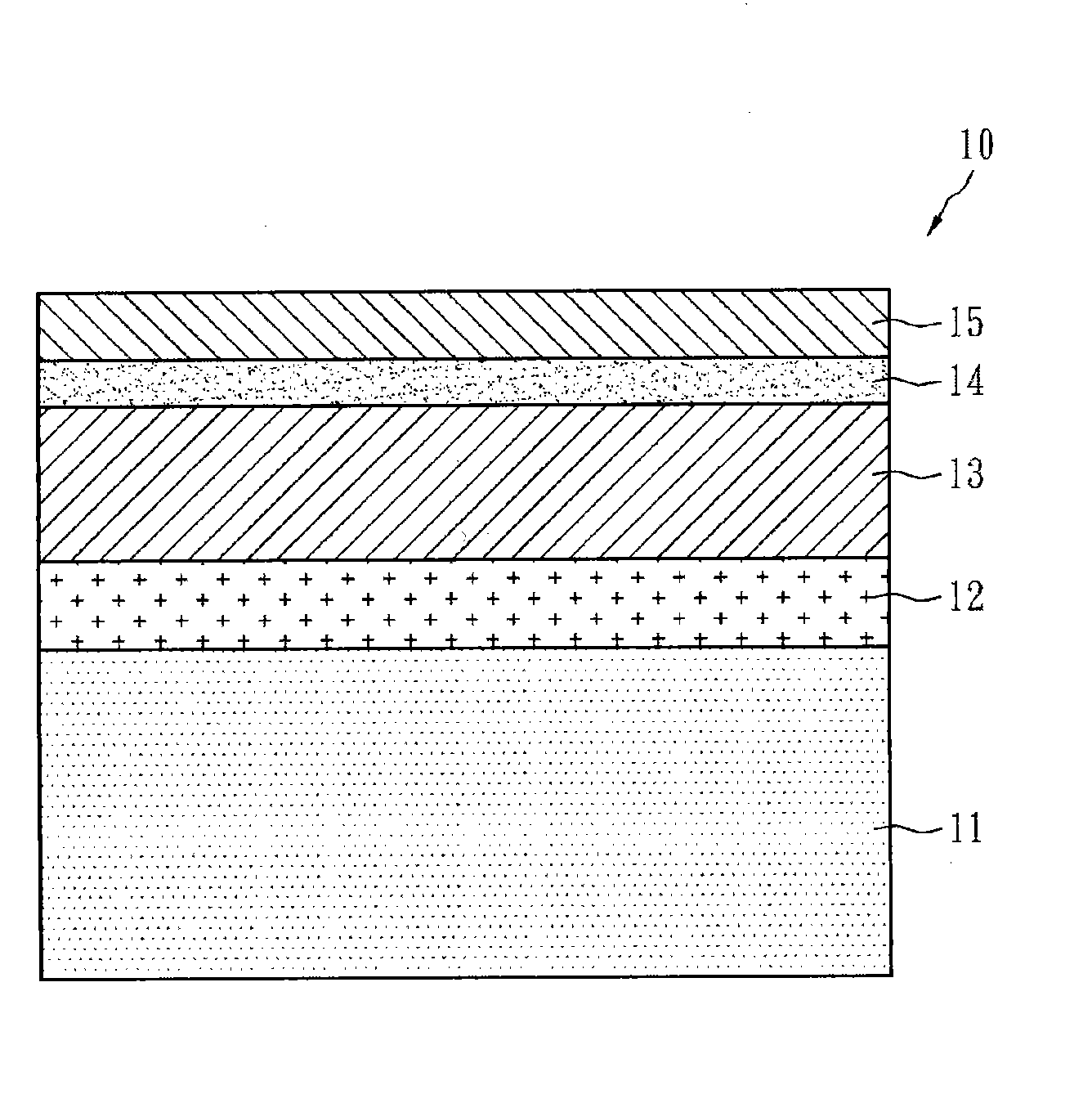
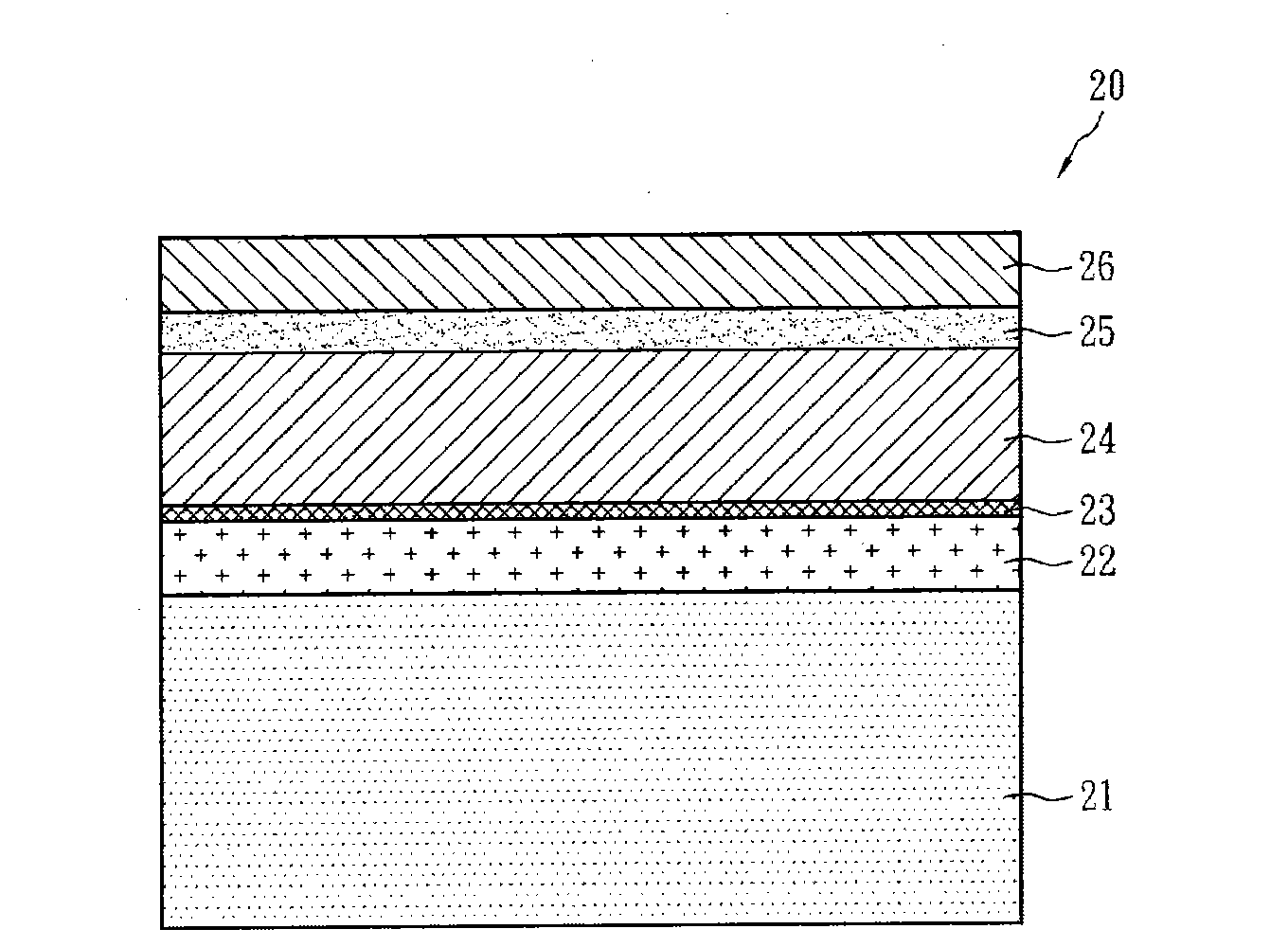
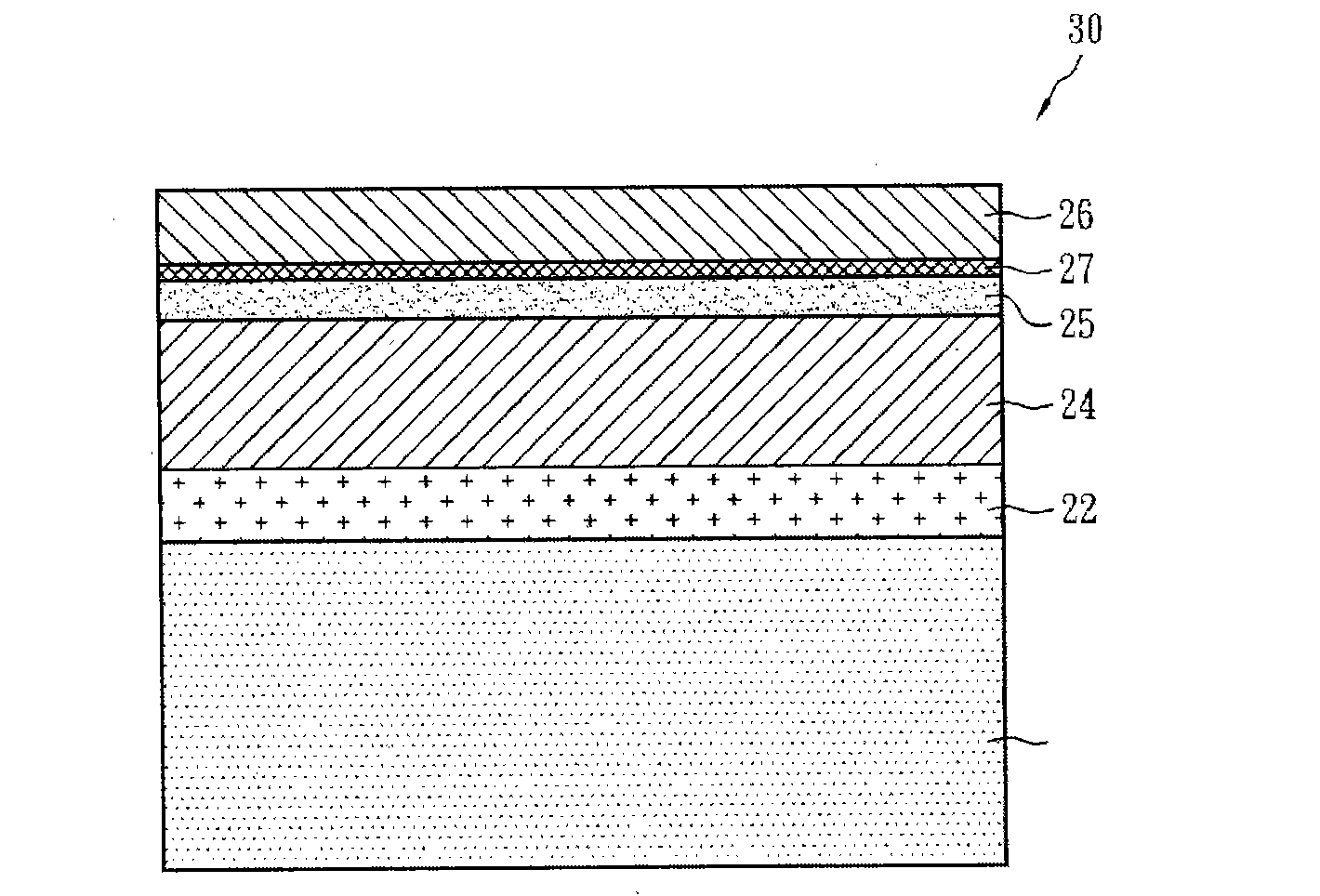
[0024] figure 2 The structure of the solar cell element according to the first embodiment of the present invention is shown. The solar device structure 20 is a laminated structure, which includes a substrate 21, a metal layer 22, a high-resistance film layer 23, a p-type semiconductor layer 24, an n-type semiconductor layer 25 and a transparent conductive layer 26. The substrate 21 is generally a glass substrate, and it may also be a metal plate or metal foil such as polyimide, stainless steel, molybdenum, copper, titanium, and aluminum. The above-mentioned substrate ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com