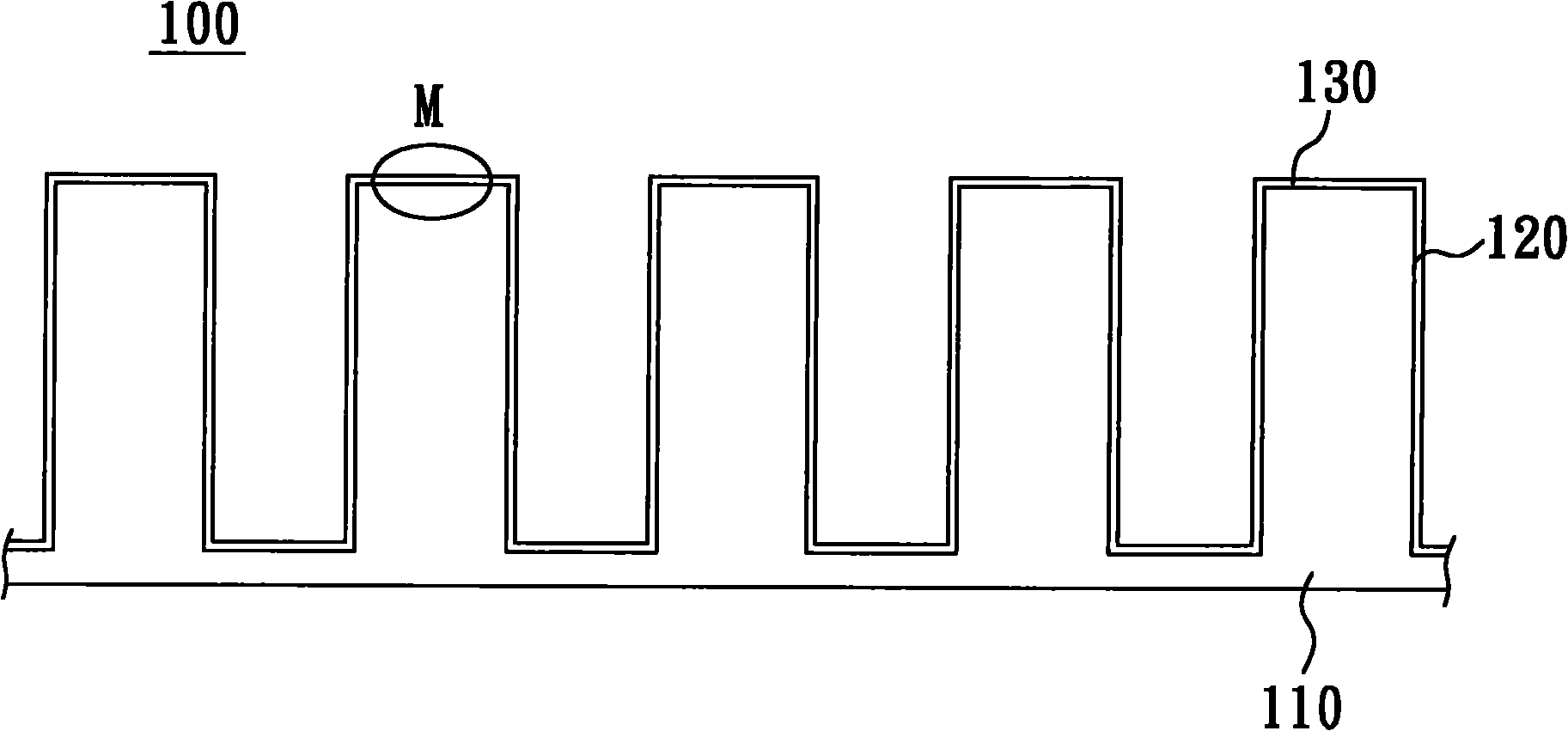
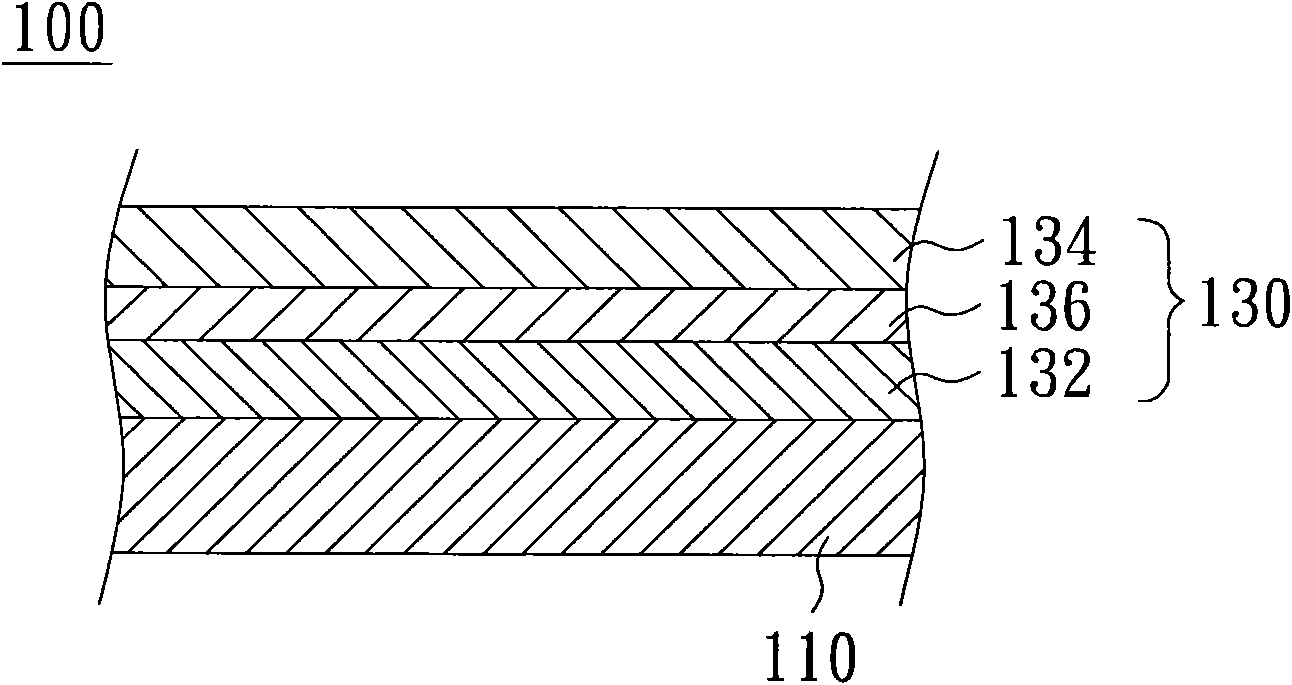
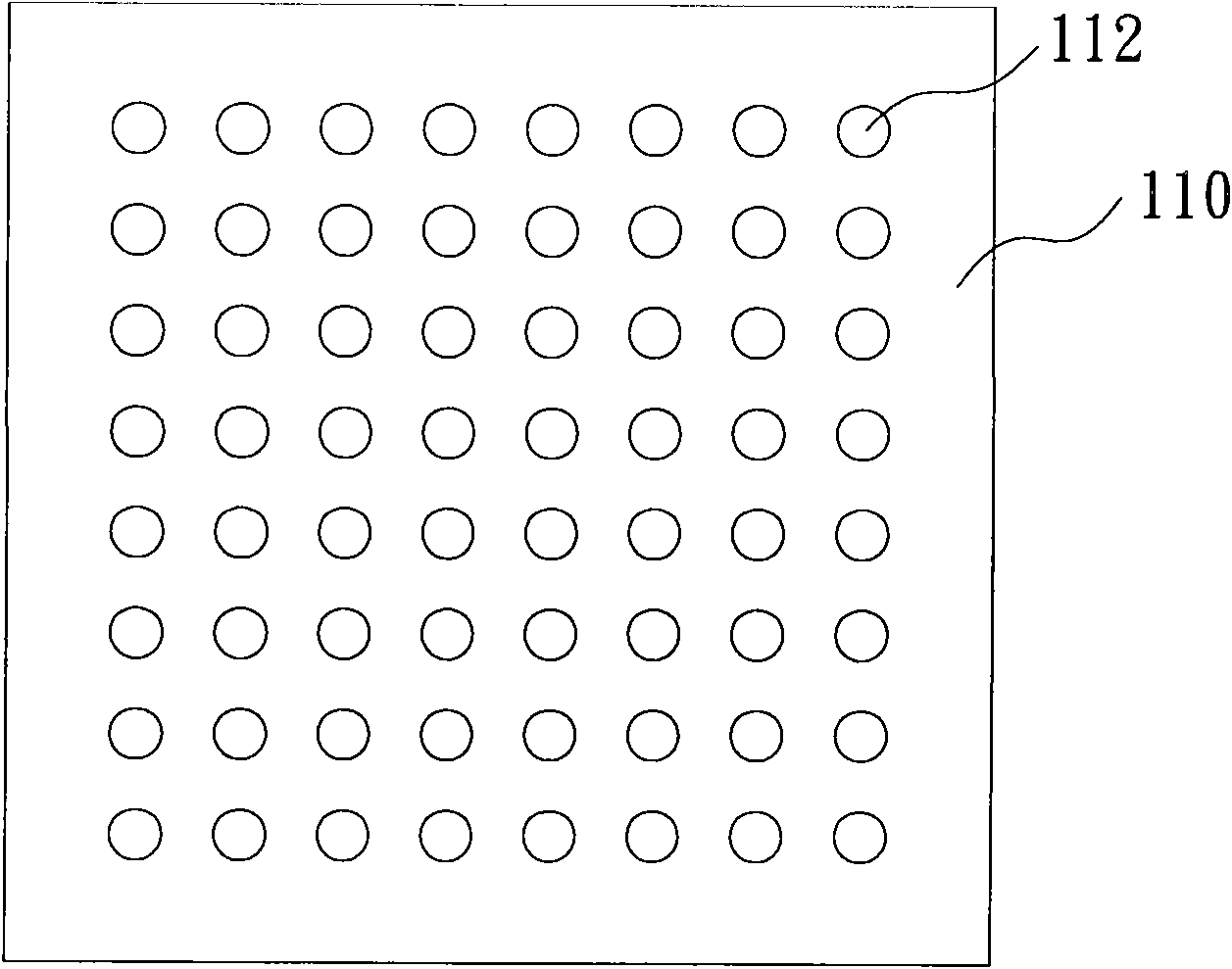
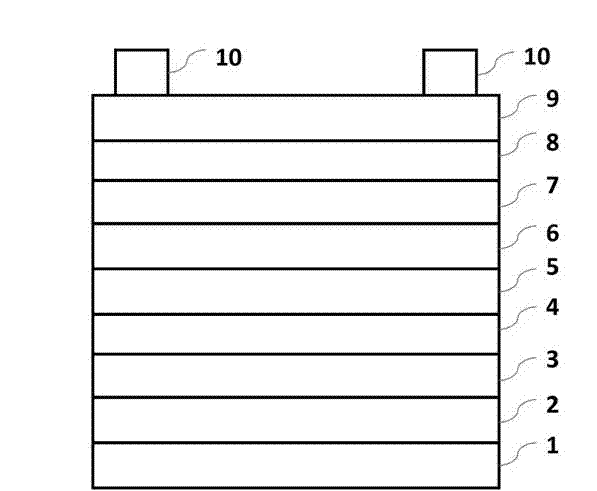
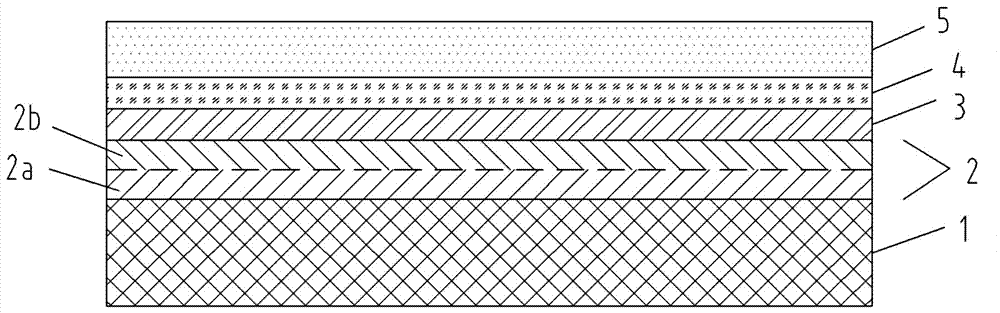
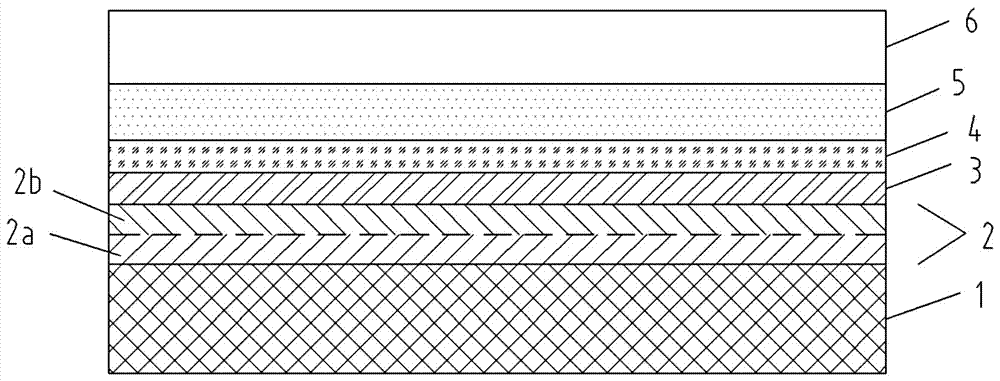
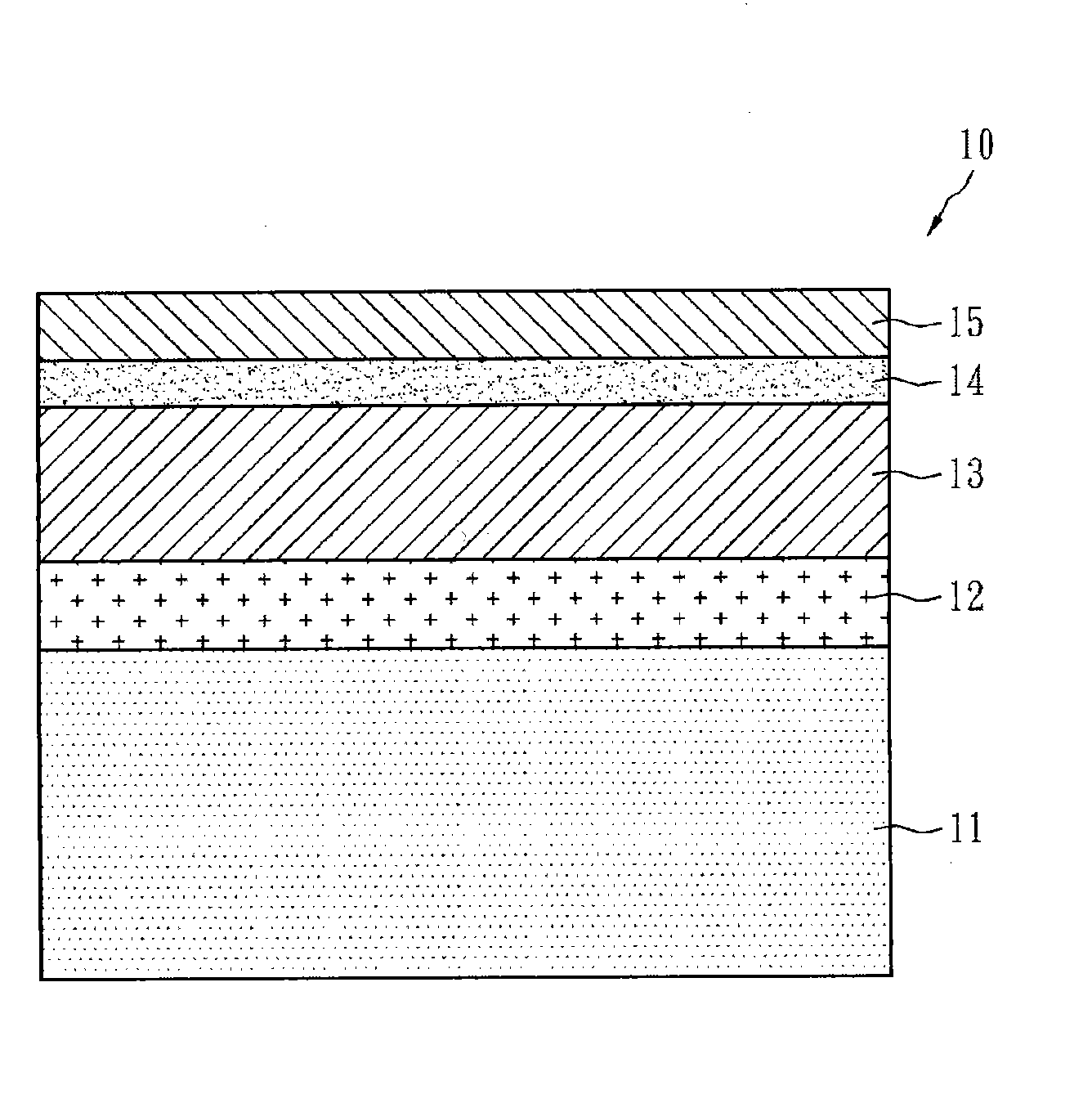
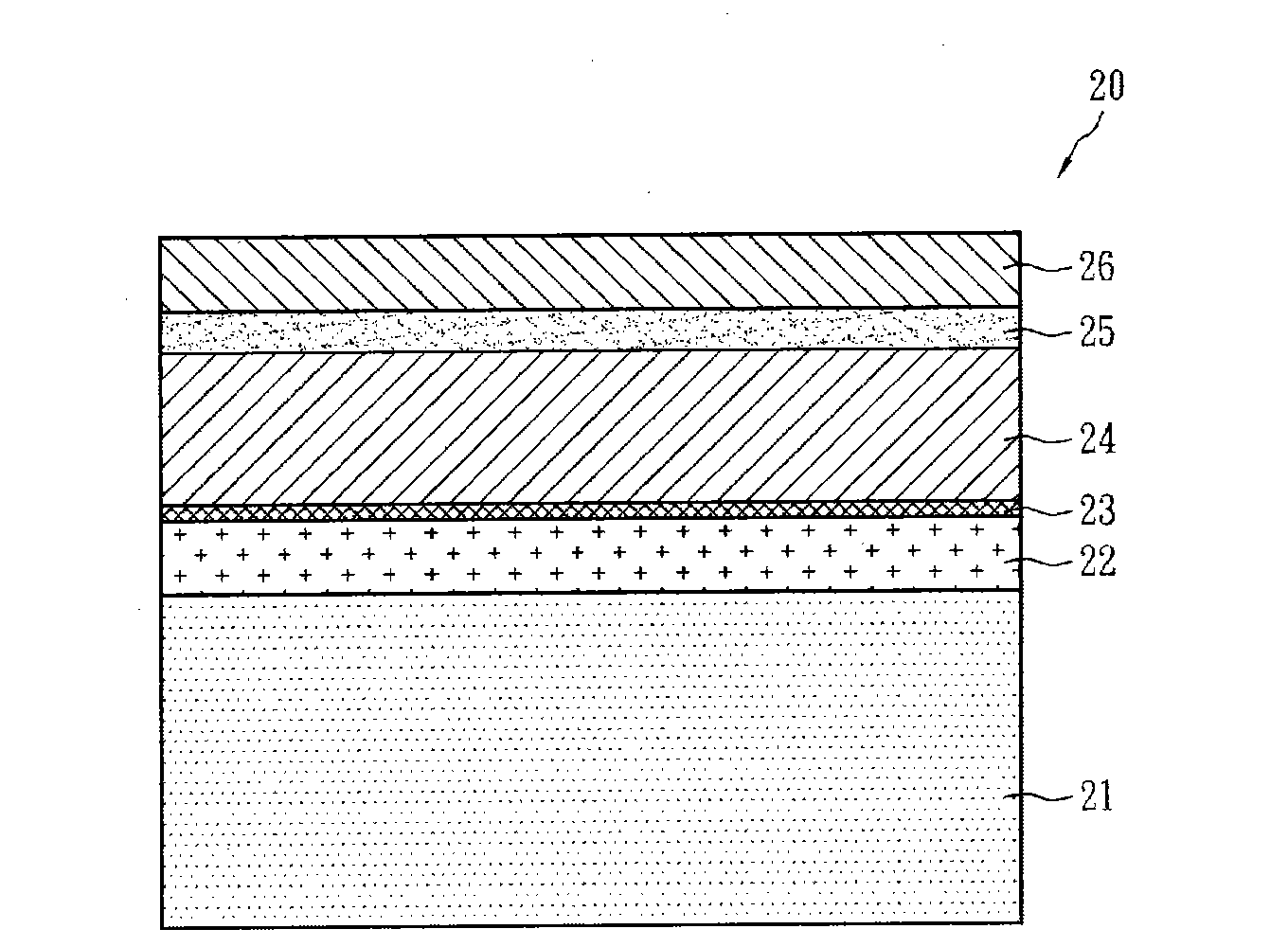
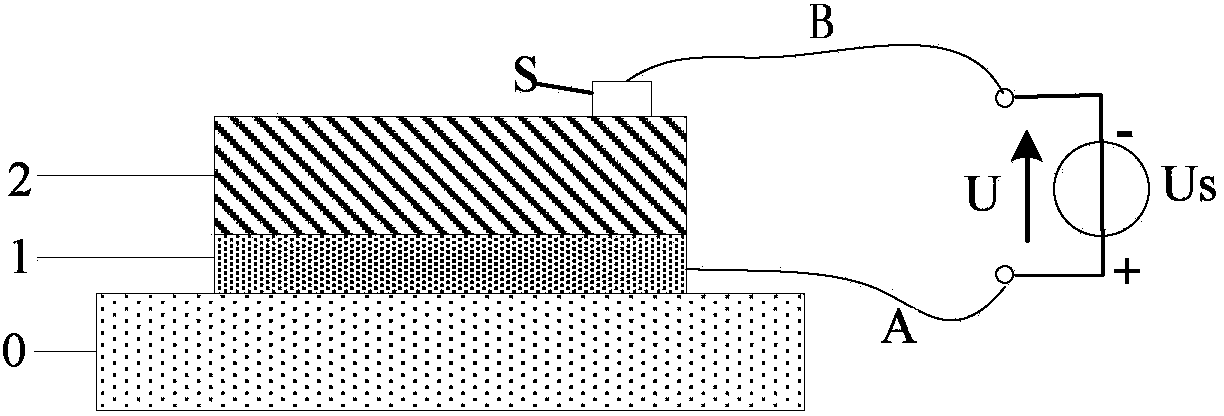
Patents
Literature
88 results about "Copper indium gallium selenide solar cells" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
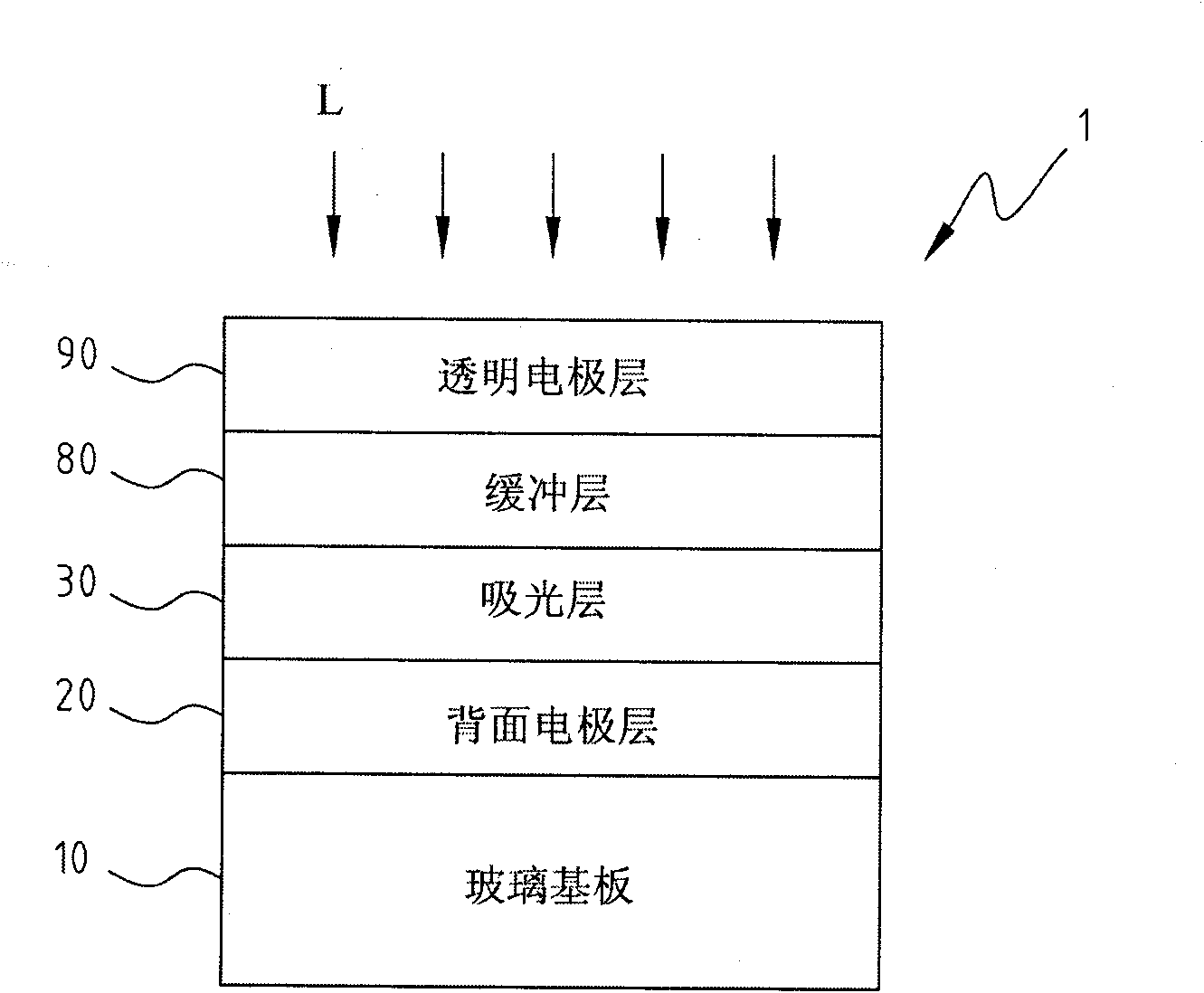
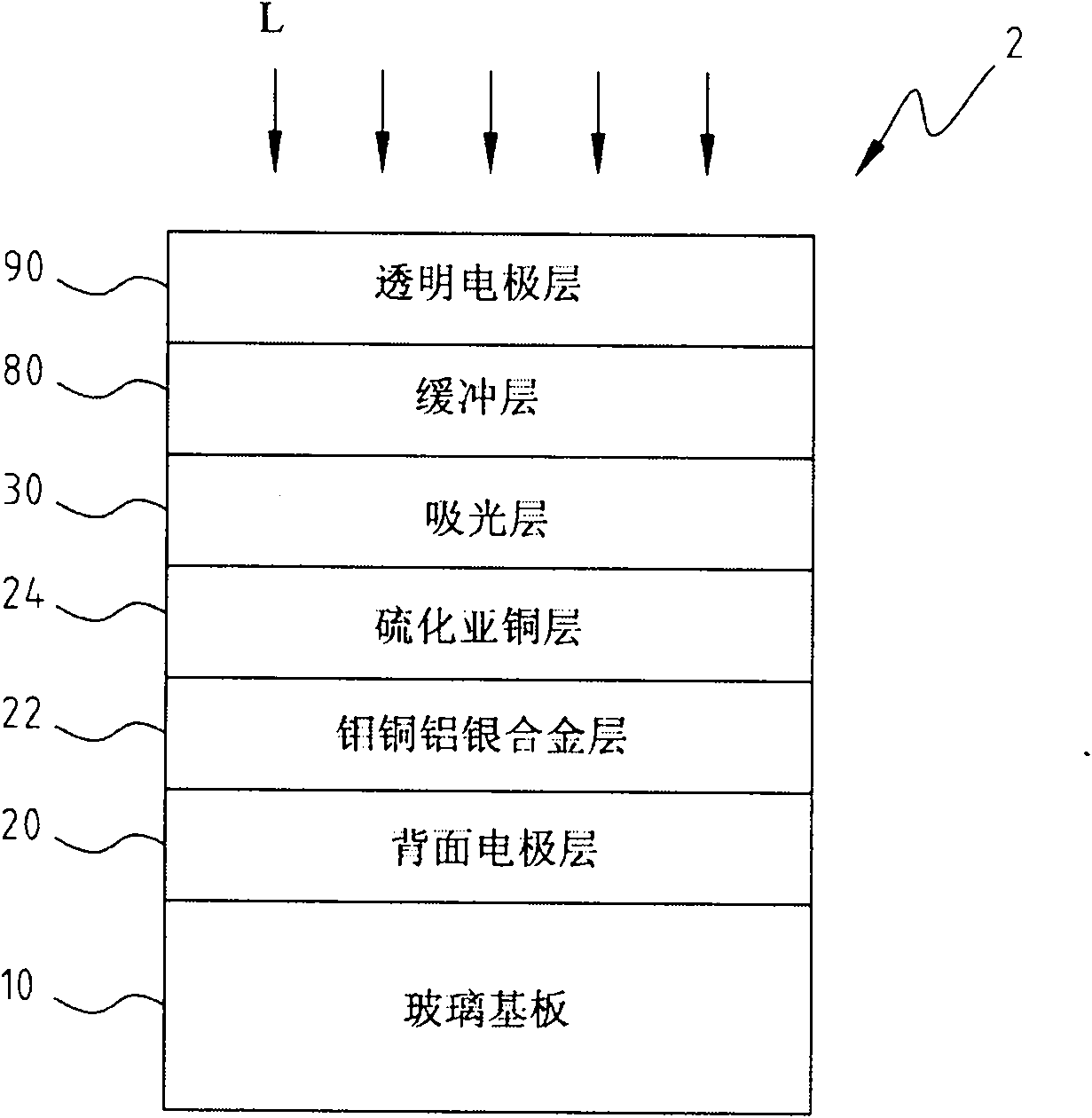
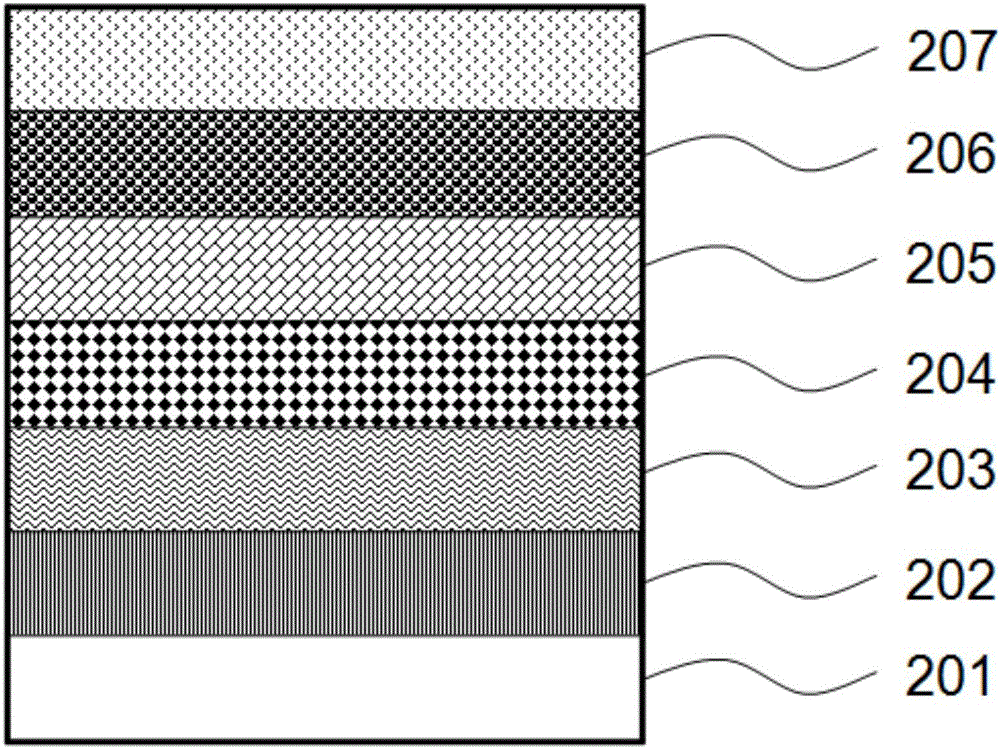
A copper indium gallium selenide solar cell (or CIGS cell, sometimes CI(G)S or CIS cell) is a thin-film solar cell used to convert sunlight into electric power. It is manufactured by depositing a thin layer of copper, indium, gallium and selenium on glass or plastic backing, along with electrodes on the front and back to collect current. Because the material has a high absorption coefficient and strongly absorbs sunlight, a much thinner film is required than of other semiconductor materials.
Method for surface modification of copper indium gallium diselenide (Cu(In, Ga)Se2) film
InactiveCN102694068AEfficient removalIncrease the open circuit voltageFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesIndiumNew energy
The invention discloses a method for surface modification of a copper indium gallium diselenide (Cu(In, Ga)Se2) film and relates to the technical field of photoelectric function materials and new energy. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: depositing a metal film or an alloy film with a certain thickness on the (Cu(In, Ga)Se2) film, performing high temperature annealing on the (Cu(In, Ga)Se2) film under reactive atmosphere and carrying out a copper selenium secondary phase (CuxSe) reaction on the surface of the deposited metal or alloy and (Cu(In, Ga)Se2) film to form a copper selenium poly-metal compound with a wide band gap so as to fulfill the aim of removing CuxSe. By the surface modification method, the defect that toxicity exists and the environment cannot be protected in etching the CuxSe by the traditional modification method by adopting KCN (potassium cyanide) are overcome; the method has the advantages of being low in cost and high in reproducibility and being suitable for large-area film growth and the like; and with the adoption of method, the band gap width on the surface of the film can be improved, a gradient band gap is formed, the pn junction interface composition is obviously reduced, and the open-circuit voltage of a device is effectively improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Light absorption layer of copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) solar cell and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102074592AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyIncrease absorbanceFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationCopper indium gallium selenide solar cellsCuprous sulfide
The invention discloses a light absorption layer of a copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) solar cell and a manufacturing method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: forming a cuprous sulfide layer by utilizing a sputtering method; forming a plurality of CIGS stacking layers by utilizing a CIGS sol-gel solution in a soaking, rotating, printing or spraying mode by matching with pre-drying; then fusing the cuprous sulfide layer and the CIGS stacking layers to form a CIGS light absorption layer by utilizing quick heating heat treatment so as to form the CIGS solar cell having high photoelectric conversion efficiency and high light absorbancy.
Owner:JENN FENG NEW ENERY CO LTD
Efficient copper indium gallium selenide/perovskite series solar cell
InactiveCN106129053AImprove energy conversion efficiencyReduce lossesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionPerovskite solar cell
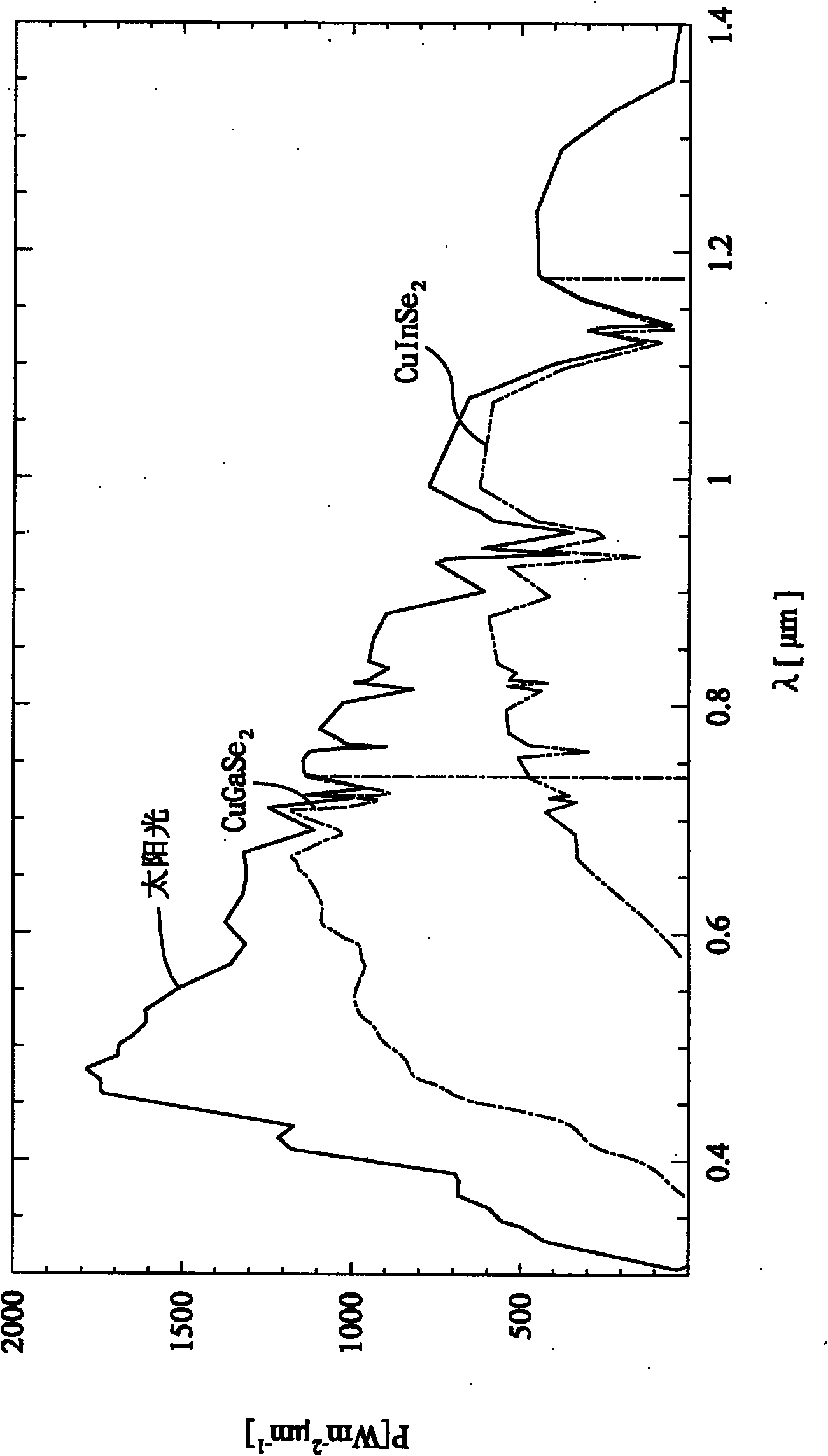
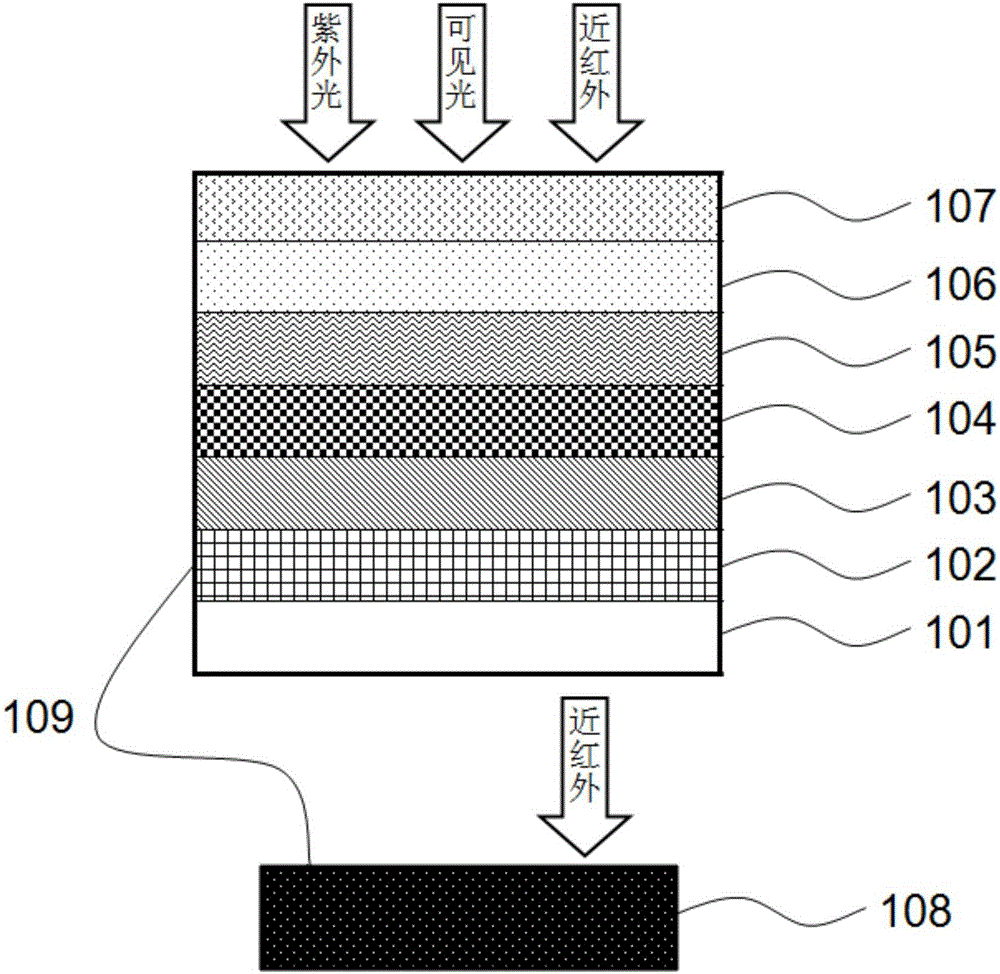
The invention provides an efficient copper indium gallium selenide / perovskite series solar cell. The four-terminal series solar cell comprises a semitransparent planar heterojunction perovskite solar cell and a copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) solar cell which are connected in series. The series solar cell can overcome the shortcoming that the perovskite solar call cannot absorb near-infrared light; the efficient copper indium gallium selenide / perovskite series solar cell can effectively absorb ultraviolet light, visible light and near infrared light, so that the solar cell efficiency can be improved; and a new thought for the final commercialization of perovskite is provided.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Manufacturing method and apparatus for a copper indium gallium diselenide solar cell
InactiveUS20110297215A1Removal costEliminate the problemFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumCopper indium gallium selenide solar cells
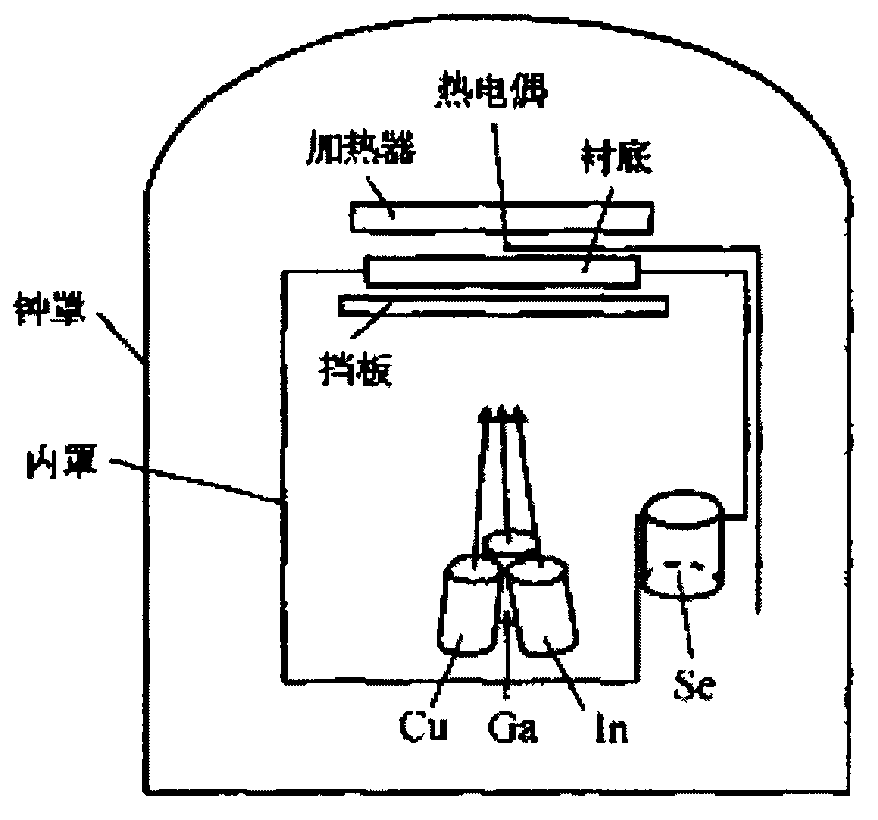
A method to manufacture Copper Indium Gallium di Selenide (Cu(In,Ga)Se2) thin film solar cell includes evaporating elemental Cu, In, Ga, and Se flux sources onto a heated substrate in a single vacuum system to form a non-intentionally doped Cu(In,Ga)Se2 p-type conductivity layer and exposing the p-type conductivity layer to a thermally evaporated flux of Beryllium (Be) atoms to convert a surface layer of the p-type conductivity layer to an n-type conductivity layer resulting in a buried Cu(In,Ga)Se2 p-n homojunction. Also, the source of Be atoms includes a circular rod of Be having a uniform cross-section that is resistively heated and having its temperature controlled by passing an electrical current through the rod.
Owner:RJM SEMICON
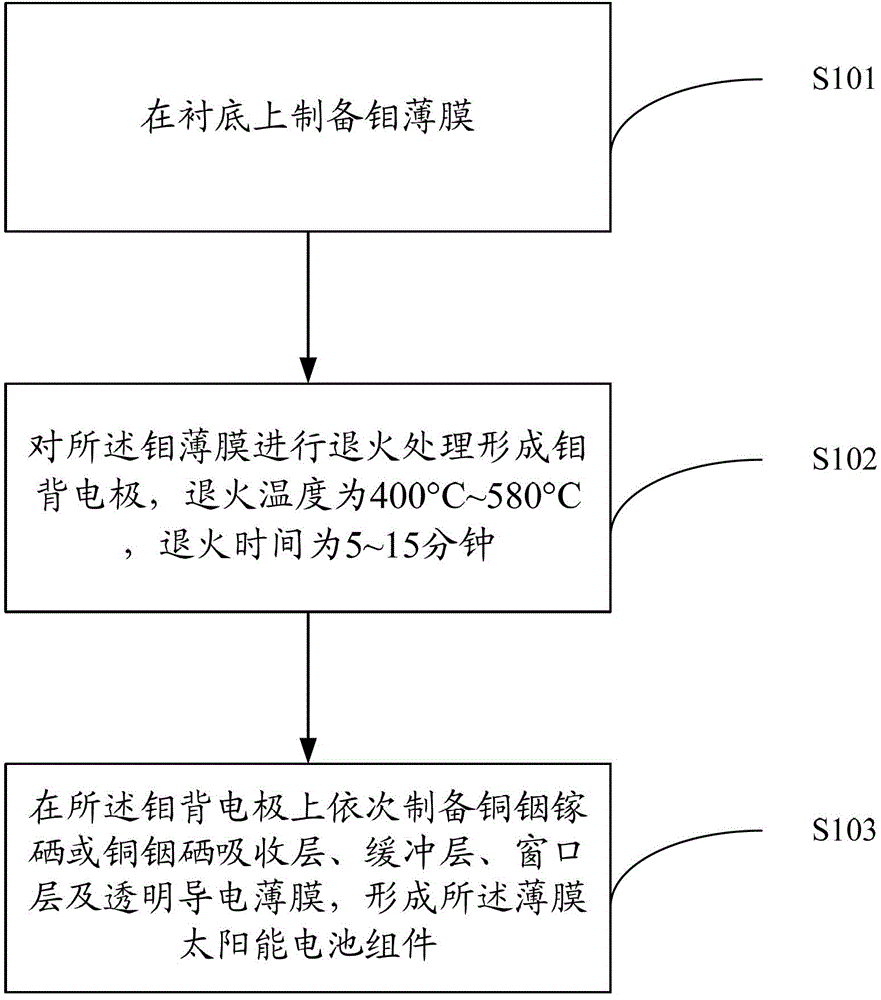
Preparation method of thin-film solar cell component
ActiveCN102983219AStrong adhesionImprove corrosion resistanceFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesIndiumCopper indium gallium selenide solar cells
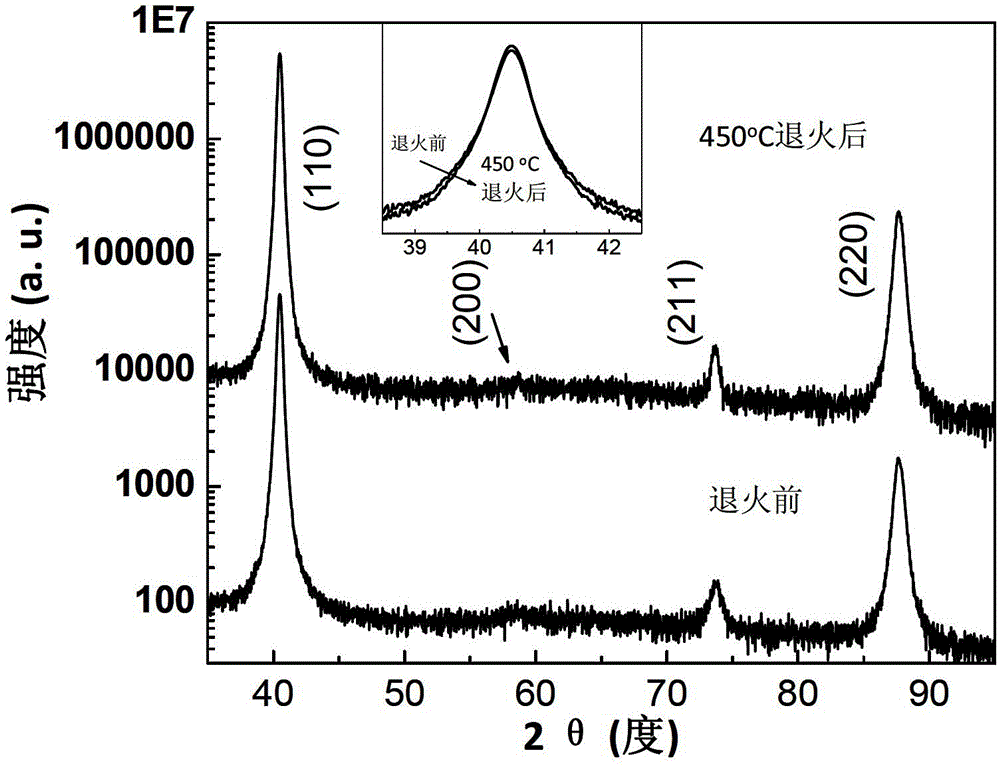
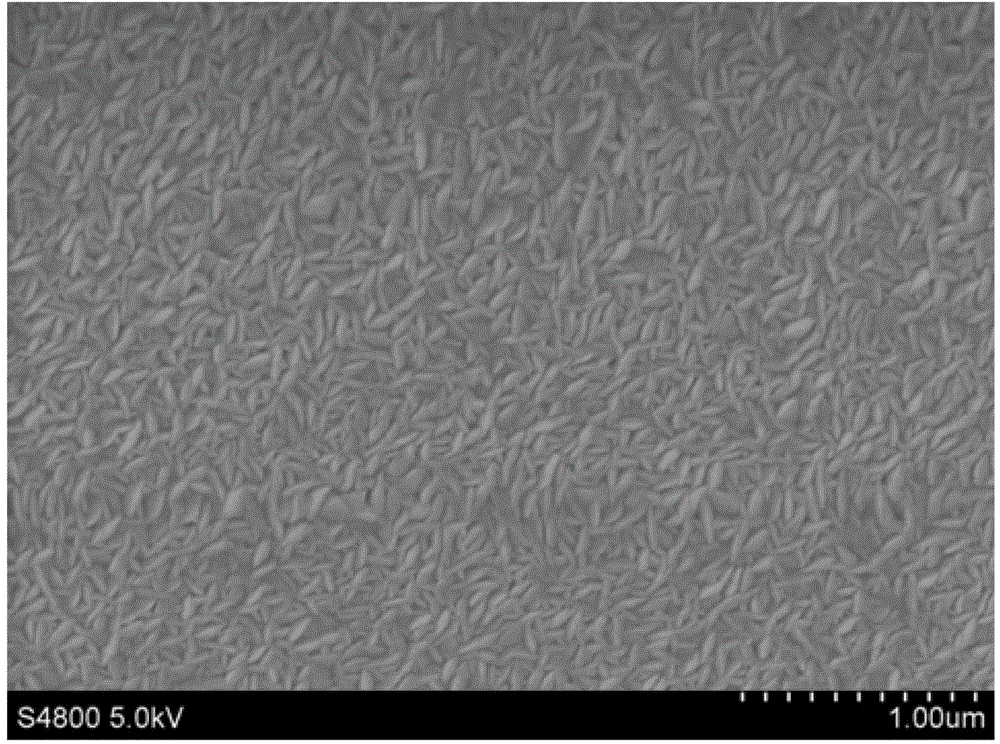
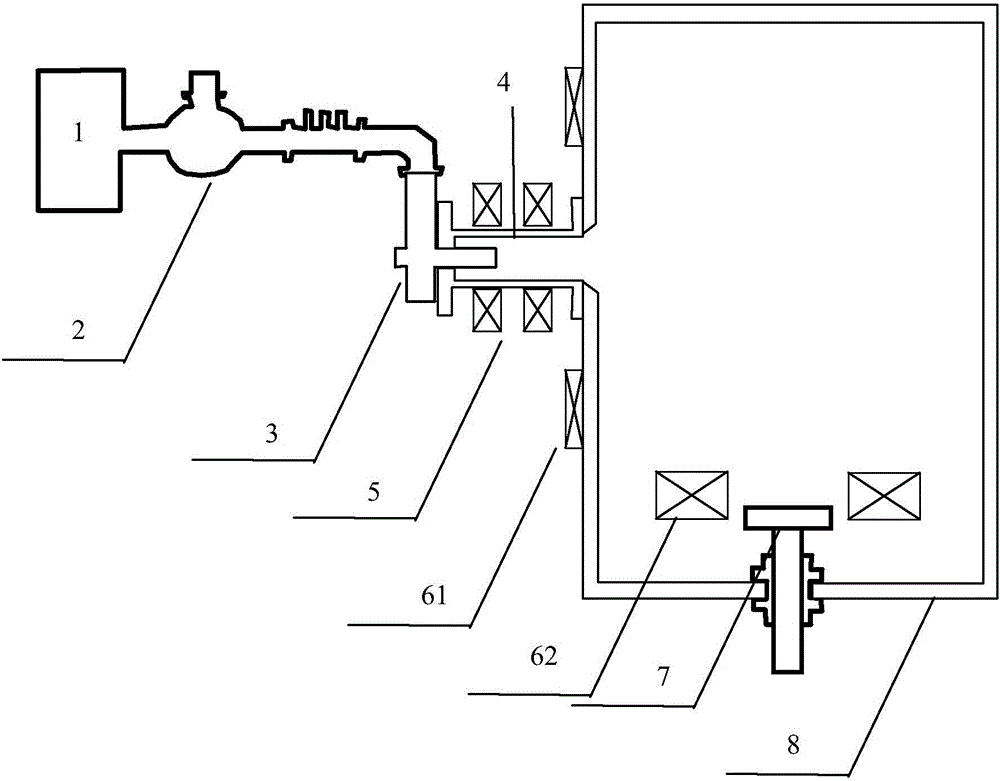
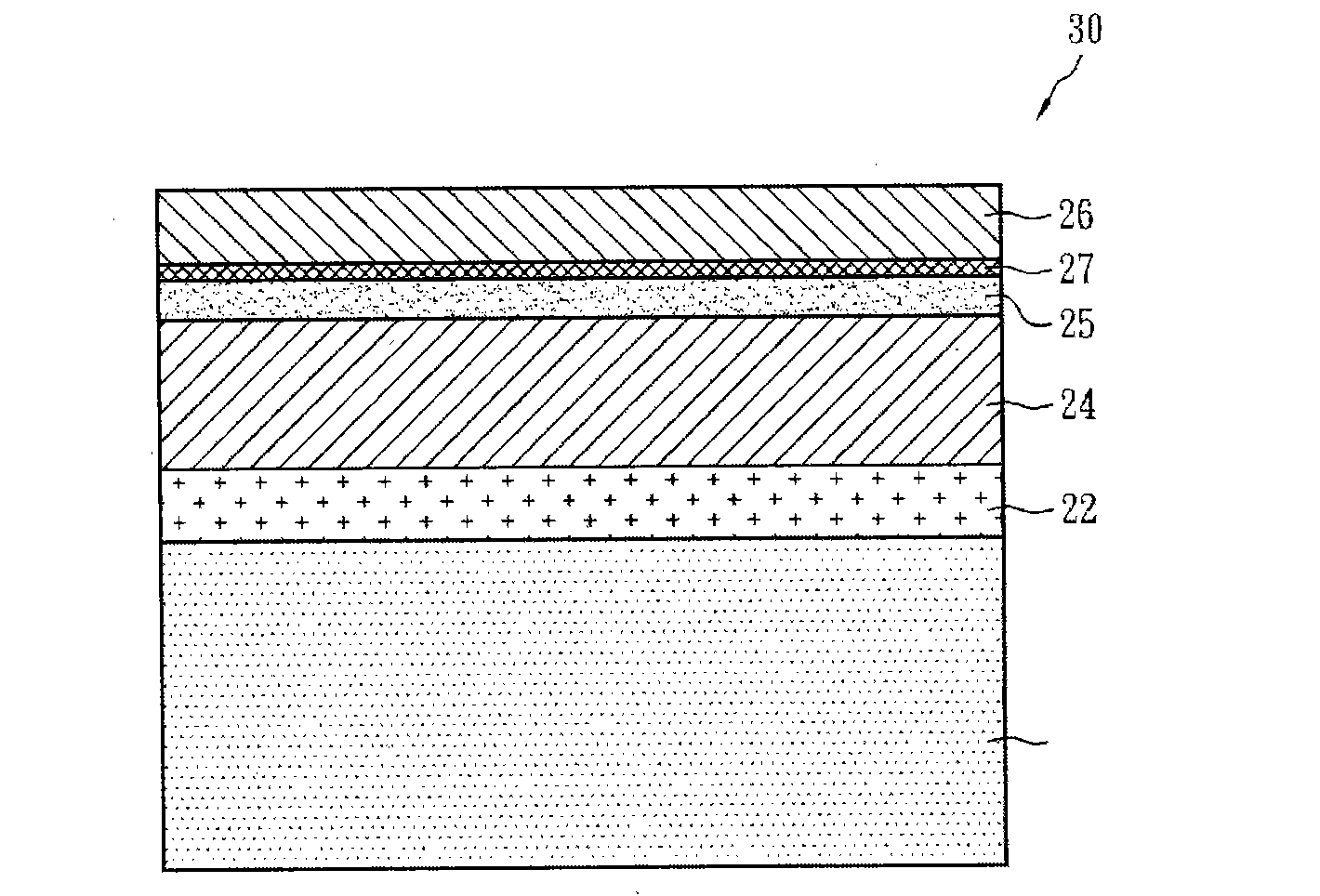
A preparation method of a thin-film solar cell component comprises the following steps: preparing a molybdenum thin film on a substrate; annealing the molybdenum thin film to form a molybdenum back electrode, wherein the annealing temperature is 400 DEG C to 580 DEG C and the annealing time is 5-15 minutes; and sequentially preparing a copper indium gallium diselenide or copper indium diselenide layer, a buffer layer, a window layer and a transparent conductive thin film on the molybdenum back electrode to form the thin-film solar cell component. In the above method, through annealing treatment, the molybdenum thin film is processed into the back electrode which is excellent in adhesion force, corrosion resistance and electric conductivity and suitable for the thin-film solar cell component. And through the improvement, the working efficiency of a device of the thin-film solar cell component is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH +1
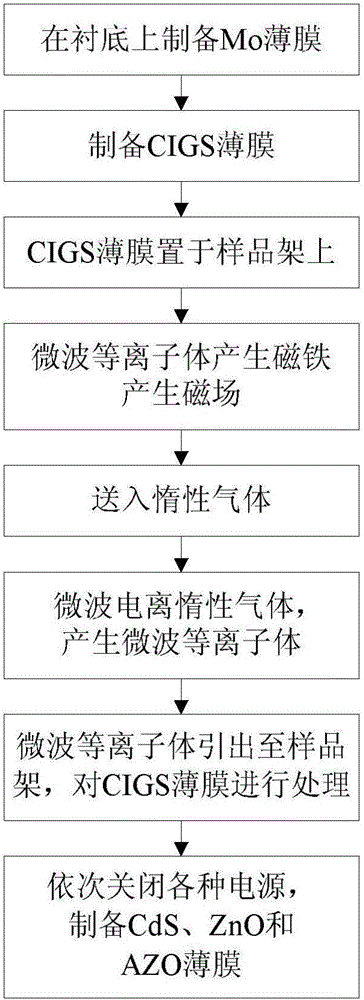
Microwave plasma-based treatment method and system for surface modification of copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS)
InactiveCN105088161AReduce unevennessImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIonizationCopper indium gallium selenide solar cells
The invention discloses a microwave plasma-based treatment method and system for surface modification of copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS).According to the invention, microwave plasma is generated through microwave ionization of inert gases and acts on the surface of a CIGS film. By micron dimension high-strength resputtering and annealing, Cu-Se phase on the surface can be removed and the film can be further annealed, so that non-uniformity of Ga can be relieved, and the purpose of material surface modification can be achieved. The CIGS film serves as a main absorption layer of a CIGS solar cell. The quality of the film directly determines the quality of the CIGS solar cell. The CIGS film subjected to ECR (Electron Cyclotron Resonance) modification lays a foundation for obtaining a CIGS cell with higher photoelectric conversion efficiency, and is feasible and practical as proved through experimental verification.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
A CIGS solar battery light absorbing layer preparation method by adopting an antivacuum preset-quantity coating method
InactiveCN102694057AIncrease surface tensionQuality improvementFinal product manufactureSolid/suspension decomposition chemical coatingIndiumCopper indium gallium selenide solar cells
The present invention discloses a CIGS solar battery light absorbing layer preparation method by adopting an antivacuum preset-quantity coating method, comprising following steps: 1 a step of forming four stable source solutions of copper, indium, gallium and selenium with copper, indium, selenide of gallium and selenium simple substance powder; 2 a step of preparing stable precursor solutions of different stoichiometric ratios with the four source solutions mentioned above respectively in stoichiometric ratios of copper, indium and gallium in a copper indium gallium selenium solar battery light absorbing layer Cu1-yIn1-xGaxSe2 (0<=x<=1, 0<=z<=0.3); 3 a step of coating the precursor solutions on all substrates to form graded distribution of gallium element and a copper indium gallium selenium precursor film with a poor copper surface based on gallium content by adopting an antivacuum preset-quantity coating method; and 4 a drying and annealing step to form a copper indium gallium selenium compound film. The preparation method is characterized by simple technology, high safety, low cost, and superior performance of the film.
Owner:HENGHUI NEW ENERGY (KUNSHAN) CO LTD
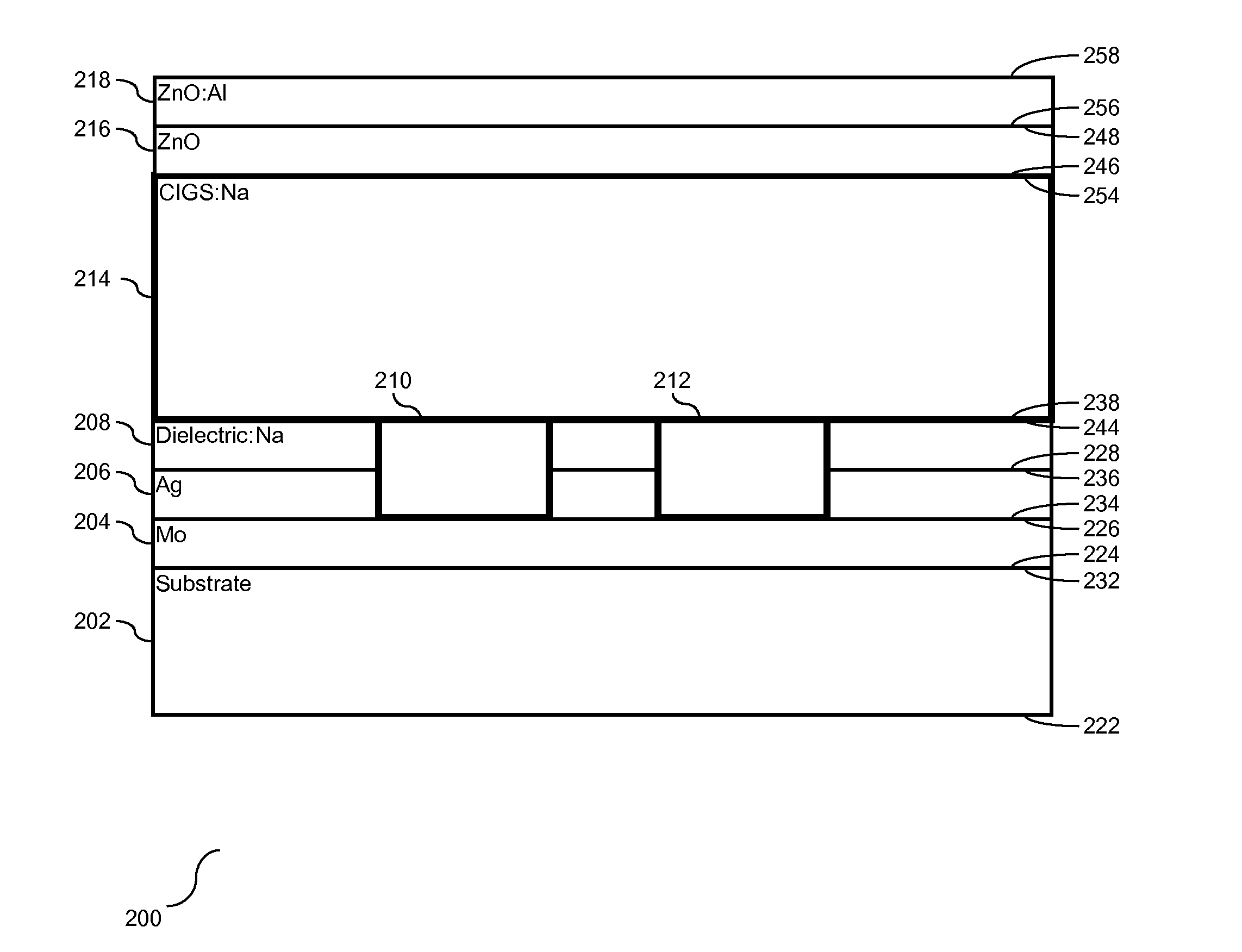
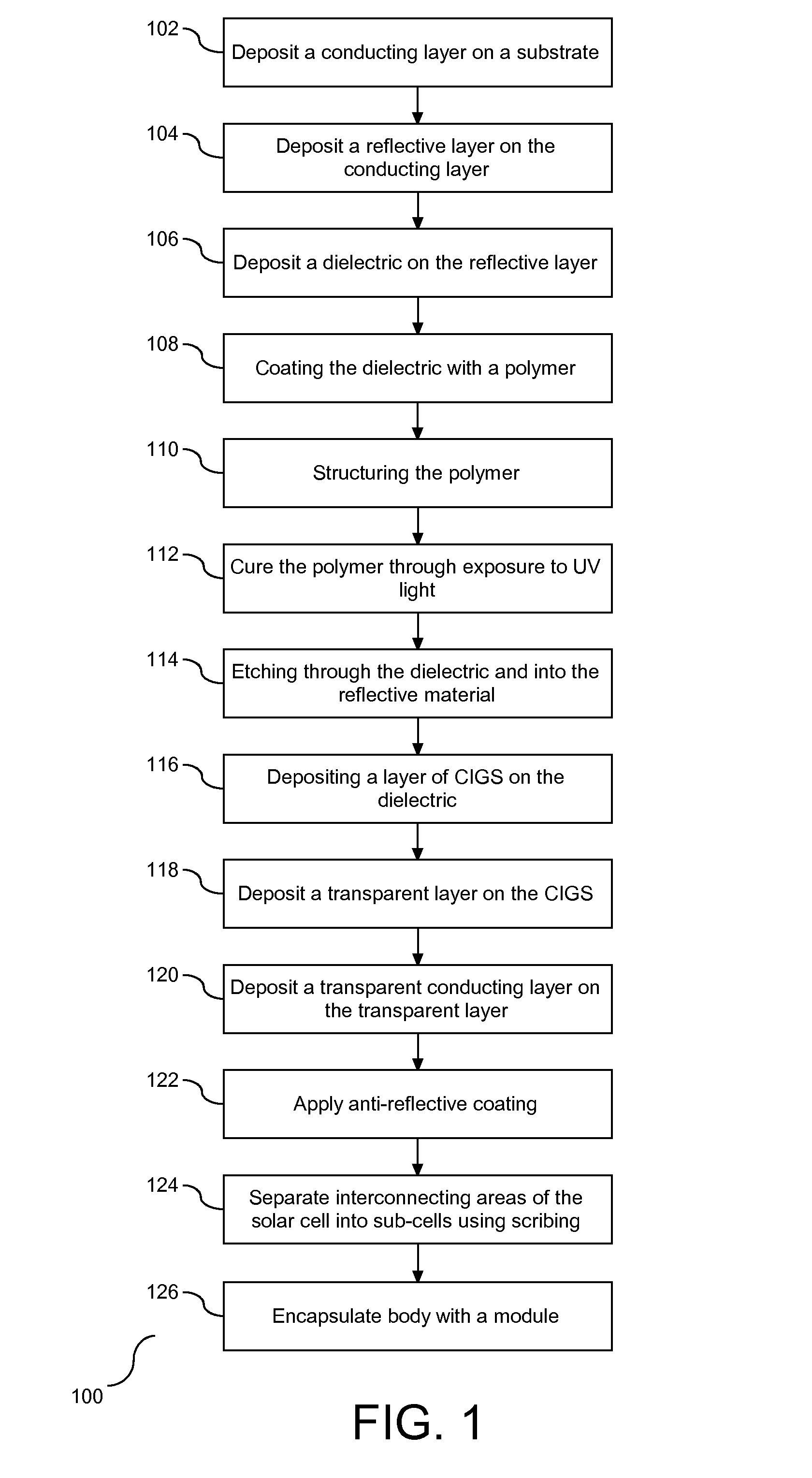
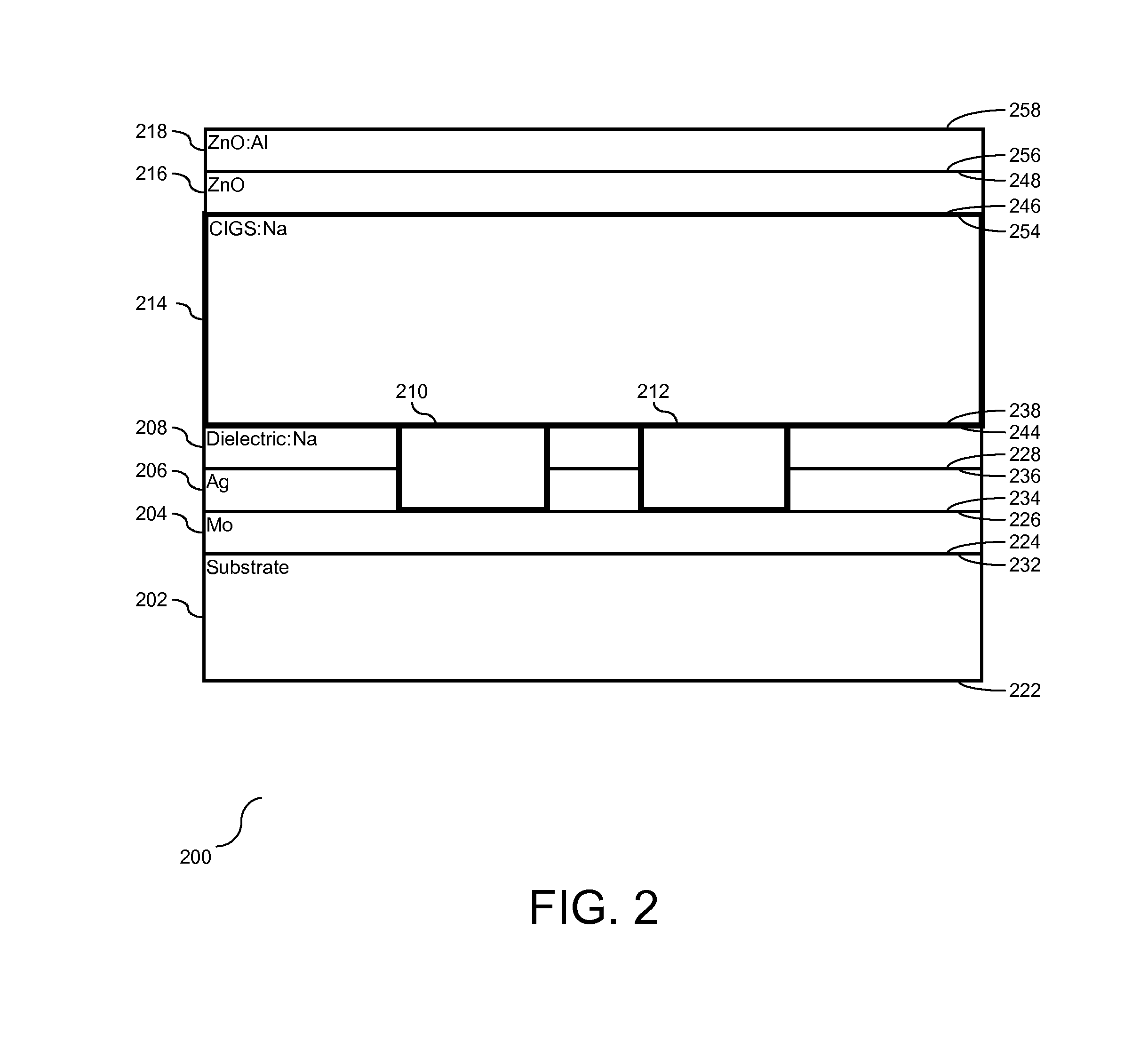
Solar cell with reduced absorber thickness and reduced back surface recombination
InactiveUS20140102509A1PV power plantsFinal product manufactureCopper indium gallium selenide solar cellsOhmic contact
Manufacture for an improved stacked-layered thin film solar cell. Solar cell has reduced absorber thickness and an improved back contact for Copper Indium Gallium Selenide solar cells. The back contact provides improved reflectance particularly for infrared wavelengths while still maintaining ohmic contact to the semiconductor absorber. This reflectance is achieved by producing a back contact having a highly reflecting metal separated from an absorbing layer with a dielectric layer.
Owner:IBM CORP
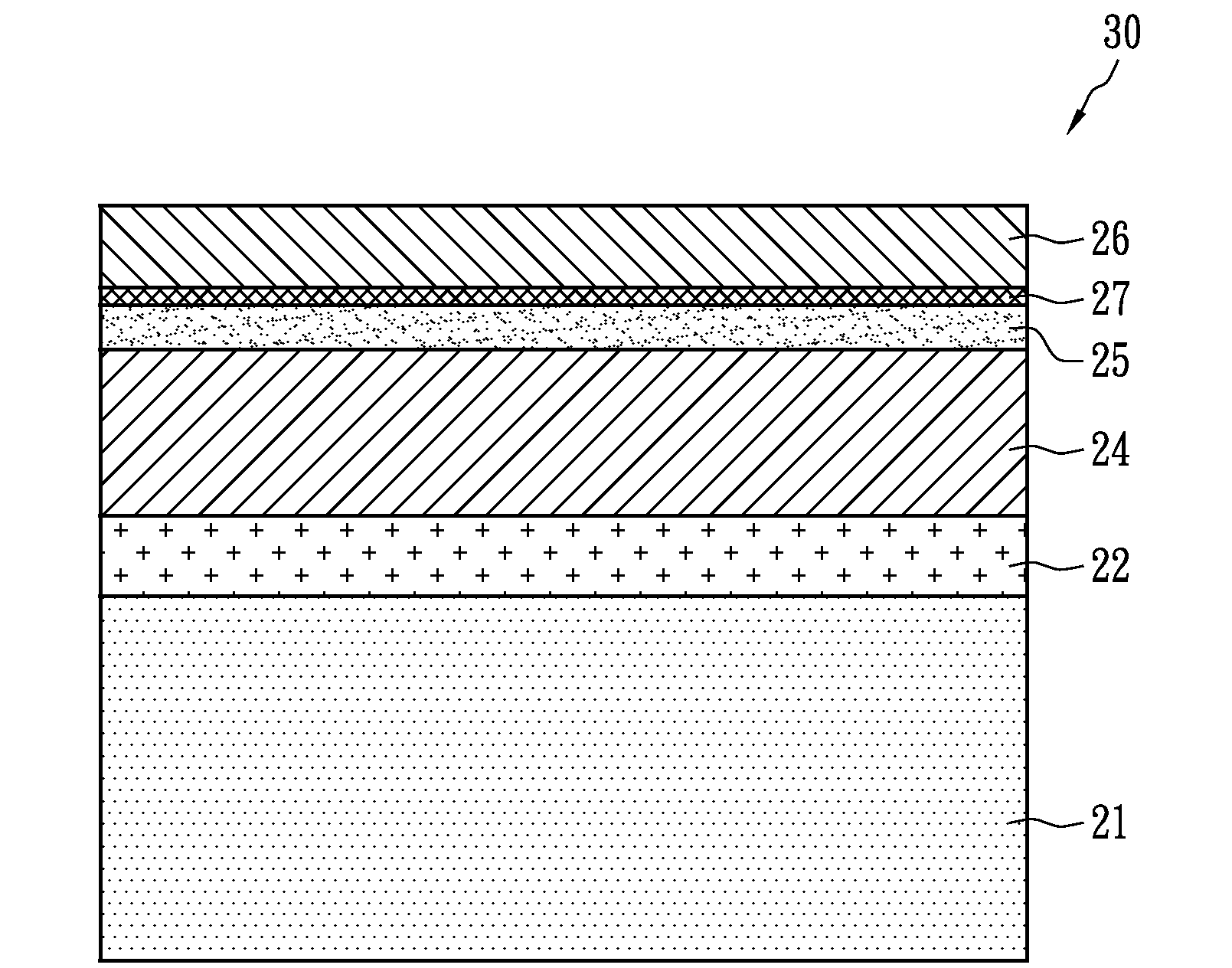
Photovoltaic cell structure
InactiveUS20100243044A1Much of contaminationMuch of wasteFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationIndiumCopper indium gallium selenide solar cells
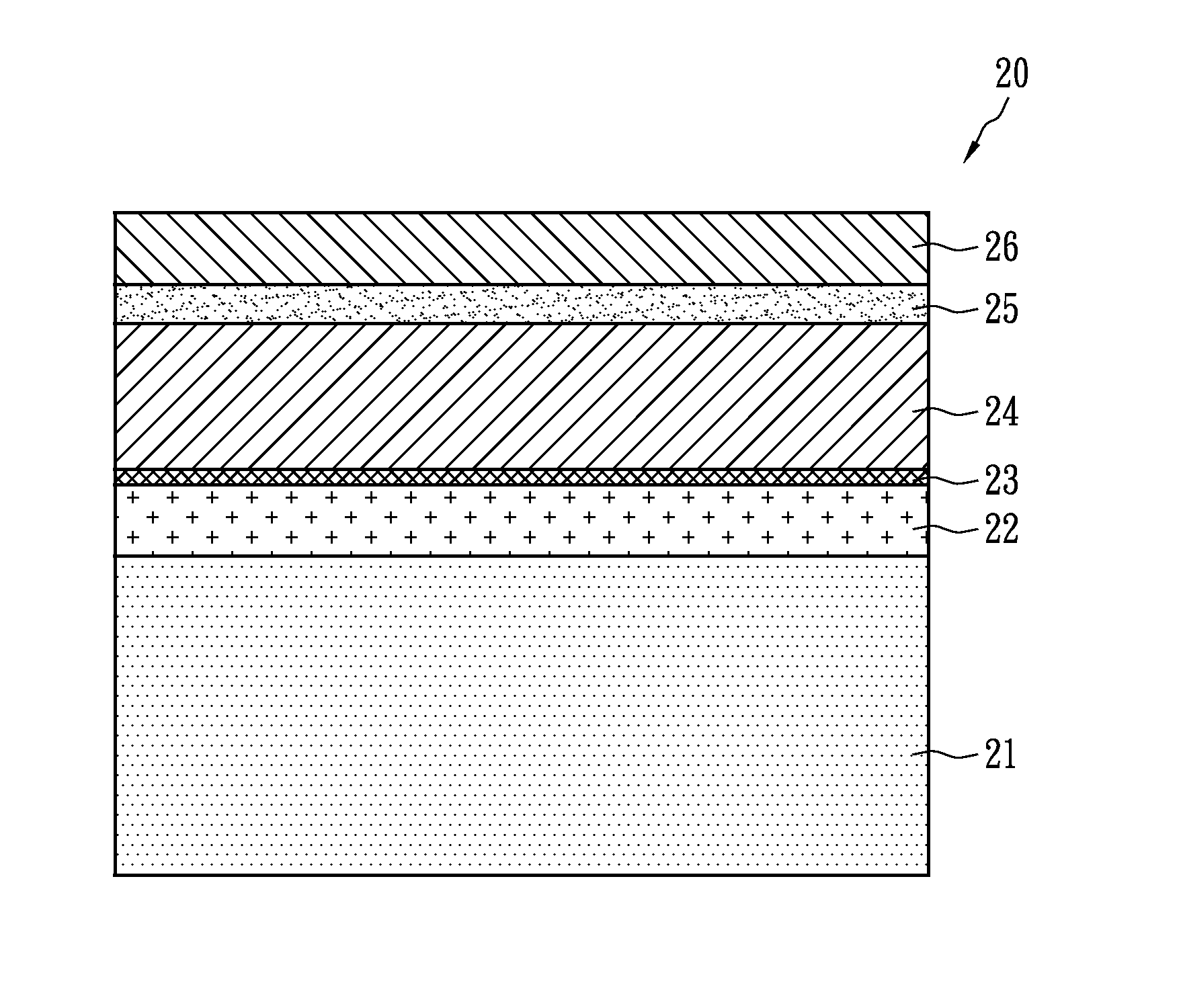
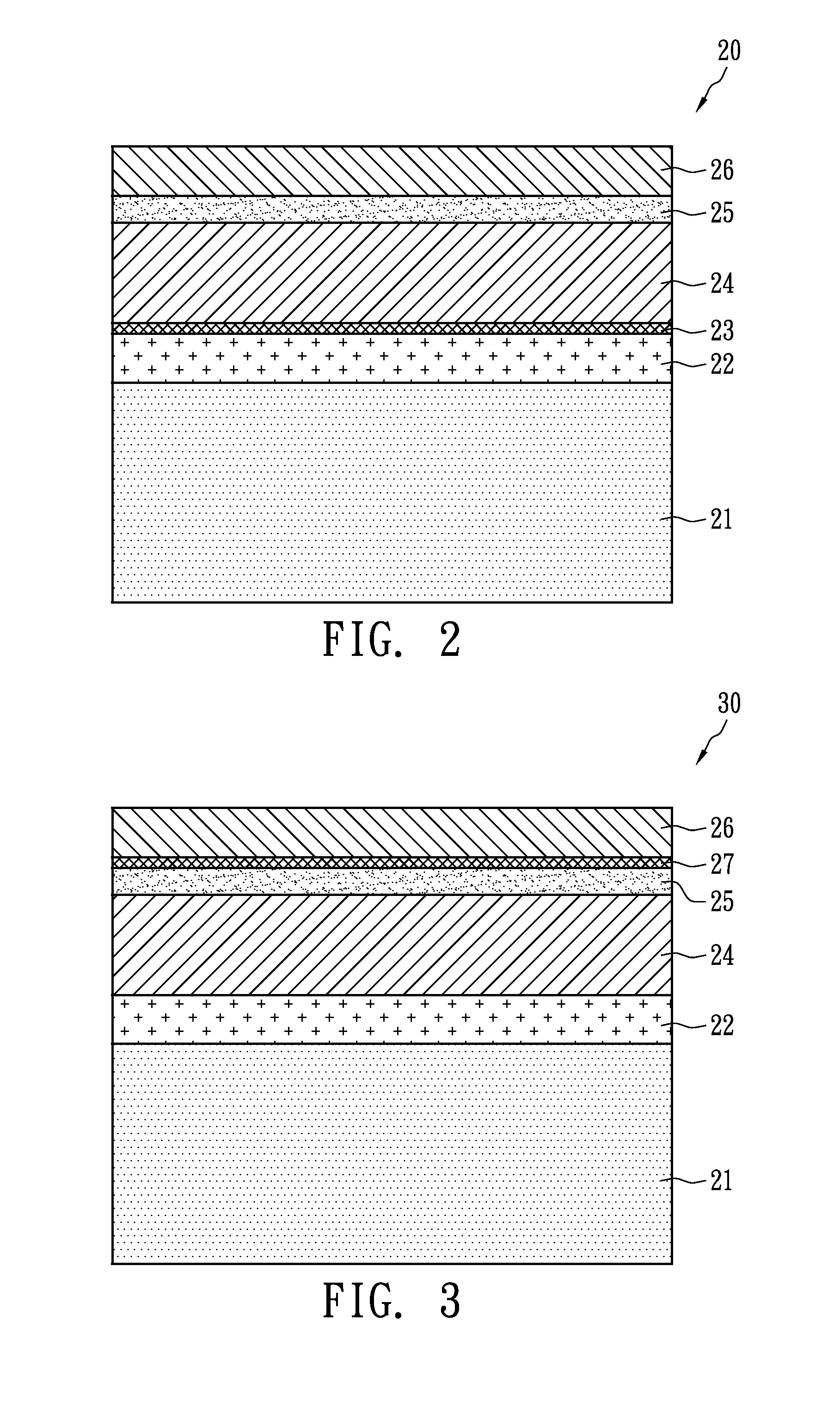
A photovoltaic cell structure includes a substrate, a metal layer, a p-type semiconductor layer, an n-type semiconductor layer, a transparent conductive layer and a high resistivity layer. The metal layer is formed on the substrate. The p-type semiconductor layer is formed on the metal layer and may include a compound of copper indium gallium selenium sulfur (CIGSS), copper indium gallium selenium (CIGS), copper indium sulfur (CIS), copper indium selenium (CIS) or a compound of at least two of copper, selenium or sulfur. The n-type semiconductor layer exhibits photo catalyst behavior that can increase carrier mobility by receiving light, and is formed on the p-type semiconductor layer, thereby forming a p-n junction. The transparent conductive layer is formed on the n-type semiconductor layer. The high resistivity layer is formed between the metal layer and the transparent conductive layer.
Owner:PVNEXT CORP
Copper indium gallium diselenide thin film cell co-evaporation linear source array configuration
ActiveCN103871851AImprove adjustment flexibilityTo achieve the purpose of process adjustmentFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingIndiumCopper indium gallium selenide solar cells
The invention relates to a copper indium gallium diselenide thin film cell technology, in particular to a linear source array configuration in the copper indium gallium diselenide thin film cell co-evaporation technology. The copper indium gallium diselenide thin film cell co-evaporation linear source array configuration comprises a glass substrate and linear evaporation sources, wherein the linear evaporation sources containing different raw materials are arranged longitudinally along the moving direction of the glass substrate and form a linear evaporation source array, and the linear evaporation sources are aligned in a line and are located right under the glass substrate. The linear evaporation sources are cylinders or cuboids, and are provided with evaporation zones in a long and narrow seam shape or point-shaped evaporation holes. The copper indium gallium diselenide thin film cell co-evaporation linear source array configuration can effectively set evaporation regions according to a preset technological ratio, and greatly improve the adjusting flexibility of a raw material ratio in a cell production technology.
Owner:紫石能源有限公司
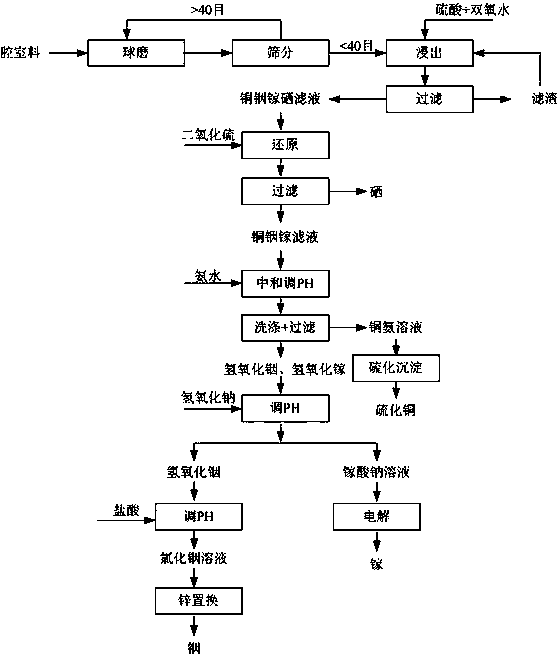
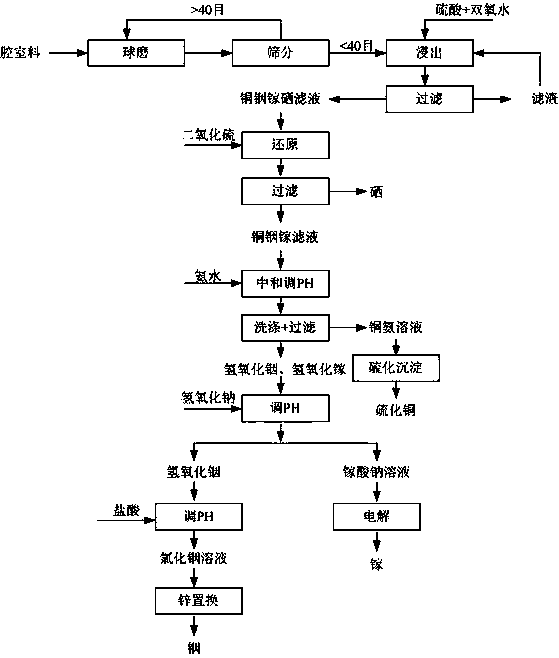
Recovery method of copper indium gallium diselenide material
ActiveCN106987717APhotography auxillary processesGallium/indium/thallium compoundsRecovery methodIndium
The invention discloses a recovery method of a copper indium gallium diselenide material. The recovery method mainly comprises the steps of sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide leaching, sulfur dioxide selenium reduction, copper ammonia complexing copper separation, alkali indium and gallium separation, indium replacement, gallium hydrolyzing and the like. According to the recovery method of the copper indium gallium diselenide material, sulfuric acid cooperates with hydrogen peroxide for leaching, the leaching rate is greatly increased, and acid gas pollution is reduced; through copper ammonia complexing copper separation, sediment cannot be generated, and metal ions can be separated well; and alkali gallium separation is adopted, indium and gallium separation can be achieved simply by adjusting the PH value of a solution, the separation effect is good, and the purity of obtained indium and gallium products is high.
Owner:HANERGY MOBILE ENERGY HLDG GRP CO LTD
Sodium-doped copper indium gallium diselenide solar cell device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN104716217AExcellent electrical propertiesImprove performanceFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationGlass compositesIndium
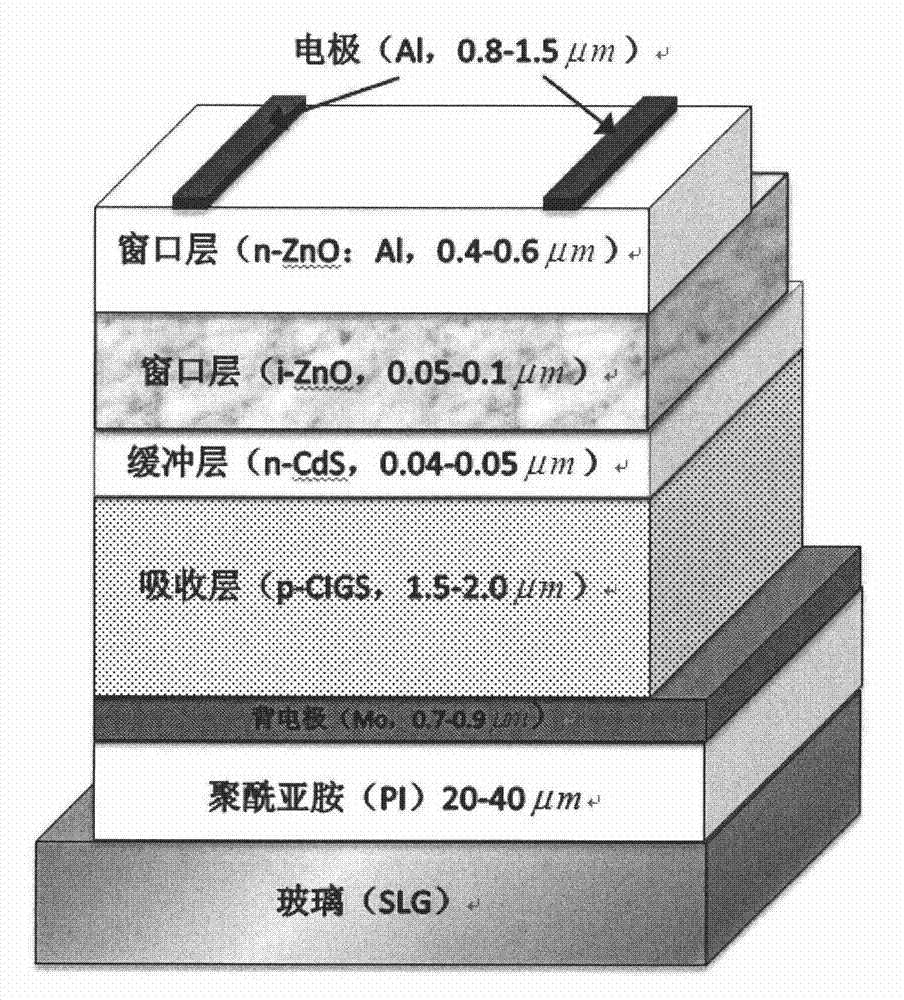
A polyimide film-soda glass composite substrate based sodium-doped copper indium gallium diselenide solar cell device is characterized in that a substrate is composed of soda glass and a polyimide film growing on the surface of the substrate, and copper indium gallium diselenide solar cells are manufactured on the surface of the composite substrate. The sodium-doped copper indium gallium diselenide solar cell device has the advantages that the polyimide film-soda glass composite substrate based copper indium gallium diselenide film is excellent in adhesion property and good in crystallization quality, crystalline grains are large, and the defects are few; after the whole copper indium gallium diselenide solar cells are manufactured, the solar cells are separated from the soda glass to form the flexible copper indium gallium diselenide solar cells using the polyimide film as the substrate, and the flexible cells are manufactured by using the rigid substrate; a manufacturing method is simple and easy to implement, and the solar cell device is suitable for large-scale popularization and application and especially has very wide application prospect in a space occasion and special occasions.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Copper indium gallium selenide film solar battery and preparation method thereof
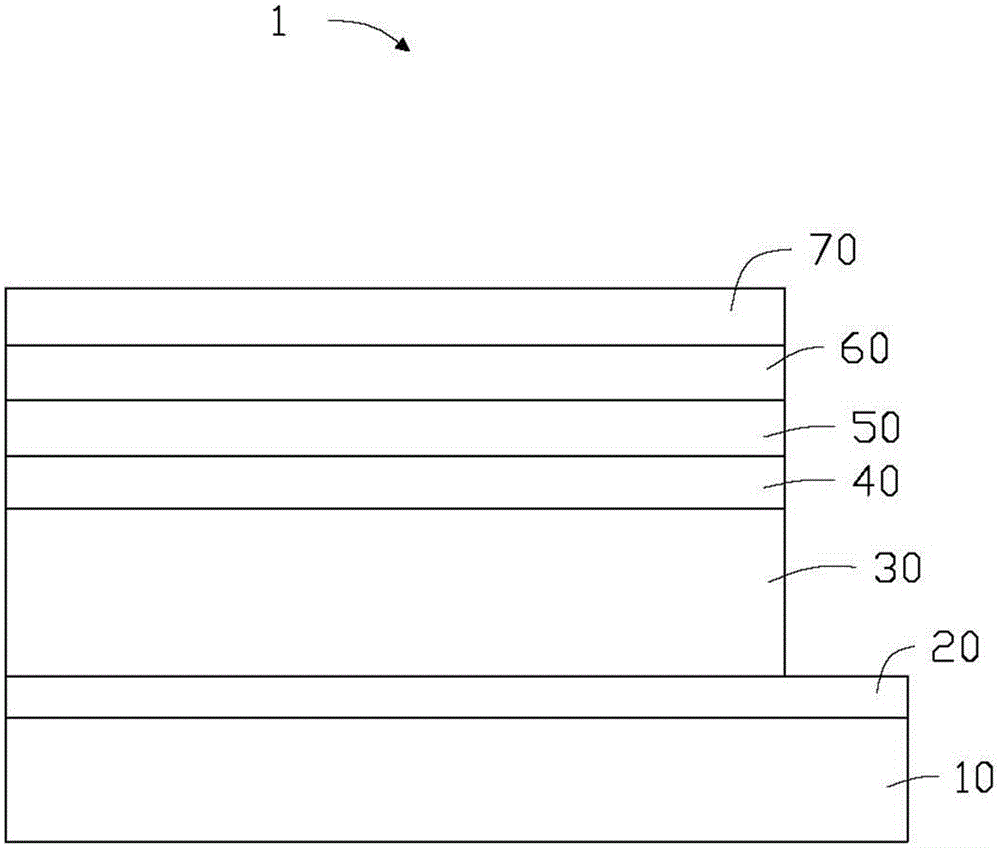
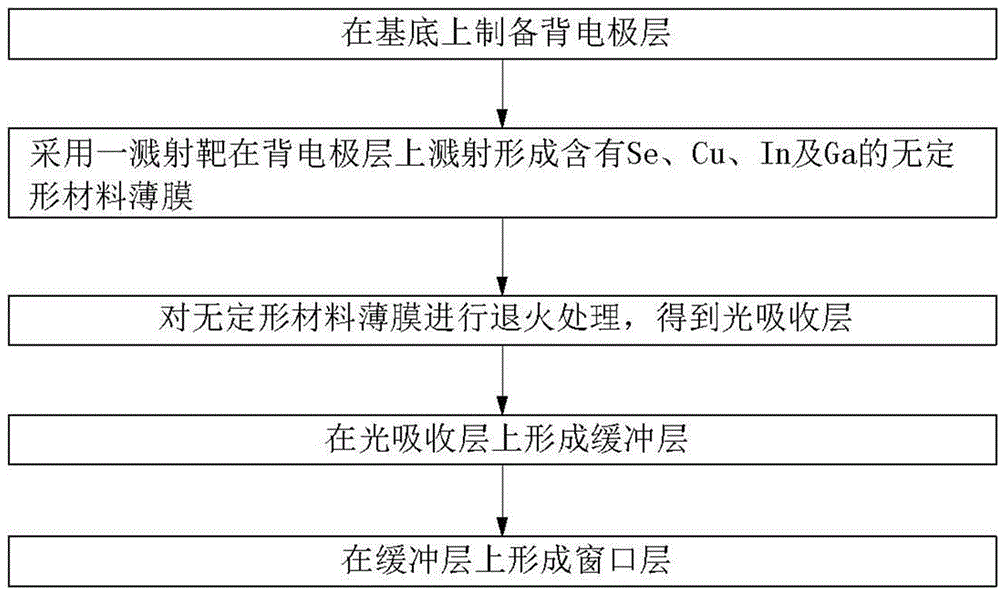
ActiveCN104835869AImprove securityReduce manufacturing costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumCopper indium gallium selenide solar cells
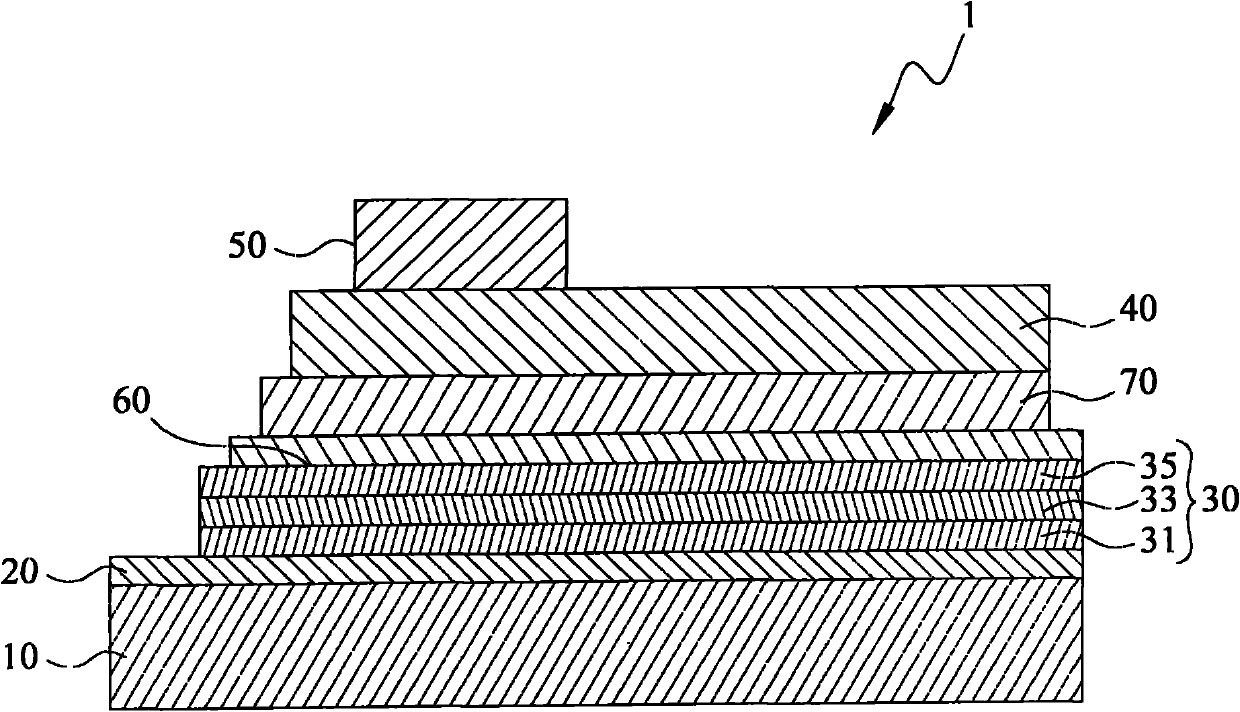
The invention relates to a copper indium gallium selenide film solar battery and a preparation method thereof. The solar battery comprises a substrate, a back electrode layer arranged on the substrate, a light absorption layer arranged on the back electrode layer, a buffer layer arranged on the light absorption layer and a window layer arranged on the buffer layer, and is characterized in that the light absorption layer comprises a copper element (Cu), an indium element (In), a gallium element (Ga) and a selenium element (Se), the light absorption layer is formed by doping the Se element in the original position of Cu<y>(In<1-x>Ga<x>)Se2, and the mol ratio among the elements Se:(Cu+In+Ga) is greater than 1.0 and smaller than and equal to 1.5. The invention further relates to a preparation method of a copper indium gallium selenide film solar battery.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of copper indium gallium diselenide thin film solar cell absorbing layer
InactiveCN102943237AHigh crystallinityImprove performanceFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingIndiumRadio frequency magnetron sputtering
The invention relates to a preparation method of a copper indium gallium diselenide thin film solar cell absorbing layer. The preparation method is characterized in that the preparation method comprises the following steps of: 1) preparing a CuIn<1-X>Ga<X>Se<2> layer on the bottom electrode of a substrate through radio-frequency magnetron sputtering by using a CuIn<1-X>Ga<X>Se<2> compound target; and 2) conducting annealing treatment to the substrate with the CuIn<1-X>Ga<X>Se<2> layer prepared in the step 1 to obtain a CuIn<1-X>Ga<X>Se<2> absorbing layer on the bottom electrode. Since the radio-frequency magnetron sputtering and heat treatment are adopted for preparing the absorbing layer on the bottom electrode of the substrate, the crystallization degree of the absorbing layer is improved, the size of crystal grains reaches micrometer-scale, the performance of the absorbing layer is improved, the performance of thin film solar cells can be effectively improved, the process is greatly simplified, the process repeatability is good and the process is controllable.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 18 RES INST
Method for manufacturing copper indium gallium diselenide thin-film solar cells
InactiveCN103474128ASimple processReduce manufacturing costFinal product manufactureNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialEpoxyManufacturing cost reduction
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing copper indium gallium diselenide thin-film solar cells. The method comprises the steps that (1), compound conductive molybdenum thick liquid is arranged on a ceramic substrate in a silk-screen printing or blade coating or spraying mode, and back electrodes are obtained after drying of 150-250 DEG C, heat processing of 450-1150 DEG C and annealing of 150-250 DEG C, wherein the compound conductive molybdenum thick liquid comprises the following components, by weight, 50-80 parts of molybdenum powder, 5-15 parts of glass powder, 10-25 parts of organic carriers and 5-10 parts of annexing agents; the organic carriers comprise epoxy resin and organic solvent, and the mass ratio between the epoxy resin and the organic solvent is (1-5):(9-20); the annexing agents comprise moderate NaOH, thickening agents, plasticizer and surface active agents; (2), the copper indium gallium diselenide thin-film solar cells are processed based on the back electrodes. Compared with the prior art, the compound conductive molybdenum thick liquid adopted in the method can process the back electrodes of the copper indium gallium diselenide thin-film solar cells through a non-vacuum processing technology, namely, the silk-screen printing method or the spraying method or the blade coating method, the process is simple and the manufacturing cost is lowered.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
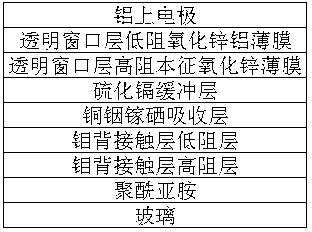
Copper indium gallium selenium solar battery device and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN103346194AIncrease roughnessPromote growthFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHigh resistanceIndium
A copper indium gallium selenium solar battery device is a copper indium gallium selenium solar battery based on a polyimide film-soda glass recombination substrate. The copper indium gallium selenium solar battery device is composed of glass, polyimide, a molybdenum back contacting layer, a copper indium gallium selenium absorbing layer, a cadmium sulfide buffering layer, a transparent window layer high resistance eigen zinc oxide thin film, a transparent window low resistance zinc oxide aluminum thin film and an aluminum top electrode, and a lamination structure is formed. A preparing method comprises the first step of coating the surface of the glass by polyimide gum, wherein the polyimide film-soda glass recombination substrate is formed in a solidifying mode, the second step of preparing all thin films on the surface of the polyimide film-soda glass recombination substrate sequentially, and the third step of separating the complete copper indium gallium selenium solar battery and the soda glass substrate after the complete copper indium gallium selenium solar battery is prepared. The soft copper indium gallium selenium solar battery with the polyimide film as the substrate is obtained. The copper indium gallium selenium solar battery device has the advantages that a copper indium gallium selenium thin film crystal based on the polyimide film-soda glass recombination substrate is large in grain; according to the preparing method of the copper indium gallium selenium solar battery device, the soft battery is prepared through the rigidity substrate, the method is easy to implement, and large-scale popularization and application are facilitated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) solar battery buffer layer
ActiveCN102110737AGuaranteed thicknessGuaranteed uniformityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesWater bathsDynamic balance
The invention discloses a method for preparing copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) solar battery buffer layer. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a plating solution, selecting a substrate, spraying the plating solution on the substrate and forming an II-VI group compound thin film on the substrate serving as a solar battery buffer layer. In the invention, a spraying method is adopted to prepare the CIGS solar battery buffer layer, a nozzle is adopted to spray plating solution in a stereo shape, such as water curtain shape, circular cone shape or column shape, on the substrate on the conveyor belt based on the dynamic crystallization principle so as to enable the plating solution to contact the substrate to crystallize; since the substrate surface contacts the fresh plating solution continuously, a dynamic balance is formed between the solution and the substrate and a deposition mode similar to the chemical water bath method is formed, new crystals are generated on the contact surface continuously; compared with the conventional chemical water bath method, the method greatly improves the production efficiency. By the adoption of a pressurized metering pump, the spraying amount of plating solution is controlled, so that the II-VI group compound thin film obtained by spraying has a guaranteed thickness, a guaranteed uniformity, a guaranteed density, low cost and good repeatability.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 18 RES INST
Copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) solar cell and making method thereof
InactiveCN102315294AEnhanced light absorptionImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationCopper indium gallium selenide solar cellsPhotoelectric conversion
The invention discloses a copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) solar cell and a making method thereof. The CIGS solar cell comprises a glass substrate, a light absorption surface and a photoelectric conversion structure; at least one surface of the glass substrate is provided with a plurality of array concave-convex parts; the light absorption surface comprises a set of the surfaces of topmost ends of the array concave-convex parts, the surfaces extending to bottommost ends from the topmost ends of the array concave-convex parts and the surface of a bottommost-end substrate of the array concave-convex parts except the array concave-convex parts; and the photoelectric conversion structure consists of an n-type semiconductor layer and a p-type semiconductor layer of a CIGS compound, and an i-type semiconductor layer positioned between the n-type semiconductor layer and the p-type semiconductor layer. In the invention, light absorption quantity is increased by increasing a light absorption area, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the CIGS solar cell is improved by combing the design of an n-i-p structure, so the production cost is reduced, and the economic value of the solar cell is improved.
Owner:GCSOL TECH
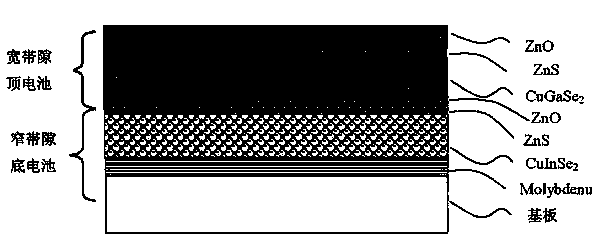
Compound semiconductor laminated film solar cell
ActiveCN102956738ASimple manufacturing processReduce manufacturing costFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationCopper indium gallium selenide solar cellsElectrical connection
The invention relates to a compound semiconductor laminated film solar cell, comprising a copper indium gallium selenide cell (CIGS) bottom cell with a low bandgap and a copper gallium selenide (CGS) top cell with a high bandgap. The compound semiconductor laminated film solar cell is characterized in that the bottom cell and the top cell are internally connected in series into a whole through a connecting layer; and the connecting layer is composed of a transparent metal oxide conductive layer positioned at the bottom cell and a nanometer metal conductive layer positioned at the top cell. According to the compound semiconductor laminated film solar cell, the combination of transparent metal oxide and a nanometer metal film is used as the connecting layer of the bottom cell and the top cell, so that the technological compatibility problem of the bottom cell and the top cell is solved, the internal electrical connection of the bottom cell and the top cell is realized, the manufacturing process of the cell is simplified, the manufacturing cost of the cell is reduced, and the cell is simple in structure.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 18 RES INST
Copper indium gallium diselenide thin film solar cell back electrode and preparation method thereof
PendingCN107452818AStop the spreadSimple structurePhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesIndiumCopper indium gallium selenide solar cells
The present invention discloses a copper indium gallium diselenide (CIGS) thin film solar cell back electrode. The back electrode comprises a substrate, a metal conduction layer, a barrier layer, an Na alloy layer and an external protection conduction layer arranged in order from down to up; the barrier layer is transition metal nitride or nitric oxide; the Na alloy layer is formed by Na and another alloy element, and the Na content in the Na alloy layer is 2-10% molar ratio; the thickness of the Na alloy layer is 20-50 nm; magnetron sputtering is employed to perform deposition of each structure layer in order on the substrate for completing preparation; the Na alloy layer is taken as an Na diffusion source to provide Na required by crystal growth for the CIGS absorption layer, the barrier layer can prevent the Na from diffusion to the direction of the substrate and also prevent the impurities in the substrate from diffusion to the CIGS absorption layer to realize the accurate control of Na, and the barrier layer prevents selenium element in the deposition process from diffusion to the metal conduction layer so as to avoid reaction between the selenium and the metal conduction layer and ensure the stability of the metal conduction layer in the growth process of the CIGS absorption layer.
Owner:蚌埠兴科玻璃有限公司 +2
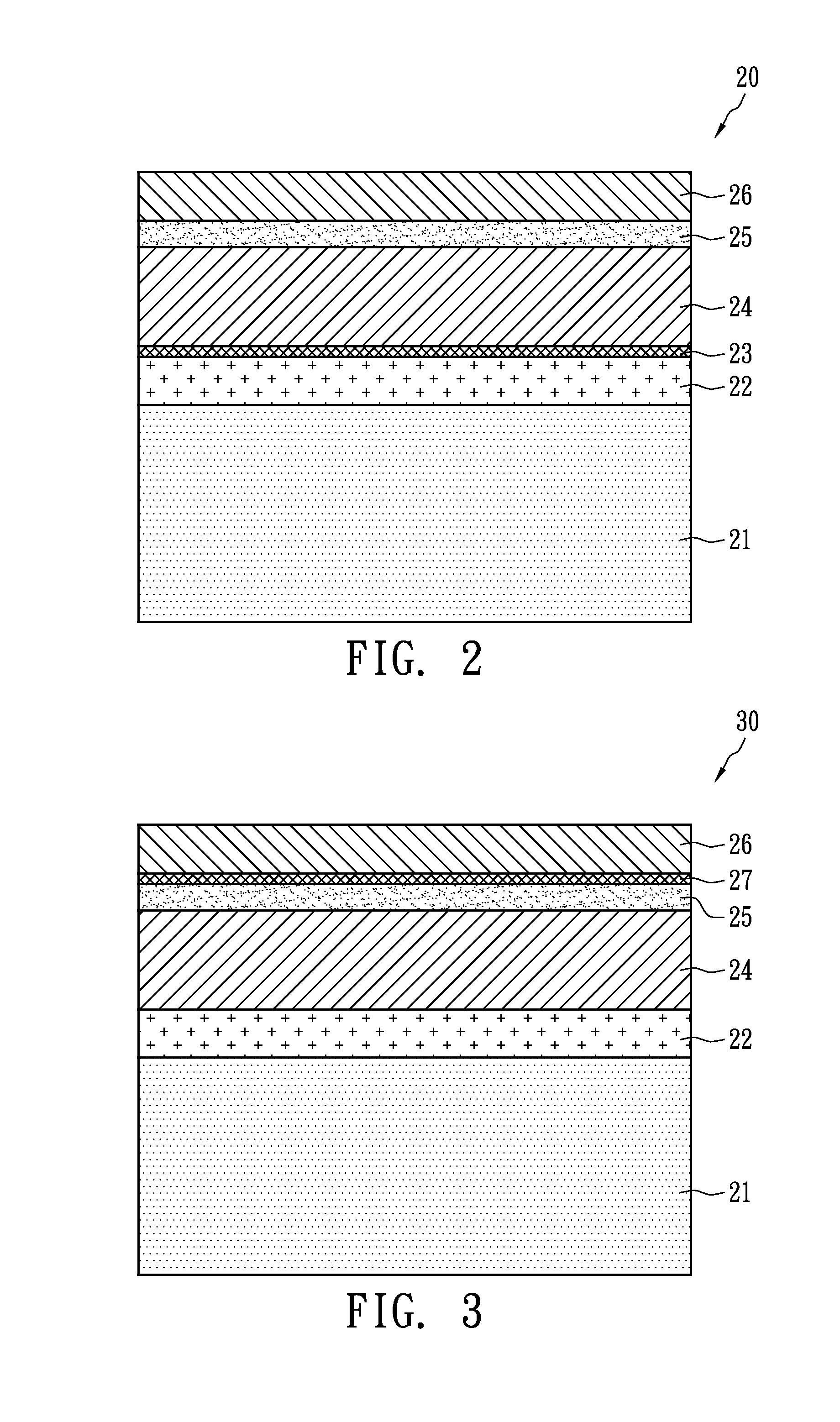
Solar cell component structure
InactiveCN102593208AReduce generationAvoid pollutionPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesHigh resistanceIndium
The invention discloses a solar cell component structure comprising a substrate, a metal layer, a p-type semiconductor layer, an n-type semiconductor layer, a transparent conductive layer and a high resistance film layer, wherein the metal layer is formed on the surface of the substrate; the p-type semiconductor layer is formed on the metal layer and comprises copper indium gallium selenium sulfur (CIGSS), copper indium gallium selenium (CIGS), copper indium sulfur (CIS), copper indium selenium (CIS) or a compound material containing two or two more of copper, selenium or sulfur; the n-type semiconductor layer has the photocatalyst characteristics (such as improvement of carrier mobility by using irradiation), is formed on the surface of the p-type semiconductor layer and forms a p-n joint surface together with the p-type semiconductor layer; the transparent conductive layer is formed on the n-type semiconductor layer; and the high resistance film layer is formed between the metal layer and the transparent conductive layer.
Owner:PVNEXT CORP
Copper indium diselenide solar cell and production method thereof
InactiveCN102569441ASingle crystal phaseUniform concentrationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesIndiumCopper indium gallium selenide solar cells
The invention discloses a copper indium diselenide solar cell and a production method thereof, wherein the solar cell comprises a substrate, a back metal electrode, a light absorption layer, a transparent electric conduction layer and a contact electrode layer, the light absorption layer comprises a plurality of copper indium gallium diselenide films or copper indium gallium diselenide sulfur compound films which have different atom ratios, different target materials can be directly sputtered into a film on the back metal electrode in a direct current or radio frequency mode during the production process, so selenylation does not need to be carried out, the copper indium diselenide solar cell is safer, has high efficiency and costs less for production, components are easy to control, crystalline phases are single, the concentration is uniform, and the conversion efficiency is also improved.
Owner:HELIOHAWK OPTOELECTRONICS CORP
Method for ohmic contact between copper indium gallium diselenide and molybdenum and solar cell preparation method
InactiveCN104134708ALower internal resistanceReduce processingFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationIndiumInternal resistance
The invention discloses a method for ohmic contact between copper indium gallium diselenide and molybdenum and a solar cell preparation method. After a CIGS thin film is formed on a Mo thin film, power voltage is applied between the CIGS thin film and the Mo thin film, a scanning assembly carries out two-dimensional scanning on the surface of the CIGS thin film, the contact-potential barrier between the Mo thin film and the CIGS thin film is broken through, internal resistance of the thin-film solar cell is reduced, and conditions are created for improving efficiency of the solar cell. According to the method for ohmic contact between copper indium gallium diselenide and molybdenum and the solar cell preparation method, through the voltage application mode, additional processing on the surface of the Mo thin film can be reduced, the number of procedures is reduced, uncontrollability caused by additional technologies is avoided, the implementation methods are quite simple, and input of subsequent industrial development is saved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
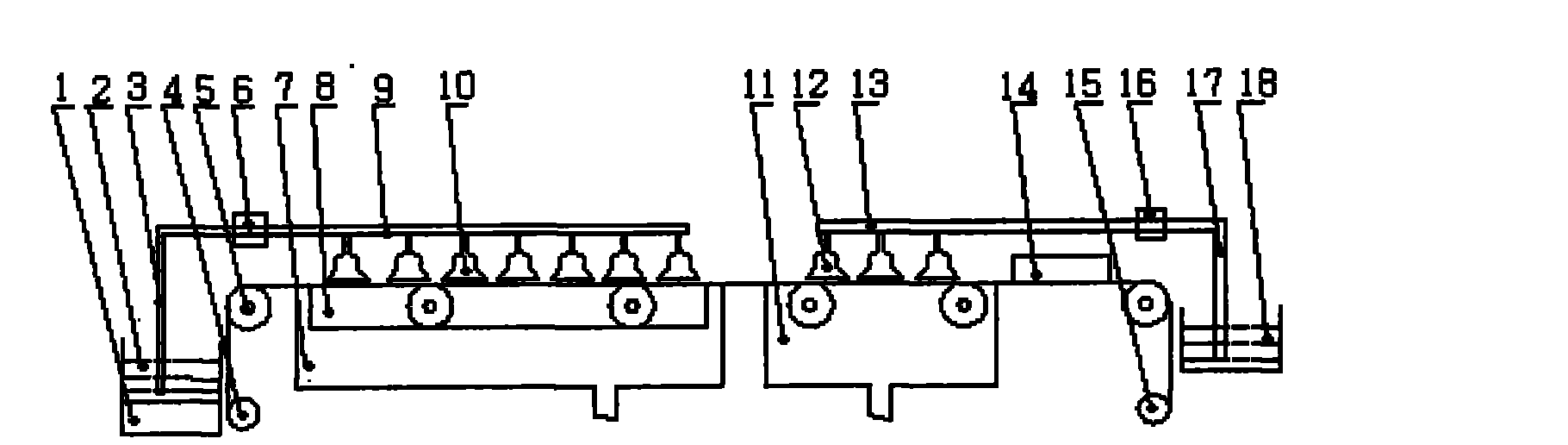
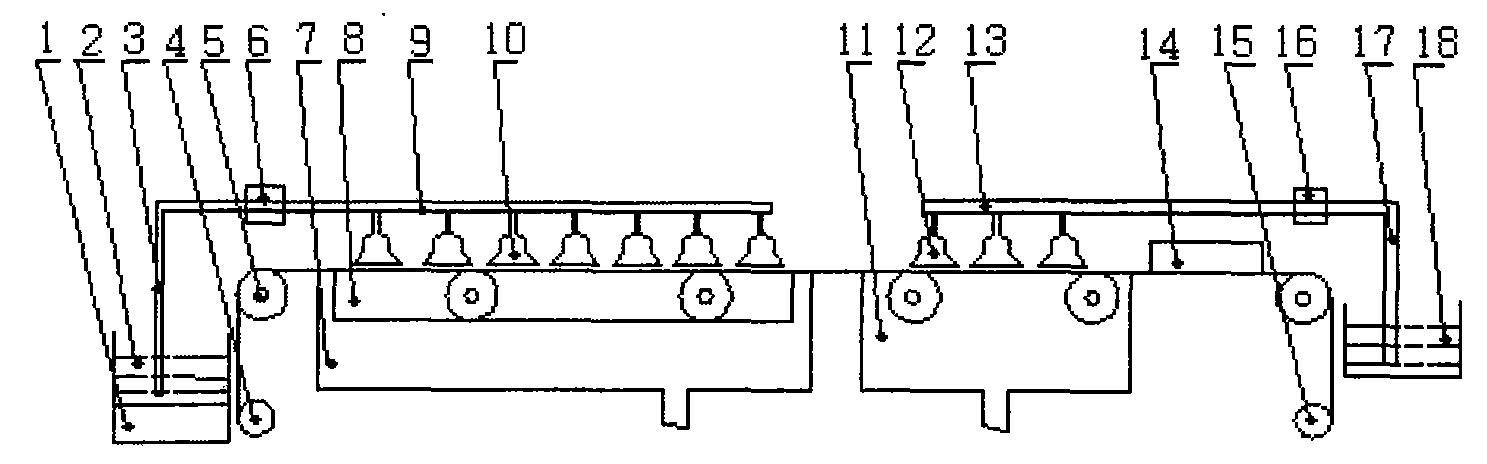
Thin-film solar cell annealing device, and preparation method of copper indium gallium selenide thin-film cell absorption layer and copper zinc tin sulfide thin-film cell absorption layer
InactiveCN103014651AQuality improvementEvenly heatedVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIndiumCopper indium gallium selenide solar cells
A thin-film solar cell annealing device is used for selenizing or vulcanizing a metal film prefabrication layer on a substrate, and comprises an annealing furnace, a substrate rack and a first heating lamp tube, wherein the annealing furnace adopts a hollow structure; a sealed annealing cavity is formed inside the annealing furnace; the substrate rack is arranged on one side wall of the annealing cavity; the substrate can be loaded on the substrate rack; one end of the first heating lamp tube is arranged on one side wall of the annealing cavity; the first heating lamp tube is positioned on one side of the substrate provided with the metal film prefabrication layer; the first heating lamp tube and the substrate are arranged at an interval; a plane positioned with the first heating lamp tube and a plane positioned with the substrate rack are parallel to each other; and the first heating lamp tube and the substrate rack can conduct relative movement. In the thin-film solar cell annealing device, heat given out from the first heating lamp tube is directly radiated to the surface of the substrate, so that the fast heating capability is improved. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a preparation method of a copper indium gallium selenide thin-film cell absorption layer and a copper zinc tin sulfide thin-film cell absorption layer.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH +1
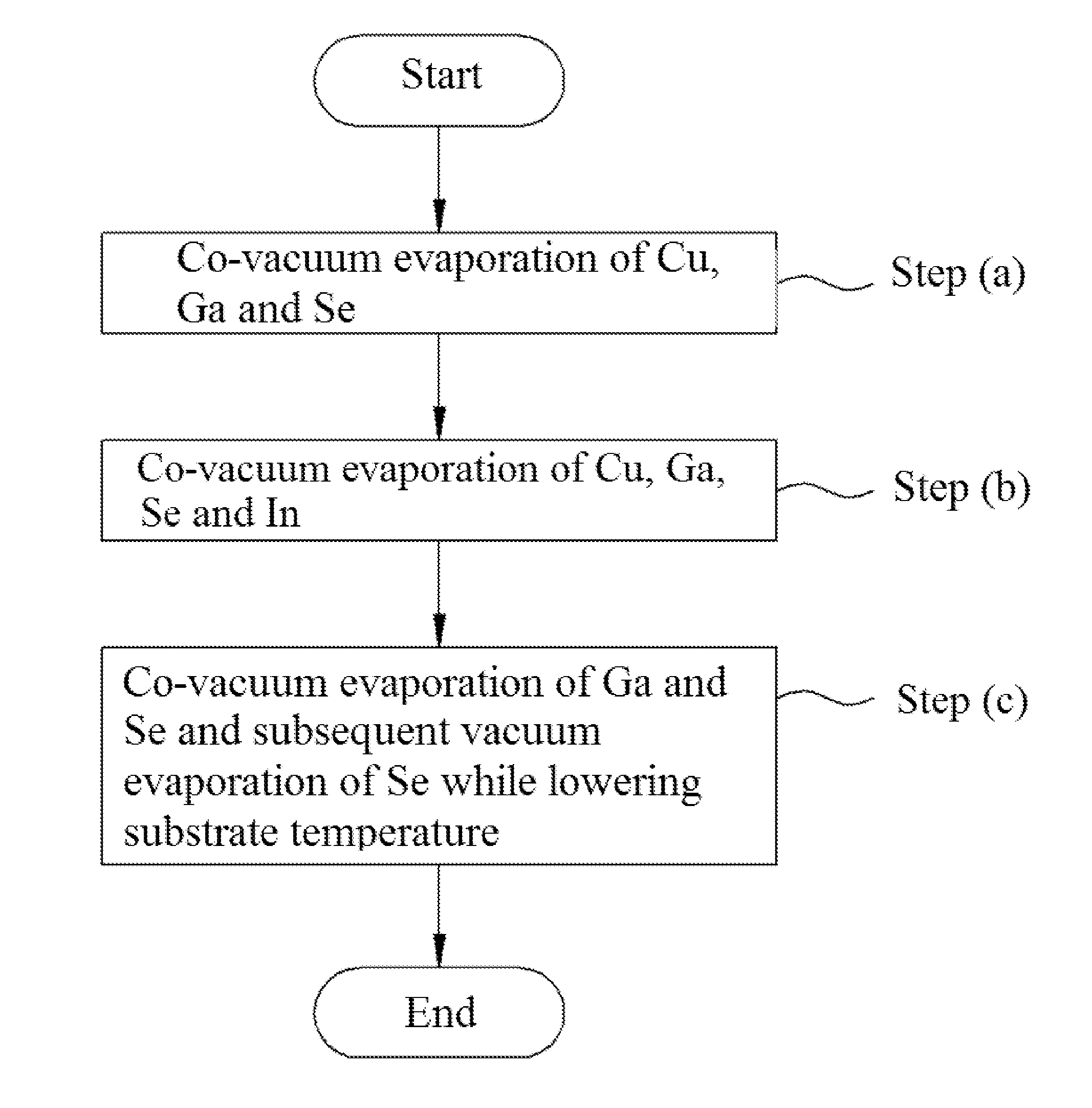
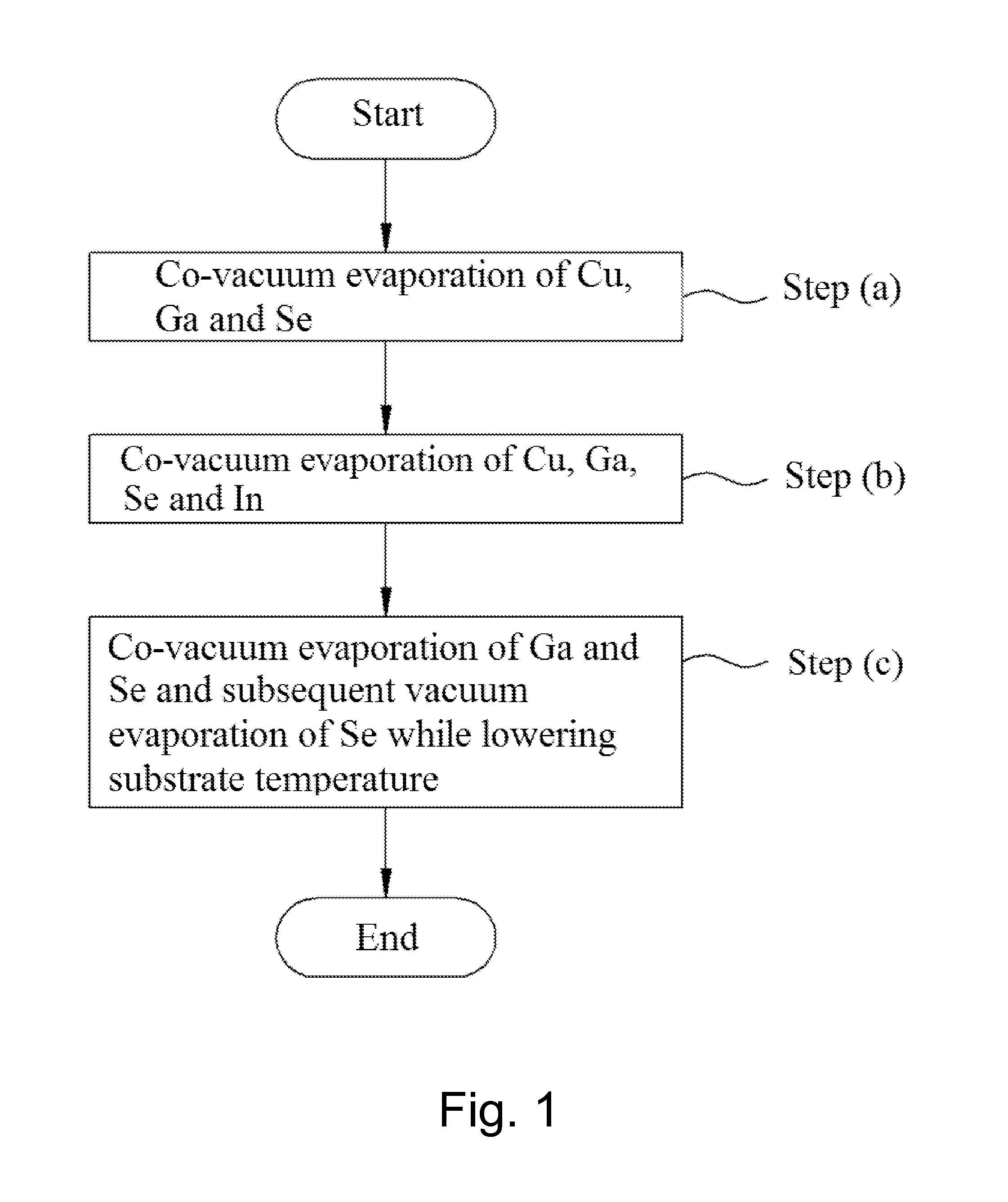
Method of fabricating copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) thin film for solar cell using simplified co-vacuum evaporation and copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) thin film for solar cell fabricated by the same
ActiveUS20140326317A1The process steps are simpleShorten the timeFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCopper indium gallium selenide solar cellsProcess efficiency
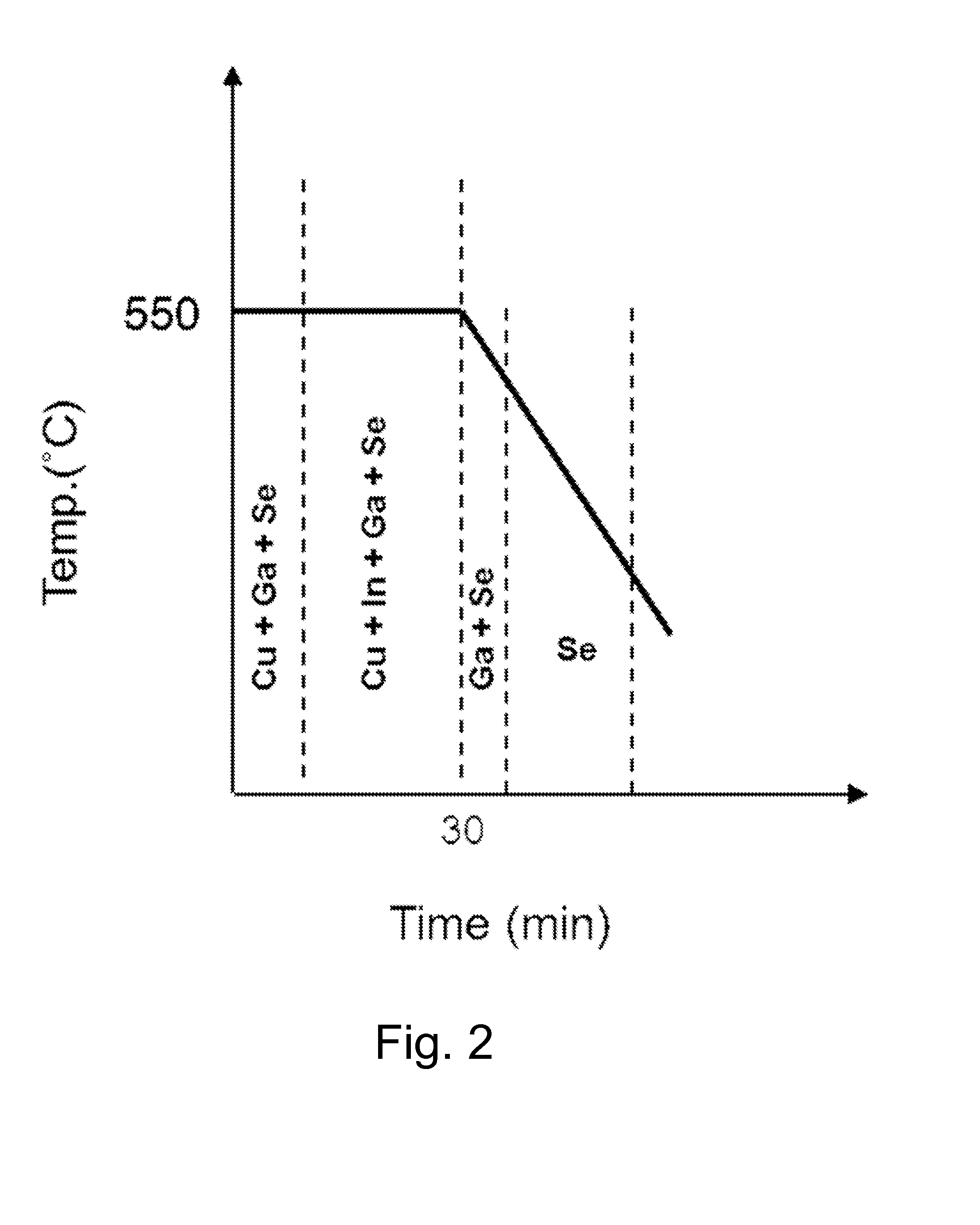
A method of fabricating a CIGS thin film for solar cells using a simplified co-vacuum evaporation process and a CIGS thin film fabricated by the method are disclosed. The method includes: (a) depositing Cu, Ga and Se on a substrate having a substrate temperature ranging from 500° C. to 600° C. through co-vacuum evaporation, (b) depositing Cu, Ga, Se and In through co-vacuum evaporation while maintaining the same substrate temperature as in step (a), and (c) depositing Ga and Se through co-vacuum evaporation, followed by depositing Se alone through vacuum evaporation while lowering the temperature of the substrate. The method can realize crystal growth and band-gap grading by Ga composition distribution while simplifying process steps and significantly reducing a film-deposition time, as compared with a conventional co-vacuum evaporation process, thereby providing improvement in process efficiency.
Owner:KOREA INST OF ENERGY RES
Preparation method of In2S3 (indium sulfide) buffer layer thin film for CIGS (copper indium gallium diselenide) solar cell
InactiveCN103311364AHigh visible light transmittanceIncrease productivityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCopper indium gallium selenide solar cellsCadmium sulfide
The invention relates to a preparation method of an In2S3 (indium sulfide) buffer layer thin film for a CIGS (copper indium gallium diselenide) solar cell. The preparation method comprises the following steps that 1, a basal body is cleaned; 2, reaction solution is prepared, a certain amount of InCl3.4H2O, CH3CSNH2 and CH3COOH solution are taken to be placed in a container, in addition, the concentration ratio of In ions to S ions is controlled to be within 1:2-1:10, the pH value of mixed solution is regulated, and reaction solution is obtained; 3, the In2S3 buffer layer thin film is deposited, the basal body is fixed in the reaction solution, the container is sealed by aluminum paper, the stirring is carried out at a certain temperature, and the basal body deposited with the In2S3 buffer layer thin film is obtained after the complete reaction; and 4, impurities are removed. The visible light transmittance of the In2S3 buffer layer thin film prepared by the preparation method exceeds 85 percent, the energy band gap reaches 2.7eV, and the In2S3 buffer layer thin film can be used as the buffer layer thin film for the CIGS solar cell for replacing a CdS (cadmium sulfide) thin film.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Method and structure for improving photoelectric conversion efficiency of copper indium gallium selenium solar cell
ActiveCN101916800AExtended propagation pathReduce thicknessFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationIndiumCopper indium gallium selenide solar cells
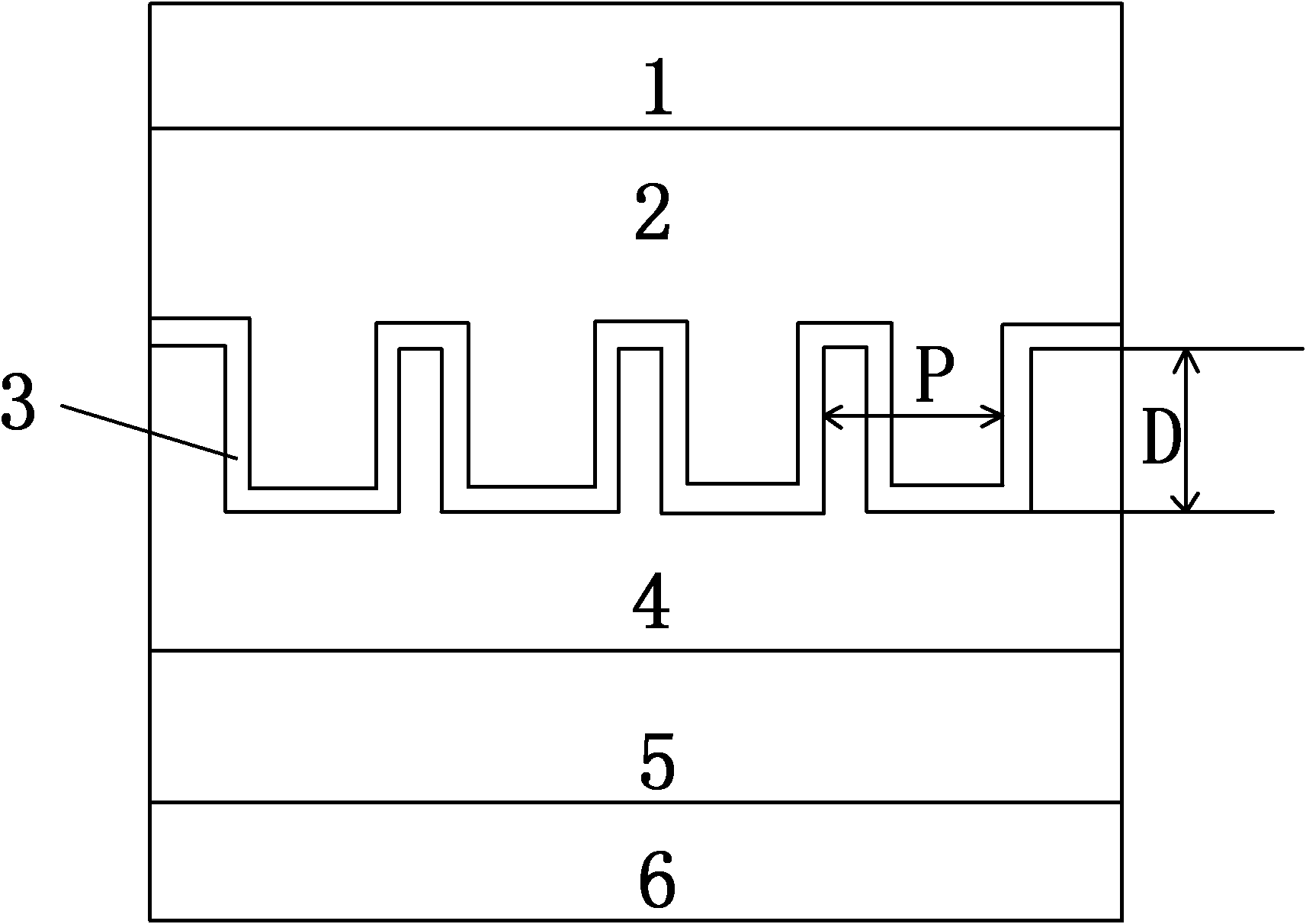
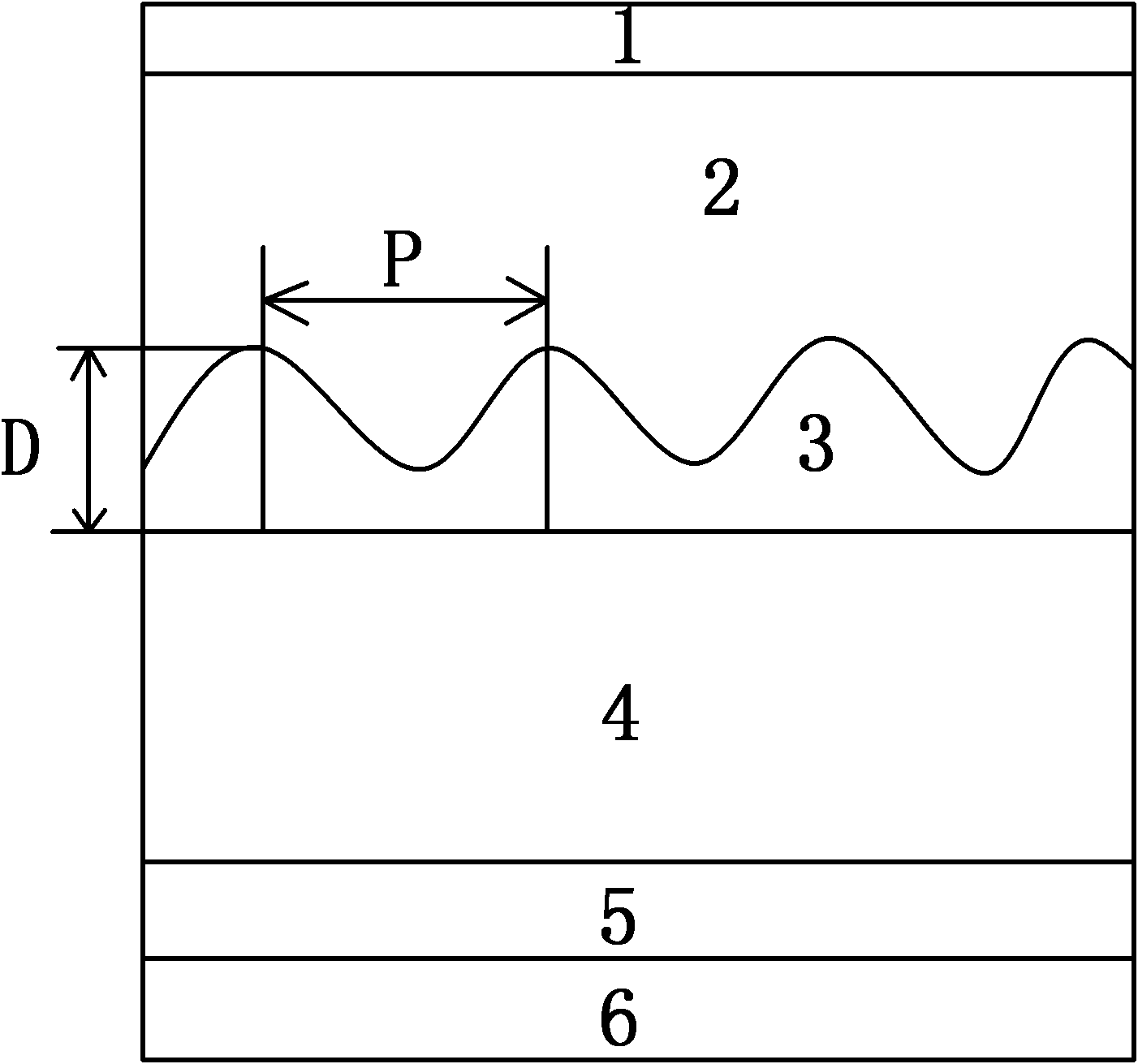
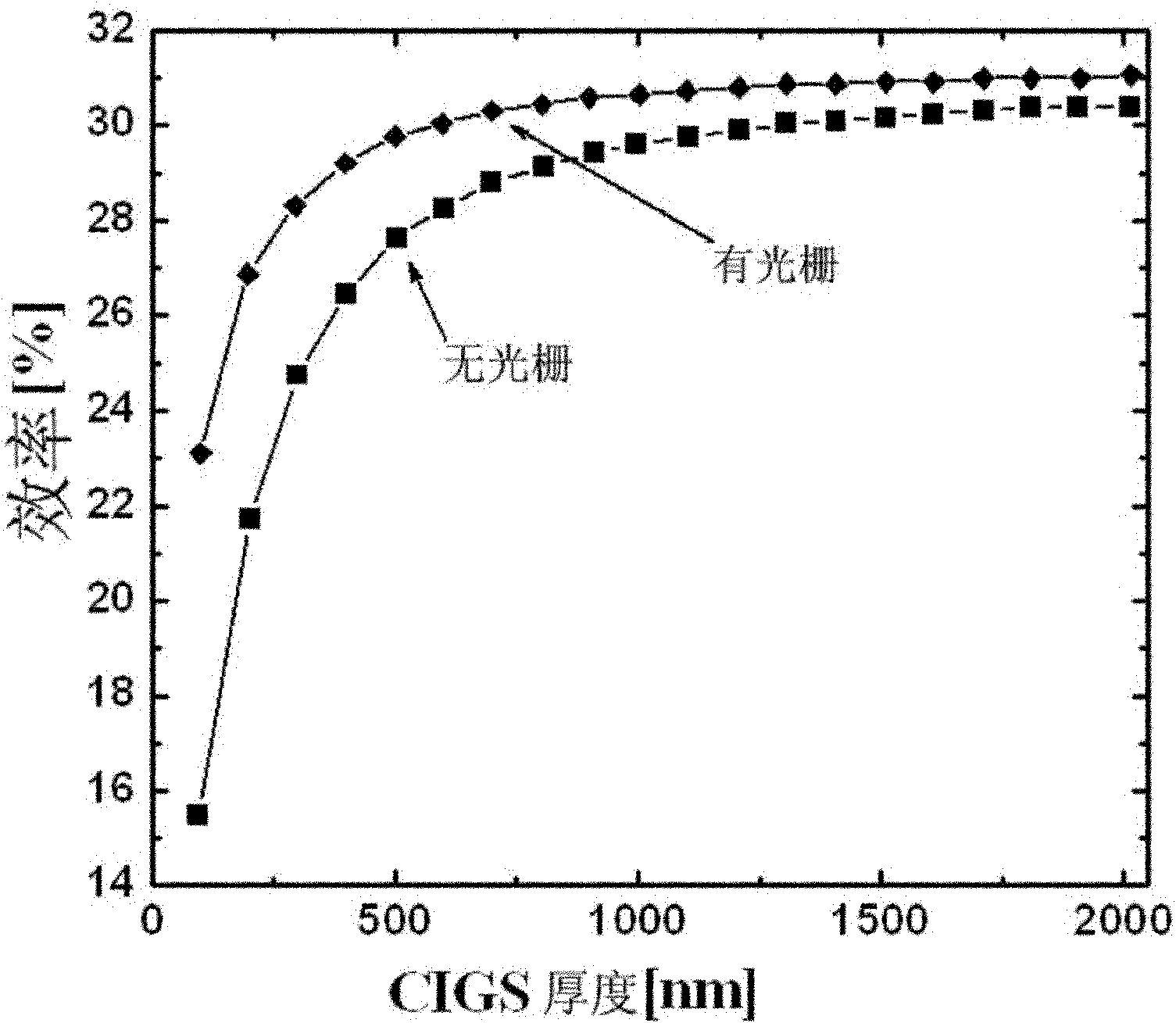
The invention discloses a method and a structure for improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency of a copper indium gallium selenium solar cell, which are characterized in that: a diffraction grating is formed between a transparent conductive film layer and a light absorption layer on the top of the copper indium gallium selenium solar cell to change the propagation direction of incident photons and prolong the effective propagation path of the photons in the light absorption layer, so that the thickness of the absorption layer is effectively reduced and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the copper indium gallium selenium solar cell is improved. Through the method, the copper indium gallium selenium solar cell can improve the photoelectric conversion efficiency by over 25 percent maximally on the basis of the conventional copper indium gallium selenium solar cell and the thickness of the light absorption layer can be reduced to one quarter of that of the conventional cell.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHANGYUE OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Copper indium gallium selenide solar cell preparation method
ActiveCN103474514ALarge grainCompliant with high performance solar cell requirementsFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCopper indium gallium selenide solar cellsSelenium
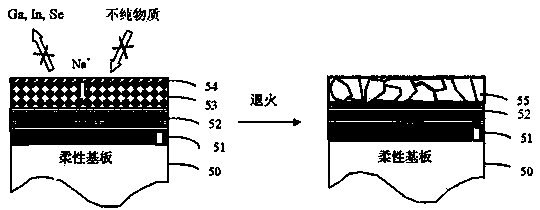
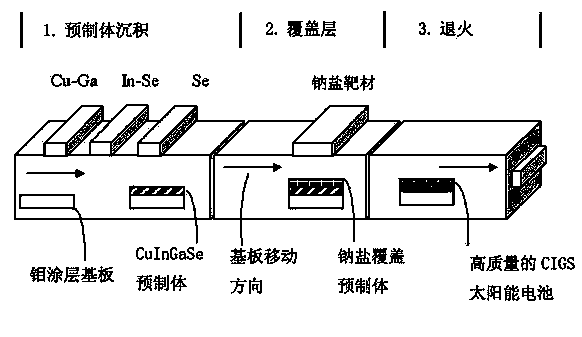
The invention provides a copper indium gallium selenide solar cell preparation method. The copper indium gallium selenide solar cell preparation method comprises the following steps: a substrate of a first electrode film is obtained and deposited; a mixed precursor layer is formed on the substrate, wherein a mixed precursor is composed of elements in a I B group, a III A group and a IV A group according to an ideal quantity relative ratio of a product; a cover top layer containing sodium salt is deposited on the mixed precursor layer; the mixed precursor layer and the cover top layer containing the sodium salt are heated and annealed together to form a high-quality I B-III A-VI A semiconductor absorption layer. Due to the addition of the cover top layer containing the sodium salt, on one hand, loss of metallic elements and selenium can be prevented, and contamination by harmful impure substance is prevented; on the other hand, a polycrystal thin-film I B-III A-IV A semiconductor absorption layer structure can be further improved, and the copper indium gallium selenide solar cell preparation method can be applied to the I B-III A-VI A semiconductor absorption layer in large-area photovoltaic production.
Owner:GUANMAT OPTOELECTRONICS MATERIALS INC
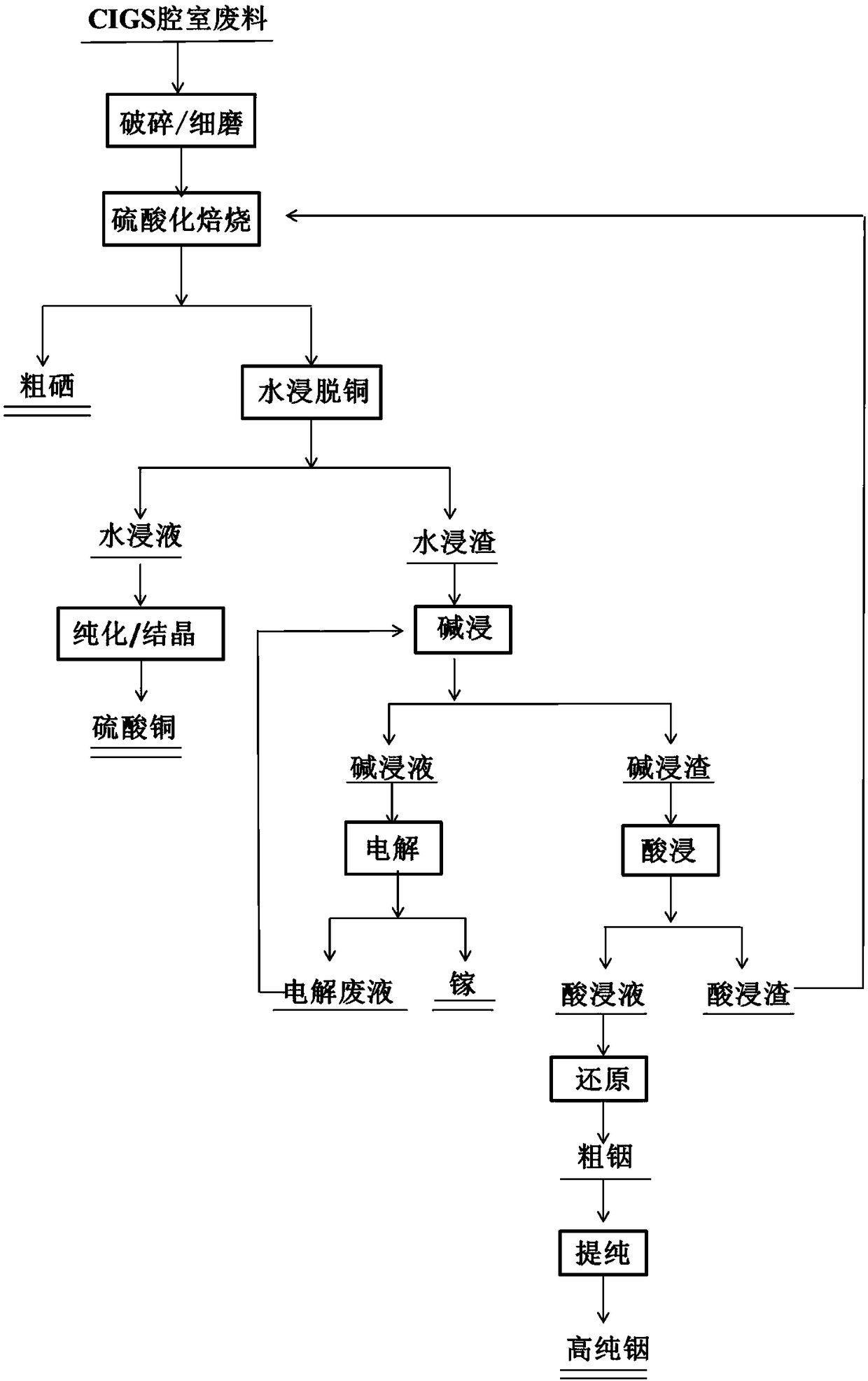
Method for recovering copper indium gallium selenium from waste of copper indium gallium selenium solar thin film cell
ActiveCN108359802AEfficient and selective separationEfficient recyclingPhotography auxillary processesEnergy inputIndiumCopper indium gallium selenide solar cells
The invention provides a method for recovering copper indium gallium selenium from waste of a copper indium gallium selenium solar thin film cell, and belongs to the technical field of resource secondary utilization. The method comprises the steps that the waste in a copper indium gallium selenium (CIGS) solar thin film cell chamber is smashed and milled, then is subjected to sulfatizing roastingto obtain crude selenium and roasting materials, the roasting materials are leached by adding water, and a copper sulfate product is obtained by purifying and crystallizing a water leaching solution;water leaching slag is subjected to alkaline leaching, then an alkali leaching solution is electrolyzed, and gallium metal is obtained; inorganic acid is added to alkali leaching slag for acid leaching, and metal indium powder is obtained by reducing and purifying an acidic leaching solution by formaldehyde, hydrazine hydrate, and iron powder or a mixture of two or three of the formaldehyde, the hydrazine hydrate, and the iron powder in any proportion; and acidic leaching slag is returned for sulfatizing roasting. The purity of the obtained crude selenium is larger than 98%, the purity of theobtained metal indium powder is less than 99%, and the purity of the obtained metal gallium is larger than 99%. The recovery rates of four valuable elements are all above 95%. The method for recovering the copper indium gallium selenium from the waste of the copper indium gallium selenium solar thin film cell is simple to operate, high in safety, high in reliability, and low in cost, scale production is easy to achieve, the environmental protection requirements are met, and the application prospects are broad.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Photovoltaic cell structure
InactiveUS20110297225A1Less harmful to the environmentMuch of contaminationFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationIndiumCopper indium gallium selenide solar cells
A photovoltaic cell structure includes a substrate, a metal layer, a p-type semiconductor layer, an n-type semiconductor layer, a transparent conductive layer and a high resistivity layer. The metal layer is formed on the substrate. The p-type semiconductor layer is formed on the metal layer and may include a compound of copper indium gallium selenium sulfur (CIGSS), copper indium gallium selenium (CIGS), copper indium sulfur (CIS), copper indium selenium (CIS) or a compound of at least two of copper, selenium or sulfur. The n-type semiconductor layer exhibits photo catalyst behavior that can increase carrier mobility by receiving light, and is formed on the p-type semiconductor layer, thereby forming a p-n junction. The transparent conductive layer is formed on the n-type semiconductor layer. The high resistivity layer is formed between the metal layer and the transparent conductive layer.
Owner:PVNEXT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com