Method for manufacturing copper indium gallium diselenide thin-film solar cells
A solar cell, copper indium gallium selenide technology, which is applied to conductive materials, circuits, electrical components and other directions dispersed in non-conductive inorganic materials, can solve problems such as increasing cost and affecting appearance, and achieves convenient high-temperature processing and reduces manufacturing costs. , the effect of simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Mix 7g molybdenum powder (particle size 0.01-50μm), 0.5g glass powder (lead-free glass powder), 0.5g terpineol, 1g polyethylene glycol-200, 0.25g polyethylene glycol-400, 0.1g epoxy Resin E44 (or E51), 0.005g NaOH, 0.1g ethyl cellulose, 0.01g dibutyl phthalate, 0.03g Span 85 (sorbitan trioleate), 0.5g ethanol, 0.005g silicone oil Put them together and mix evenly to prepare a composite conductive molybdenum paste.
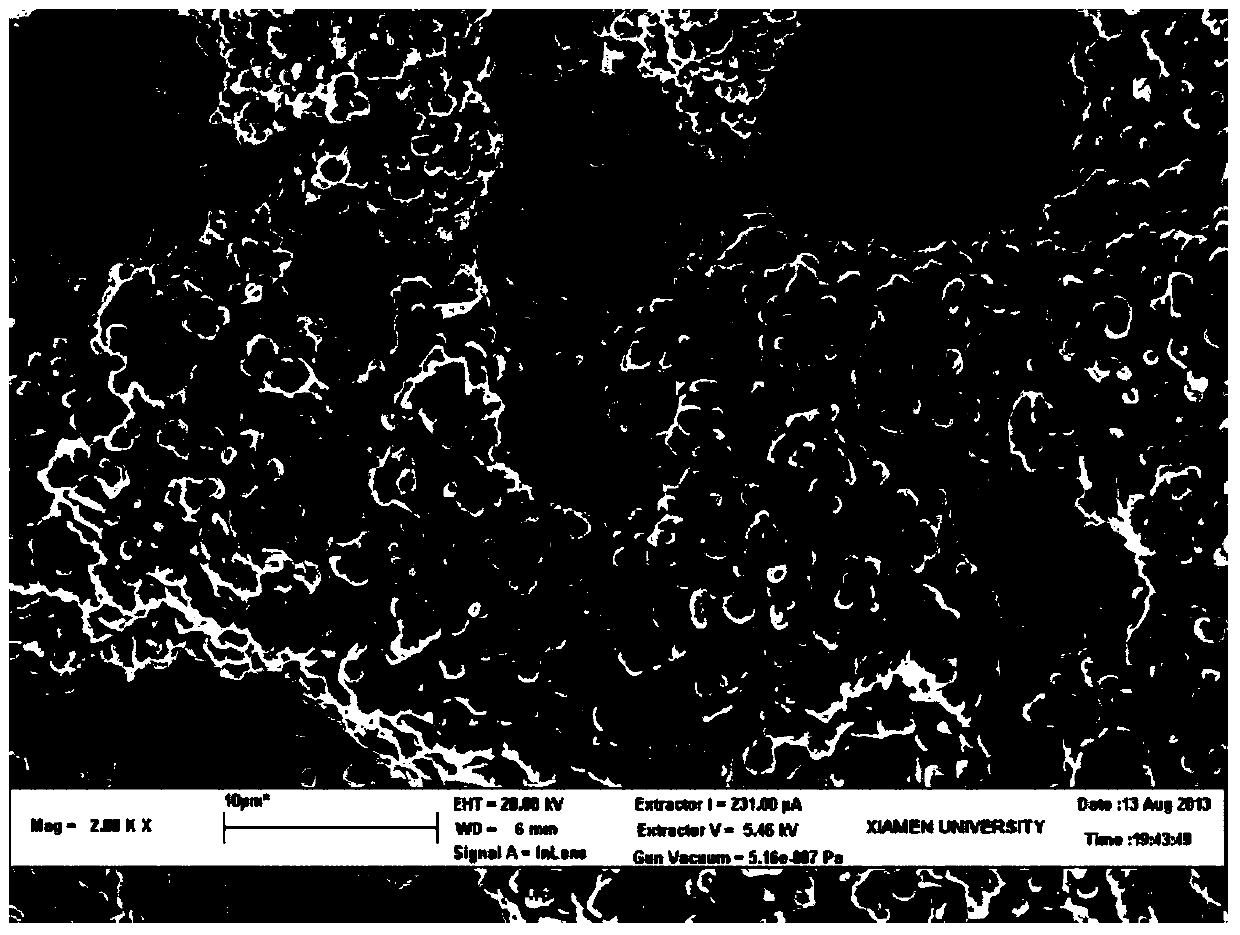
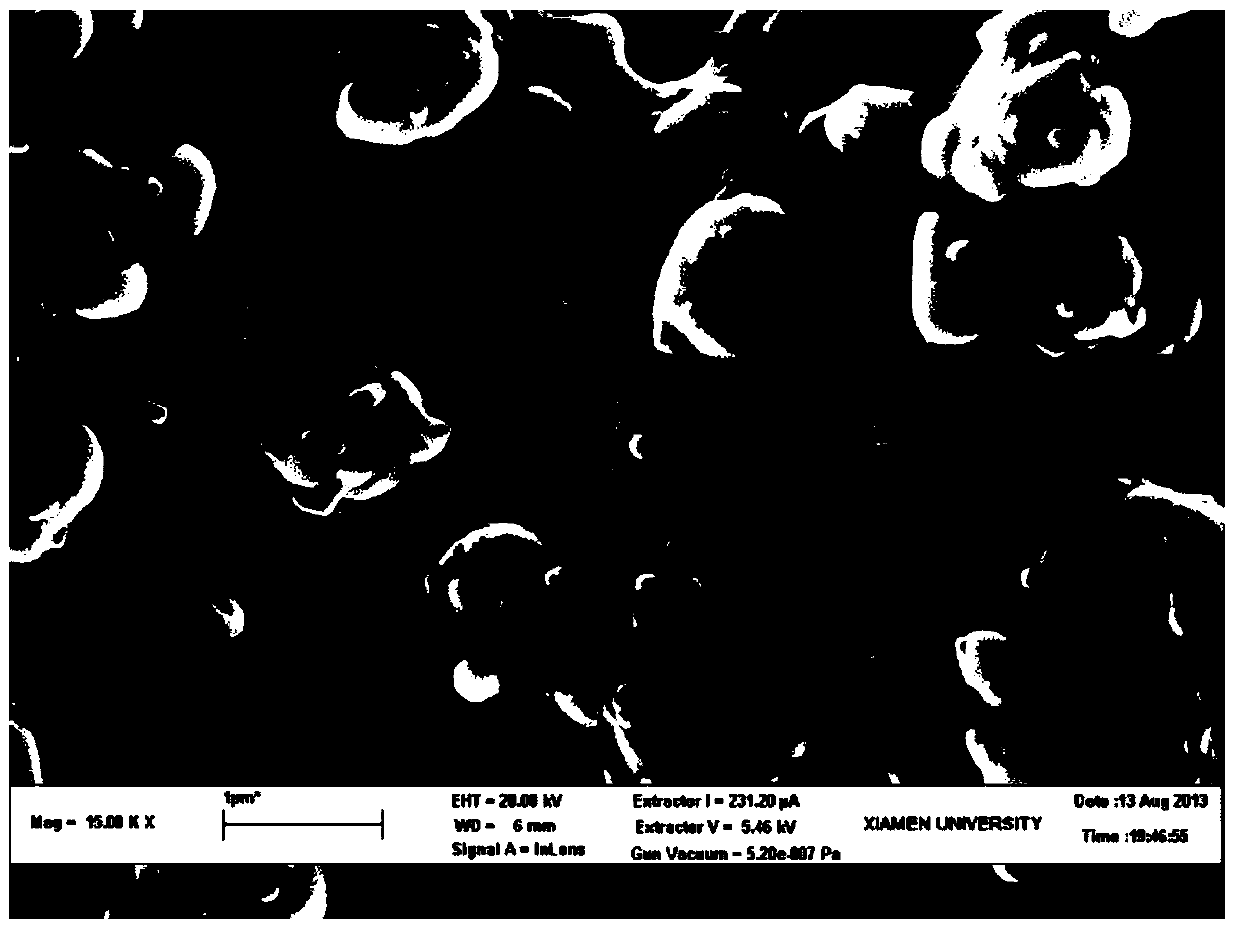
[0033] The molybdenum paste was screen printed or scraped on the ceramic substrate, dried at 200°C, then heat treated at 1100°C for 0.5 hours, and kept at 200°C for 2 hours to prepare a conductive molybdenum film electrode (ie, the back electrode). By using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) to observe their surfaces and cross-sections (eg figure 1 and figure 2 Shown), using a four-probe resistance tester to measure the sheet resistance of the film for characterization, and calculate the resistivity. The American Society for Testing Materials (ASTM) sta...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Mix 7g molybdenum powder (particle size 0.01-50μm), 0.5g glass powder (lead-free glass powder), 0.5g terpineol, 1g polyethylene glycol-200, 0.25g polyethylene glycol-400, 0.1g epoxy Resin E44 (or E51), 0.005g NaOH, 0.1g ethyl cellulose, 0.01g dibutyl phthalate, 0.03g Span 85 (sorbitan trioleate), 0.5g ethanol, 0.005g silicone oil Put them together and mix evenly to prepare a composite conductive molybdenum paste.
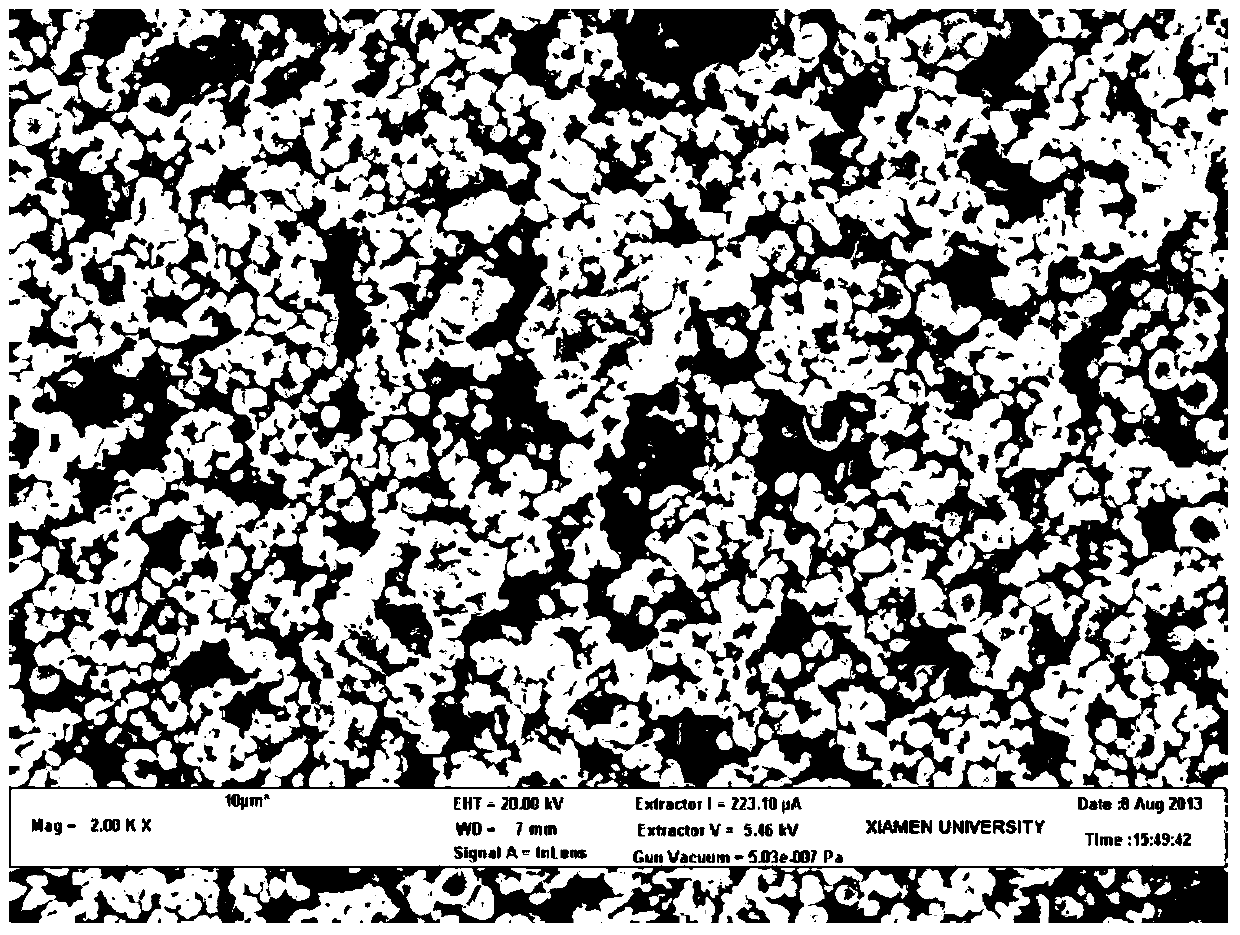
[0039] Molybdenum paste was screen-printed or scraped-coated on a ceramic substrate, dried at 200°C, then heat-treated at 900°C for 0.5 hours, and kept at 200°C for 2 hours to prepare a conductive molybdenum film electrode. By using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) to observe their surfaces and cross-sections (eg image 3 and Figure 4Shown), using a four-probe resistance tester to measure the sheet resistance of the film for characterization, and calculate the resistivity. The American Society for Testing Materials (ASTM) standard test method ASTM-D33...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com