Multiplex (+/-) stranded arrays and assays for detecting chromosomal abnormalities associated with cancer and other diseases
A chromosome and array technology, applied in the field of multi-strand arrays, can solve problems such as non-existence of translocations, missed opportunities to detect translocations, and incomplete characterization of translocations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0264] Exemplary (+ / -) CGH method
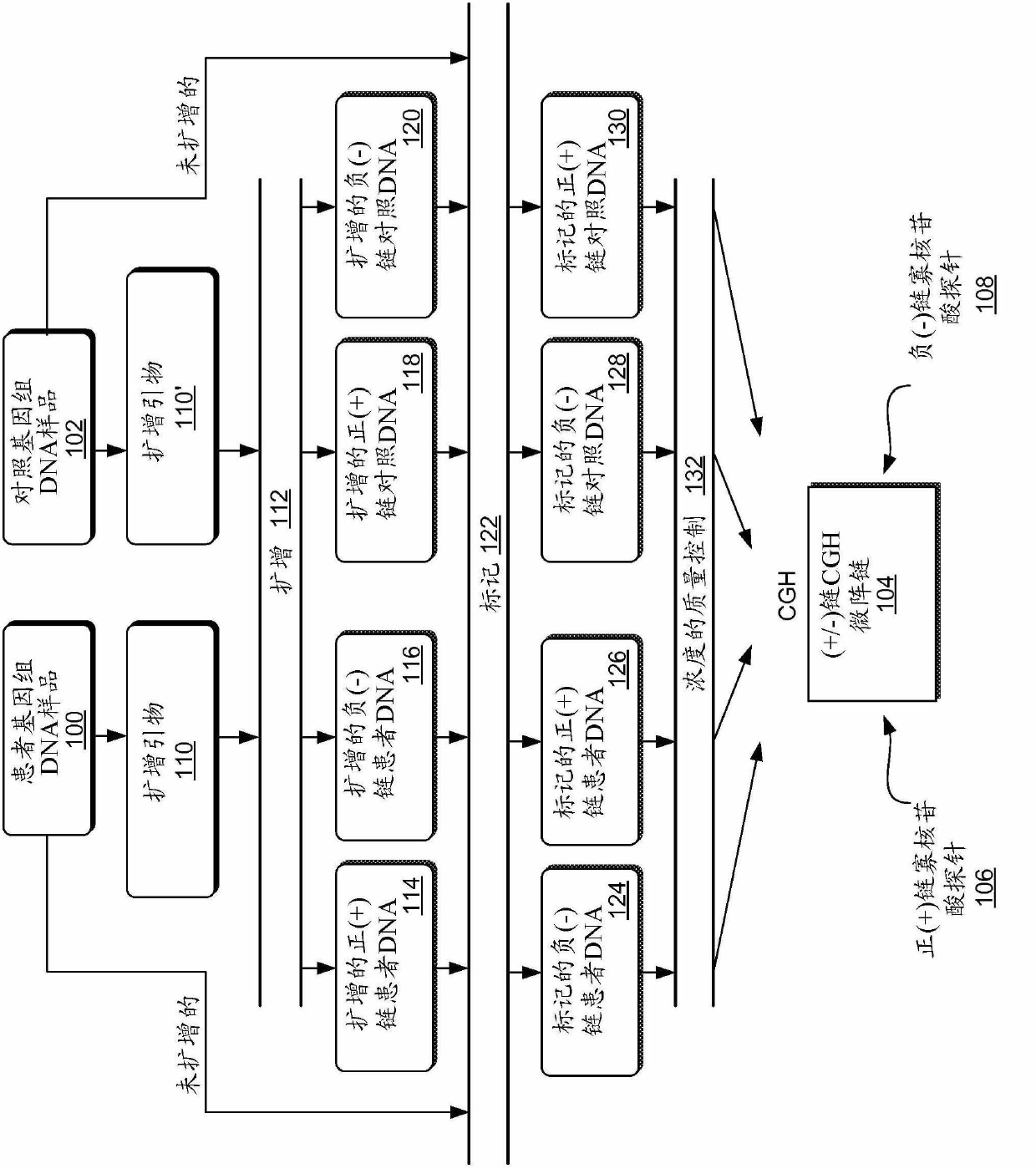
[0265] figure 1 An overview of the (+ / -) chain array CGH program is shown. The CGH procedure compares a patient genomic DNA sample 100 with a control genomic DNA sample 102 . In this case, the samples compete for the hybridization targets (oligonucleotides) arrayed on the (+ / -) strand CGH microarray 104 . (+ / -) strand CGH microarray 104 includes positive (+) strand oligonucleotide probes 106 and negative (-) strand oligonucleotide probes 108 . Amplification primers 110 and 110' (e.g., the same primers) are added to patient genomic DNA sample 100 and control genomic DNA sample 102 for carefully moderated amplification 112, e.g., linear amplification, to generate , that is, probes for regions where balanced translocations are likely to occur. The primers extend selected chromosomal regions by approximately 10,000 to 20,000 bases each, thereby providing a rich mixture of positive (+) and negative (-) strand DNA hybridization probes represen...
Embodiment 2
[0285] Exemplary (+ / -) CGH Microarrays
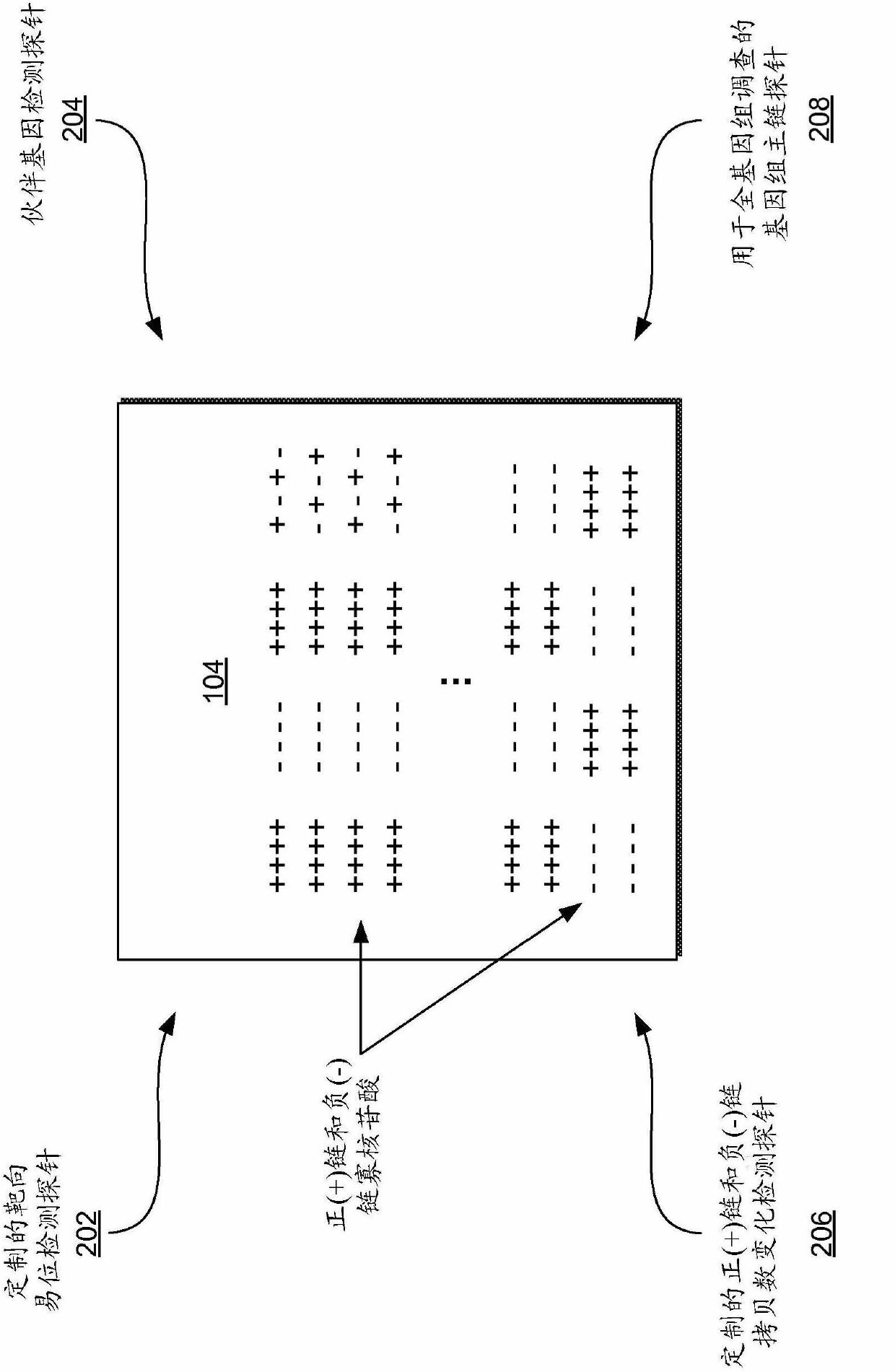
[0286] figure 2 Schematically shows in more detail figure 1 Multiplex (+ / -) strand CGH microarrays in 104 . The plus (+) and minus (-) strand oligonucleotides making up the hybridization targets on the array can be arranged in any suitable order or pattern. See, e.g., U.S. Patent Application No. 11 / 057,088, to Shaffer et al., entitled "Method and Apparatuses for Achieving Precision Diagnoses," the contents of which are incorporated by reference incorporated into this article. The (+ / -) strand CGH microarray 104 may be a chimeric density DNA microarray. Each (+ / -) strand CGH microarray 104 is typically both a whole genome array and a custom targeted array. As a gene-wide array, the (+ / -) strand CGH microarray 104 can detect DNA copy number changes that may occur genome-wide. As a custom targeting array, the (+ / -) strand CGH microarray 104 specifically targets loci in many regions of diagnostic interest. The (+ / -) strand CGH micro...
Embodiment 3
[0292] Exemplary Hardware Environment for Implementing (+ / -) CGH Microarrays
[0293] figure 1 Most of the steps in the exemplary processes shown in can be performed directly or indirectly in a computing environment. That is, amplification 112, labeling 122, and quality control 132 are typically computer-controlled, computer-assisted, or computer-monitored. Scanning, analysis, display and reporting of results in array CGH are also mediated by computer equipment.
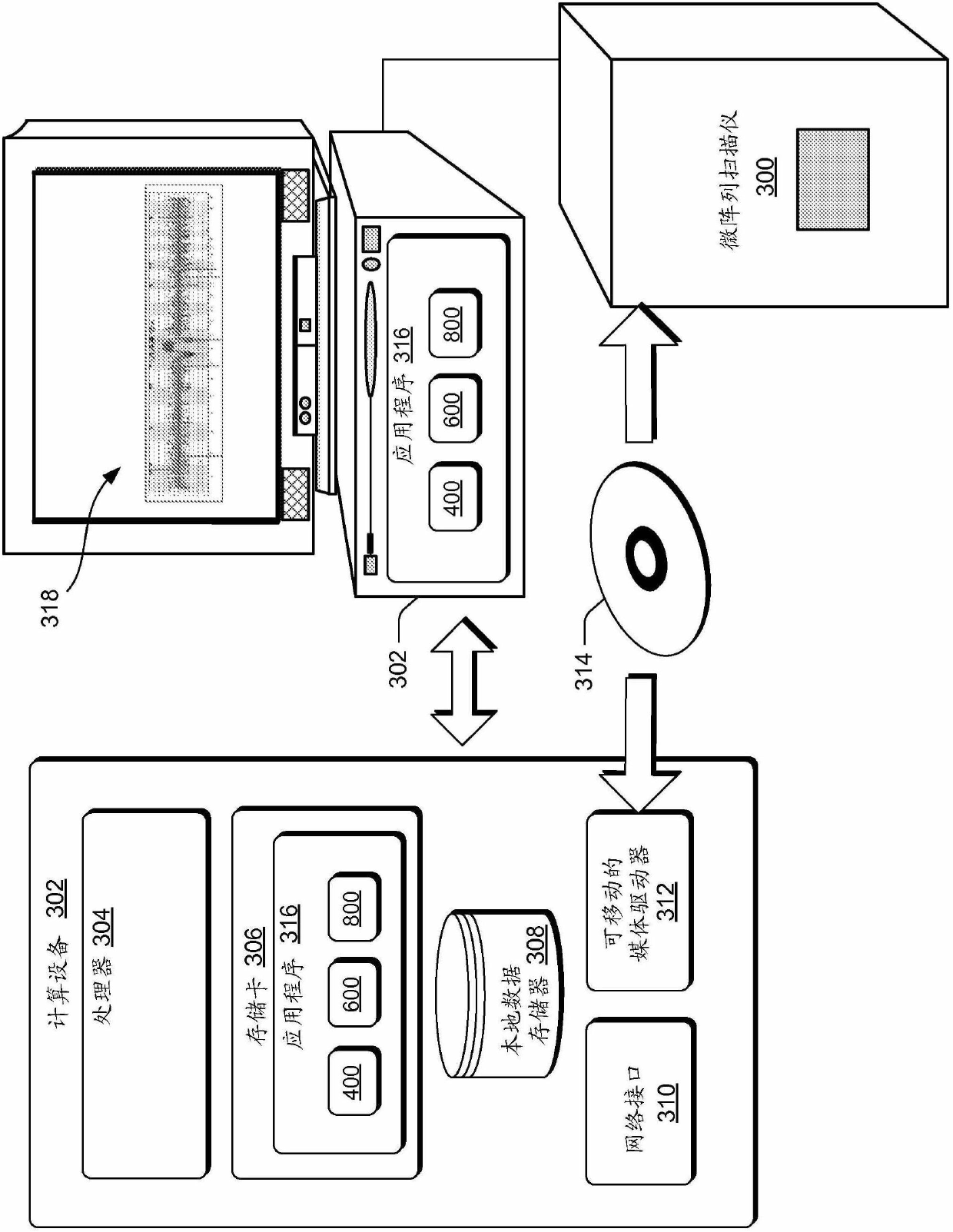
[0294] image 3 An exemplary computing environment and components of a (+ / -) chain array CGH system are shown. An exemplary hardware component is a microarray scanner 300, as image 3 A placeholder in , typically representing a molecular diagnostic device. Microarray scanner 300 may include a computing device and / or may be communicatively coupled to computing device 302 . The set-up shown is relatively rudimentary compared to the set-up of an actual clinical diagnostic laboratory, but shows some examples betwee...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com