Rapid identification method and kit of novel mycobacterium strain
A technology of mycobacteria and kit, applied in the field of medical molecular biology diagnosis, can solve the problems of cross-contamination, complicated operation, difficult to popularize and apply, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
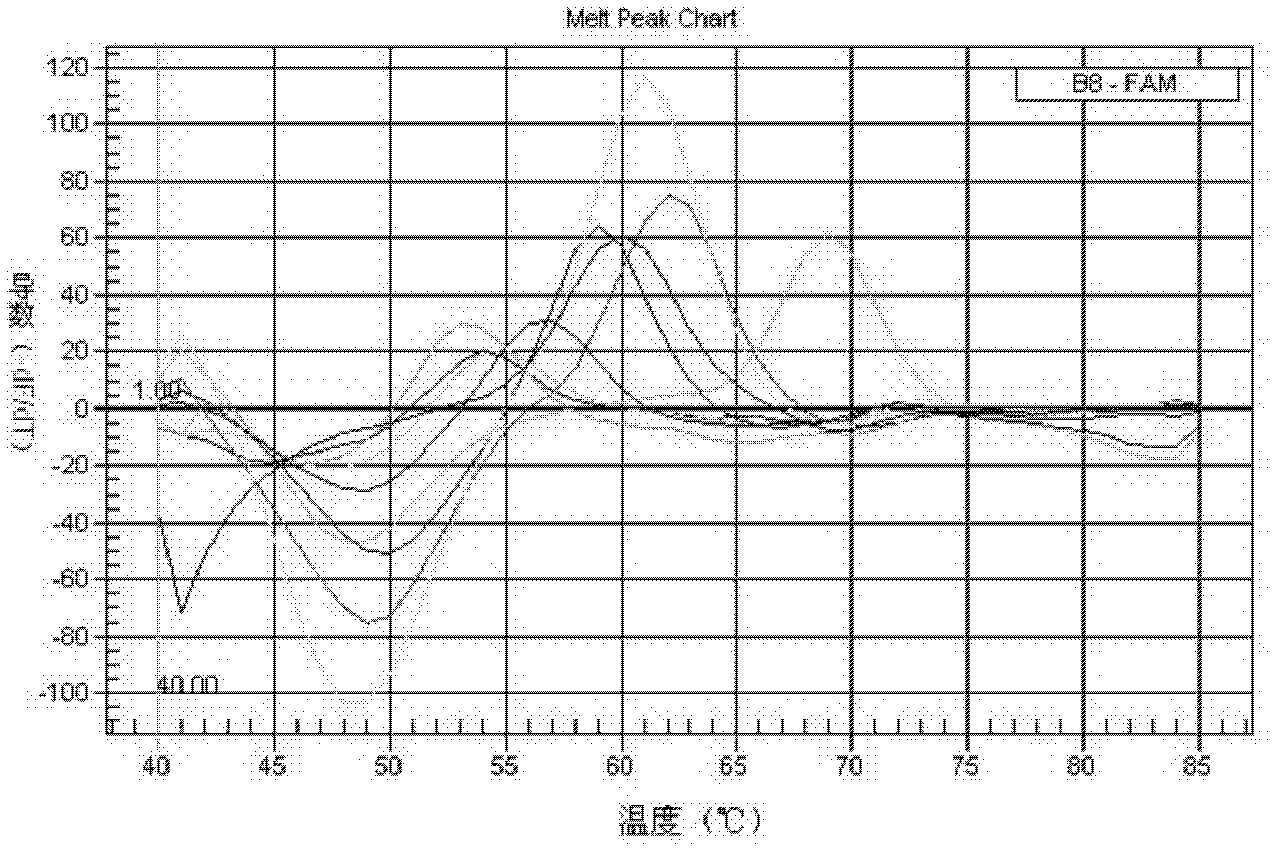
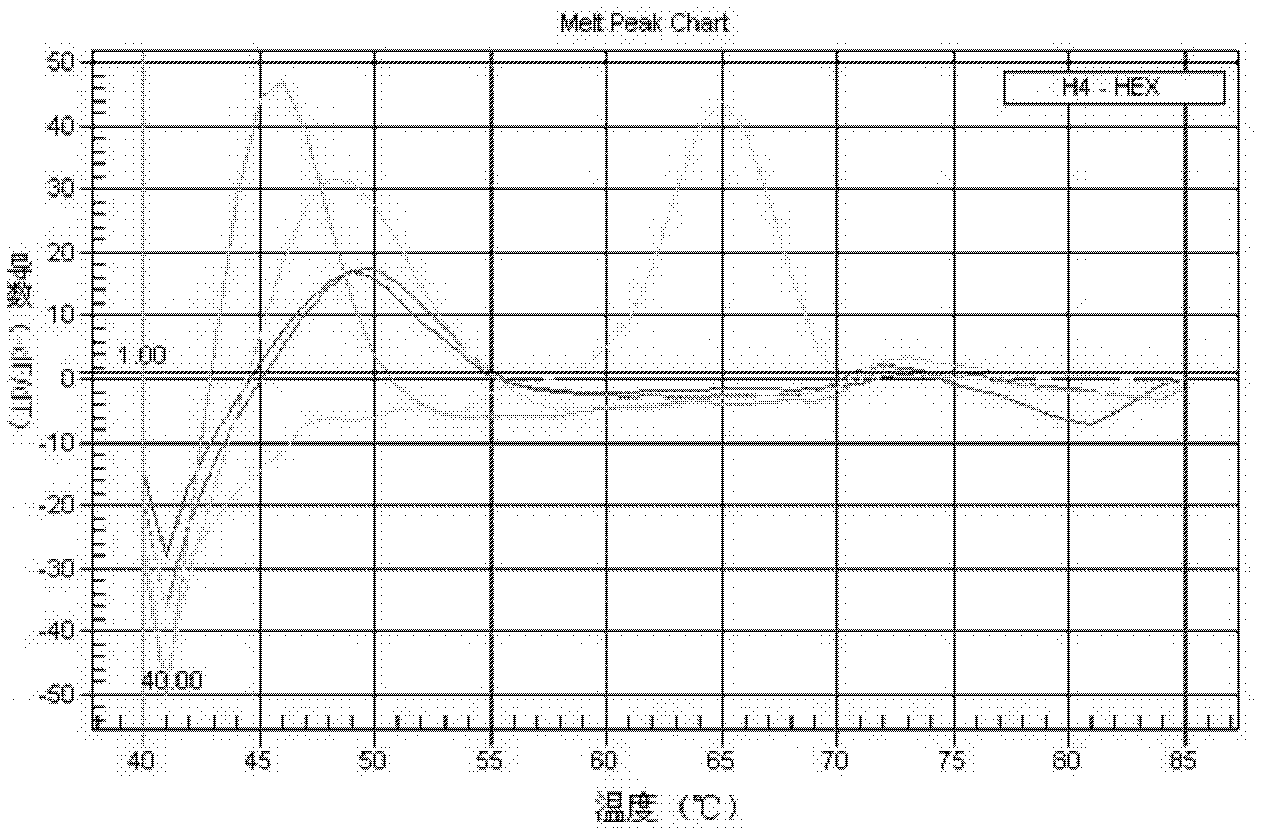
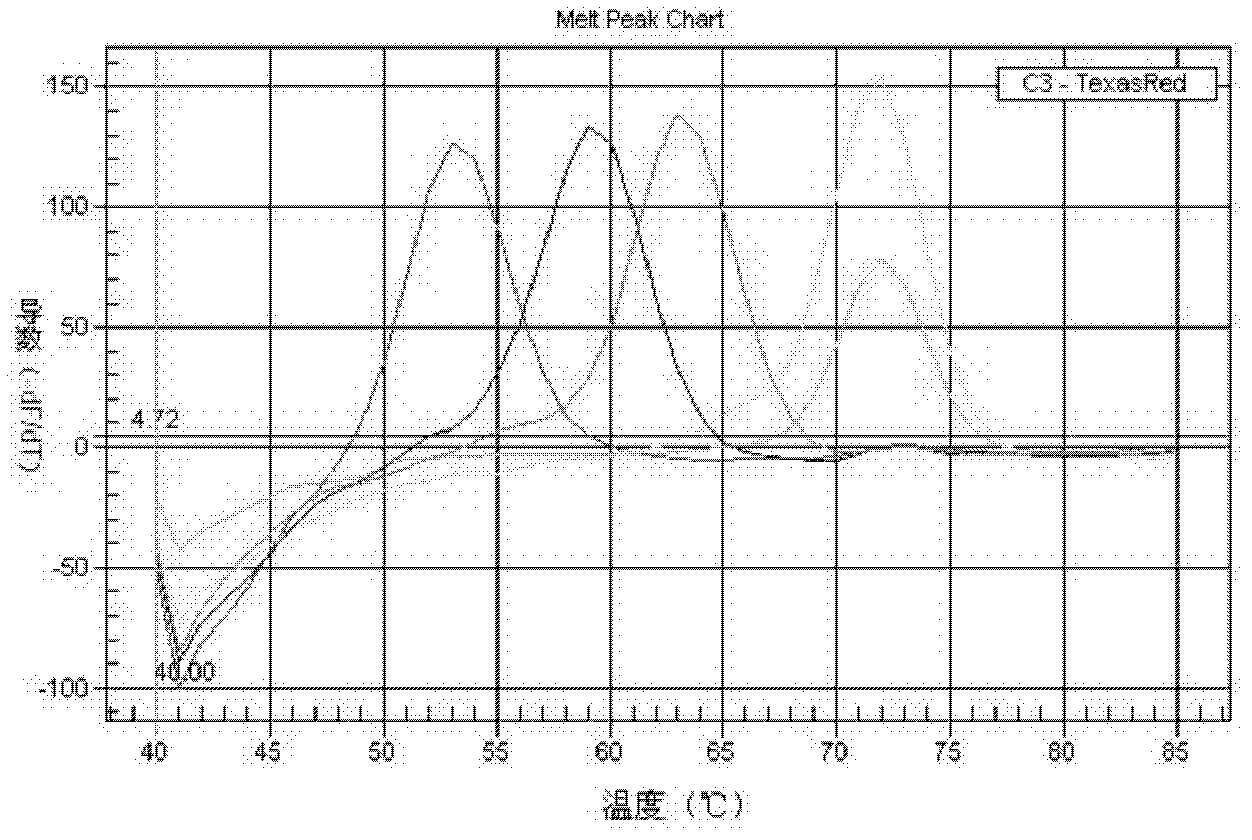
[0053] Example 1: Design and synthesis of primers and probes
[0054]The 16S rRNA gene is a traditional target gene sequence identified in bacterial taxonomy. The invention analyzes the disclosed 16S rRNA gene sequences of various species of Mycobacterium, and finds Mycobacterium-specific nucleotide sequences and species-specific variable regions. According to the three variable regions of the mycobacterial 16S rRNA gene sequence, three sets of mycobacterium-specific nested primers and mycobacterium species-specific probes were designed, among which the variable region 1 is located in the sequence X55588.1 in the NCBI database The variable region 2 is located between the 55th and 251st bases, the variable region 2 is located between the 1110th and 1314th bases, and the variable region 3 is located between the 366th and 539th bases. Use the software to design primer pairs in the mycobacteria-specific region, and design probes for the species-specific variable regions within th...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Embodiment 2 Mycobacterium strain identification method and establishment of standard curve
[0060] 2.1 Extraction of sample DNA
[0061] Standard strains: Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tuberculosis), Mycobacterium kansasii (M.kansasii), Mycobacterium scrofula (M.scrofulaceum), Mycobacterium simiae (M.simiae), Mycobacterium gastrice (M. .gastri), M. marinum, M. ulcerans, M. nonchromogenicum, M. aichiense, M. avium M. avium, M. diernhoferi, M. triviale, M. fortuitum, M. terrae, mycobacterium M.intracellulare, M.gordonae, M.xenopi, M.chelonae subsp.chelonae, M.chelonae M.chelonae subsp.abscessus, M.smegmatis, M.thermoresistibile, M.agri, Mycobacterium vaccae (M.vaccae), Mycobacterium phlei (M.phlei) standard strains were purchased from China Institute of Biological Products.
[0062] The genomic DNA of each of the above standard strains was extracted separately for strain identification and detection, or stored at -20°C for later use.
[0063] 2.2PCR amplification ...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Embodiment 3 clinical identification test
[0098] 3.1 Identification test I
[0099] 187 clinical isolates of Mycobacterium were collected, and the DNA was extracted according to the above method and then dissolved with ddH2O.
[0100] Add 10×PCR buffer (Mg 2+ Free) 2μl, 25mM MgCl 2 1.6 μl, 0.4 μl of 10 mM dNTPs, 0.1 μl of each of 10 μM TBleft1, TBleft2 and TBright1, 0.6 μl of 10 μM TBright2, 0.4 μl of each of 10 μM TBProbe1, TBProbe2 and TBProbe3, 0.1 μl of 5 U / μl aTaq DNA polymerase, add 2 μl of the above-mentioned extract to be tested DNA, followed by ddH 2 O Supplement the reaction system to 20 μl. Negative control and blank control were set up in the reaction at the same time, so as to extract from other 14 non-mycobacterium strains (including Acinetobacter baumannii, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Enterobacter cloacae, Klebsiella, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus hominis subsp. hominis, Citrobacter freundii, Acinetobacter lophi, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com