Method of in-situ assembly, electrochemical reduction and representation of graphene oxide
An in-situ assembly and electrochemical technology, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of difficulty in meeting detection requirements, low detection accuracy, and easy contamination of samples, and achieves good application prospects and simple detection methods.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
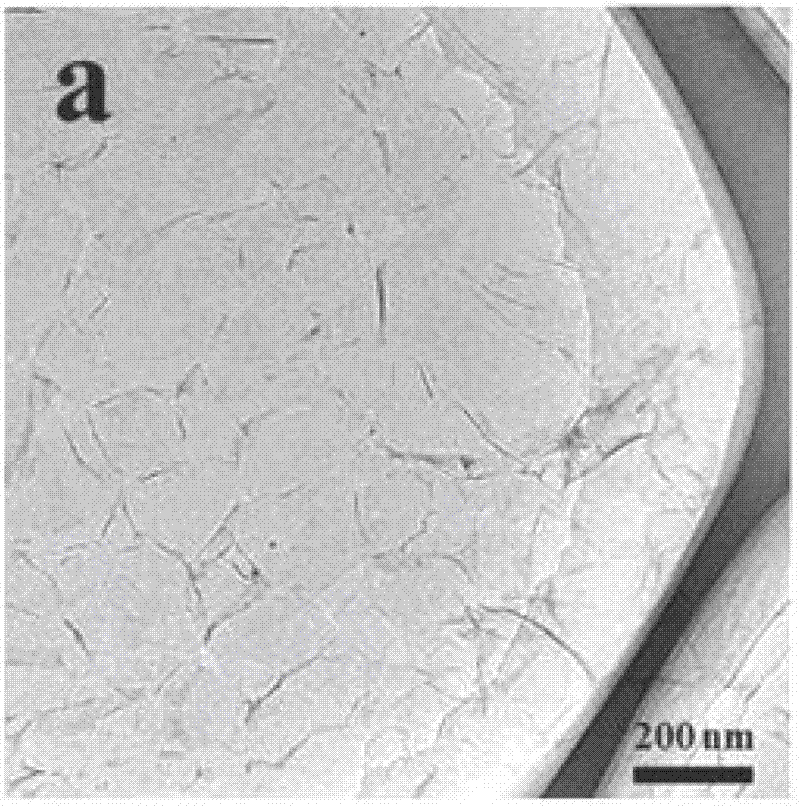
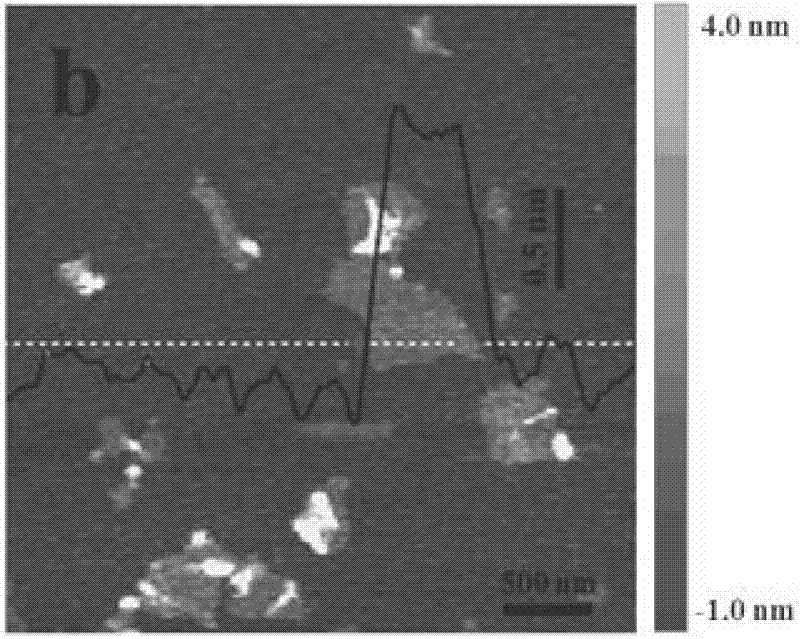
[0028] Dissolve graphene oxide prepared by the improved Hummers method in water, and obtain a well-dispersed graphene oxide solution by ultrasonic exfoliation. The concentration of graphene oxide solution is (0.01, 2, 10) mg / ml; drop GO on mica On-chip, perform transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) characterization, see Figure 1.
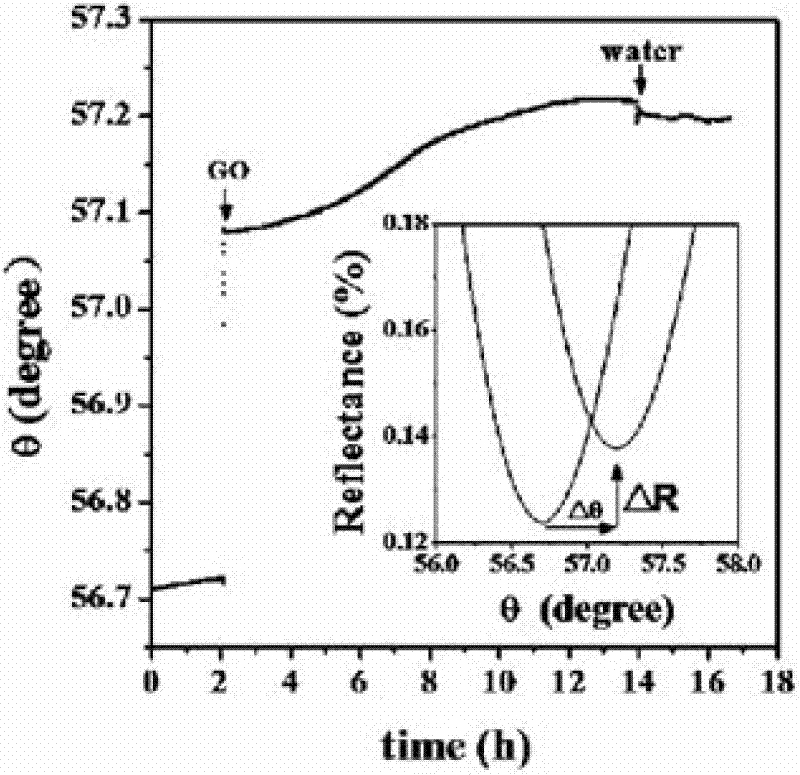
[0029] Real-time monitoring of the GO assembly process on the gold film surface of the sensor chip. Assemble and test the SPR curve of the gold film in the air, add deionized water, pass 2mg / mL GO aqueous solution into the sample cell, assemble (1, 12, 16) h, then rinse off the unassembled GO solution with deionized water, SPR kinetic curves during assembly refer to figure 2 . Then use high-purity nitrogen to dry the surface of the gold film of the sensor chip, and test the SPR curve of the gold film surface of the sensor chip after assembling GO.
[0030] Pass the PBS (pH=7.4) solution after deoxygenation with ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com