Infrared sequence thermography analysis method for impact defects of carbon fiber composite material
A composite material and analysis method technology, applied in the field of ultrasonic infrared nondestructive testing defect quantitative analysis, can solve the problems of different loss, not yet formed, insufficient theoretical basis, etc., to achieve the effect of correcting gradient error, improving effectiveness and accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
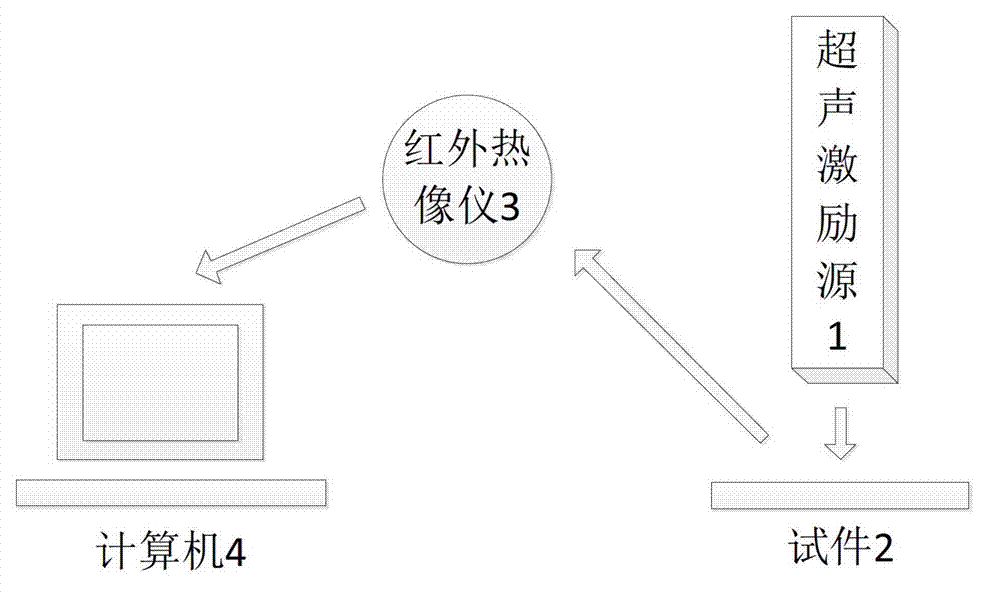
[0024] The research object of the present invention comes from the non-destructive testing experiment of ultrasonic infrared thermal imaging. The experimental system is shown in Figure 1. The viewing angle is aimed at the test piece 2, and the infrared camera 3 is connected to the computer 4 for data transmission. The ultrasonic excitation source 1 generates thermal excitation on the test piece 2, and the detected material with defects produces different temperature field distributions on the surface due to the difference in internal damage, and the infrared thermal imager 3 is used to obtain the infrared heat map during the heating or cooling process synchronously, And transmit it to the computer 4 for recording, and then process the recorded infrared sequence heat map, and further analyze the defects on the test piece.
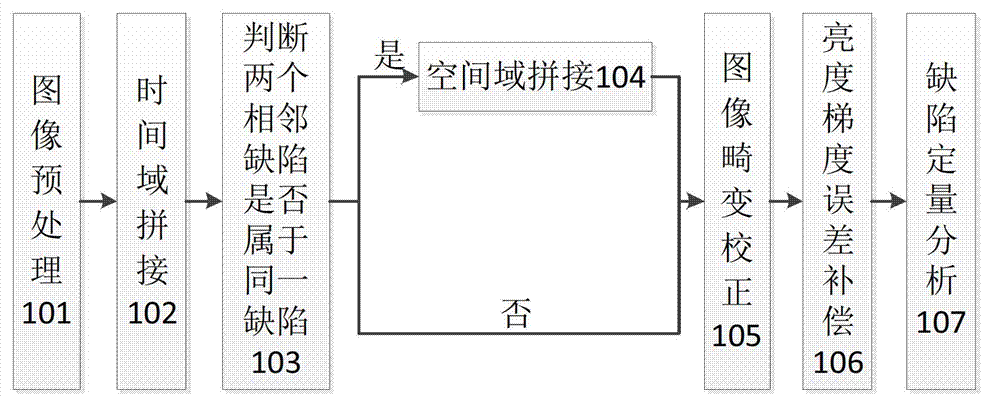
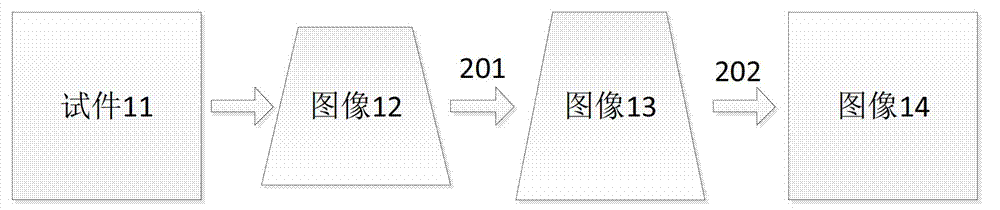
[0025] As shown in Figure 2, the infrared sequence heat map analysis method of the carbon fiber composite material impact defect comprises the following ste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com