Vanadium-dioxide-based composite film, transparent structure comprising same and application of transparent structure
A vanadium dioxide and composite film technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, synthetic resin layered products, layered products, etc., can solve the problems of low visible light transmittance, weak infrared regulation, and poor intelligent energy-saving effect, etc. Achieve good economic benefits, improve transmittance, and expand the scope of application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] First, deposit an aluminum-doped zinc oxide film 2 on a glass substrate 1 by sputtering: deposit a thickness h on a quartz glass substrate 1 by conventional radio frequency magnetron sputtering 2 Al-doped zinc oxide film 2 with a thickness of 75nm.
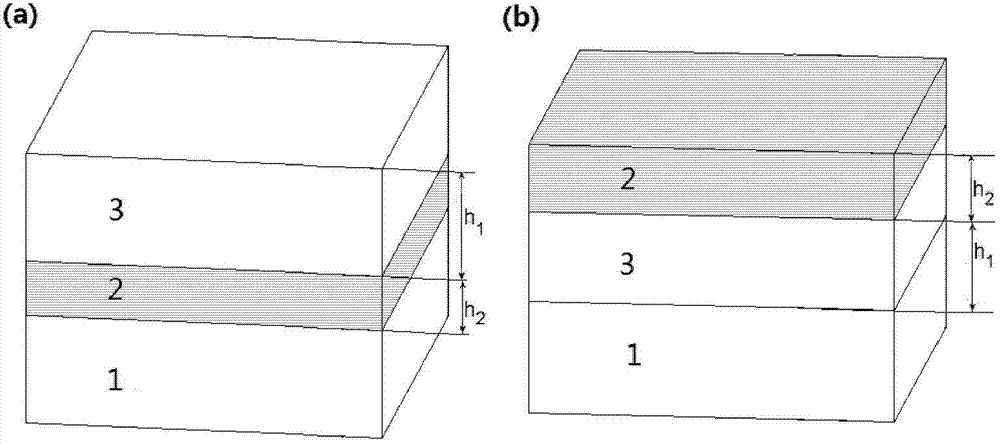
[0037] Then, sputter-deposit a vanadium dioxide film 3 on the formed aluminum-doped zinc oxide film 2: deposit a thickness h on the aluminum-doped zinc oxide film 2 by radio frequency magnetron sputtering 1 40nm vanadium dioxide thin film 3 . Thus obtain a light-transmitting structure with the vanadium dioxide-based composite film of the present invention (it is made of aluminum-doped zinc oxide film 2 and vanadium dioxide film 3), figure 1 (a) is a schematic diagram showing such a light-transmitting structure. Such as figure 1 As shown in (a), the light-transmitting structure includes a glass substrate 1 and a vanadium dioxide-based composite film, wherein the aluminum-doped zinc oxide film 2 is arranged on the glass su...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A light-transmitting structure with the vanadium dioxide-based composite thin film of the present invention was prepared in a manner similar to that of Example 1, except that the vanadium dioxide thin film was first arranged on a glass substrate, and the inorganic transparent thin film was arranged on the vanadium dioxide thin film On, and use the indium-doped tin oxide film as the inorganic transparent film. More specifically as follows:
[0045] First, on the quartz glass substrate 1, a vanadium dioxide film 3 is deposited by sputtering: on the quartz glass substrate 1, a thickness h is deposited by conventional radio frequency magnetron sputtering 1 42nm vanadium dioxide thin film 3 .
[0046] Then, on the vanadium dioxide film 3, deposit indium-doped tin oxide 2 by sputtering: on the formed vanadium dioxide film 3, deposit a thickness h by conventional radio frequency magnetron sputtering 2 Indium-doped tin oxide film 2 with a thickness of 205 nm. Thus obtain a l...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Prepare in a similar manner to Example 2 figure 1 (b) shows the light-transmitting structure with the vanadium dioxide-based composite film of the present invention, except that the indium-doped zinc oxide film is used as the inorganic transparent film.
[0052] First deposit a thickness h on a glass substrate 1 1 Be the vanadium dioxide film 3 of 50nm, then deposit thickness h on this vanadium dioxide film 2 215nm Indium-doped Zinc Oxide 2.
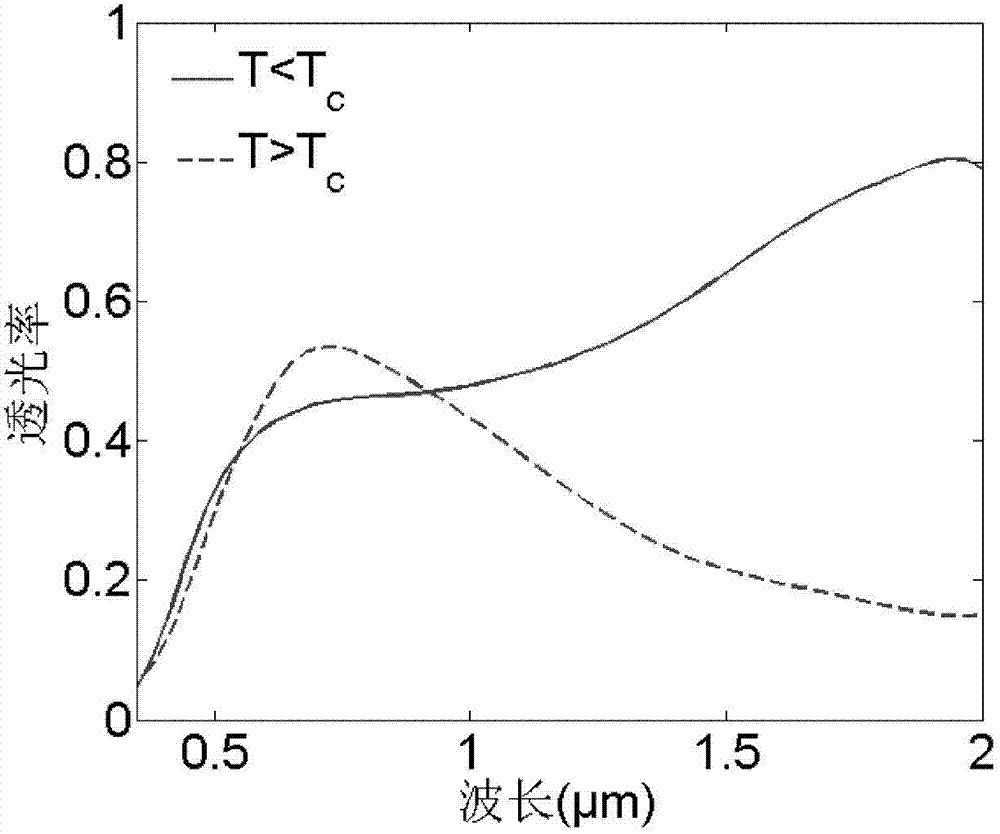
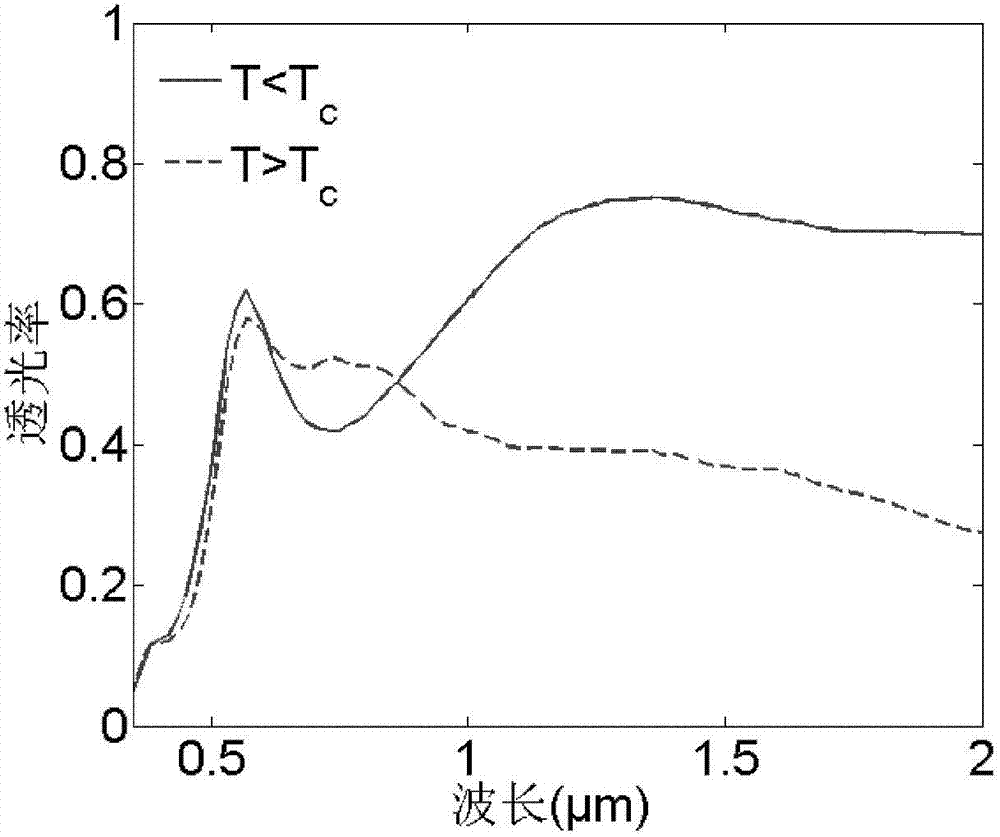
[0053] Similarly, for the light-transmitting structure obtained in Example 3, the present invention conducts electromagnetic field finite element simulation testing on its performance. Figure 4 shows the obtained by this Example 3 figure 1 (b) The electromagnetic field finite element simulation ultraviolet-visible-near-infrared transmission spectrum of the light-transmitting structure shown before and after the phase transition of the vanadium dioxide-based composite film, in which the vanadium dioxide-based composite film is ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com