Treatment Of Cancer Or Tumor Induced By The Release Of Heat Generated By Various Chains Of Magnetosomes Extracted From Magnetotactic Bacteria And Submitted To An Alternative Magnetic Field
A technology of magnetotactic bacteria and alternating magnetic field, applied in the field of thermal therapy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0163] Preparation of different types of particles used as heat source:
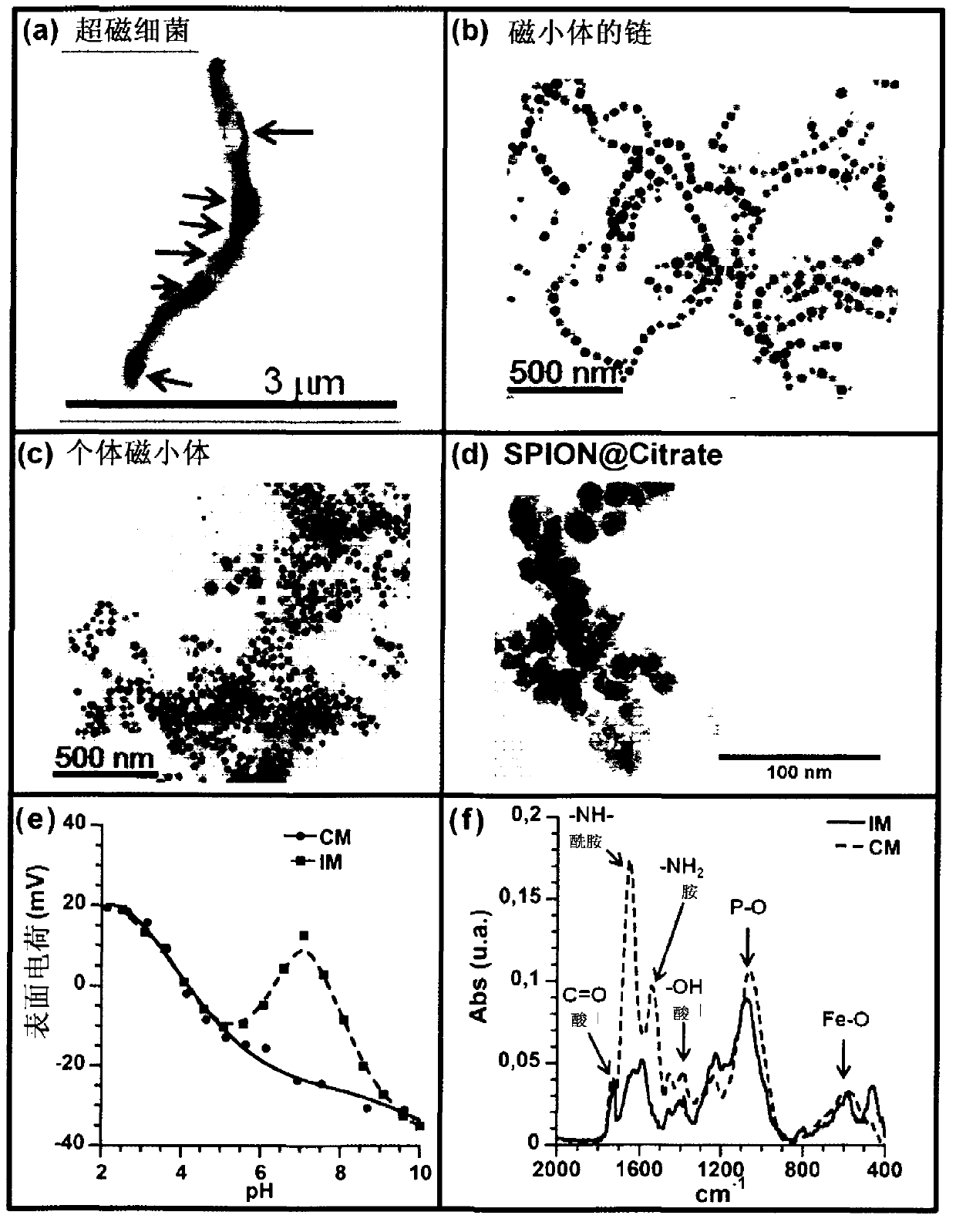
[0164] In this example, we describe the method by which different types of particles are prepared for use as heat sources. These particles are the particles contained in the whole magnetotactic bacteria, the chains of magnetosomes were extracted from the magnetotactic bacteria, the individual magnetosomes were extracted from the magnetotactic bacteria and detached from the chains by heating and SDS treatment, and the magnetosomes were covered with citrate ions. Chemically synthesized superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONCitrate) or commercially available chemically synthesized nanoparticles covered with PEG molecules (SPIONPEG). SPIONPEG was purchased from the German company Micromod (product name: -D-spio, product number: 79-00-201).
[0165] SPIONCitrate is used as standard nanoparticles because they possess a similar size to most nanoparticles used for magnetic hyperthermia (see for exa...
Embodiment 2
[0175] Heat production by exposure of bacterial magnetosomes to an oscillating magnetic field
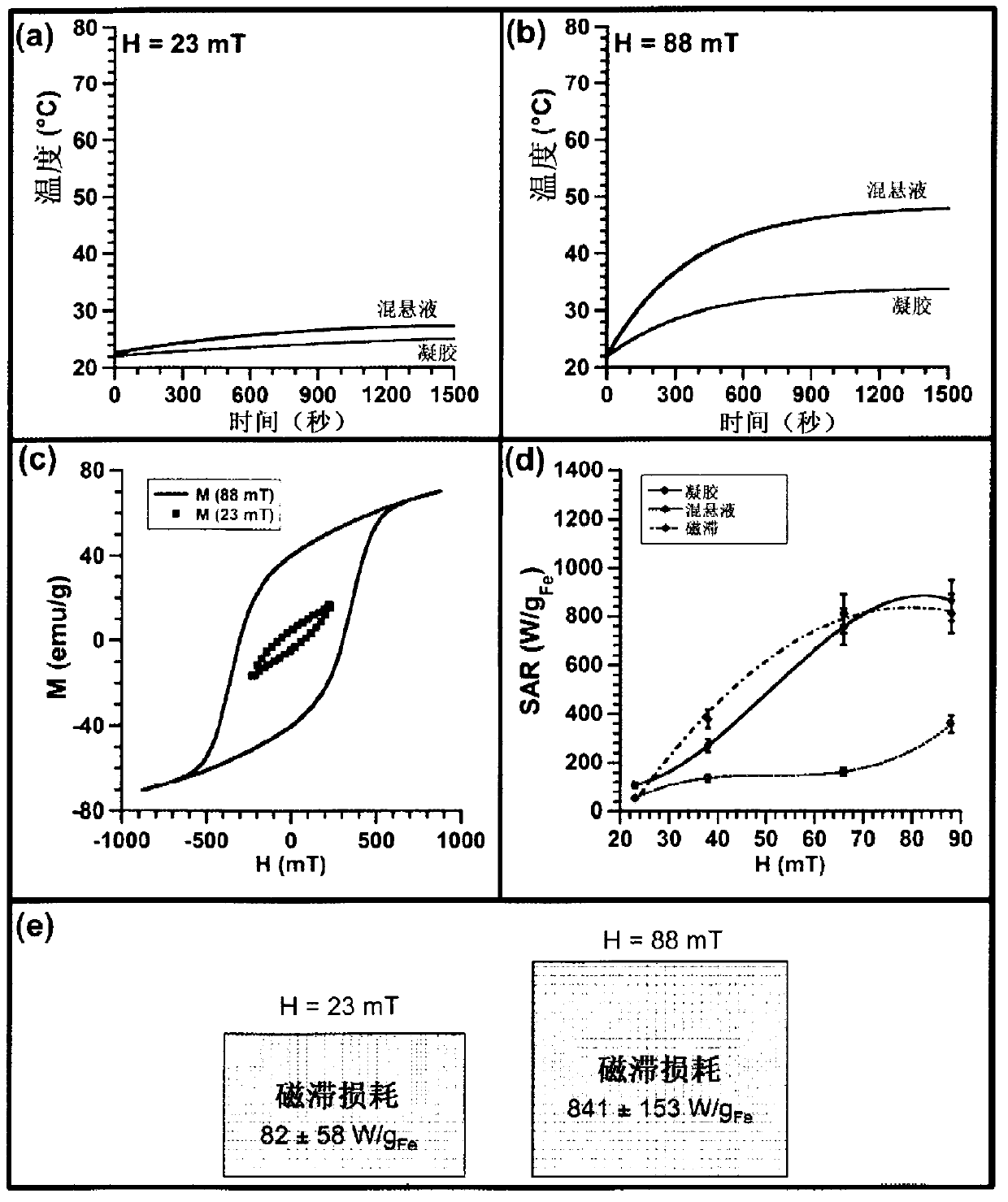
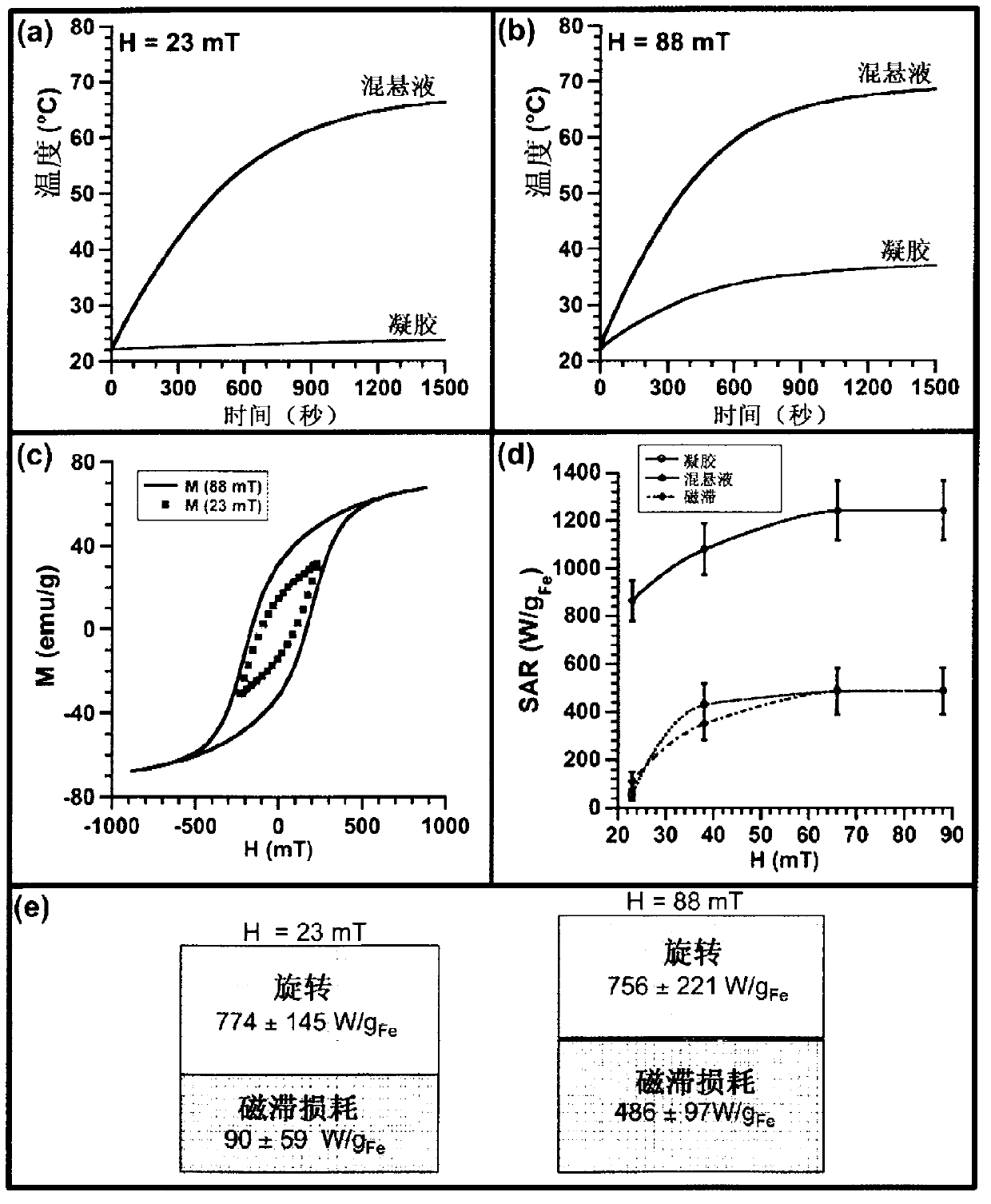
[0176] In this example, we provide a detailed study of the mechanism of heat generation of magnetosomes biomineralized by magnetotactic bacteria. The values of magnetic field frequency (108kHz) and magnetic field amplitude (23 to 88mT) used to heat different samples were within the range of magnetic field parameters used for high-frequency high-amplitude AMF (alternating magnetic field) superheating (Ivkov et al., Clin. Cancer Res., 2005, 11, 7093s-7103s; De Nardo et al., Clin. Cancer Res., 2005, 11, 7087s-7092s; De Nardo et al., The J. Nucl. Med., 2007, 48, 437-444). For AMF overheating, the recommended magnetic field frequency is between 50 kHz and 1 MHz, while the magnetic field amplitude needs to be kept below 100 mT (Mornet et al., J. Mater. Chem., 2004, 14, 2161-2175). We compared the thermogenic properties of three different types of magnetosome arrangements (Alphandéry et a...
Embodiment 3
[0195] Improved heating efficiency of chains of extracted magnetosomes obtained by synthesizing magnetotactic bacteria in the presence of various chelating agents and / or transition metals.
[0196]In this example, we describe various methods for improving the heating efficiency of chains of extracted magnetosomes suspended in water. These methods use various additives introduced into the growth medium of AMB-1 magnetotactic bacteria. These additives are chelating agents such as bisphosphonate molecules, dopamine, rhodamine, EDTA or transition metals such as cobalt.
[0197] Materials and methods:
[0198] First, a growth medium for magnetotactic bacteria was prepared by following the same method as described in Example 1. Then one of the following additives was added to the growth medium of magnetotactic bacteria: 0.4 μM, 4 μM or 40 μM of different types of bisphosphonates (alendronate, risedronate or neridronate), 4 μM , 20 μM or 400 μM rhodamine solution, 0.4 μM or 4 μM E...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Saturation magnetization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com