Recurrent Gene Fusions In Prostate Cancer
A technology for prostate cancer and fusion, which is applied in the direction of drug combination, microbial determination/inspection, instrument, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0360] Embodiment 1: ERG and ETV1 gene fusion
[0361] A. Materials and methods
[0362] Cancer Outlier Profile Analysis (COPA)
[0363] COPA analysis was performed on 132 gene expression datasets containing 10,486 microarray experiments in Oncomine 3.0. In addition, data from 99 expanded laser capture microdissected prostate tissue samples were included in the COPA analysis. COPA works in three steps. First, the gene expression values are centered around the median and the median expression value for each gene is set to zero. Second, the median absolute deviation (MAD) was calculated and scaled to 1 by dividing each gene expression value by its MAD. Transformations were performed using median and MAD rather than mean and standard deviation so that outlier expression values did not unduly affect distribution estimates and thus were preserved after normalization. Third, for each gene transform 75 of the expression values th 、90 th and 95 th Percentile tabulation, fo...
Embodiment 2
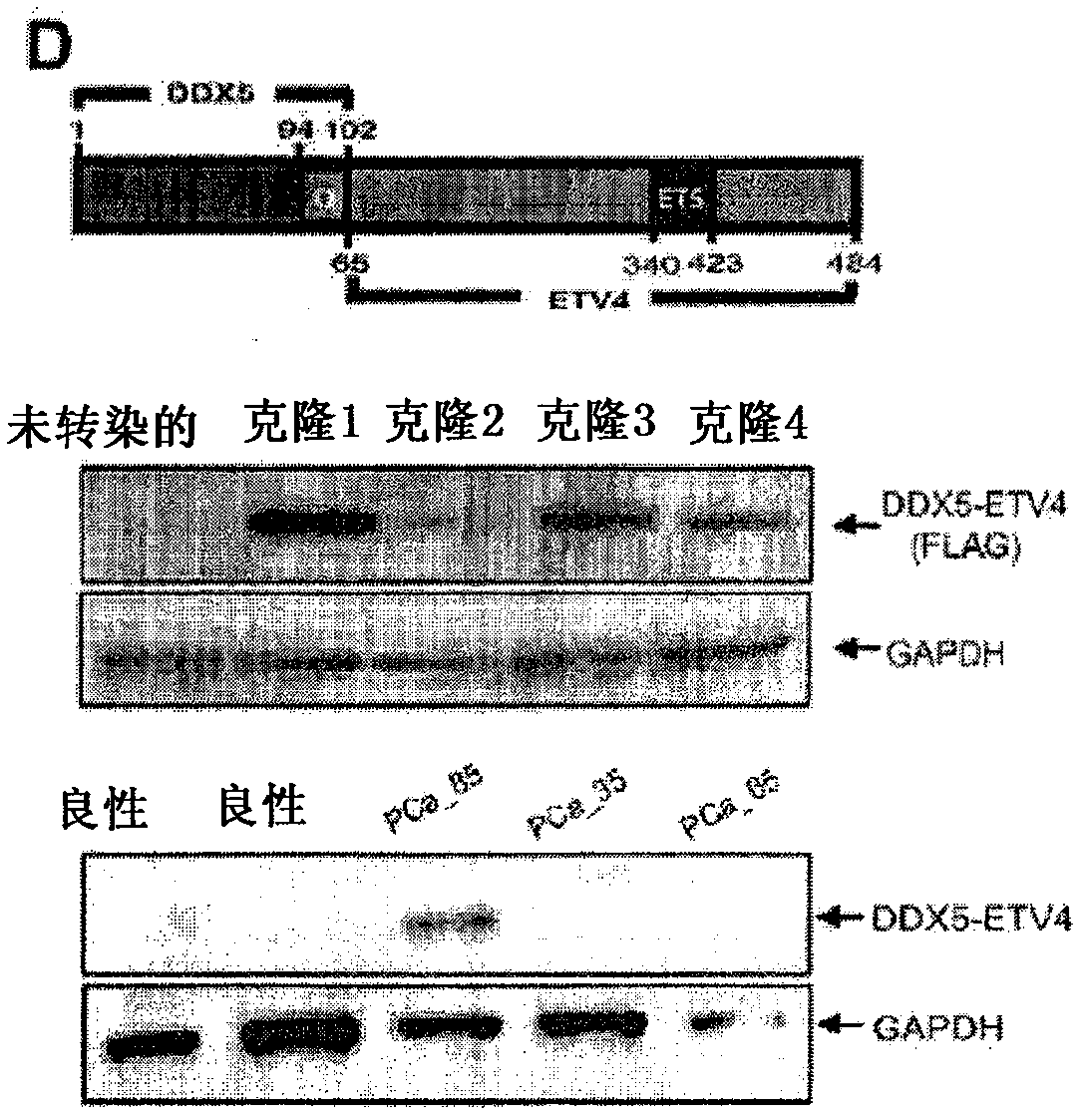
[0418] Example 2: ETV4 Gene Fusion
[0419] A.Materials and methods
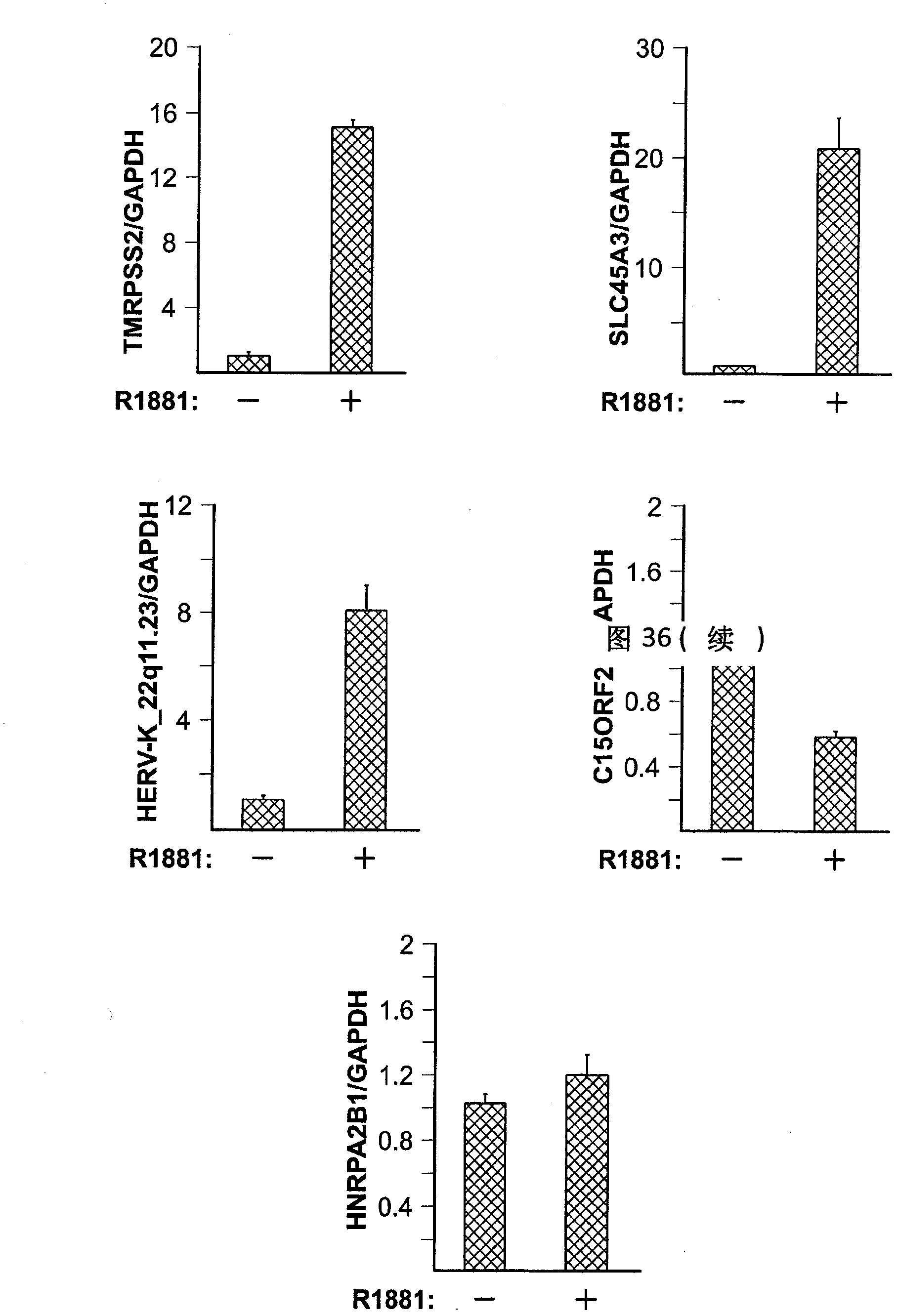
[0420] Expression of ETS families in profiling studies
[0421] To investigate the expression of ETS family members in prostate cancer, two prostate cancer profiling studies (Lapointe et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101:811-6 and Tomlins et al., Science 2005;310:644-8). Genes with ETS domains were identified by Interpro filter 'Ets' (Interpro ID: IPR000418). Heat map images were generated in Oncomine using the "median-center per gene" option, and the color contrast was set to highlight the differential expression of ERG and ETV1.
[0422] sample
[0423] Prostate cancer samples (PCA1-5) were obtained from the radical prostatectomy series at the University of Michigan as part of the Specialized Program of Research Excellence in Prostate Cancer (S.P.O.R.E.) organizational core at the University of Michigan. All samples were collected after obtaining patient informed consent and academic review boar...
Embodiment 3
[0439] Embodiment 3: the detection of gene fusion RNA
[0440] This example describes the target capture, amplification and qualitative detection of RNA containing the sequences of four gene fusions: TMPRSS2:ETV1a, TMPRSS2:ETV1b, TMPRSS2:ERGa and TMPRSS2:ERGb in four independent qualitative assays ( IVT) using APTIMA formulation reagents and HPA detection, each incorporating appropriate target-specific oligonucleotides, primers and probes. Table 5 shows the sequences of the oligonucleotides used in the assay.
[0441] table 5
[0442]
[0443] A. Materials and methods
[0444] RNA target capture
[0445] Lysis buffer contained 15 mM monobasic sodium phosphate monohydrate, 15 mM disodium hydrogen phosphate anhydrous, 1.0 mM EDTA disodium dihydrate, 1.0 mM EGTA free acid, and 110 mM lithium lauryl sulfate, pH 6.7. The target capture reagent contained 250 mM HEPES, 310 mM lithium hydroxide, 1.88 M lithium chloride, 100 mM EDTA free acid, pH 6.4, and 250 μg / ml of 1 micron m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com