Method for welding transparent material
A transparent material and combined technology, applied in welding equipment, laser welding equipment, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve the problems of welding efficiency limitation, low peak power, low power, etc., and achieve the goal of improving welding efficiency, realizing welding and reducing costs Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the implementation manner of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
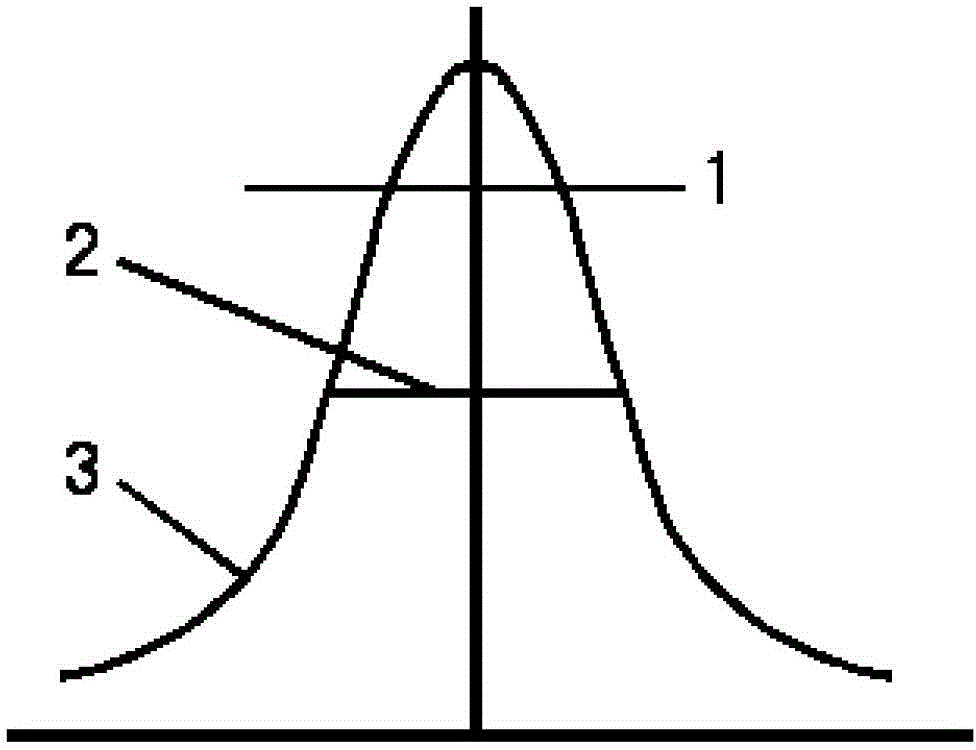
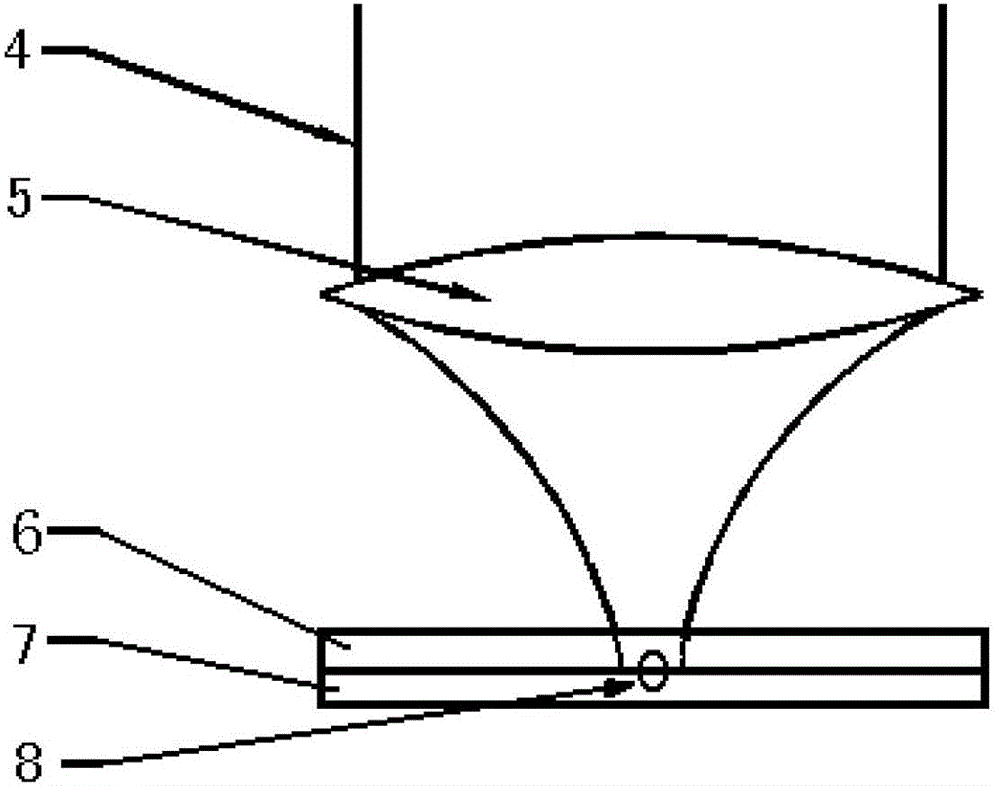
[0023] In order to reduce costs and improve welding efficiency, an embodiment of the present invention provides a method for welding transparent materials, see figure 1 , figure 2 with image 3 , the method includes the following steps:
[0024] 101: Choose two lasers that can penetrate the transparent material to be welded, one is an ultrashort pulse laser, the other is a long pulse laser, the power of the two laser beams matches, and the two laser beams are adjusted to be synchronized and beamed together;
[0025] In actual implementation, the power of the two lasers needs to be determined according to the materials in practical applications. Ultrashort pulse lasers usually choose a pulse width of femtosecond or picosecond order o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| laser radiation transmission | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com