Non-volatile storage device and method for manufacturing the same
A non-volatile storage and manufacturing method technology, applied in the field of non-volatile storage devices, can solve the problems of reduced stress migration resistance, easy migration, and increased stress variation, so as to improve the stress migration resistance and stabilize the memory Characteristics, effect of resistance change stabilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0061] [Structure of variable resistance nonvolatile memory device]
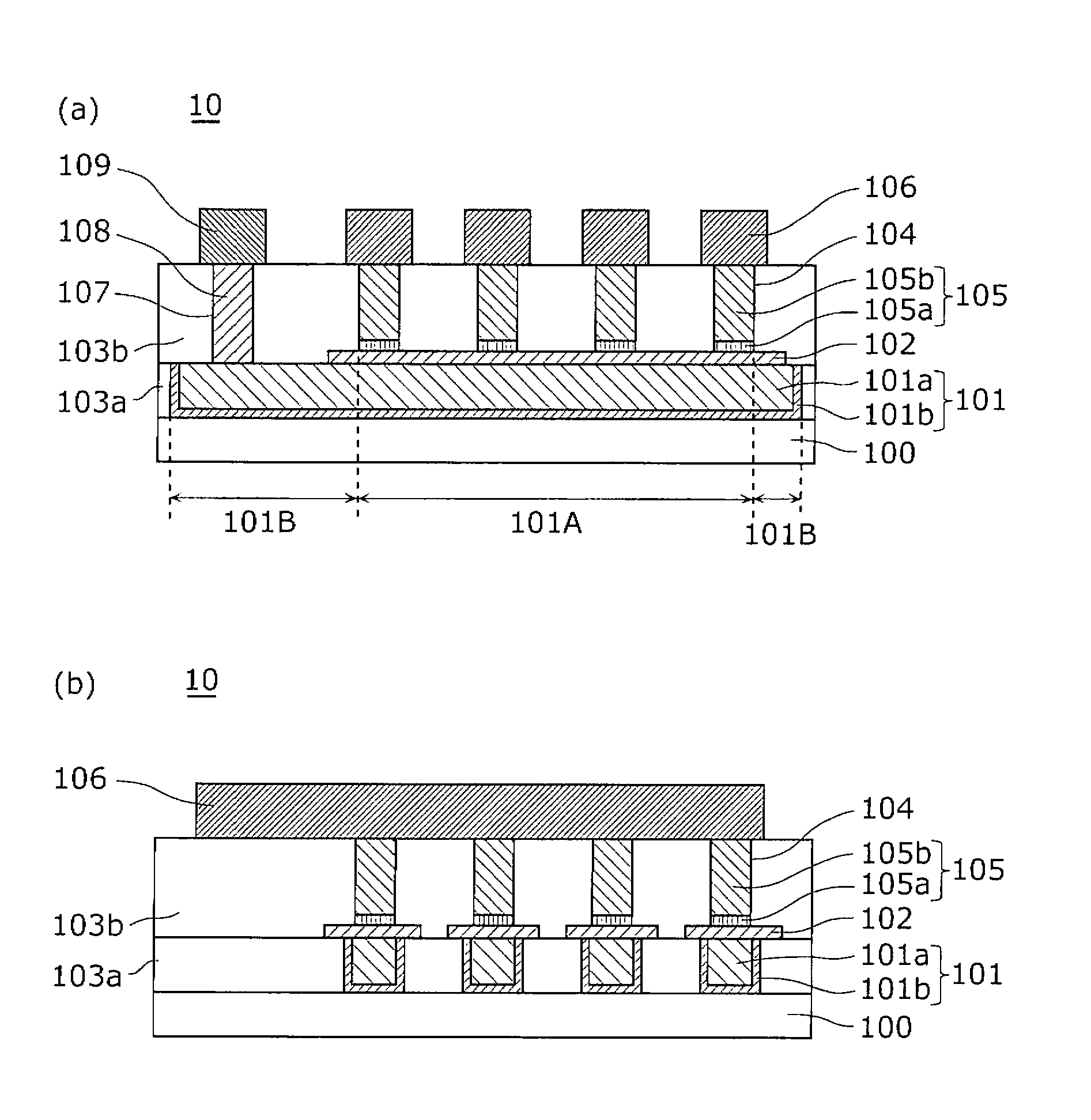
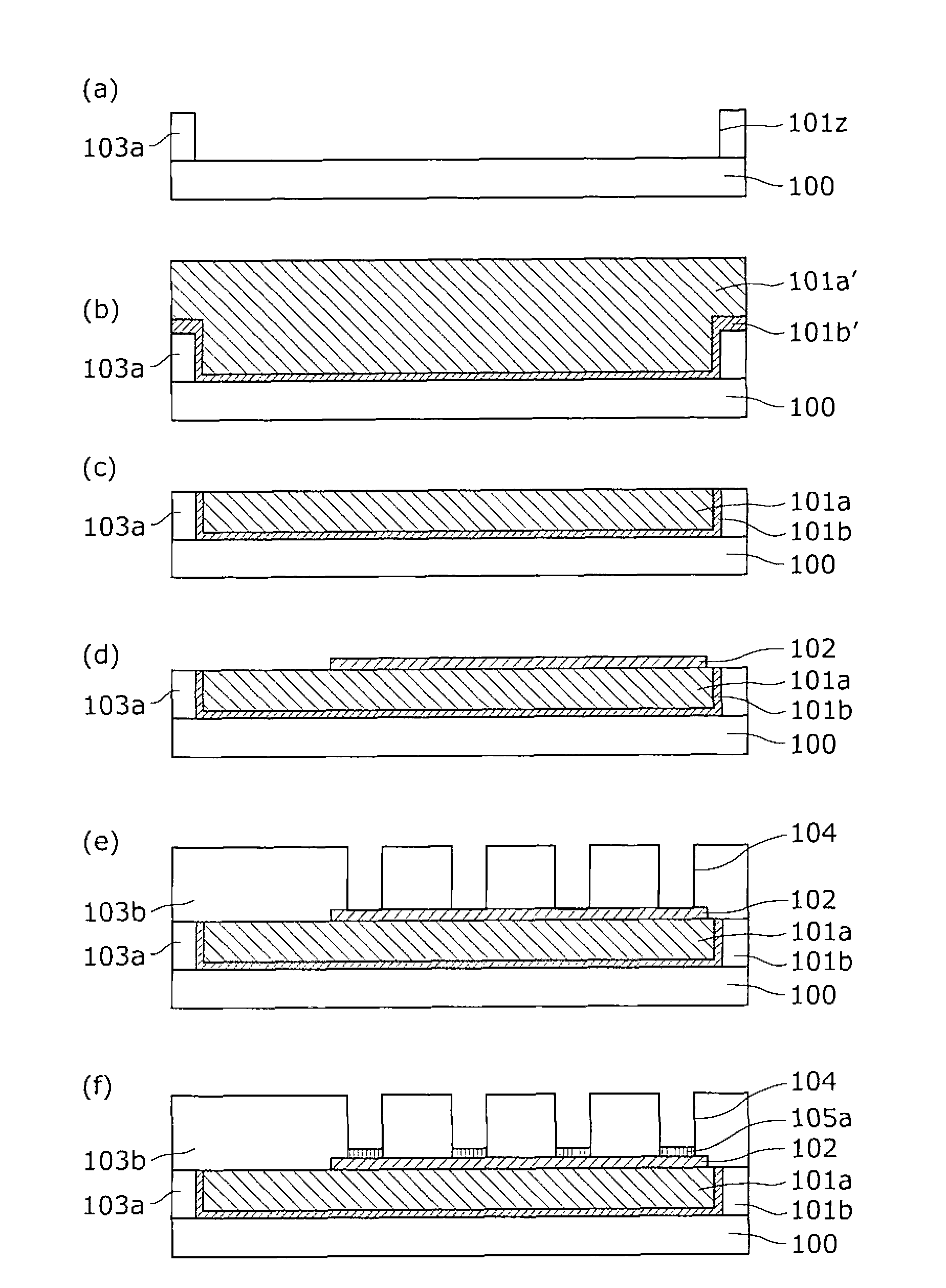
[0062] figure 1 It is a plan view showing a structural example of the nonvolatile memory device 10 according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention (the following nonvolatile memory devices 20 , 30 , 40 , 50 , and 60 have the same structure in plan view). figure 2 (a) means viewing along the direction of the arrow figure 1 The cross-sectional view of the single-dot dash line part shown in 1A-1A', figure 2 (b) means viewing along the direction of the arrow figure 1 The cross-sectional view of the single-dot dash line part shown in 1B-1B' in .
[0063] Such as figure 1 with figure 2 As shown, the first wiring 101 and the second wiring 106 each have a line shape and cross each other through the second interlayer insulating layer 103b. A memory cell hole 104 is formed penetrating through the second interlayer insulating layer 103 b at the intersection position, and a variable resistance element is...
Embodiment approach 2
[0105] [Structure of variable resistance nonvolatile memory device]
[0106] Figure 8 (a) and (b) are cross-sectional views showing a configuration example of the resistance variable nonvolatile memory device 30 according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. Figure 8 (a) means viewing along the direction of the arrow figure 1 The cross-sectional view of the single-dot dash line part shown in 1A-1A', Figure 8 (b) means viewing along the direction of the arrow figure 1 The cross-sectional view of the single-dot dash line part shown in 1B-1B' in .
[0107] Among them, there are the following two points of difference from the nonvolatile memory device 10 of the first embodiment.
[0108] The first point is that the end face of the first electrode 102 made of noble metal and the end face of the first wiring 101 are located in the same plane in the direction perpendicular to the cross section of the line 1B-1B' (see Figure 8 (b)). The first electrode 102 and the fir...
Embodiment approach 3
[0122] Figure 13 (a) and (b) are cross-sectional views showing a configuration example of the resistance variable nonvolatile memory device 40 according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. Figure 13 (a) means viewing along the direction of the arrow figure 1 The cross-sectional view of the single-dot dash line part shown in 1A-1A', Figure 13 (b) means viewing along the direction of the arrow figure 1 The cross-sectional view of the single-dot dash line part shown in 1B-1B' in .
[0123] The difference from the nonvolatile memory device 10 of Embodiment 1 is that the first variable resistance layer 105 a of the variable resistance element is formed not only on the bottom of the memory cell hole 104 but also on the sidewall. The first variable resistance layer 105 a is formed in a ring shape along the inner wall (side wall) of the memory cell hole 104 when viewed from a plan view, and the second variable resistance layer 105 b is formed inside it.
[0124] The fir...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com