Liquefaction system for producing LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) by using pressure energy of pipeline
A pipeline pressure and channel technology, applied in the field of liquefaction system, can solve the problems of high energy consumption, extra power consumption required by the system, low utilization rate of pressure energy, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing purification pressure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
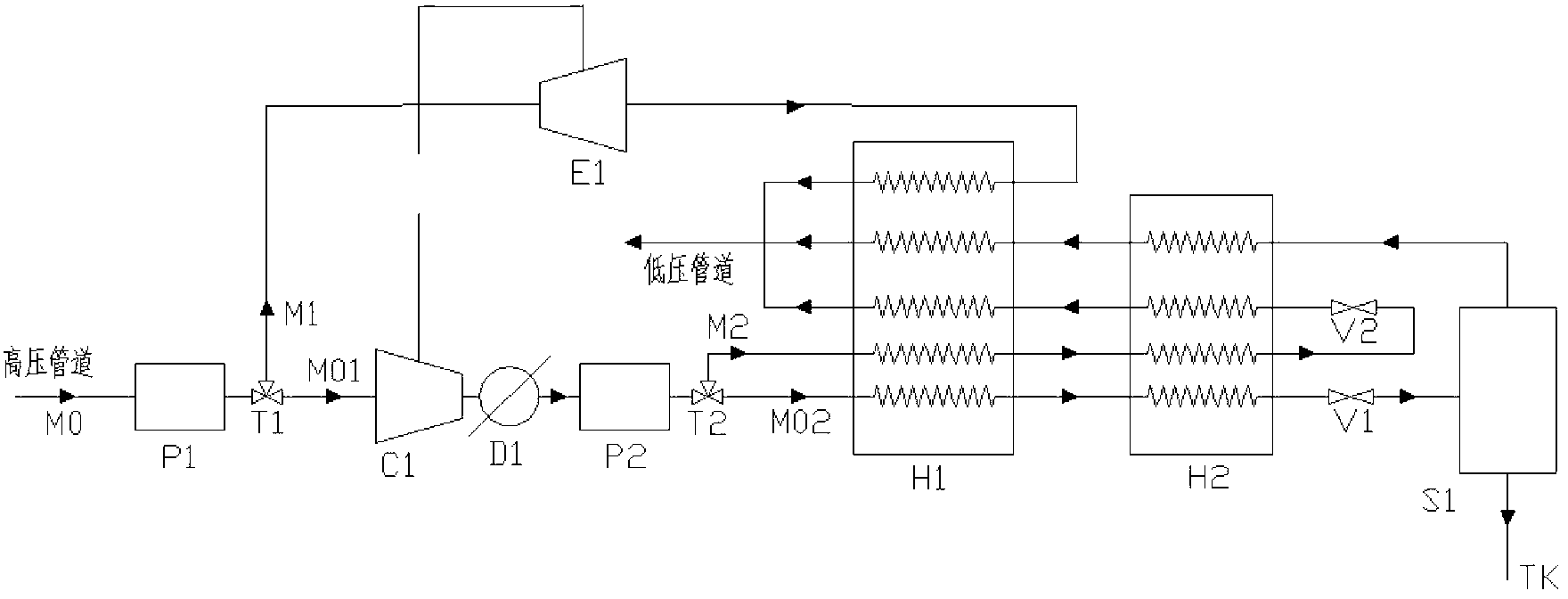
[0031] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 As shown, the liquefaction system in this embodiment 1 includes a primary purifier P1, a secondary purifier P2, a first compressor C1, a first cooler D1, a first expander E1, a first recuperator H1, The second regenerative heat exchanger H2, the first throttle valve V1, the second throttle valve V2 and the gas-liquid separator S1;
[0032]The natural gas from the high-pressure pipeline is first roughly purified and dehydrated by the primary purifier P1, and then divided into two paths after the first distribution valve T1, the two paths are the first pre-cooling branch M1 and the first liquefaction branch M01;
[0033] The natural gas flow entering the first liquefaction branch M01 flows through the first compressor C1 and the first cooler D1 to be compressed and cooled in sequence; then enters the secondary purifier P2, where acid gas and gas are removed After the impurities are deeply purified, they are divided into two paths after the secon...
Embodiment 2
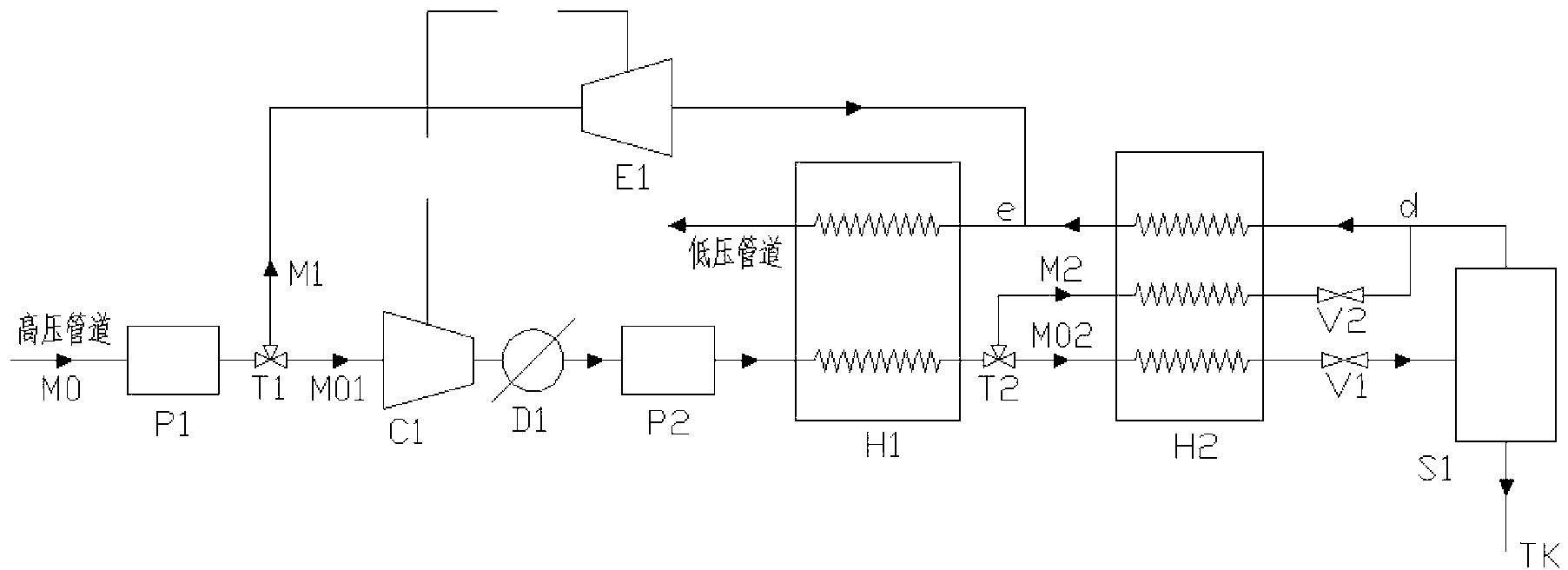
[0041] Such as figure 2 As shown, the difference between this embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is:
[0042] The second distribution valve T2 is located between the first regenerative heat exchanger H1 and the second regenerative heat exchanger H2;
[0043] The outlet pipeline of the second throttle valve V2 in the main cooling branch M2 is connected to the liquefaction branch M02 at d of the upper outlet pipeline of the gas-liquid separator S1; the outlet of the first expander E1 of the first precooling branch M1 The pipeline is connected to the liquefaction branch M02 at point e between the first recuperation heat exchanger H1 and the second recuperation heat exchanger H2;
[0044] The rest of the system is the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0045] Compared with Embodiment 1, the system in Embodiment 2 has the advantage that the first recuperative heat exchanger H1 has two channels, and the second recuperative heat exchanger H2 has three channels, and its manufacturing difficulty...
Embodiment 3
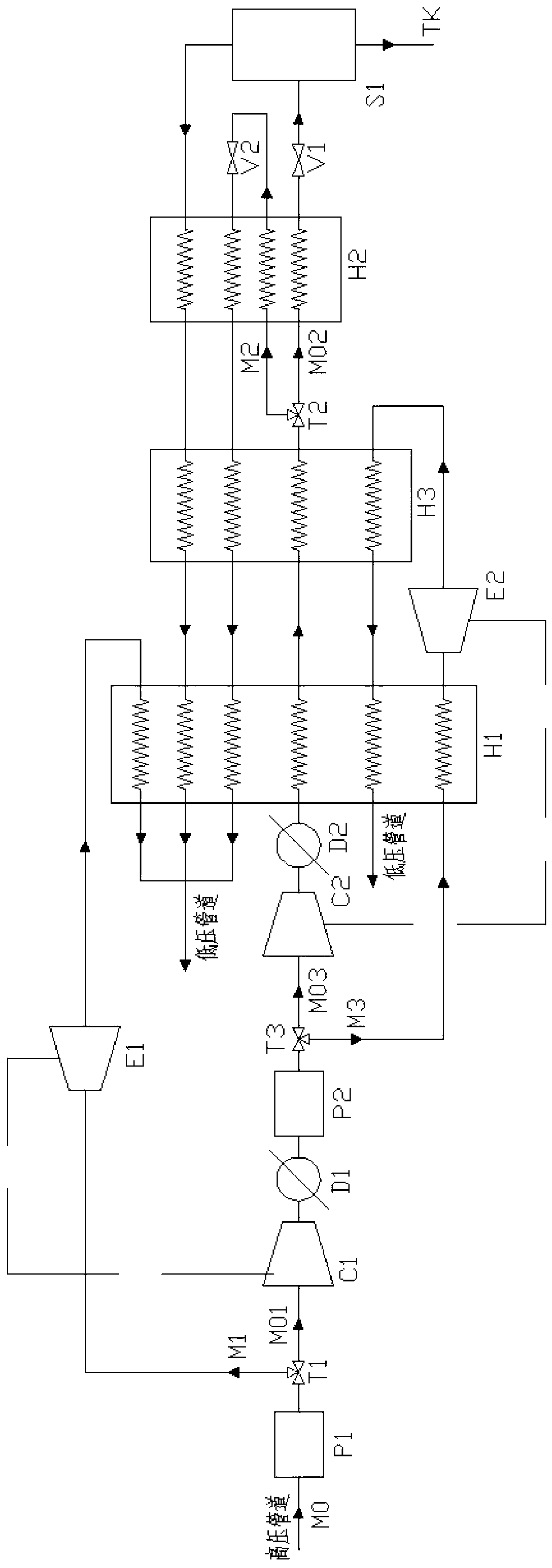
[0047] Such as image 3 As shown, the difference between Embodiment 3 and Embodiment 1 is that the throttling expansion device of the main cooling branch M2 selects the second expander E2, and adds the second compressor C2 and the second cooler D2, specifically:
[0048] After the main cooling branch M2 is separated from the distribution valve T2 at the outlet of the secondary purifier P2, it enters the second expander E2 through the second high-pressure channel of the first recuperator H1, and expands through the second expander E2 The final natural gas flows through the second low-pressure passage of the second recuperator H2 and the second low-pressure passage of the first recuperator H1 to recover cooling capacity, and finally enters the low-pressure pipeline;
[0049] The natural gas in the first liquefaction branch M01 comes out of the secondary purifier P2, passes through the second compressor C2 and the subsequent second cooler D2, and then enters the first high-pressu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com