LED chip cutting method and LED chip manufactured by same
A technology of LED chip and cutting method, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable light extraction, and achieve the effect of improving light extraction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015] The preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, so that the advantages and features of the present invention can be more easily understood by those skilled in the art, so as to define the protection scope of the present invention more clearly.
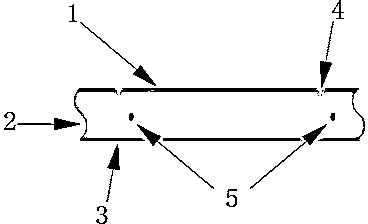
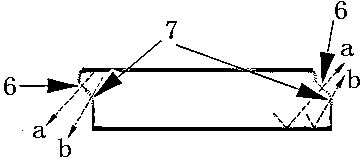
[0016] See attached figure 1 with attached figure 2 As shown, a method for cutting LED chips is provided in this implementation, including the following steps:
[0017] (1) Provide a sapphire substrate 2 with a GaN epitaxial light-emitting layer 1, perform laser scribing on the front side of the sapphire substrate 2 to form grooves 4 to divide the crystal grains, and use wet etching to etch the laser ablation area to form a groove in the groove Form a rough surface 7, according to the traditional chip manufacturing process, on this basis to complete the follow-up manufacturing of the chip;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com