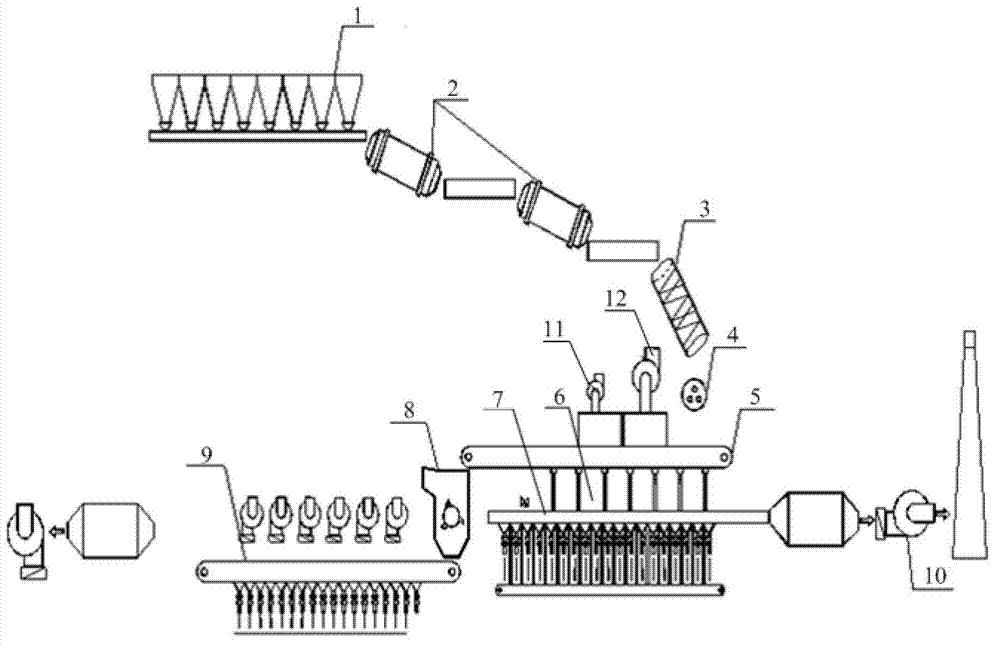
Negative pressure control method and negative pressure control system for main exhaust fan of sintering machine
A technology of negative pressure control and exhaust fan, applied in the field of sintering process, can solve the problems of high power consumption and loss, and achieve the effect of saving power, reducing energy consumption and saving power.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
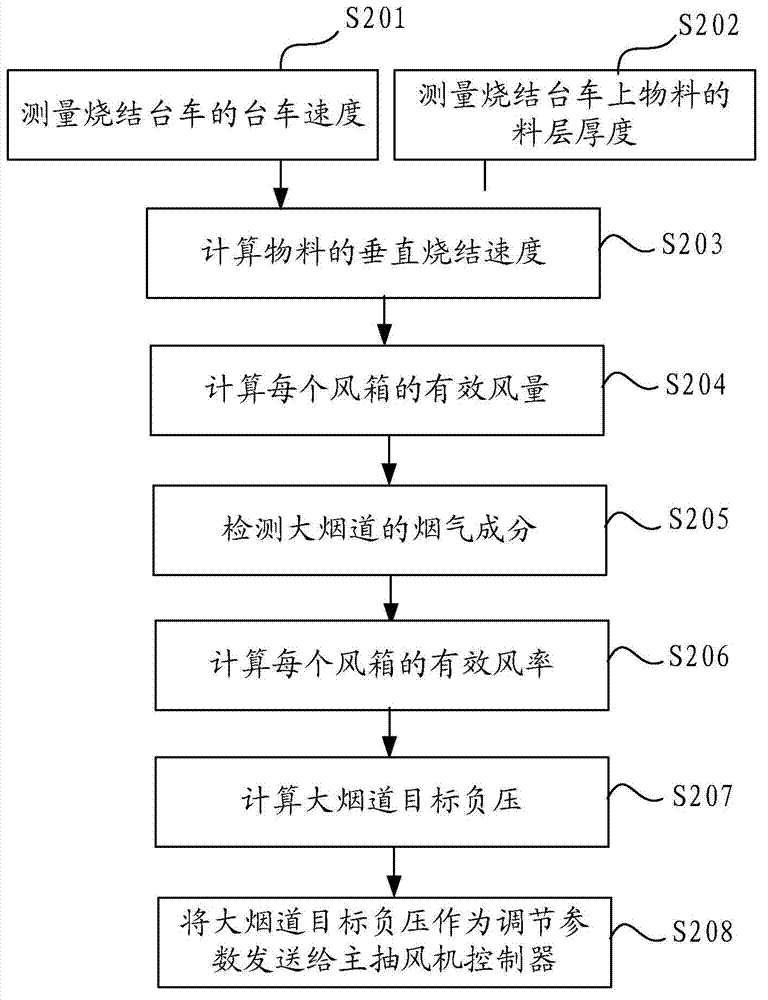
[0045] figure 2 It is a flow chart of the method for controlling the negative pressure of the main exhaust fan provided in Embodiment 1 of the present application.
[0046] Such as figure 2 As shown, the method includes:
[0047] S201: Measure the material layer thickness of the material on the sintering trolley.
[0048] In this embodiment, the thickness of the material layer of the material can be measured by a direct detection method, or the material layer thickness of the material can be calculated by indirectly detecting the amount of material discharged by the distributing machine per unit time. Since the material layer on the sintering machine trolley usually takes 40 minutes or more from the sintering start point to the sintering end point during the sintering process, this results in that when detecting the material layer thickness, the closer to the sintering end point, the greater the time lag for starting adjustment. big. Therefore, in the embodiment, when th...
Embodiment 2
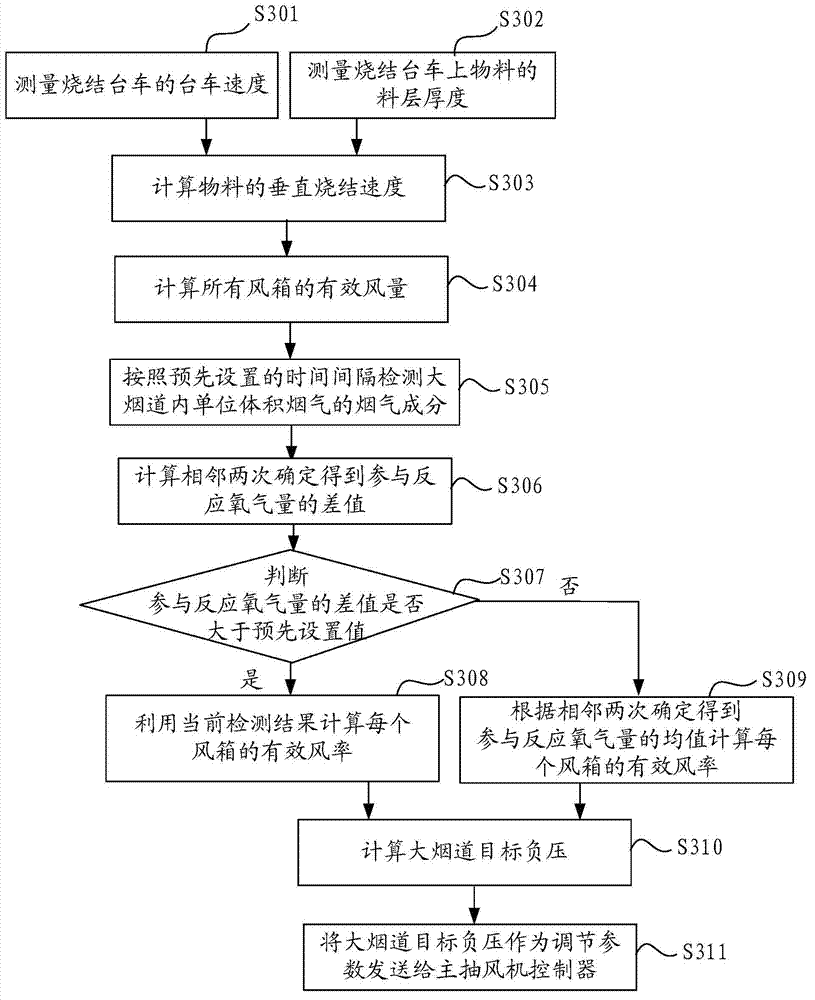
[0106] image 3 It is a flow chart of the method for controlling the negative pressure of the main exhaust fan provided in the second embodiment.
[0107] according to image 3 As shown, steps S301-S304 are equivalent to steps S201-S204 in Embodiment 1. For detailed descriptions of steps S301-S304, please refer to the description of steps S201-S204 in Embodiment 1 above, which will not be repeated here.
[0108] S305: Detect the smoke components in the unit volume of smoke in the large flue according to the preset time interval.
[0109] Here, in this embodiment, the flue gas component in the unit volume flue gas in the large flue is O in the unit volume flue gas 2 , CO, CO 2 , N 2 , NO, NO 2 content. When detecting the smoke composition of the large flue, the smoke composition of the large flue is detected according to the preset time interval, which can make the detection more adaptable to the change of the system load. For example, when the system load, such as mate...
Embodiment 3
[0128] This example refers to Figure 4 process shown. according to Figure 4 As shown, steps S401-S407 are equivalent to steps S201-S207 in Embodiment 1. For detailed descriptions of steps S401-S407, please refer to the description of steps S201-S207 in Embodiment 1 above, which will not be repeated here.
[0129] S408: Calculate the difference between the target negative pressure of the large flue obtained from two adjacent calculations.
[0130] S409: Determine whether the difference is greater than a preset value.
[0131] When the judgment result is greater than, execute step S410; otherwise, execute step S411.
[0132] S410: Use the currently calculated target negative pressure of the large flue as an adjustment parameter.
[0133] S411: Using the mean value of the large flue target negative pressure obtained by two adjacent calculations as an adjustment parameter.
[0134] S412: Send the adjustment parameters to the main exhaust fan controller.
[0135] When the tar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com