Magnetic random access memory (mram) cell and method for reading the mram cell using a self-referenced read operation
A random access memory and storage layer technology, applied in static memory, digital memory information, information storage, etc., can solve the problems of dipole coupling and other problems, and achieve the effect of low power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
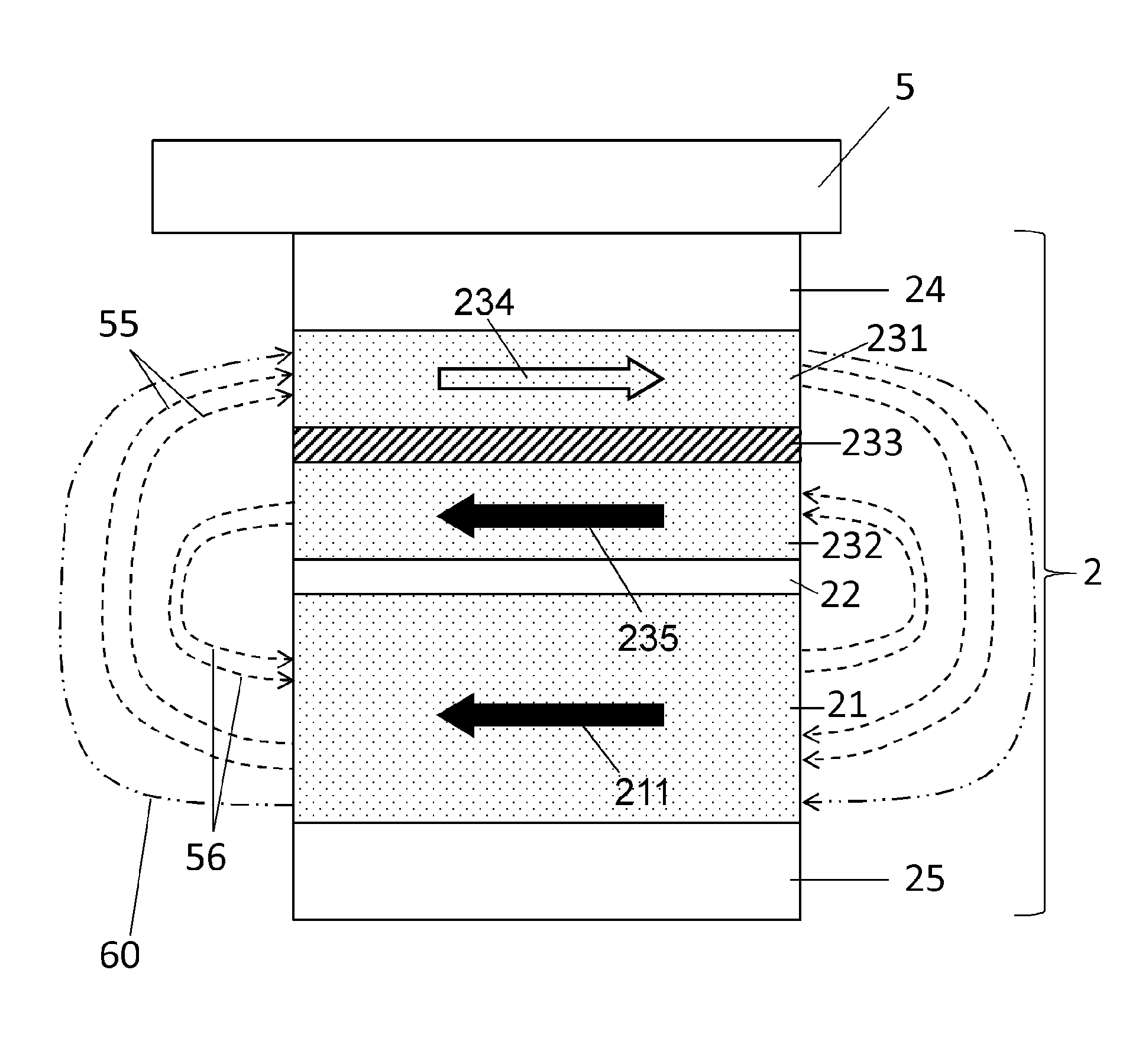
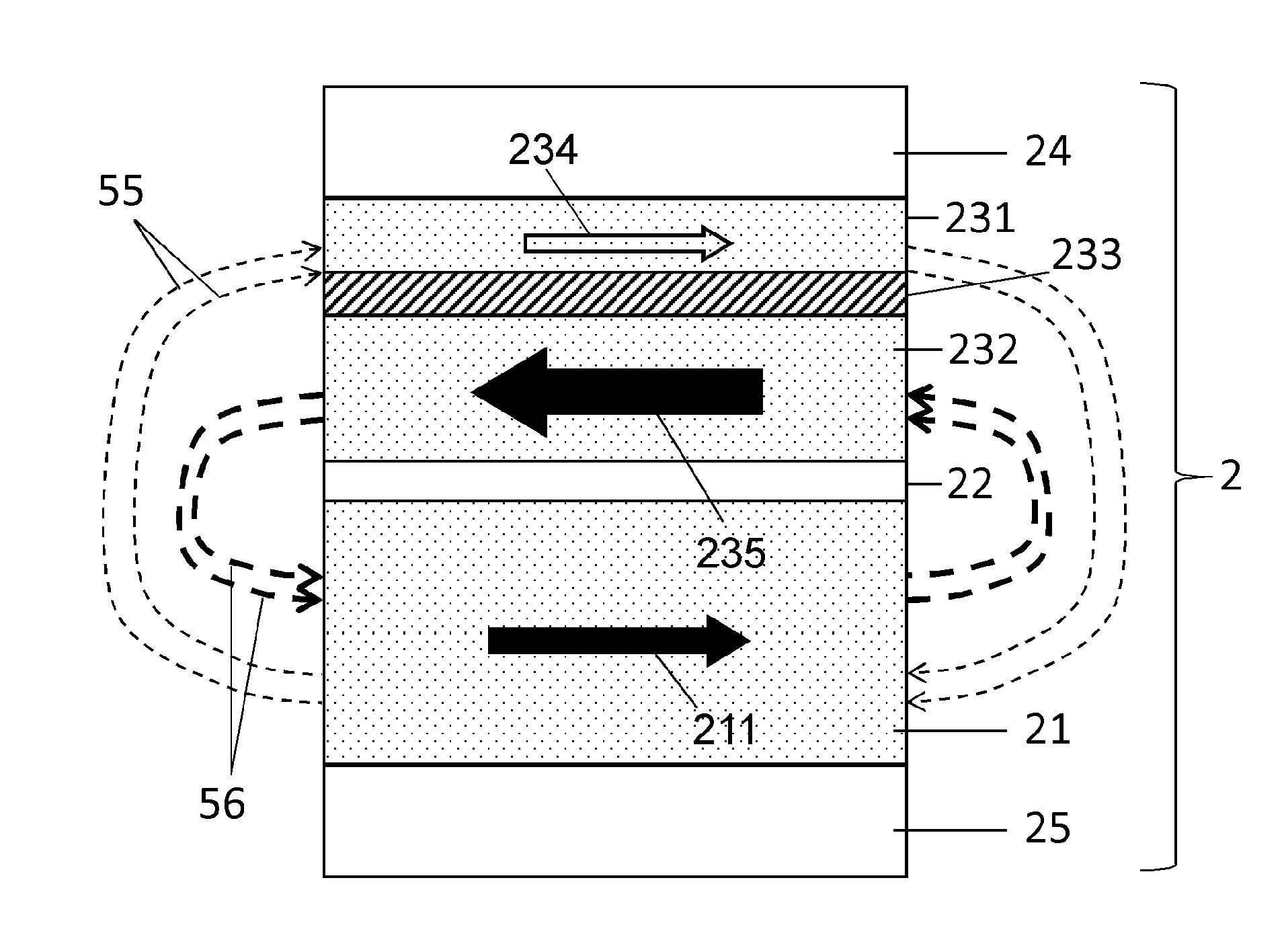
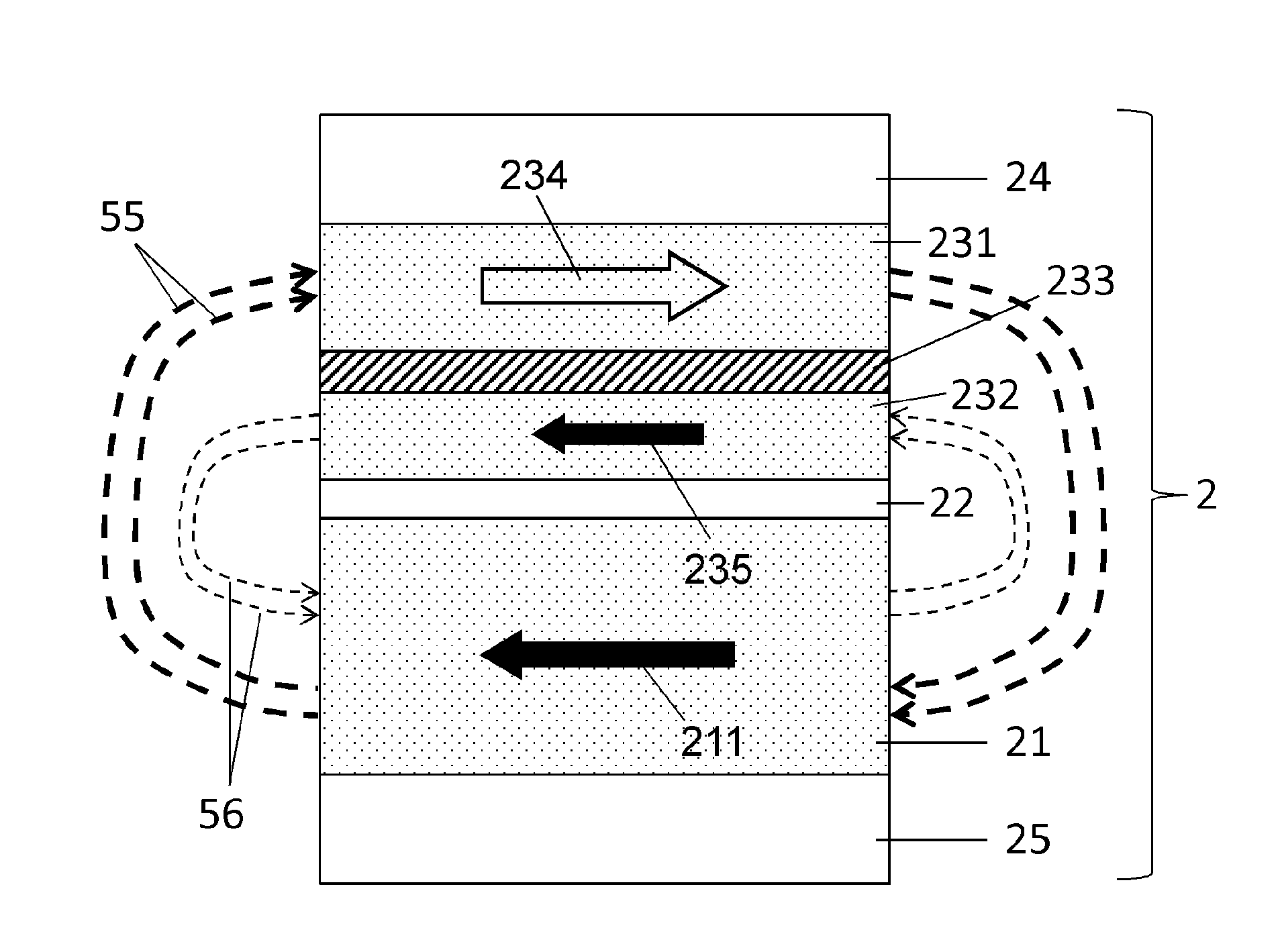
[0041] In one embodiment shown in FIG. 1 , a magnetic random access memory (MRAM) cell 1 includes a magnetic tunnel junction 2 . The magnetic tunnel junction 2 comprises a synthetic storage layer 23 formed of a synthetic ferromagnetic multilayer comprising a first ferromagnetic layer 231 with a first storage magnetization 234 and a second storage magnetization 235 The first and second ferromagnetic layers 231 , 232 are separated by a spacer layer 233 . The ferromagnetic layers 231 and 232 may be made of materials such as, for example, cobalt iron (CoFe), cobalt iron boron (CoFeB), nickel iron (NiFe), cobalt (Co), and the like. The thickness of the first and second ferromagnetic layers 231 , 232 may for example be comprised between 1 nm and 10 nm.
[0042]Dimensions (eg, thickness) of spacer layer 233 may be selected to promote magnetic coupling of first and second ferromagnetic layers 231 and 232 such that first storage magnetization 234 is oriented antiparallel to second mag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com