Nylon 6/plant fiber composite material and preparation method thereof
A plant fiber and composite material technology, applied in the field of composite materials, can solve the problems of incomplete plasticization of nylon, inferior mechanical properties to extrusion injection molding, short hot pressing time, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
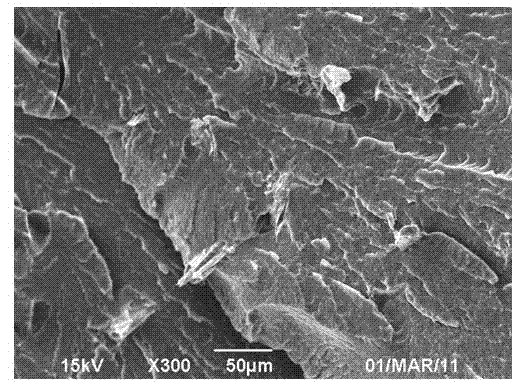
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
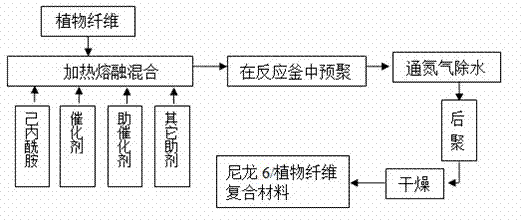
[0040] In parts by weight, 100 parts of caprolactam (abbreviation for ε-caprolactam) in 90 o Melting in a constant temperature water bath, after the melting is completed, add 0.5 parts of wood plant fiber, stir and mix evenly at a high speed, so that the wood plant fiber is dispersed in the molten caprolactam, and then add 0.4 part of catalyst 6-aminocaproic acid and cocatalyst sodium phosphate 0.6 parts, 1.5 parts of activator, 5 parts of water, at 90 o Stir and mix evenly in a constant temperature water bath; add it to the reaction kettle, replace the air in the kettle with nitrogen for at least three times and protect it with nitrogen. o C temperature, 7×10 5 React under Pa pressure for 6 hours; feed nitrogen into the reactor and discharge the nitrogen, and remove the small molecule water produced in the prepolymerization stage; exhaust and vacuumize the reaction system, and the reaction system is at 210 oC Under the temperature, the degree of vacuum (gauge pressure) is ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] In parts by weight, 100 parts of caprolactam at 90 o Melting in a constant temperature water bath, after the melting is completed, add 0.8 parts of wood plant fiber, stir and mix evenly at a high speed, so that the wood plant fiber is dispersed in the molten caprolactam, and then add 0.5 part of catalyst phosphoric acid and 0.7 part of cocatalyst sodium nucleotide , 2 parts of activator, 8 parts of water, at 90 o Stir and mix evenly in a constant temperature water bath; add it to the reaction kettle, replace the air in the kettle with nitrogen for at least three times and protect it with nitrogen. o C temperature, 8×10 5 React under Pa pressure for 5 hours; feed nitrogen into the reactor and discharge the nitrogen, and remove the small molecule water produced in the prepolymerization stage; exhaust and vacuumize the reaction system, and the reaction system is at 200 o C temperature, vacuum degree (gauge pressure) is -0.085MPa, react for 1.5 hours, and obtain nylon 6 / p...
Embodiment 3
[0044] In parts by weight, 100 parts of caprolactam at 90 o Melting in a constant temperature water bath, after the melting is completed, add 1.2 parts of hemp plant fiber, stir and mix evenly at a high speed, so that the single fiber of hemp plant is dispersed in the molten caprolactam, and then add 0.5 part of catalyst phosphoric acid and 0.7 part of cocatalyst sodium nucleotide , 2.5 parts of activator, 6 parts of water, at 90 o Stir and mix evenly in a constant temperature water bath; add it to the reactor, replace the air in the reactor with nitrogen for at least three times and protect it with nitrogen. o C temperature, 1×10 6 React under Pa pressure for 4.5 hours; feed nitrogen into the reactor and discharge the nitrogen, and remove the small molecule water produced in the prepolymerization stage; exhaust and vacuumize the reaction system, and the reaction system is at 220 o C temperature, vacuum degree (gauge pressure) is -0.09MPa, react for 2 hours, and obtain nylon...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| impact strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com