Continuous subcutaneous administration of interferon-alpha to hepatitis b infected patients
A hepatitis B, subcutaneously administered technology, applied in the field of methods and systems, capable of addressing issues affecting patient compliance and outcomes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0155] Example 1: The general treatment plan for continuous administration of interferon-alpha to patients
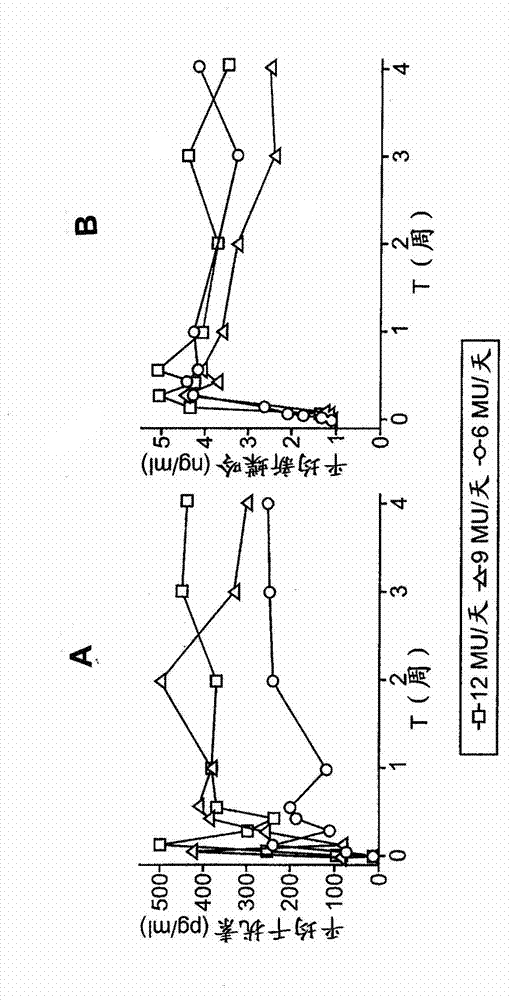
[0156] A variety of art-accepted therapeutic regimens for treating HBV may be suitable for use in embodiments of the present invention. For example, an exemplary treatment regimen may include ambulatory infusion pumps (e.g. Model 508 microinfusion pump) for the continuous administration of interferon-alpha thereby maintaining the circulating level of administered interferon-alpha above a certain threshold, for example sufficient to maintain the circulating level of interferon-alpha in the serum of said patient high A treatment regimen at a steady state concentration of at least 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600 or 700 pg / mL. Such regimens may include, for example, administration of 6, 9 or 12 MIU of IFN-α (eg, Triclonal ) / day for at least 1 week to at least 48 weeks, for example as discussed in detail in Example 2 below. Another exemplary regimen comprises: continuous...
Embodiment 2
[0159] Example 2: Administering subcutaneously to patients with HCV infection who cannot respond to conventional treatment regimens Clinical Study on Continuous Infusion of Interferon-α
[0160] Background and Principles
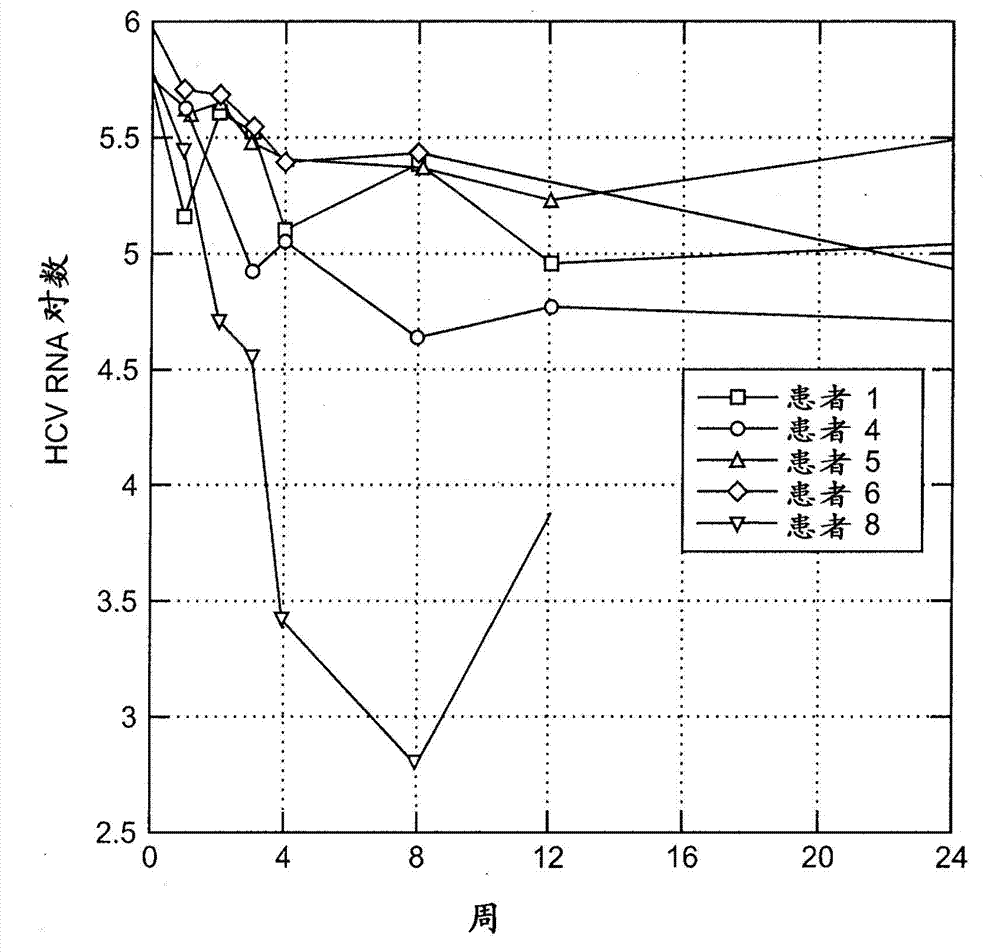
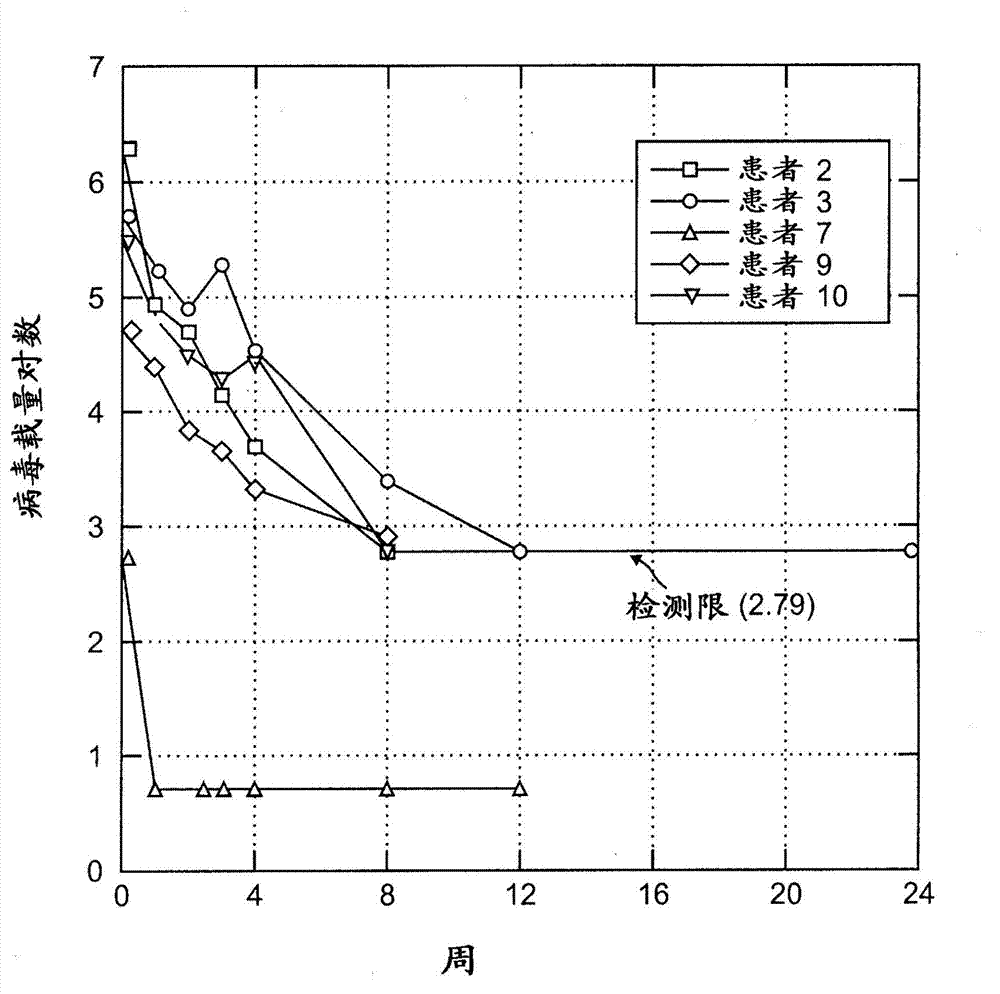
[0161] Treatment of chronic hepatitis C has shown uneven success, with current clinical practice eliminating HCV in only about 50% of infected individuals. As a result, there is a remaining set of factors, such as viral genotype, that may, for example, reduce the response rate in genotype 1 . Optimal treatment of HCV genotype 1 patients with peginterferon-α and ribavirin has resulted in sustained virologic response (SVR) rates between 41-60% (see, e.g., Manns et al. Al Lancet 2001;358:958-965; Fried et al. N Engl J Med 2002;347:975-982; Hadziyannis et al. Ann Intern Med 2004;140:346-355; -257). Improvement of these outcomes, and retreatment of former non-responders, is considered to be the greatest challenge in the field.
[0162] Pegylation of inter...
Embodiment 3
[0357] Example 3: Individualized treatment plan
[0358]In an exemplary embodiment of the invention, a treatment regimen according to the parameters disclosed herein may be tailored to take into account patient-specific factors that may affect the patient's response to treatment, such as the HBV genotype of the infected patient and / or the patient's body weight, Treatment history, health status, individual exogenous interferon-α clearance rate, etc. In an exemplary embodiment of the invention in relation to patient-specific treatment regimens, interferon-alpha is administered to the patient according to a first treatment regimen that strives to generate The average or intermediate circulating levels of interferon-α, the target ranges are, for example, 100-200pg / mL (or 150-250pg / mL), 200-300pg / mL (or 250-350pg / mL), 300-400pg / mL (or 350-450pg / mL), up to 700pg / mL, etc. Pharmacokinetic and / or pharmacodynamic parameters can then be obtained from the patient to observe the patien...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com