Dynamic enabling and disabling of SIMD units in a graphics processor
A processor and dynamic technology, applied in image data processing, data processing power supply, 3D image processing, etc., can solve problems such as low efficiency and increased power consumption of graphics processors, and achieve optimal use and power saving effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
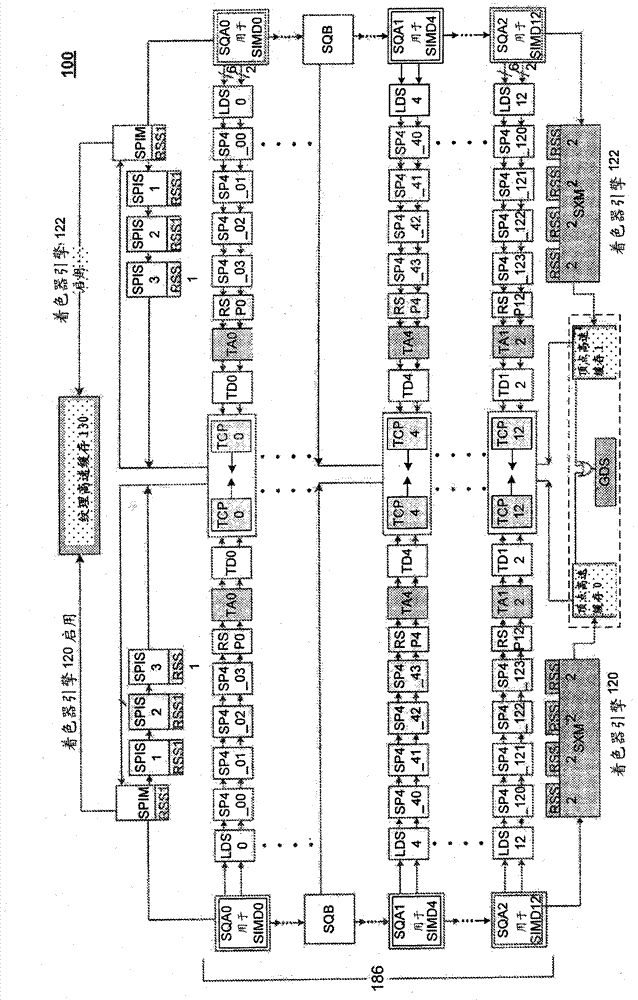
[0030] As discussed above, embodiments of the present invention achieve power savings by dynamically activating and deactivating individual SIMDs in shader compositors.
[0031] Embodiments dynamically disable SIMD for reduced performance needs of graphics processing units or to reduce thermal design power (TDP). Furthermore, embodiments enable disabled SIMD for high performance applications without refreshing the graphics pipeline of the graphics processing unit. This is achieved by dynamically switching several SIMDs without flushing the SP. Dynamic control (or switching) is achieved in part by appropriately programming groups of registers.
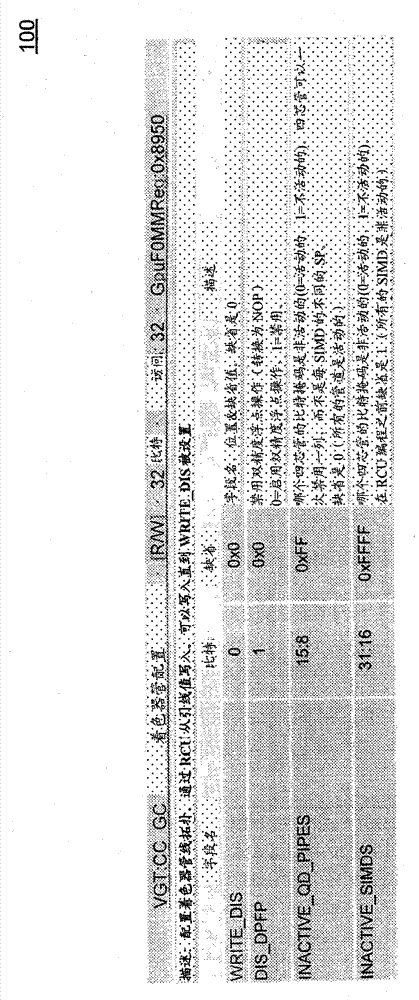
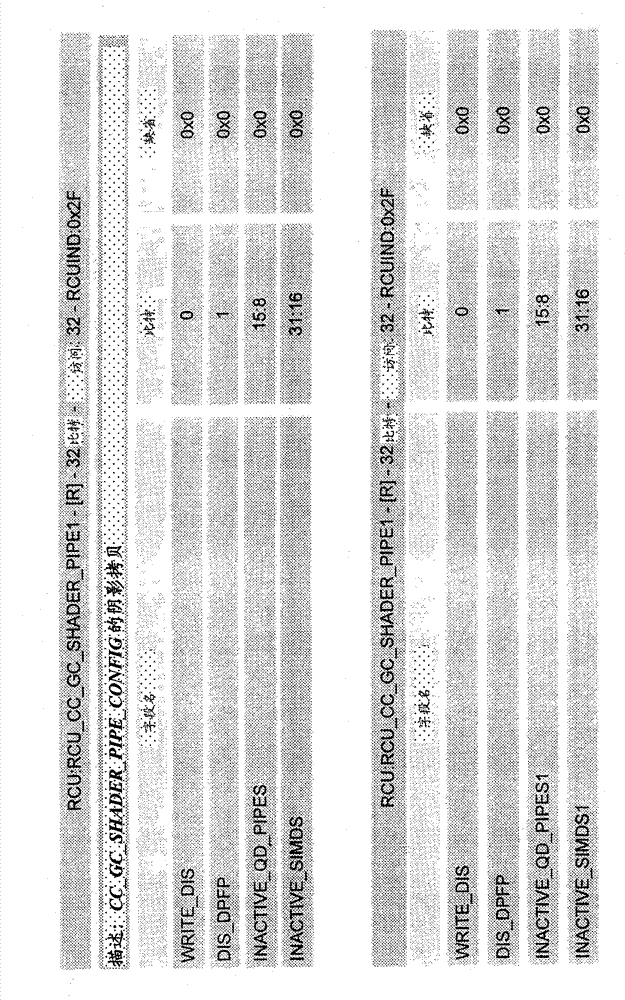
[0032] In an embodiment, a Shader Pipe Interposer (SPI) allocates new work (or threads) according to registers configured to dynamically indicate which SIMDs are activated. In one embodiment, this dynamic configuration takes effect after currently outstanding requests (or pending requests) are serviced by a disabled SIMD. Once disabl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com