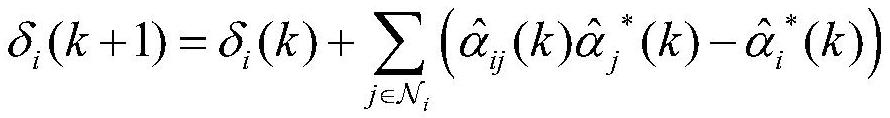Patents
Literature
72 results about "Logical clock" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
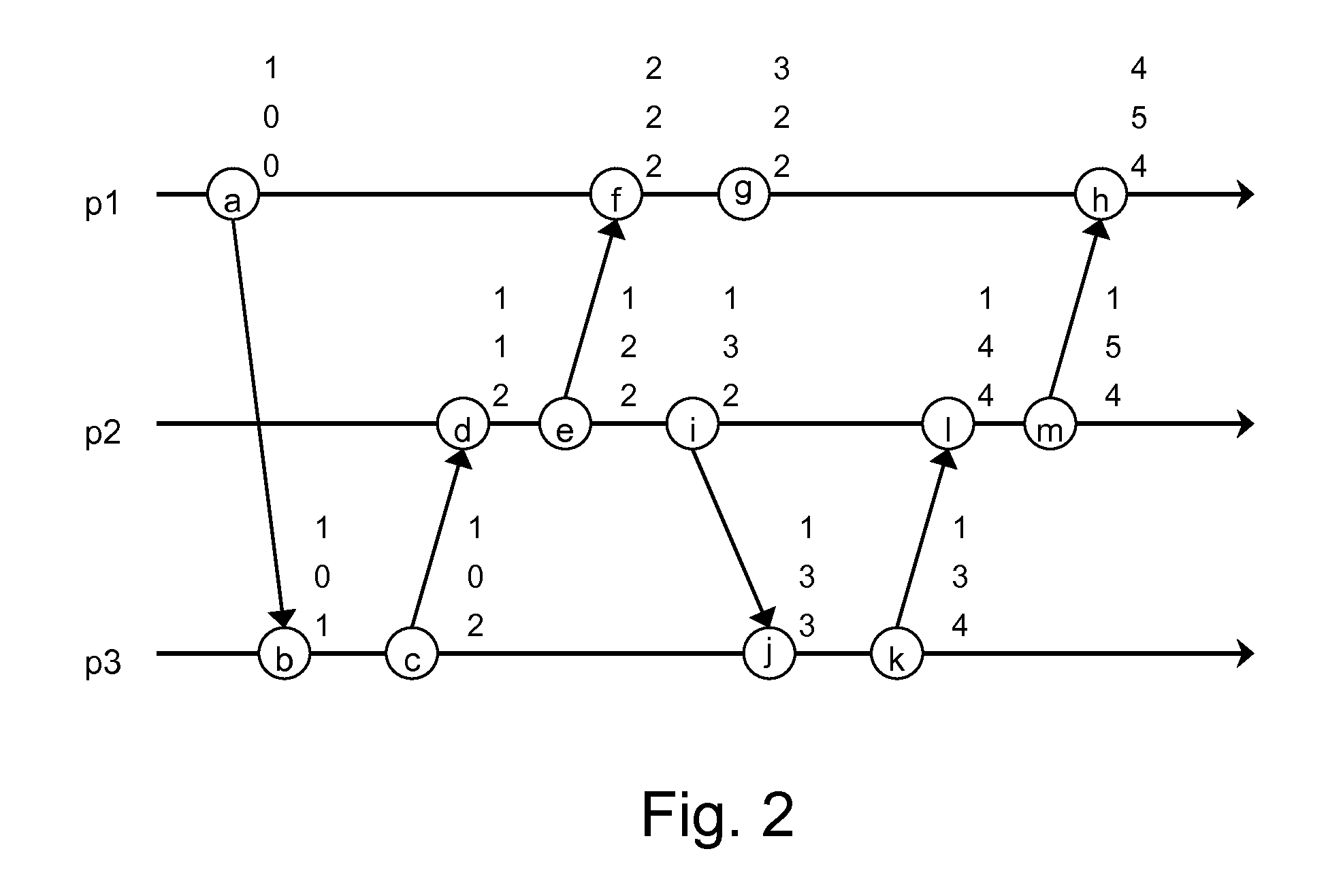
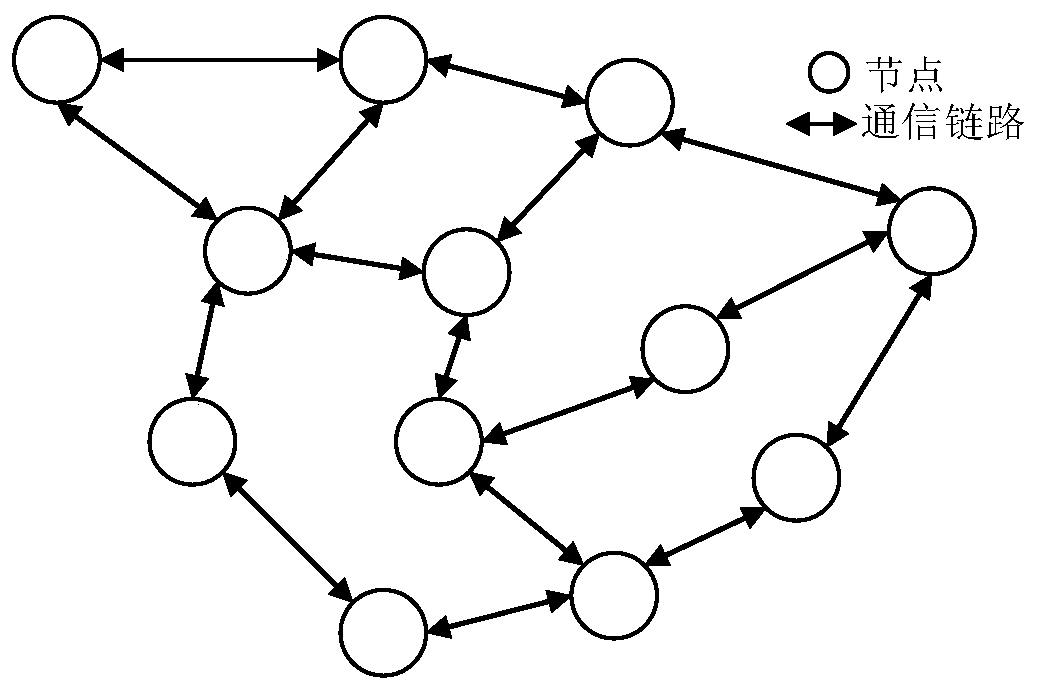
A logical clock is a mechanism for capturing chronological and causal relationships in a distributed system. Distributed systems may have no physically synchronous global clock, so a logical clock allows global ordering on events from different processes in such systems. The first implementation, the Lamport timestamps, was proposed by Leslie Lamport in 1978 (Turing Award in 2013).
Techniques for a linearizable primary-secondary database system that replicates database data with eventual consistency
ActiveUS20190197173A1Input/output to record carriersDatabase distribution/replicationLogical clockDatabase
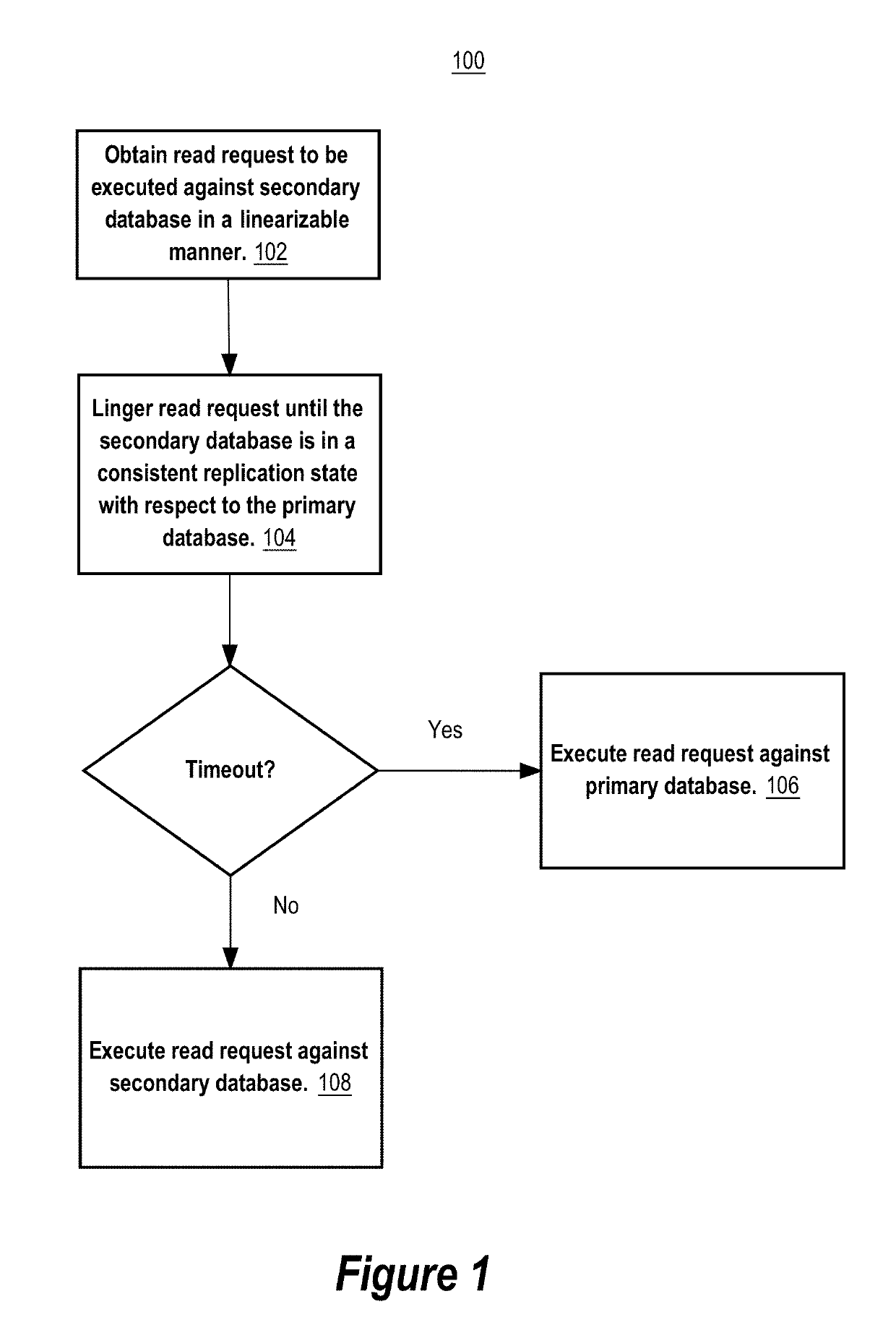
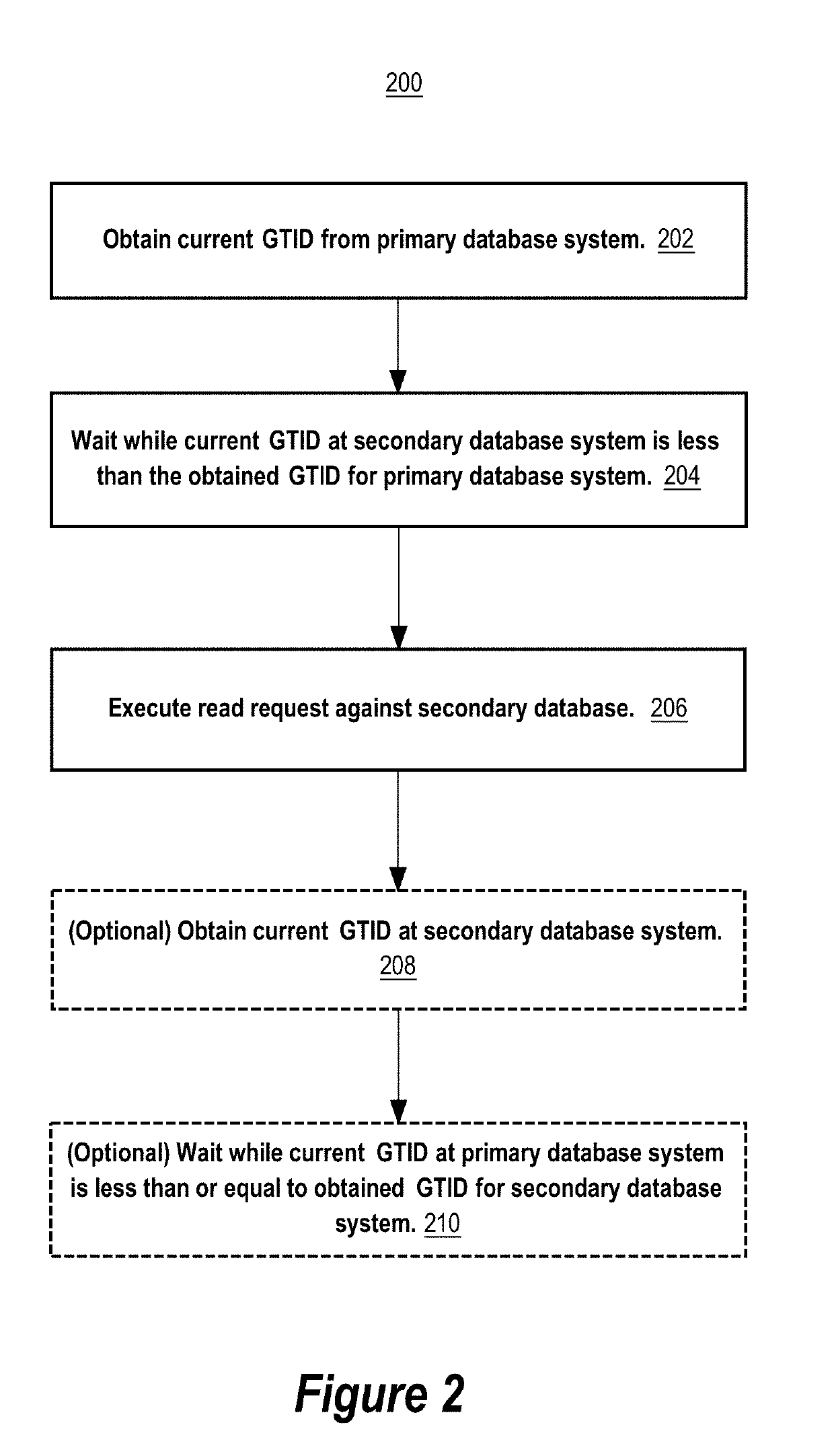
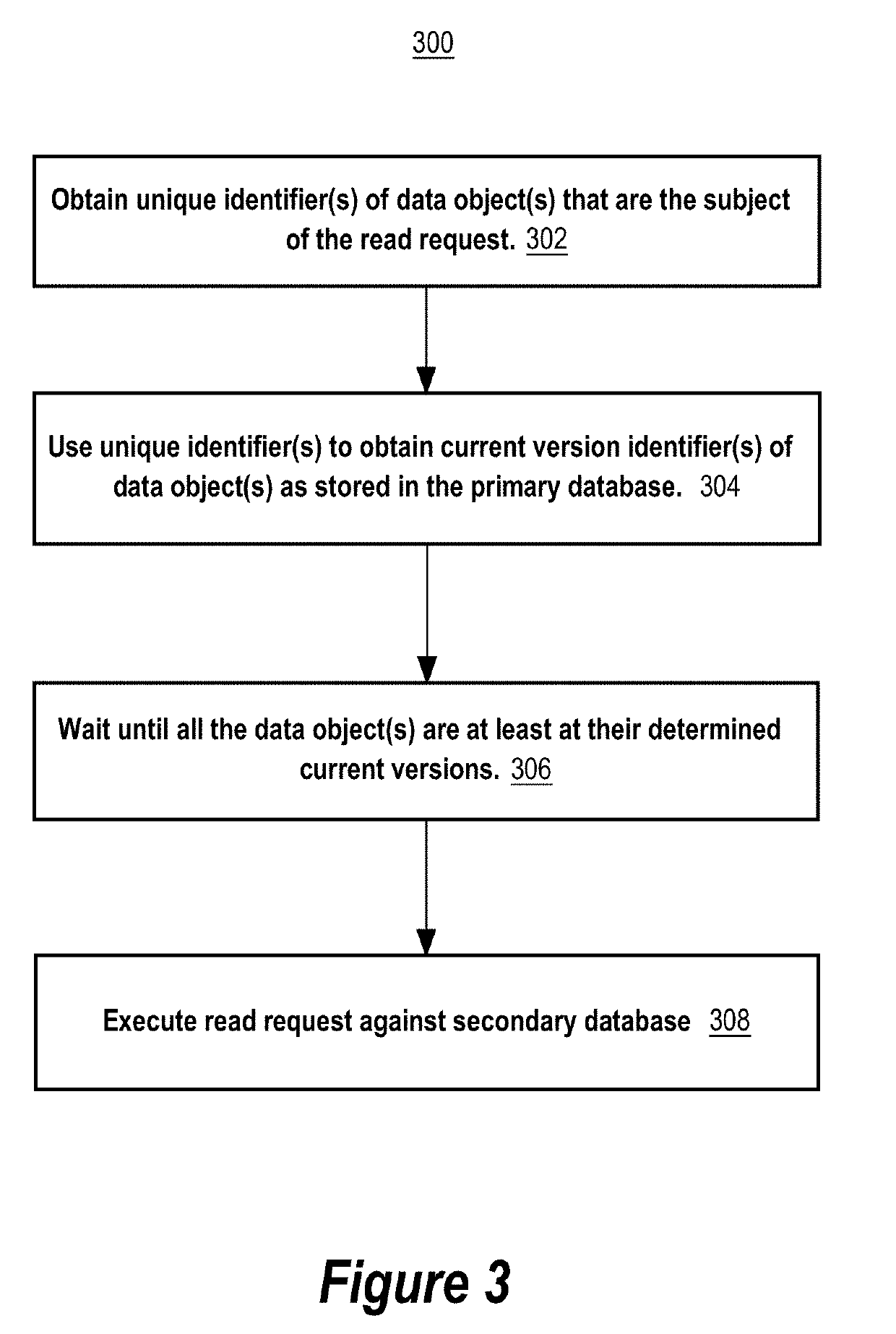
Techniques are provided for a linearizable primary-secondary database system that replicates database data with eventual consistency. The techniques include obtaining a logical clock value of a logical clock that orders transactions committed at a primary database system that includes a primary database. The logical clock value is obtained after a write transaction is committed at the primary database system and while processing a read request. The logical clock value is used to determine whether a secondary database is in a consistent replication state corresponding to the logical clock value with respect to the primary database. The read request is maintained in a linger state while the secondary database is not yet in the consistent replication state. The read request exits the linger state and is allowed to be processed against the secondary database after the secondary database has reached the consistent replication state.
Owner:DROPBOX
Transaction processing method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN111338766AImprove single point bottleneck problemImprove scalabilityDatabase distribution/replicationRedundant operation error correctionSoftware engineeringLogical clock
The invention discloses a transaction processing method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium, and belongs to the technical field of databases. The method comprises the steps of obtaining state information of a target transaction in response to an execution request of the target transaction, verifying a logic life cycle determined based on the state information, executing the targettransaction in response to successful verification of the logic life cycle, and submitting the target transaction in response to successful conflict verification of the target transaction. According to the invention, the transaction processing process does not depend on a certain global logic clock, but depends on the verification of the logic life cycle; the logic life cycle can be adjusted according to a conflict detection result in a transaction execution and verification process; the transaction processing process can be completed by verifying the logic life cycle, so that the single-pointbottleneck problem of the database system is improved, the expansibility of the database system is improved, and the system performance cannot be reduced along with the expansion of the database system.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Secure logical vector clocks
ActiveUS20100091984A1Improve security levelImprove distributionKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationCommunication unitLogical clock
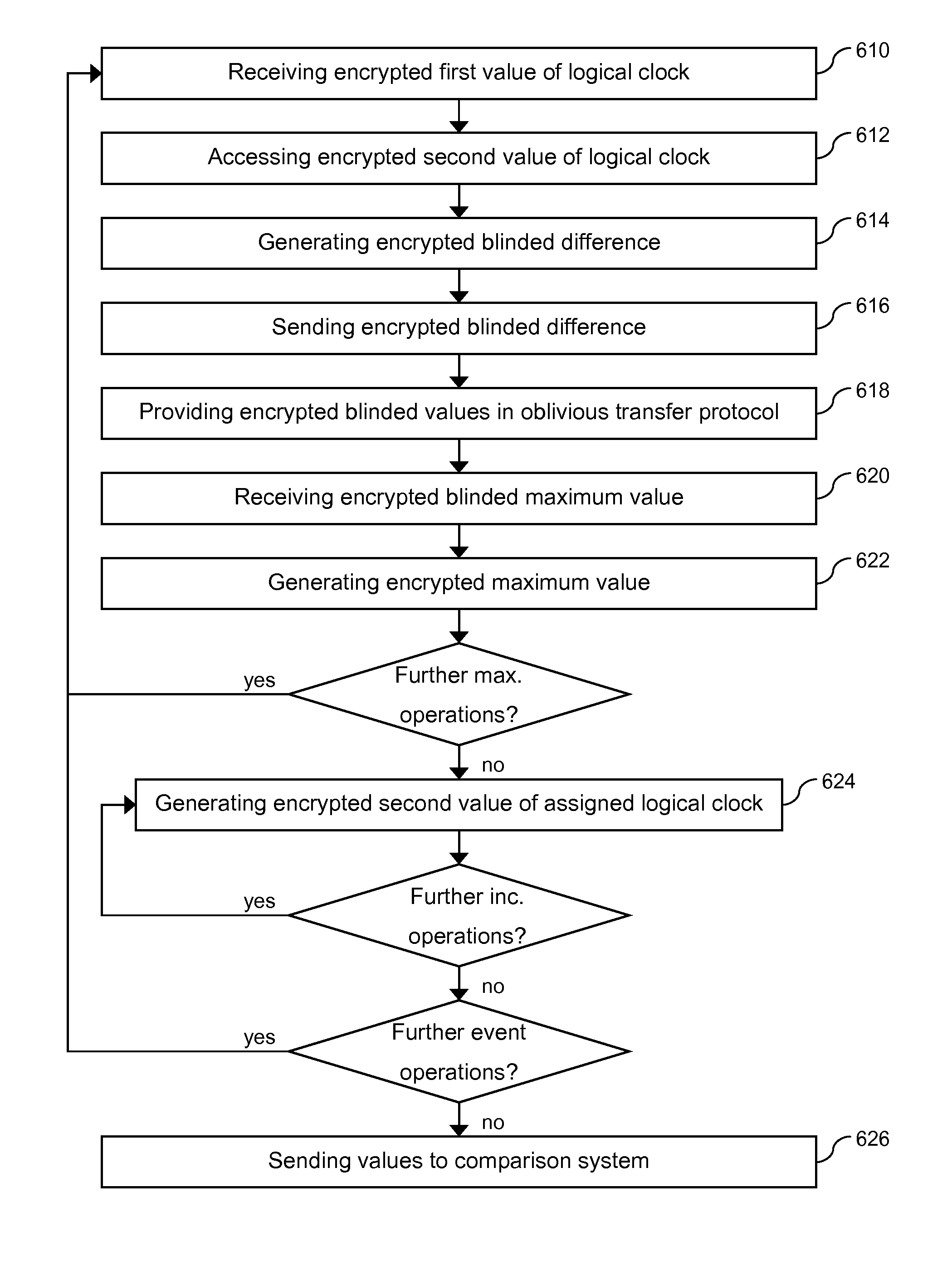
Embodiments include a system for processing logical clock values according to a secure maximum operation. The system may include a communication unit and a processing unit. The communication unit may be configured to receive an encrypted first value of a logical clock, send an encrypted blinded difference, receive an encrypted blinded maximum value, and receive a maximum value. The processing unit may be configured to access an encrypted second value of the logical clock, generate the encrypted blinded difference between the first value and the second value, provide an encrypted blinded first value and an encrypted blinded second value in an oblivious transfer protocol, and generate an encrypted maximum value from the encrypted blinded maximum value.
Owner:SAP AG
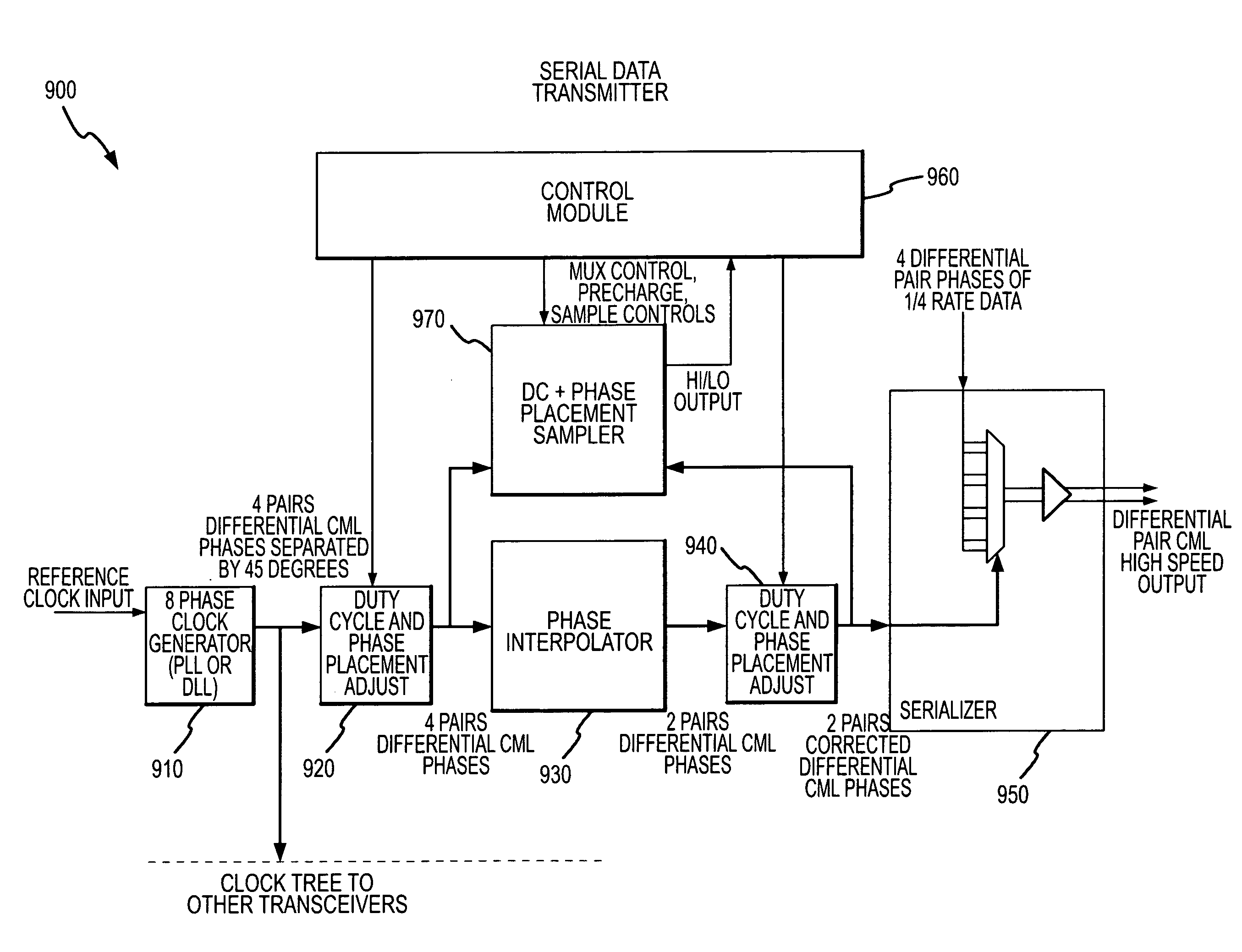
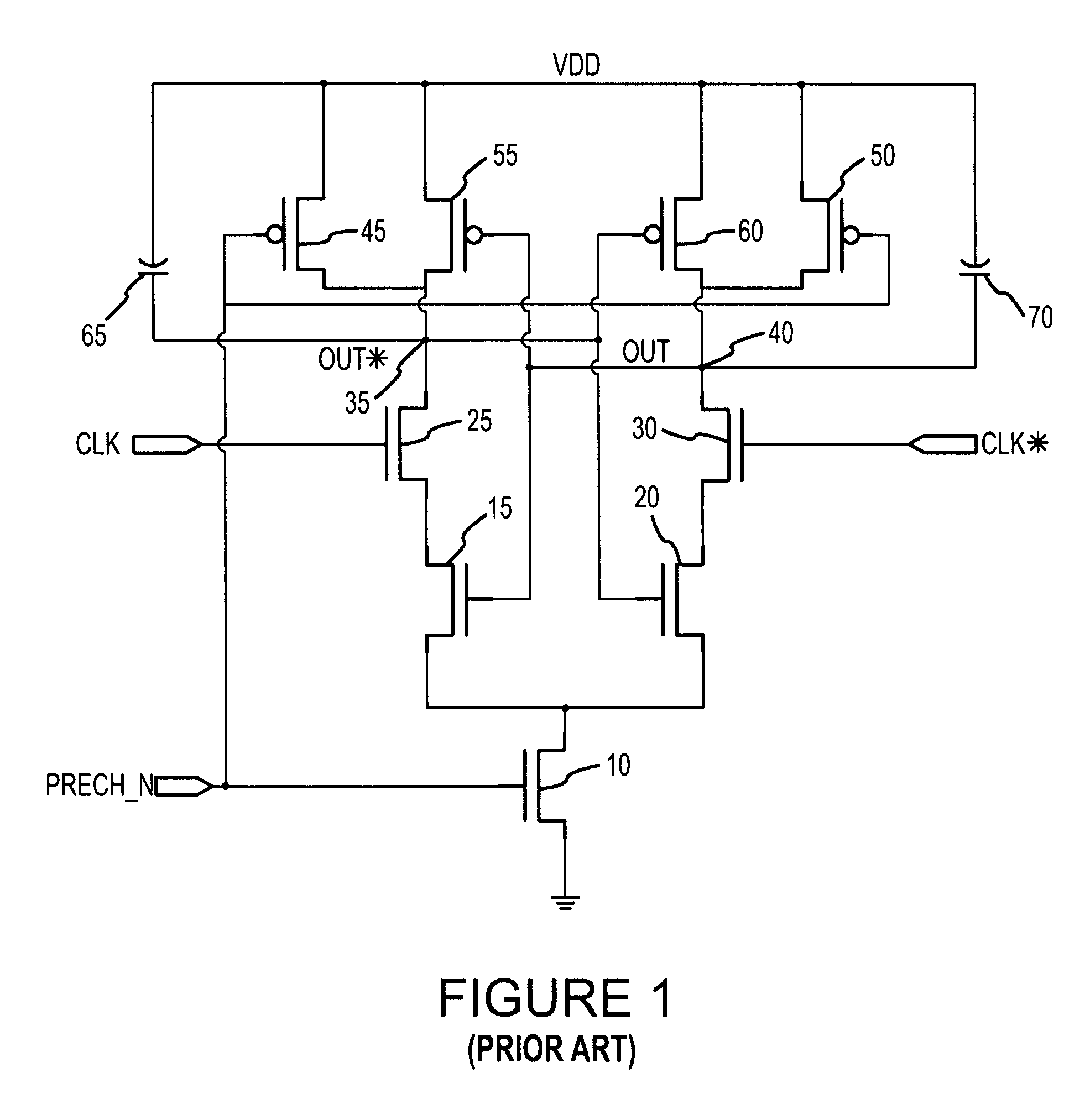
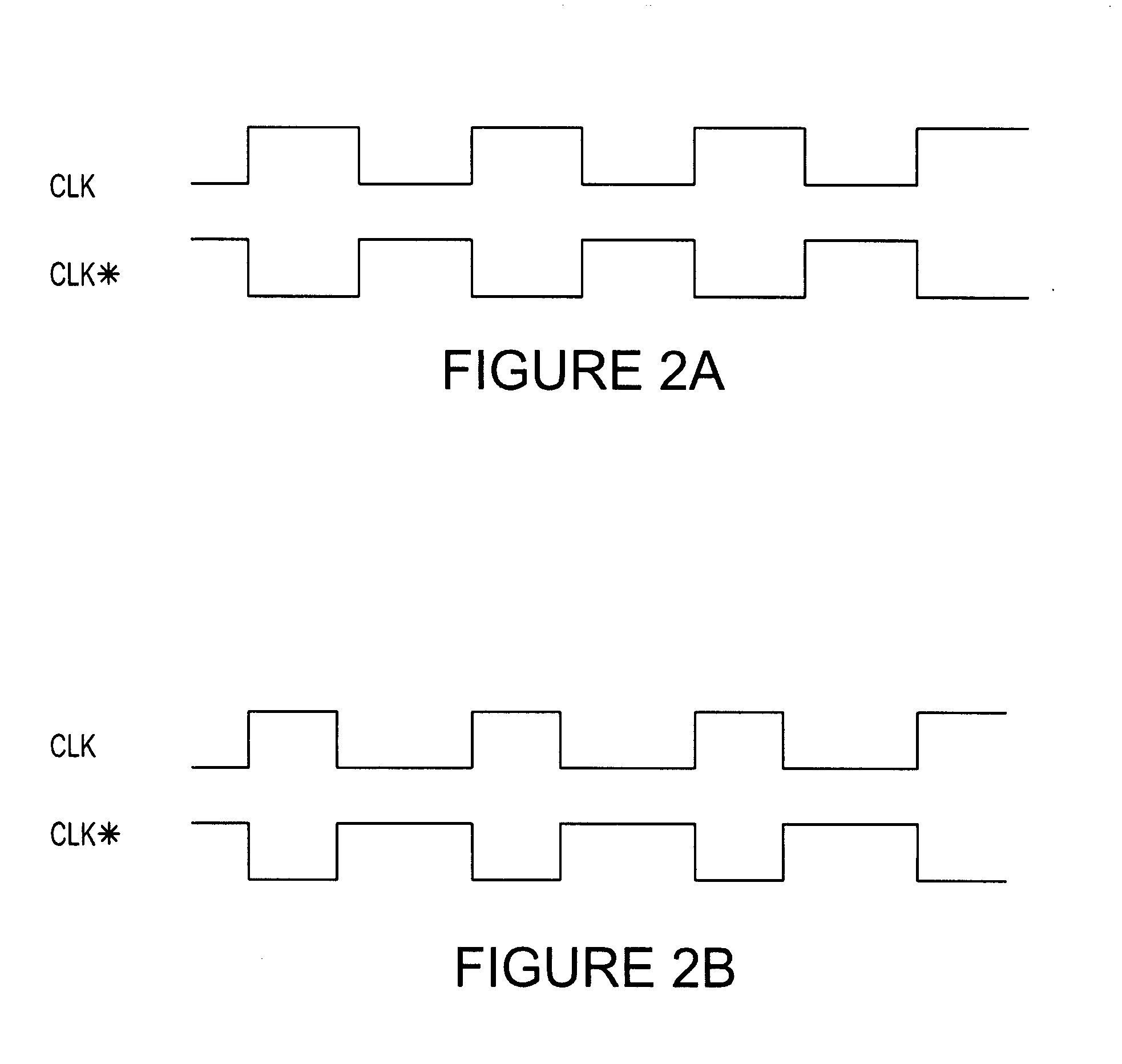
High accuracy current mode duty cycle and phase placement sampling circuit
A duty cycle and phase placement sampling circuit that can be used for high accuracy sampling and correcting the duty cycle and placement of differential clock signals is provided. The duty cycle and phase placement sampling circuit includes dual differential input stages and re-timed precharge signals that allow for high accuracy sampling of common mode logic clock phases.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Clock synchronous circuit
ActiveCN101867376AEffective balanceMake up for lack of balanceParallel/series conversionPulse manipulationShift registerCMOS
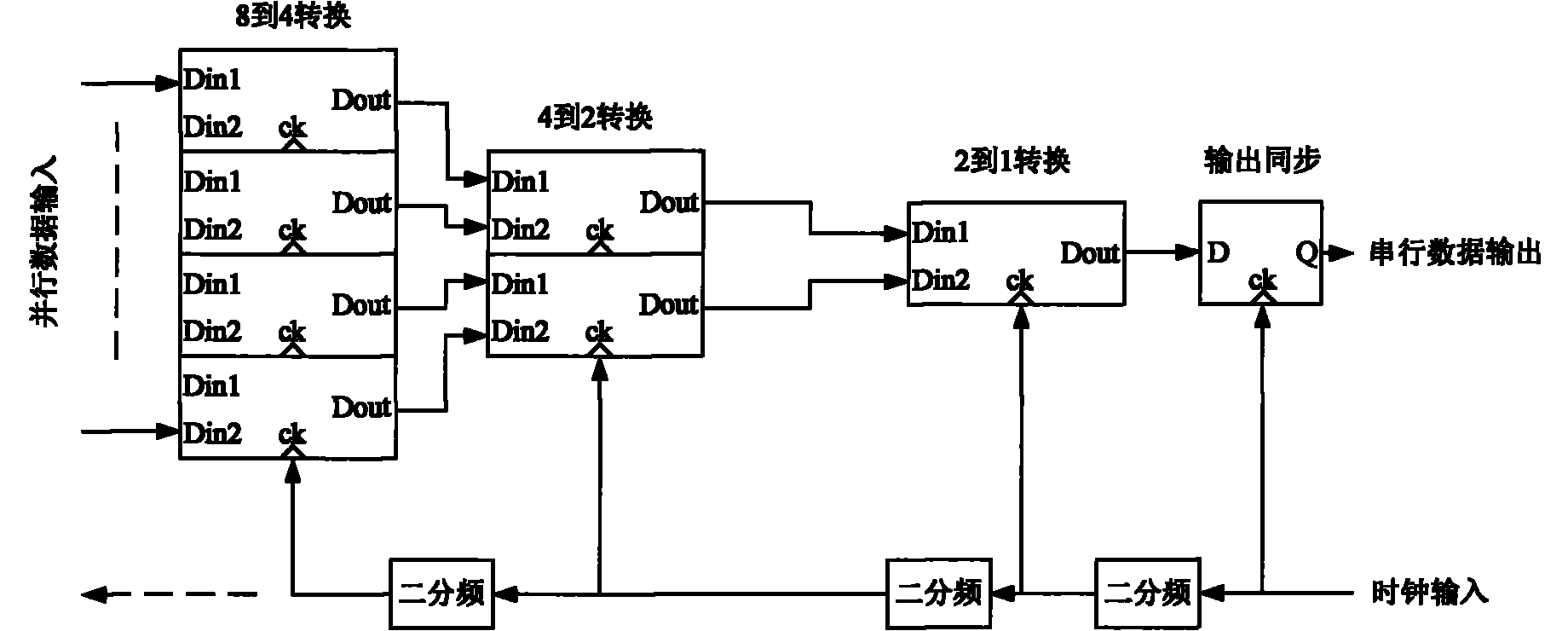
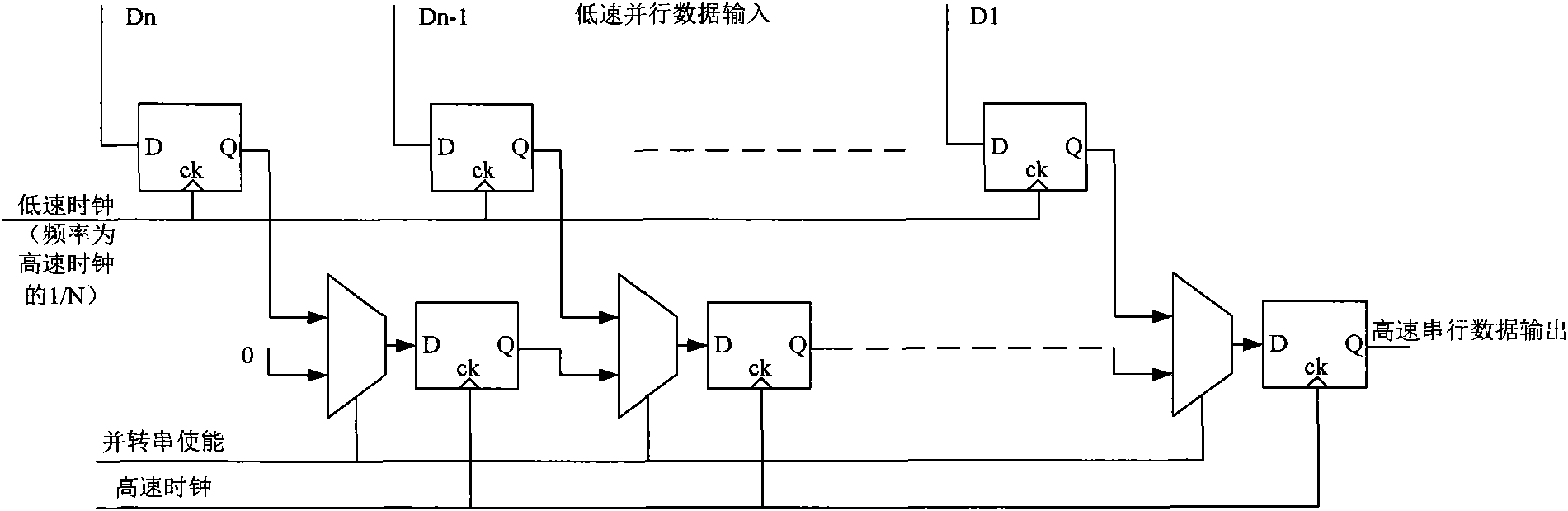
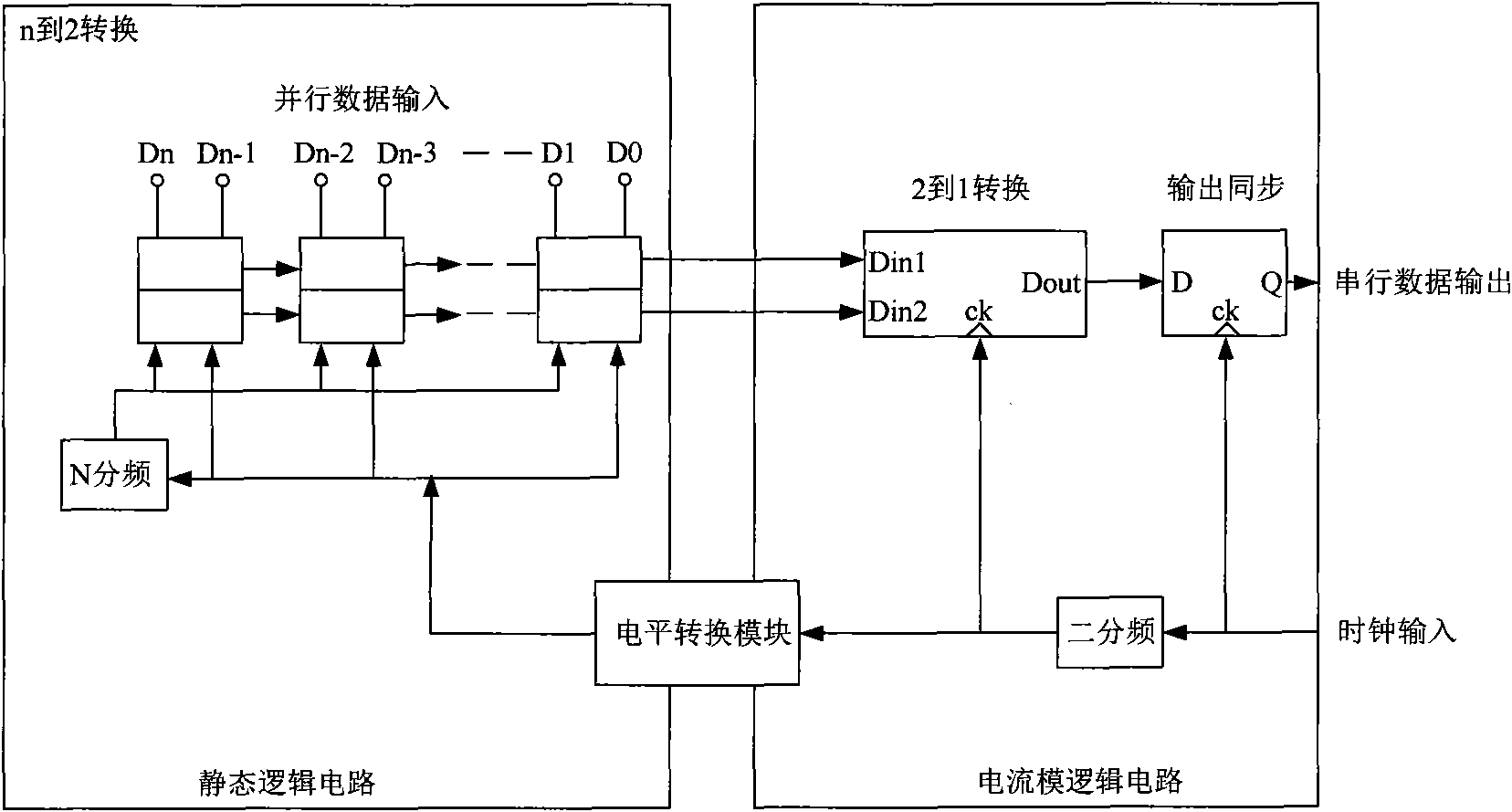
The invention discloses a clock synchronous circuit applied in a high-speed parallel data serialization system, which comprises a delay chain module, a delay chain control module, a sampling module and a level conversion module. The modules form a controllable delay chain circuit in a high-speed parallel data serialization system with the combination of a tree-structure parallel and serial conversion circuit and a shifting register parallel and serial conversion circuit, and the synchronization of two different level clocks is achieved via the delay on CMOS Logical clock level. Compared with the prior art, the delay is controllable, and the power consumption of the system is greatly saved.
Owner:BRITE SEMICON SHANGHAI CORP
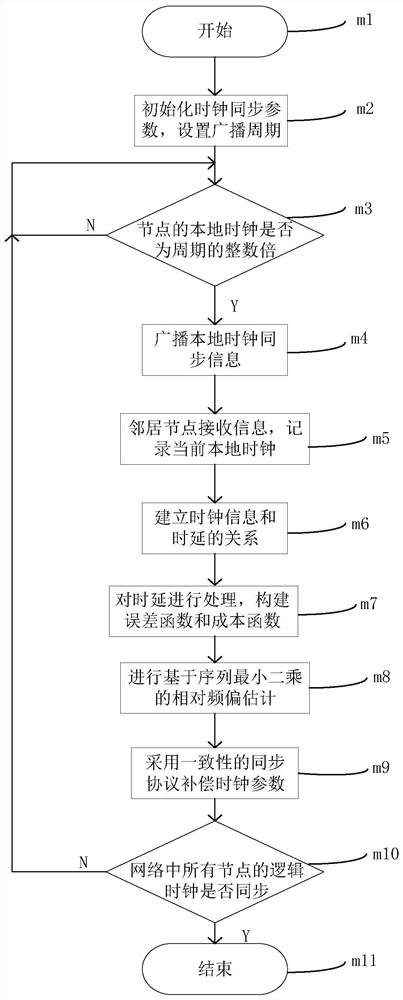
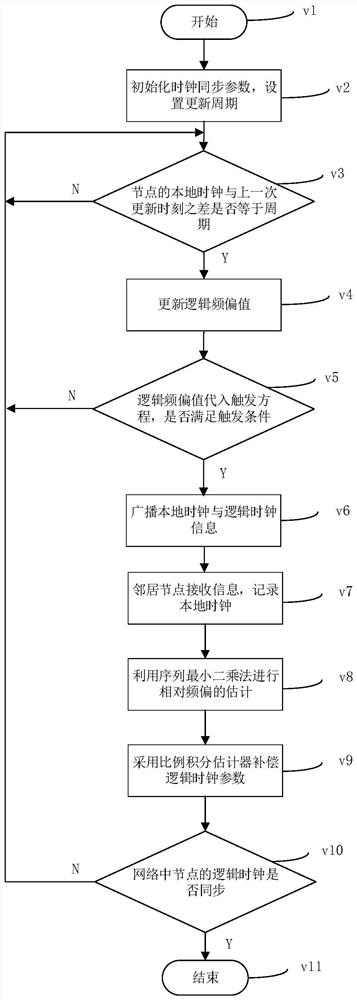
Frequency offset estimation method for average consistency clock synchronization
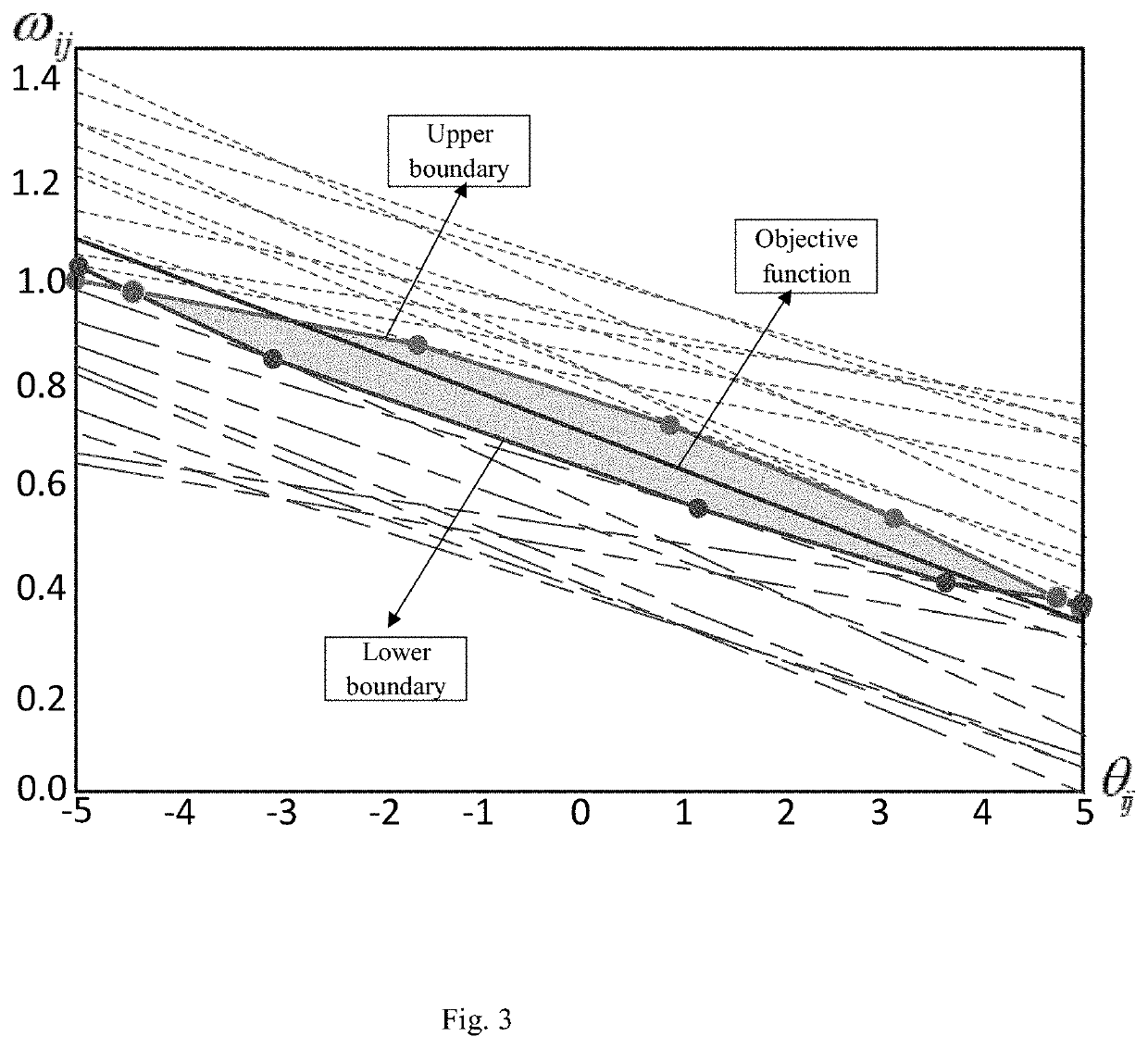
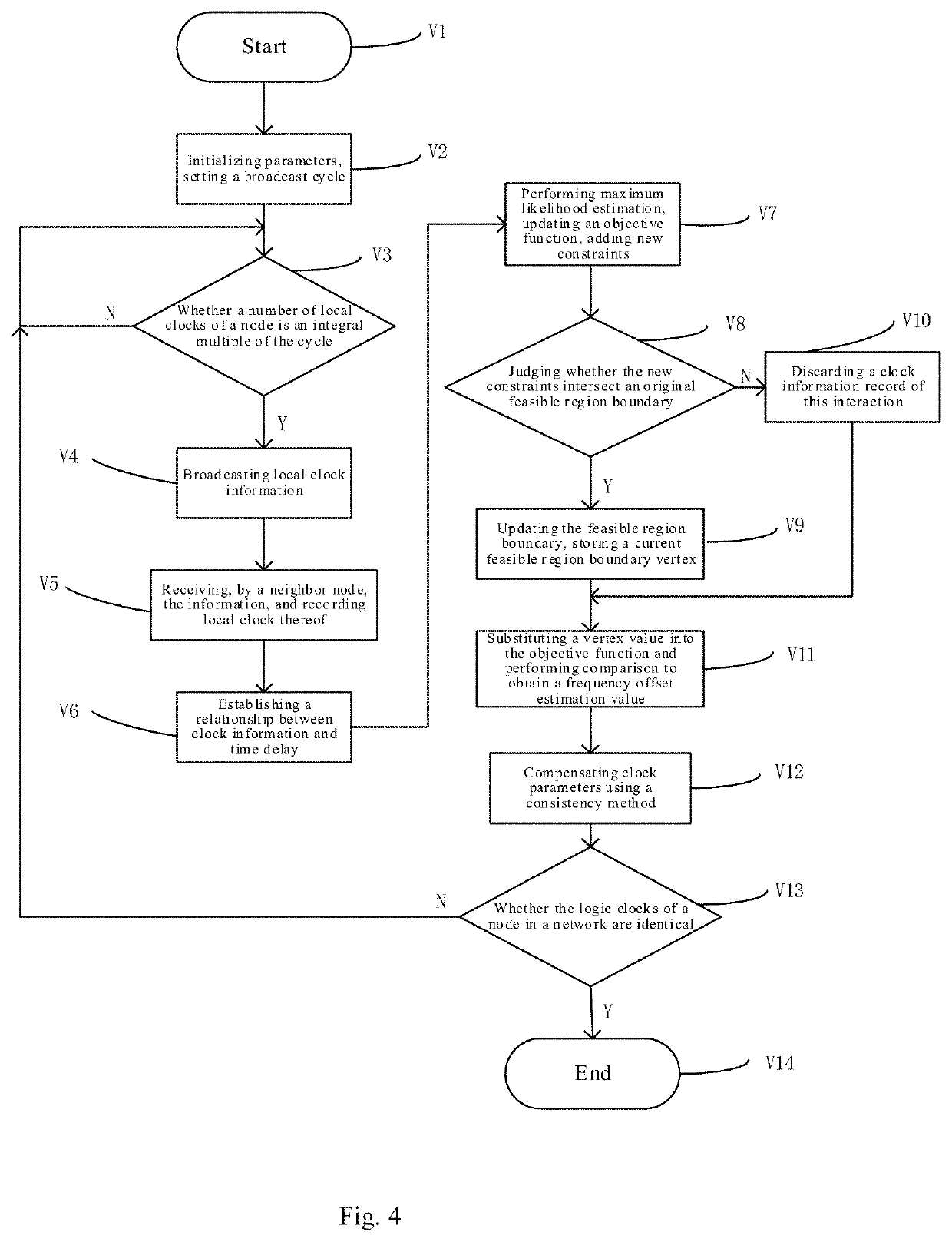
ActiveCN110505683AAccurate frequency offsetImprove coherent clock synchronization performanceSynchronisation arrangementCarrier regulationEstimation methodsWireless sensor networking
The invention relates to a frequency offset estimation method for average consistency clock synchronization, and belongs to the technical field of wireless sensor networks. According to the method, solving of maximum likelihood estimation is converted into a linear optimization problem in combination with distributed one-way broadcast characteristics, and a relative frequency offset estimation value is obtained by adopting an iterative method. By applying the estimated value to inter-node logic clock parameter compensation, the effect of keeping logic clocks of network nodes consistent can beachieved. According to the method, the distribution characteristics of the communication time delay are fully considered, accurate relative frequency offset estimation can be realized, so that the synchronization precision of average consistency clock synchronization is effectively improved, the maximum likelihood estimation solution is carried out by adopting an iterative method, the estimation algorithm is simplified, and the storage overhead is reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Glitch-free clock switcher
InactiveUS20080012605A1No short cycling outputReduce power consumptionElectronic switchingGenerating/distributing signalsState variableLogical clock
A glitch-free, clock switching circuit in which an asynchronous, sequential logic circuit has as inputs a clock select signal and a pair of clock signals. A plurality of operating state variable signals are generated in the sequential logic circuit in response to transitions in the input signal. A combinational logic clock output circuit is responsive to the input clock signals and predetermined ones of the operating state variable signals for outputting a newly selected clock signal only when said predetermined operating state variable signals indicate the sensing of a falling edge of the currently outputted clock signal followed by a falling edge of the newly selected clock signal.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Method to prevent firmware defects from disturbing logic clocks to improve system reliability
InactiveUS7568138B2Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionData processing systemLogical clock
A computer implemented method and data processing system are provided for preventing firmware defects from disrupting logic clocks. In response to a firmware interface requesting a scan operation for a functional unit, protection logic allows a scan enable to activate to the functional unit only if the logic clocks are stopped to that functional unit, otherwise the scan enable is not activated, an error is indicated, and an interrupt is presented to firmware. Also, in response to a command from a firmware interface to stop the logic clocks to a functional unit, protection logic allows the clocks to be stopped to the functional unit only if the functional unit is already indicating a catastrophic error, otherwise the clocks are not stopped, an error is indicated, and an interrupt is presented to firmware.
Owner:IBM CORP
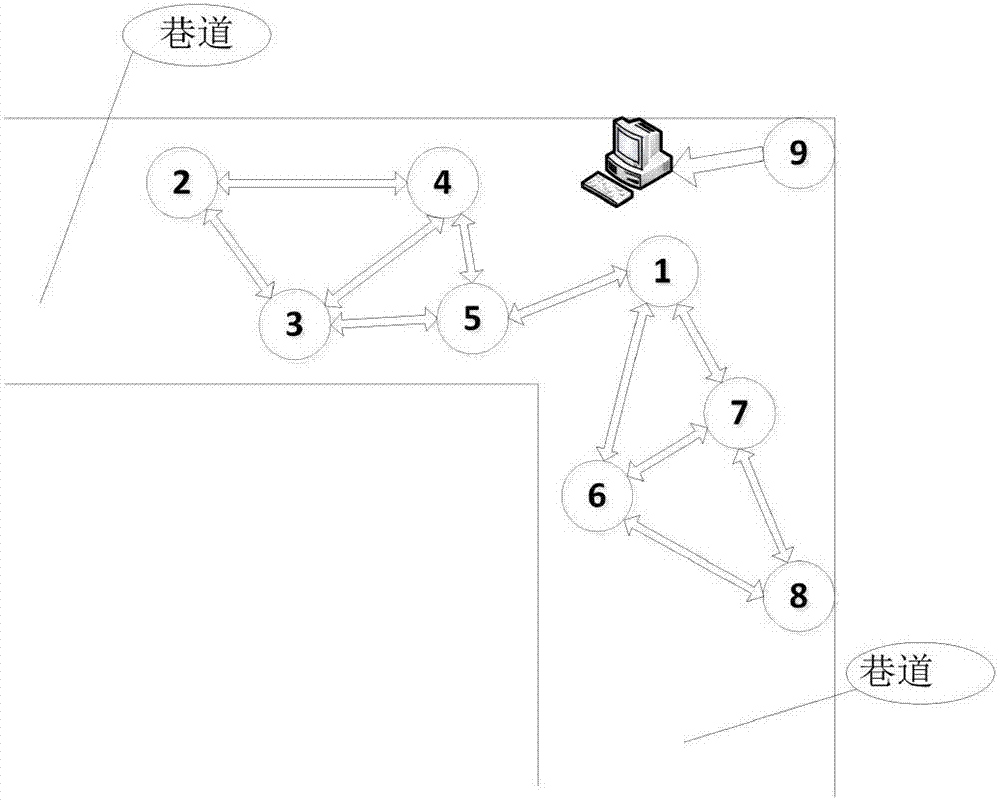
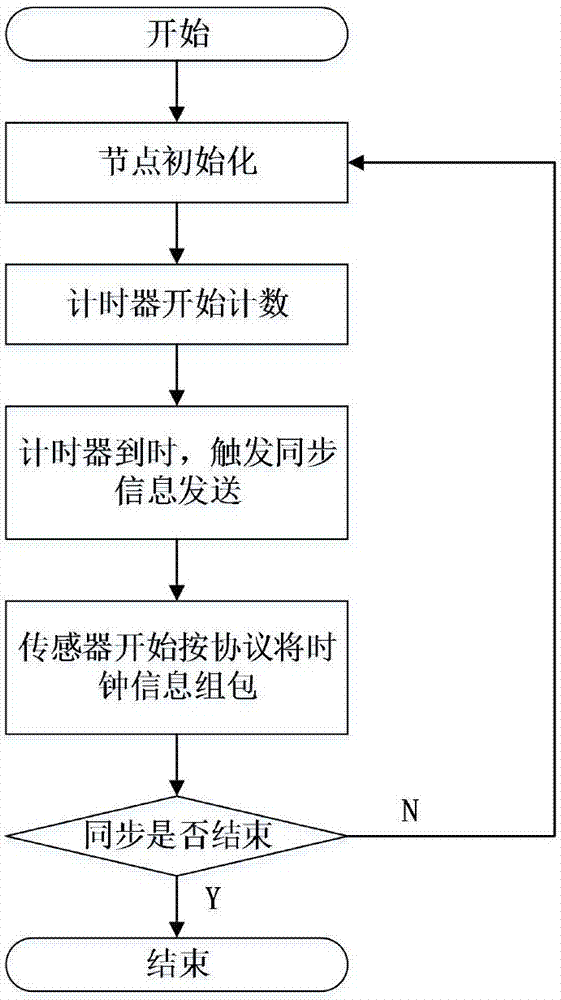
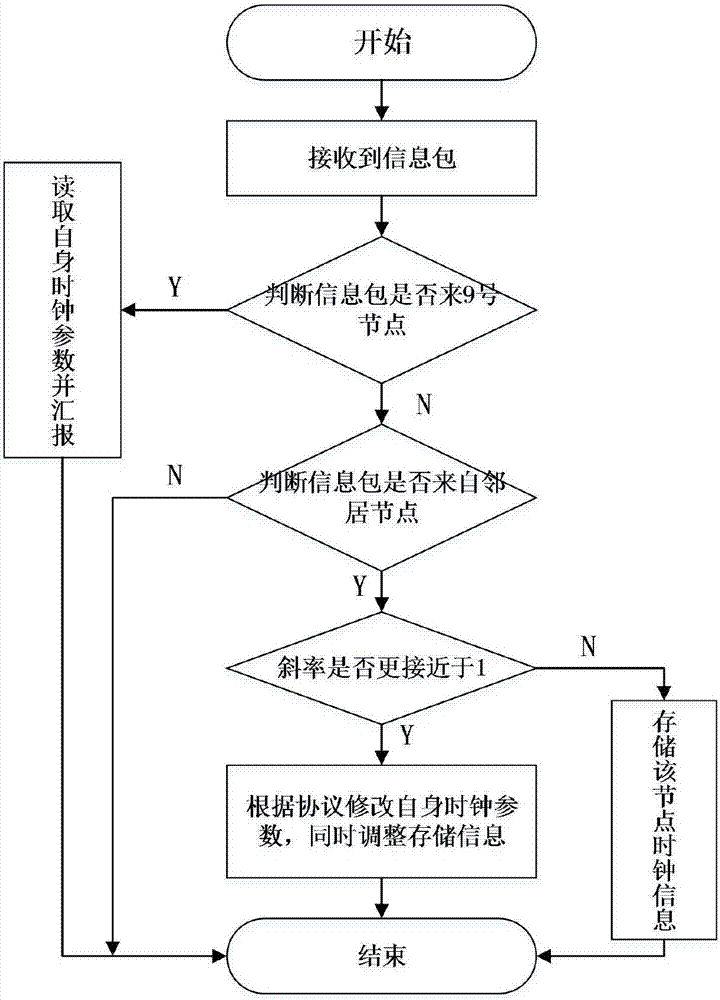
Time synchronization method of distributed mine seismic monitoring system
ActiveCN107147464AImprove robustnessSimplified Time Synchronization AlgorithmTime-division multiplexMonitoring systemLogical clock
The invention discloses a time synchronization method of a distributed mine seismic monitoring system, relating to a time synchronization method. Two time synchronization algorithms are designed for nodes in clusters and cluster head nodes of the clusters and refer to an intra-cluster slope consistency time synchronization algorithm and an inter-cluster simplified clock phase offset frequency offset joint estimation algorithm. First, nodes in the clusters synchronize clocks of all nodes to a unified virtual logic clock of the whole network through an STS synchronization algorithm, and then the cluster head nodes and anchor nodes are synchronized through an SJMLE algorithm, so that a synchronous operation between cluster head nodes is realized indirectly. A hardware platform experiment and simulation analysis are performed on the intra-cluster time synchronization algorithm and the inter-cluster time synchronization algorithm, and experiment and simulation results verify the effectiveness of the algorithms and prove that the synchronization algorithms have high robustness, expandability and high synchronization accuracy. The method fully combines advantages of the distributed time synchronization algorithm and the structural time synchronization algorithm, and can adapt to a special environment in which the mine seismic monitoring system is.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
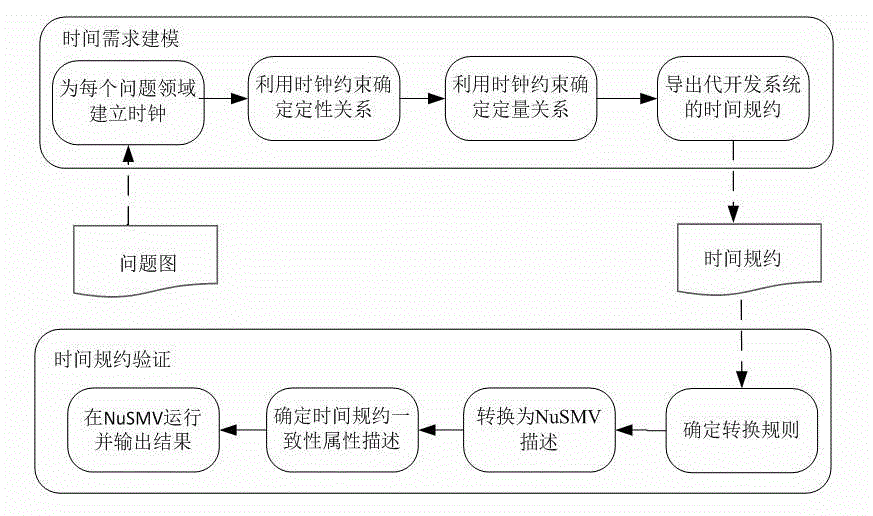
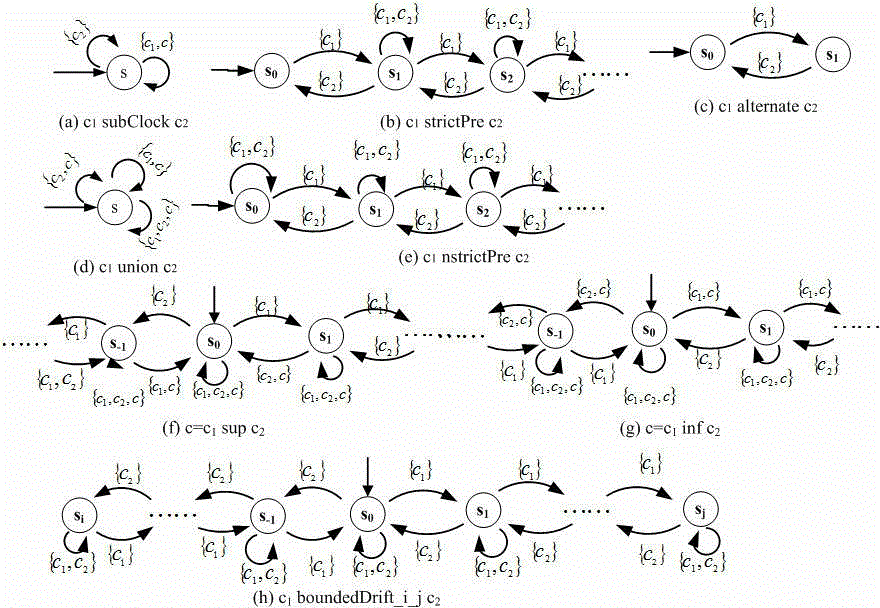
Time requirement modeling and verification method based on problem frame method
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
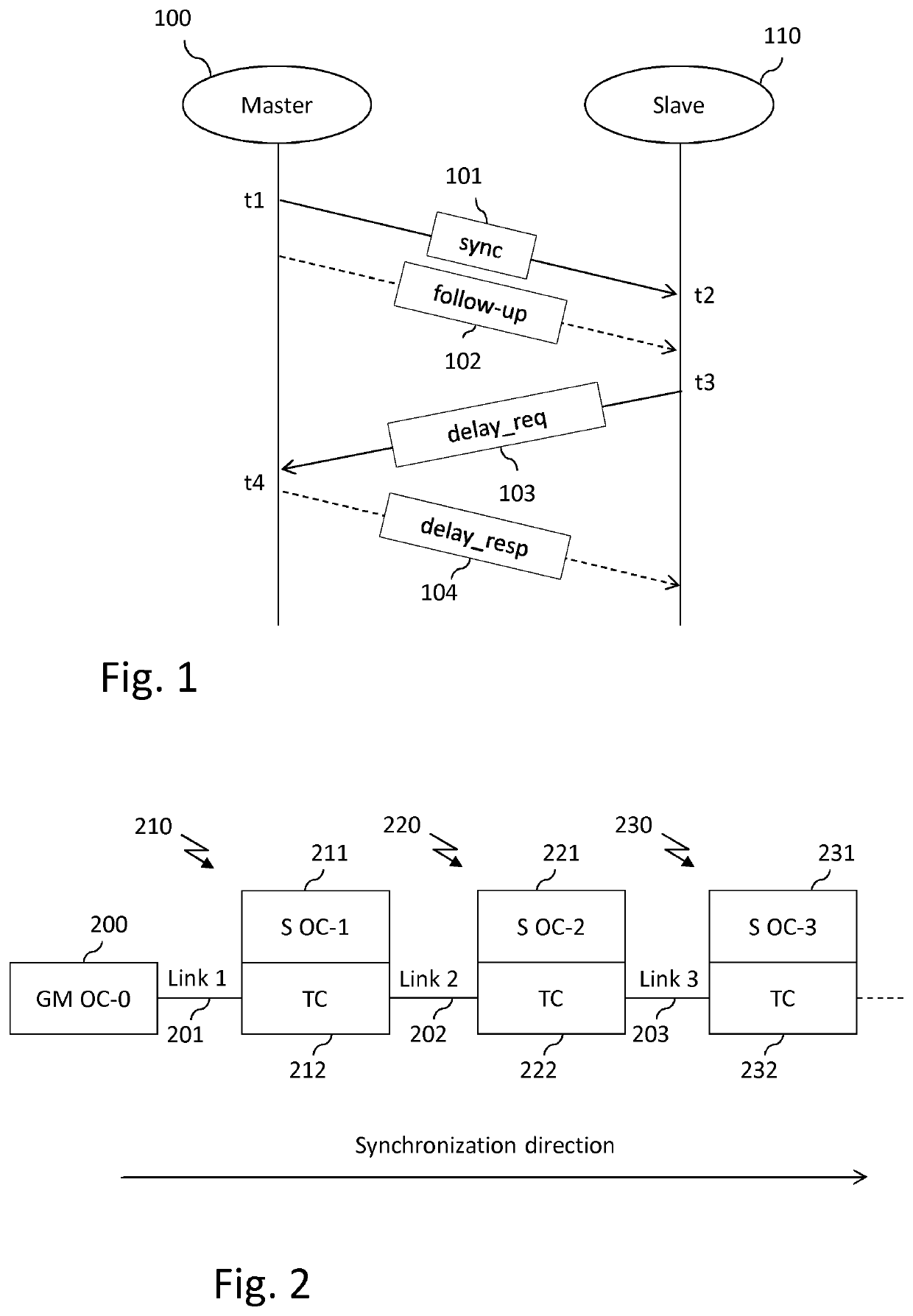
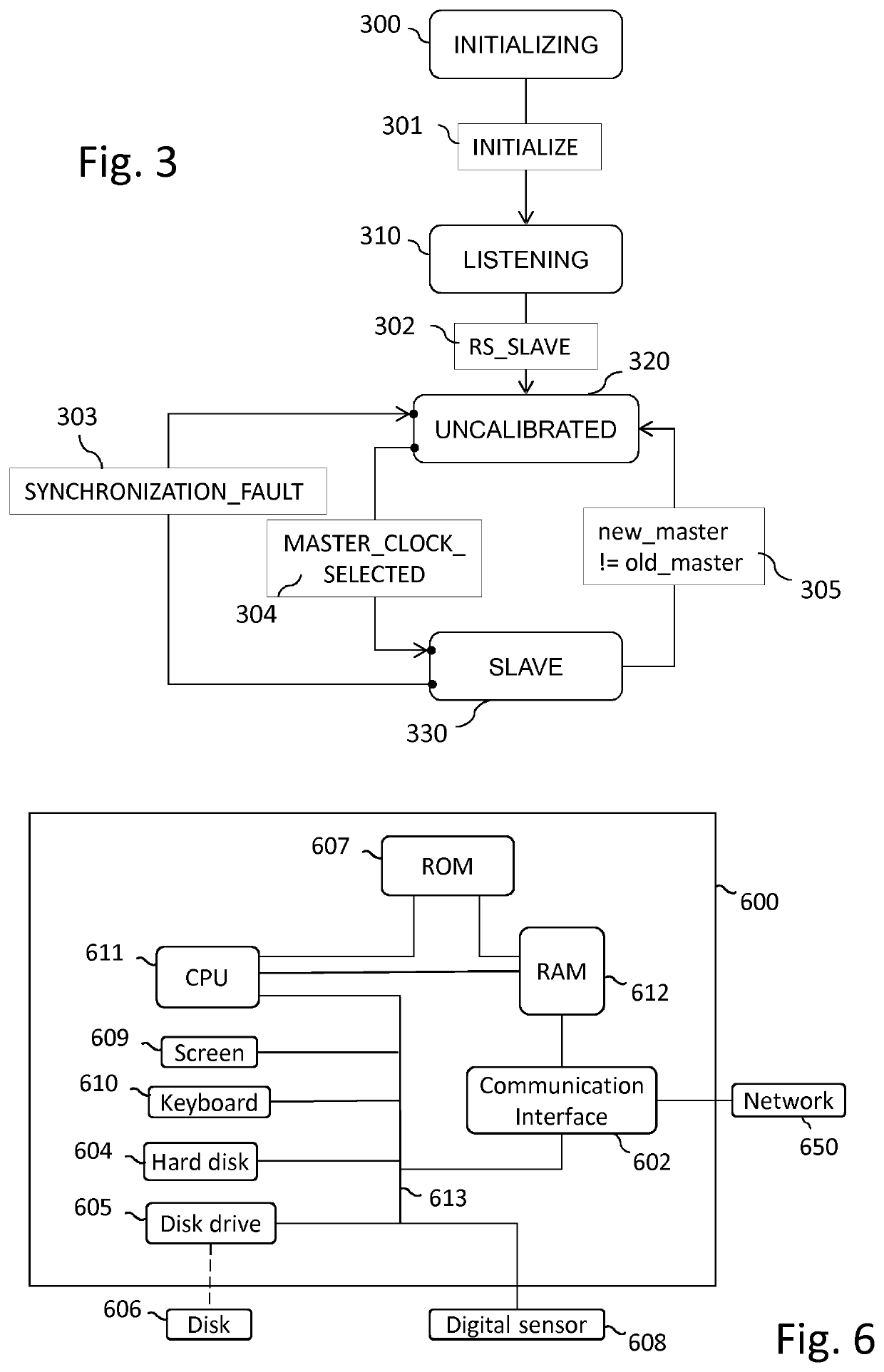
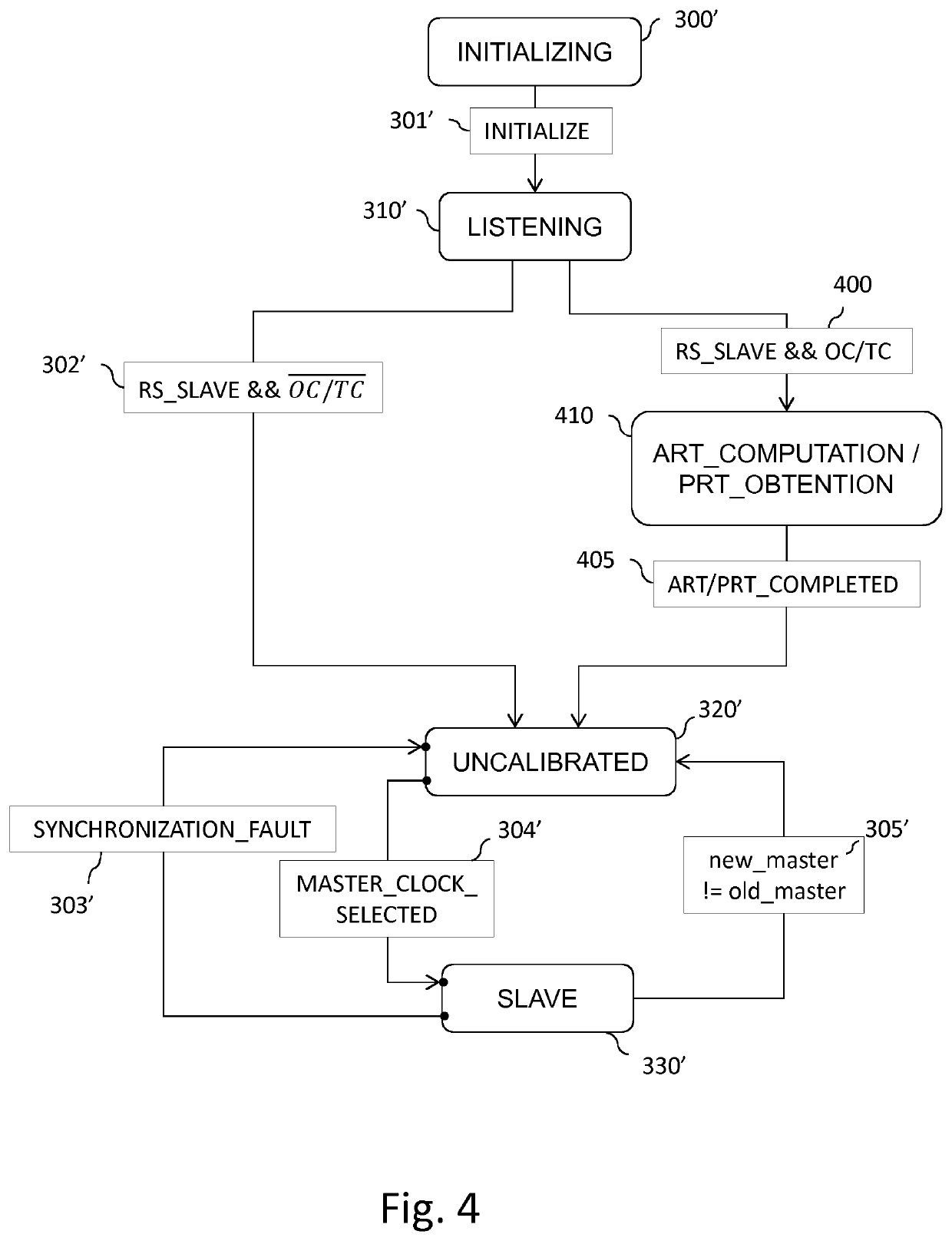
Method, device, and computer program for improving synchronization of clocks in devices linked according to a daisy-chain topology
ActiveUS20210288736A1Optimize synchronization of clockImprove accuracyTime-division multiplexClock timeDaisy chain
At least one embodiment of a method for synchronizing a logical clock in a device comprising a physical clock, an input port, and an output port, the device further comprising a logical clock and a time compensation clock sharing the physical clock, the time compensation clock making it possible to determine a residence time, comprises:obtaining a theoretical residence time;during a pre-synchronization phase according to which the logical clock is not synchronized, adding a value representative of the obtained theoretical residence time to a residence time value stored in a synchronization message to be forwarded,during a synchronization phase according to which the logical clock is synchronized, obtaining a residence time and adding a value representative of the obtained residence time to a residence time value stored in a synchronization message to be forwarded, andsynchronizing the logical clock as a function of a residence time value stored in a received synchronization message.
Owner:CANON KK
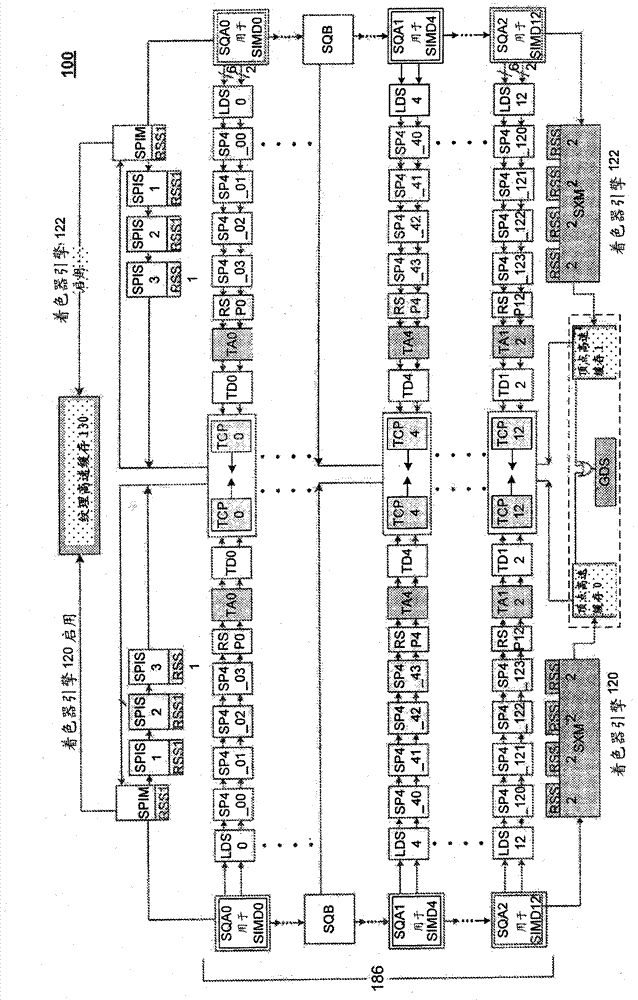
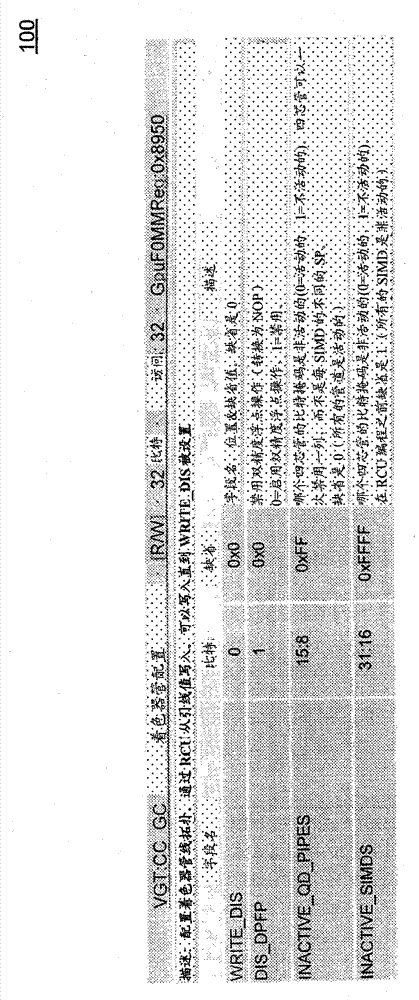
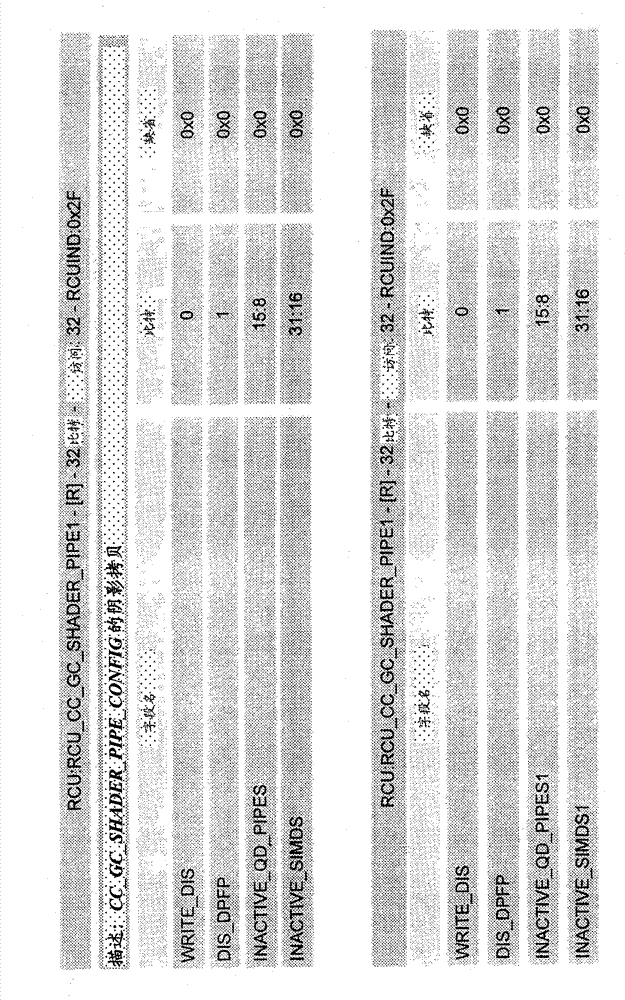
Dynamic enabling and disabling of SIMD units in a graphics processor
ActiveCN103080899AEasy to useLow powerEnergy efficient ICTResource allocationComputational scienceClock tree
Systems and methods to improve performance in a graphics processing unit are described herein. Embodiments achieve power saving in a graphics processing unit by dynamically activating / deactivating individual SIMDs in a shader complex that comprises multiple SIMD units. On-the-fly dynamic disabling and enabling of individual SIMDs provides flexibility in achieving a required performance and power level for a given processing application. In this way, embodiments achieve optimal usage of a graphics processing unit. Embodiments of the invention also achieve dynamic grain (e.g., medium grain) clock gating of SIMDs in a shader complex. Embodiments reduce switching power by shutting down clock trees to unused logic by providing a clock on demand mechanism. In this way, embodiments enhance clock gating to save more switching power for the duration of time when SIMDs are idle (or assigned no work).
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Method for realizing global ordered replaying under micro-service architecture
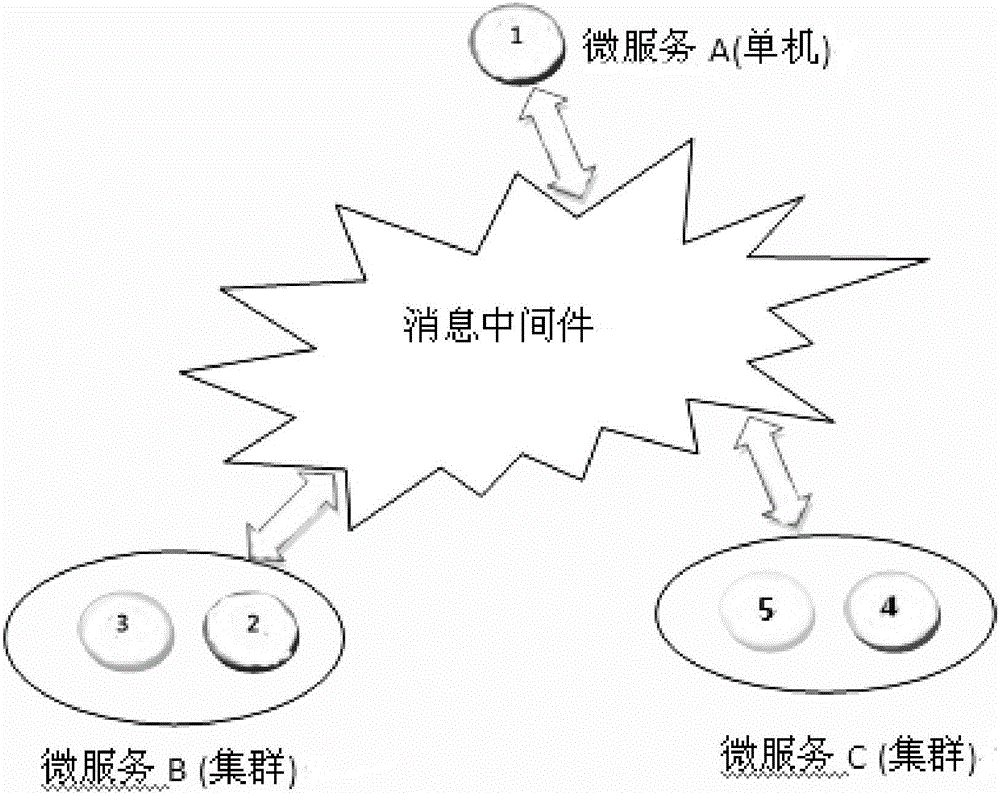
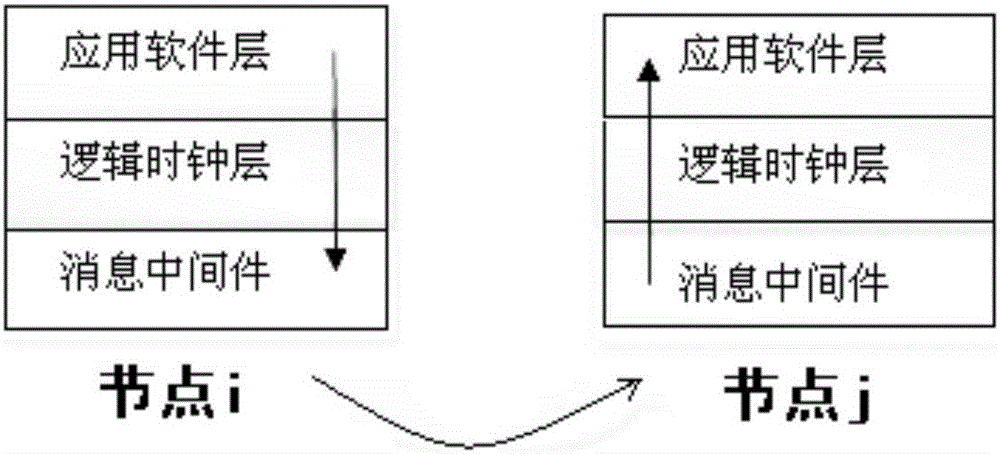
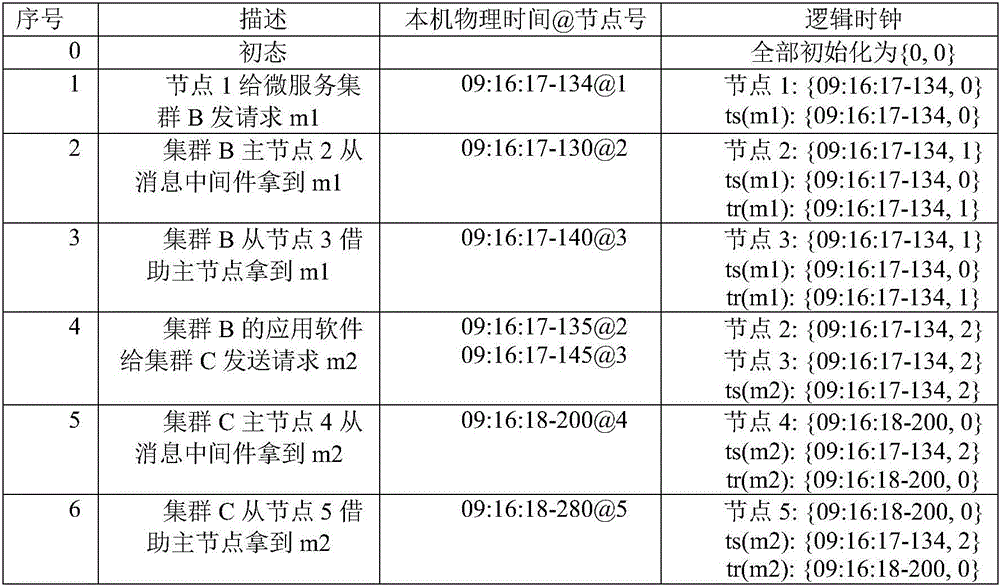
ActiveCN107181805AEasy to replayEasy to repeatInterprogram communicationTime-division multiplexLogical clockApplication software
The present invention relates to the information data processing technology field under the micro-service architecture, especially to a method for realizing global ordered replaying under micro-service architecture. A logic clock {T, C} in a two-tuple mode is maintained at the internal portion of the logic clock layer of each node, T is initialized to 0, and C is initialized to 0. Each transmitted message m carries two logic time stamps: ts(m) corresponding to m sending and tr(m) corresponding to m receiving. The formats of the ts(m) and the tr(m) are also the two tuples {T, C} as shown above. Compared to the prior art, a logic clock layer is arranged between an application software layer and message middleware and is taken as the maintenance logic of the logic clock and the logic time stamps, the logic clock can refer to the local physical clock and the message transmission cause and effect timing sequence, and because the T component of the logic clock is very close to the physical time of events, it is easy to perform replaying according to assigned multiplication speed.
Owner:上交所技术有限责任公司
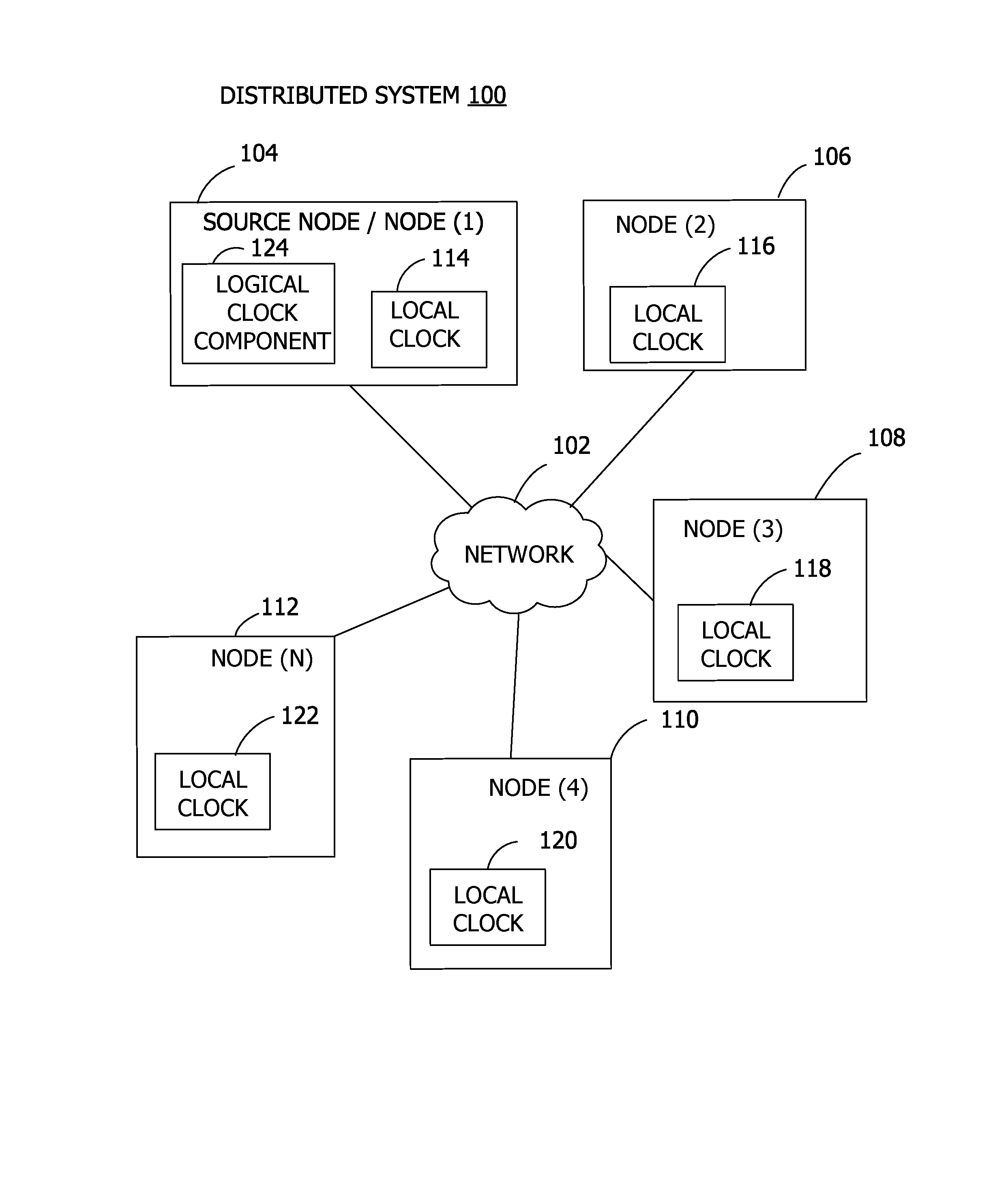
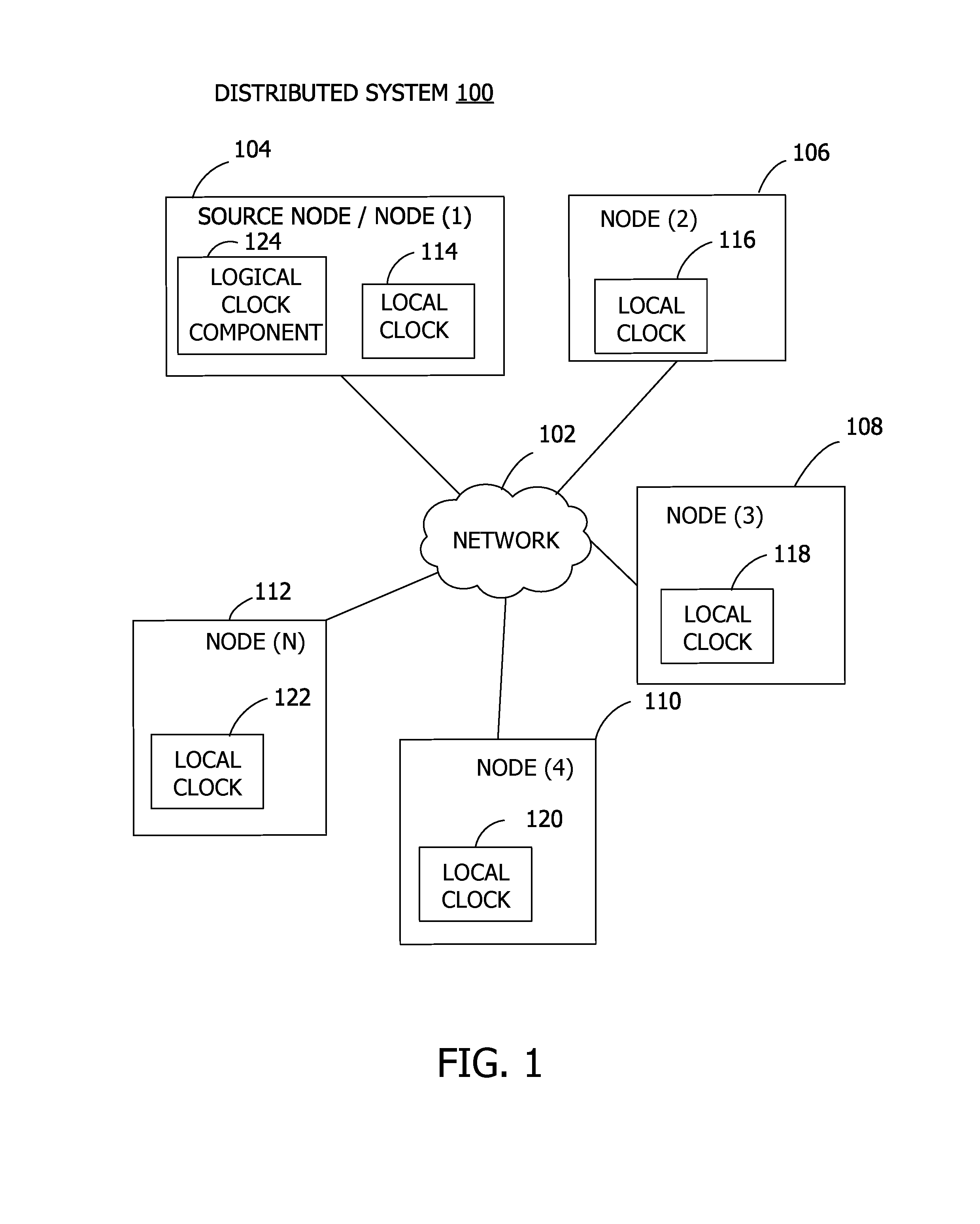
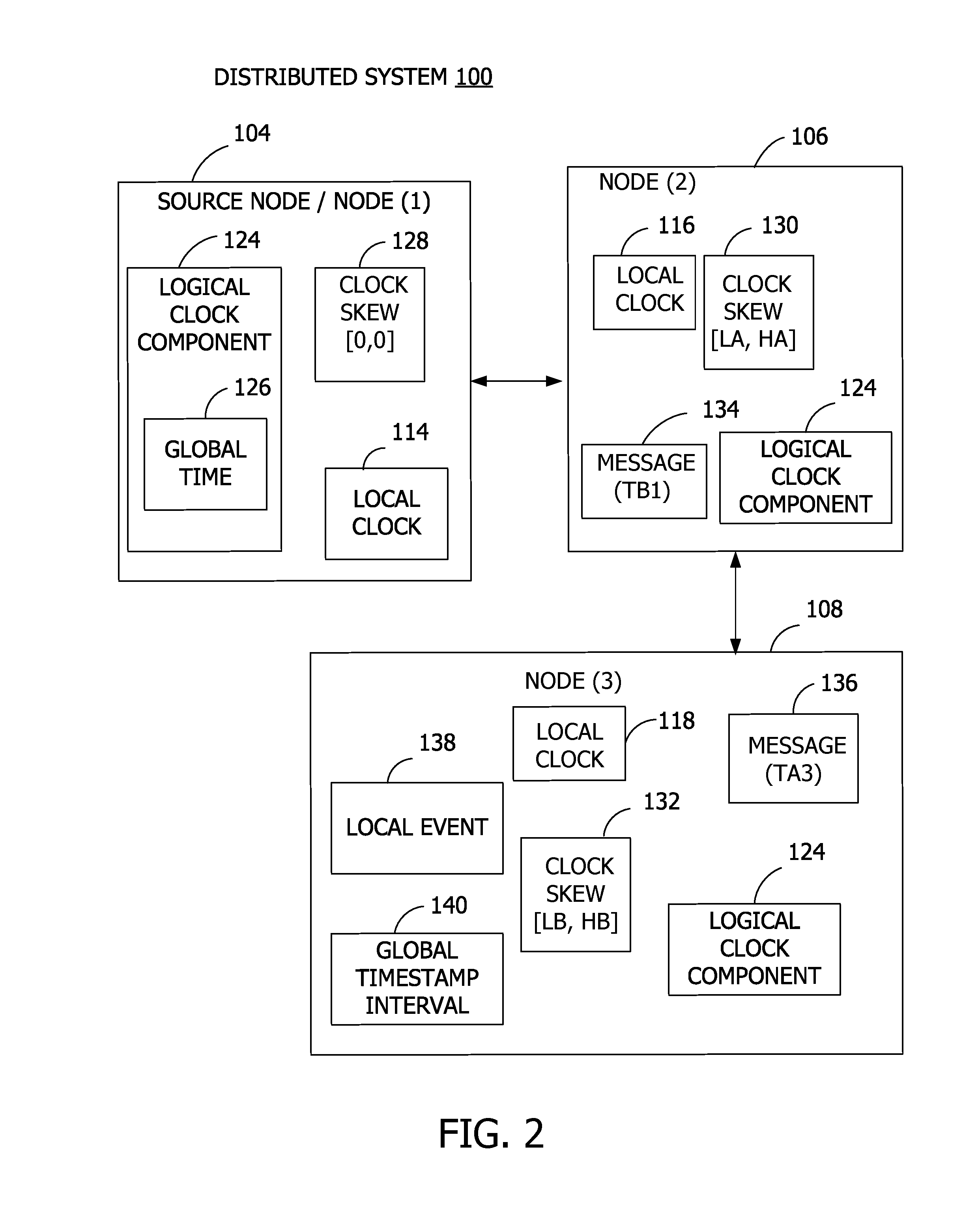
Global Logical Timestamp
ActiveUS20170063985A1Well formedTime-division multiplexGenerating/distributing signalsTimestampNetwork connection
Examples of the disclosure provide for providing a global timestamp in a distributed system. A plurality of nodes are connected via a network. A logical clock is implemented on a node of the plurality of nodes. The logical clock sets a global time for the network, such that another node of the plurality of nodes labels a local event with a global timestamp interval based on the global time provided by the logical clock.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
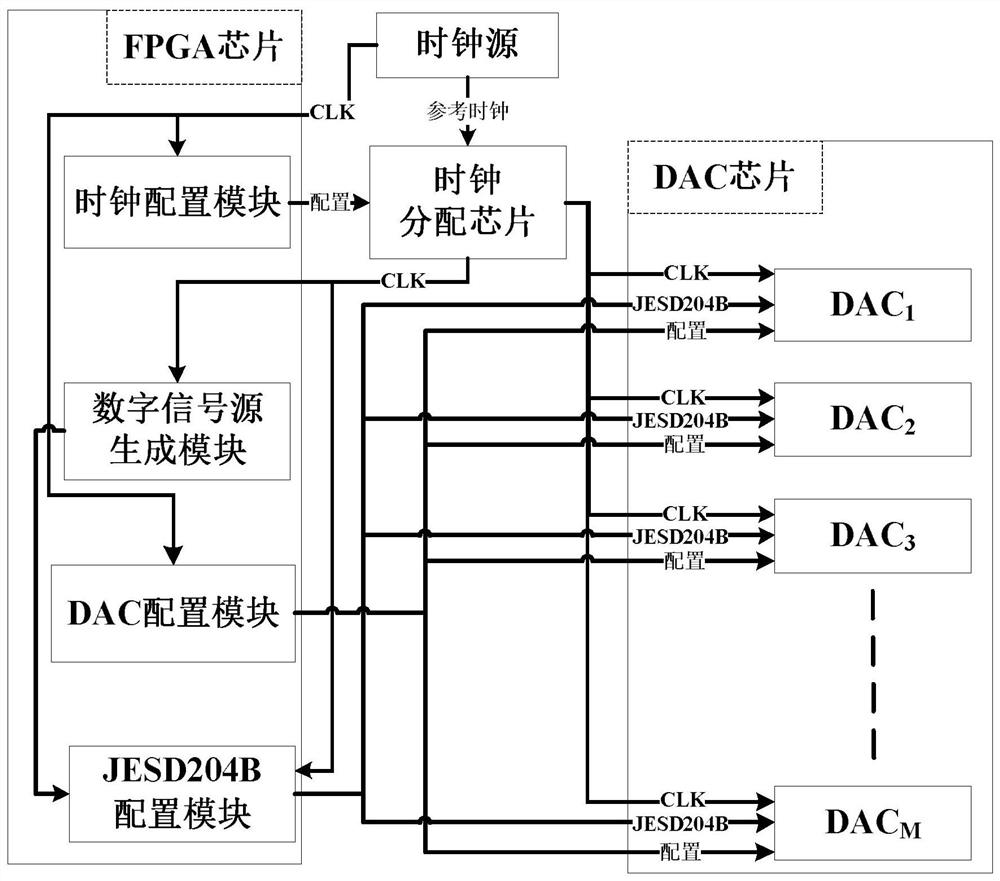
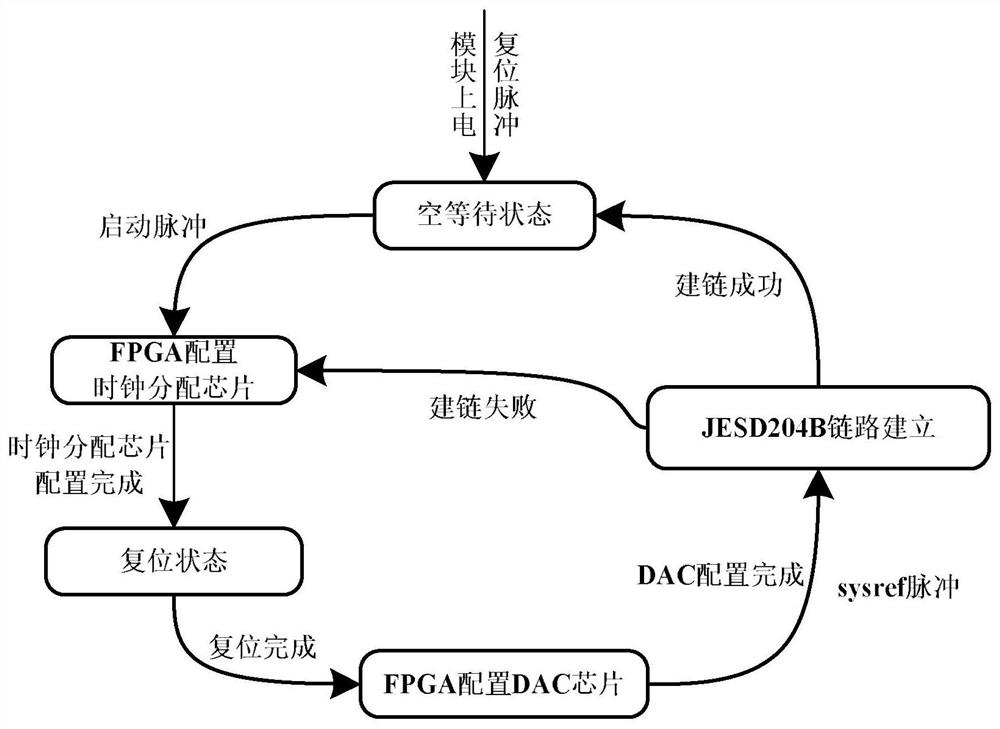
Multi-channel DAC sampling synchronization system
ActiveCN112187276ASimple structureImplement configurationDigital-analogue convertorsConvertersChannel data
The invention discloses a multi-channel DAC sampling synchronization system, and belongs to the technical field of high-speed serial interface chips. The invention aims to provide a DAC synchronization system capable of meeting high-speed sampling. The system is realized through the following technical scheme: a clock source and an FPGA loading program are externally provided, a digital signal source generation module generates a digital signal source according to a logic clock provided by a clock distribution chip, the digital signal source is sent to a JESD204B configuration module, multi-channel data framing and packaging are performed according to information such as the number of channels of a DAC chip and the number of DAC converters, and an IP core is called to extract frame data and the frame data is mapped into effective coded words, high-speed serial data required by each DAC converter is formed by adopting different sorting modes, frames of control characters in a high-speedserial data stream is aligned by the DAC chip according to configuration, frame decoding is completed according to the requirements of a JESD204B protocol and the frames are output to multiple channels, thereby realizing high-speed DAC sampling multi-channel synchronization.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
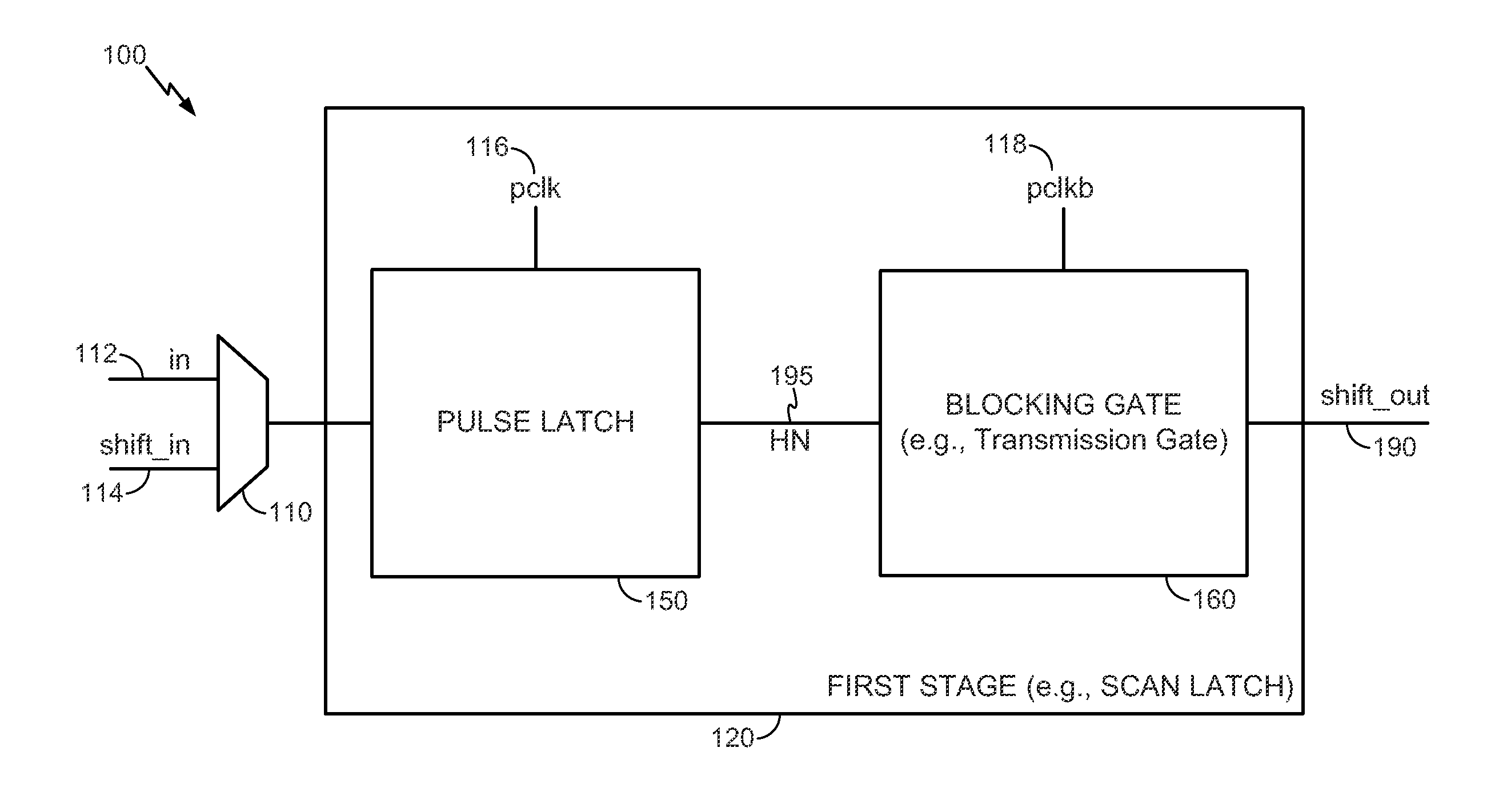
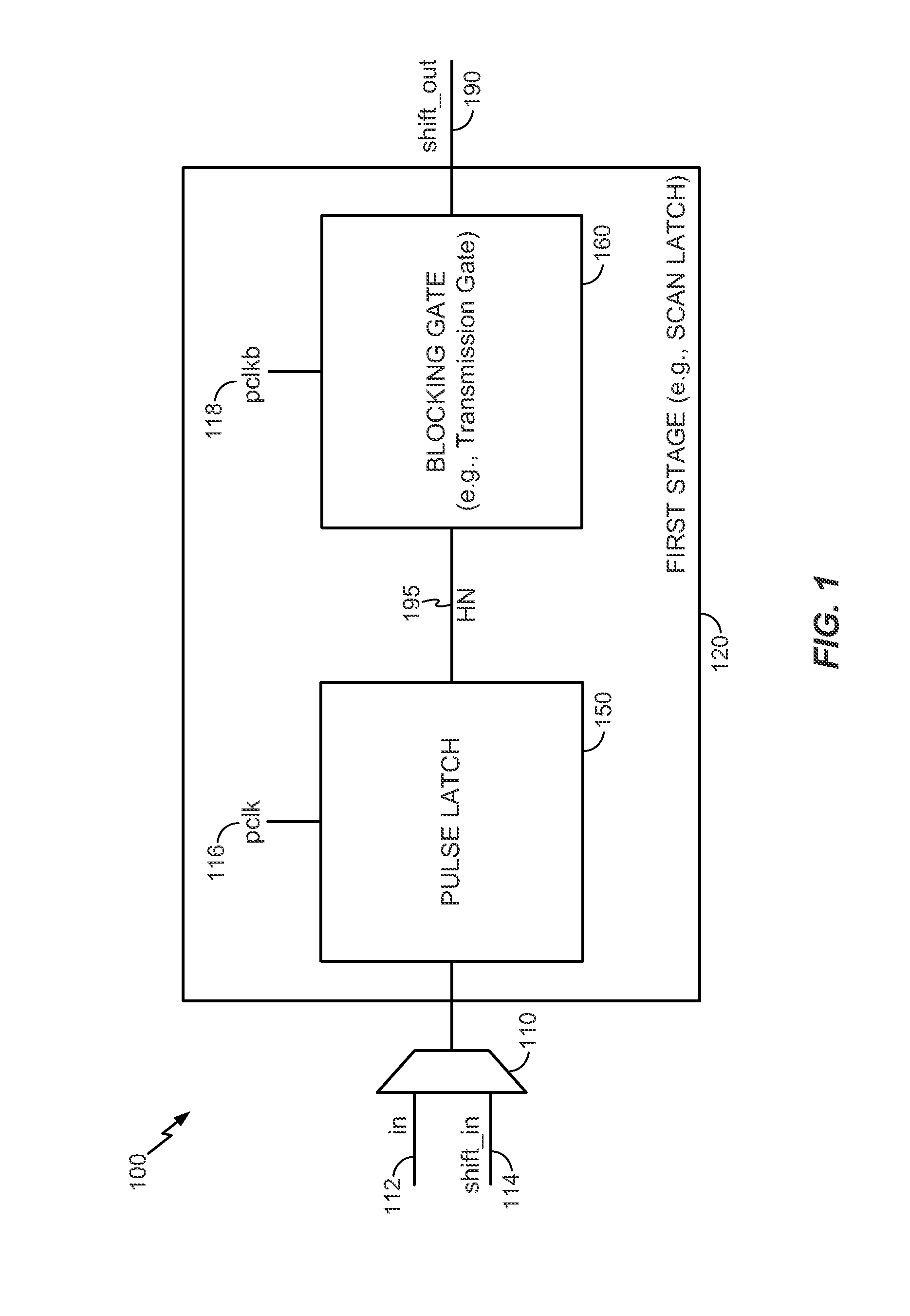
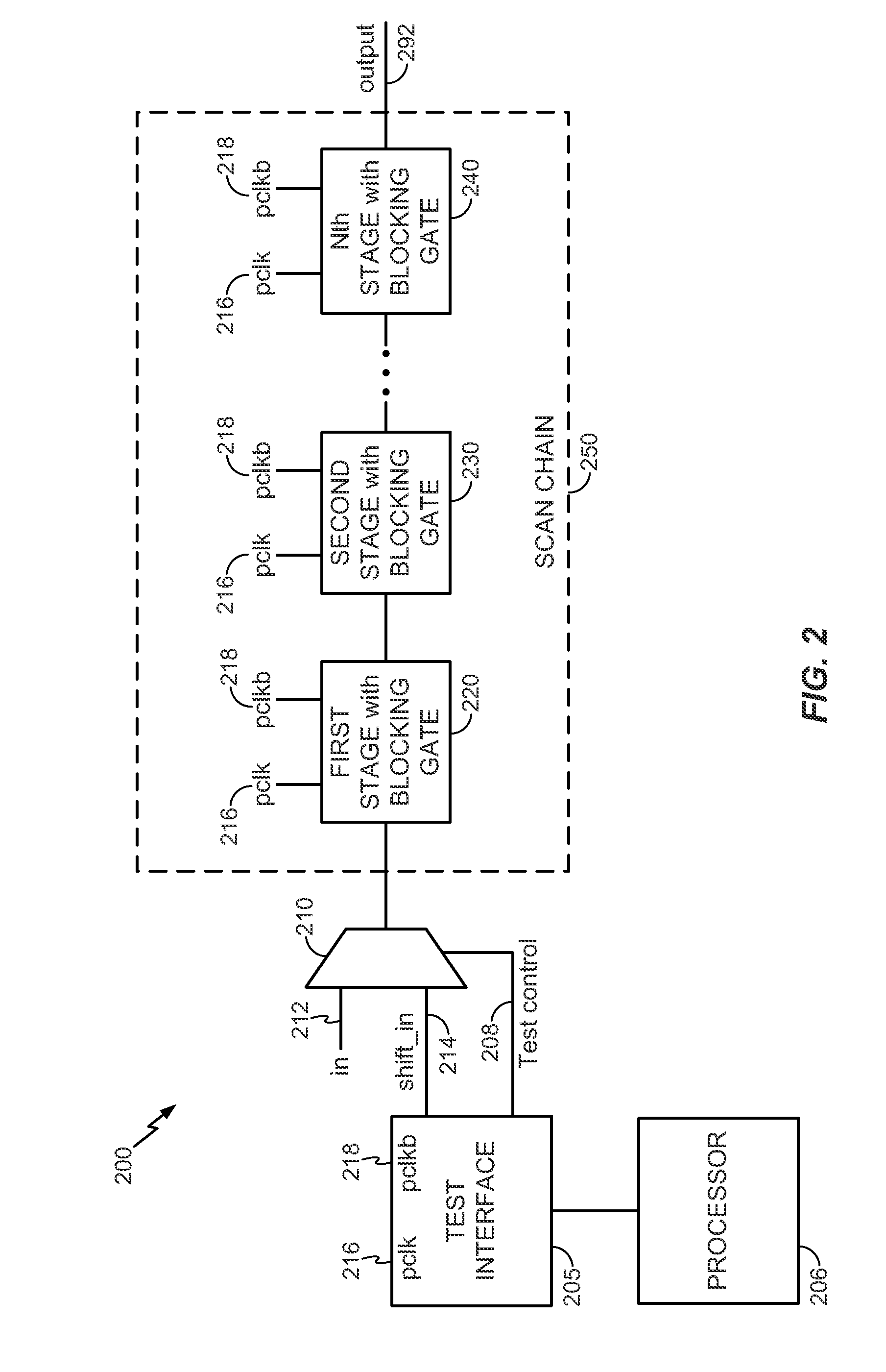
System and method to perform scan testing using a pulse latch with a blocking gate
ActiveUS20140035645A1Reduce probabilityReduce in quantityElectric pulse generatorCAD circuit designLogical clockEngineering
A system and method to perform scan testing using a pulse latch with a blocking gate is disclosed. In a particular embodiment, a scan latch includes a pulse latch operable to receive data while a pulse clock signal has a first logical clock value and a blocking gate coupled to an output of the pulse latch. The blocking gate is operable to propagate the data from the output of the pulse latch while the pulse clock signal has a second logical clock value.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
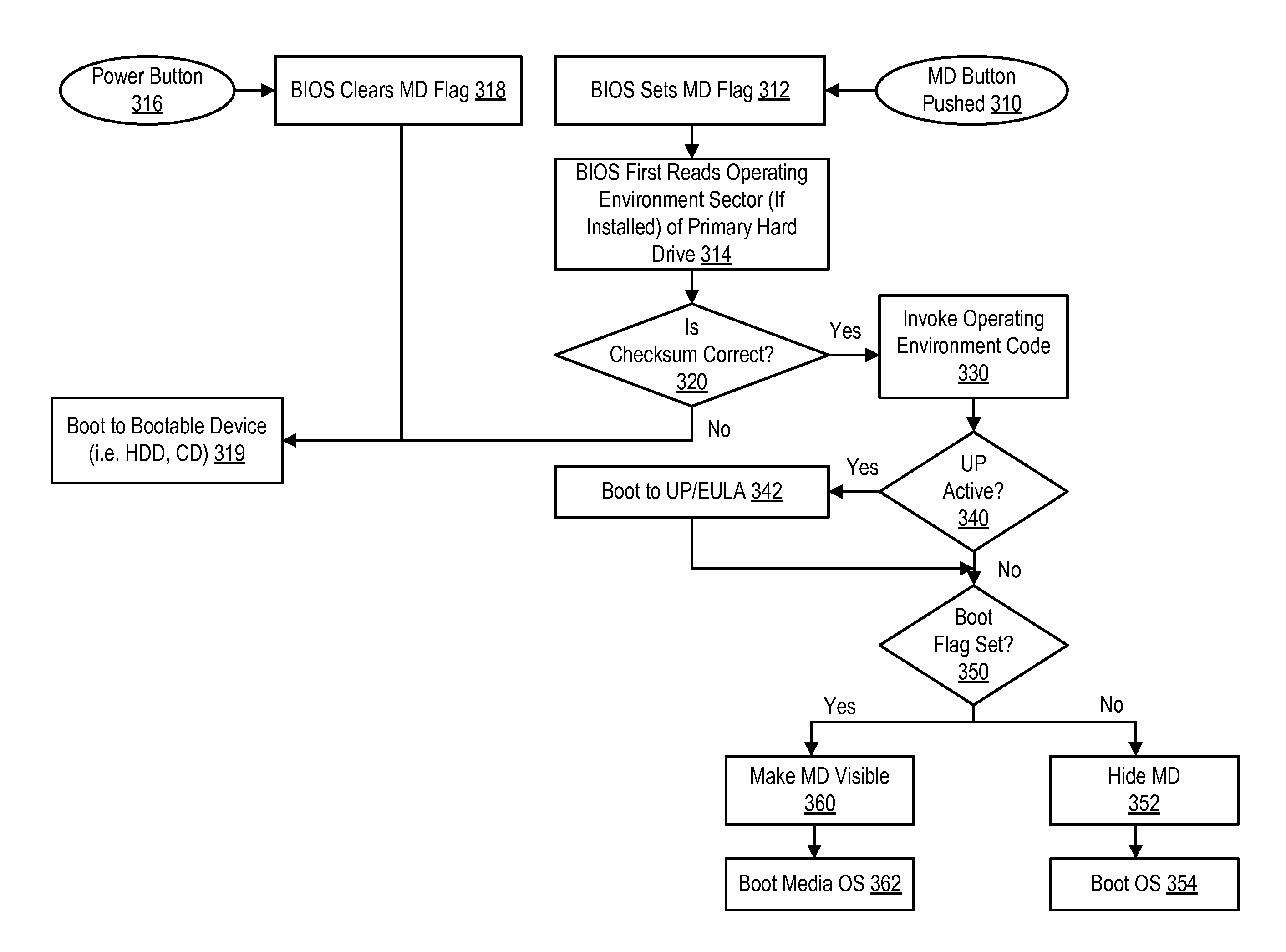
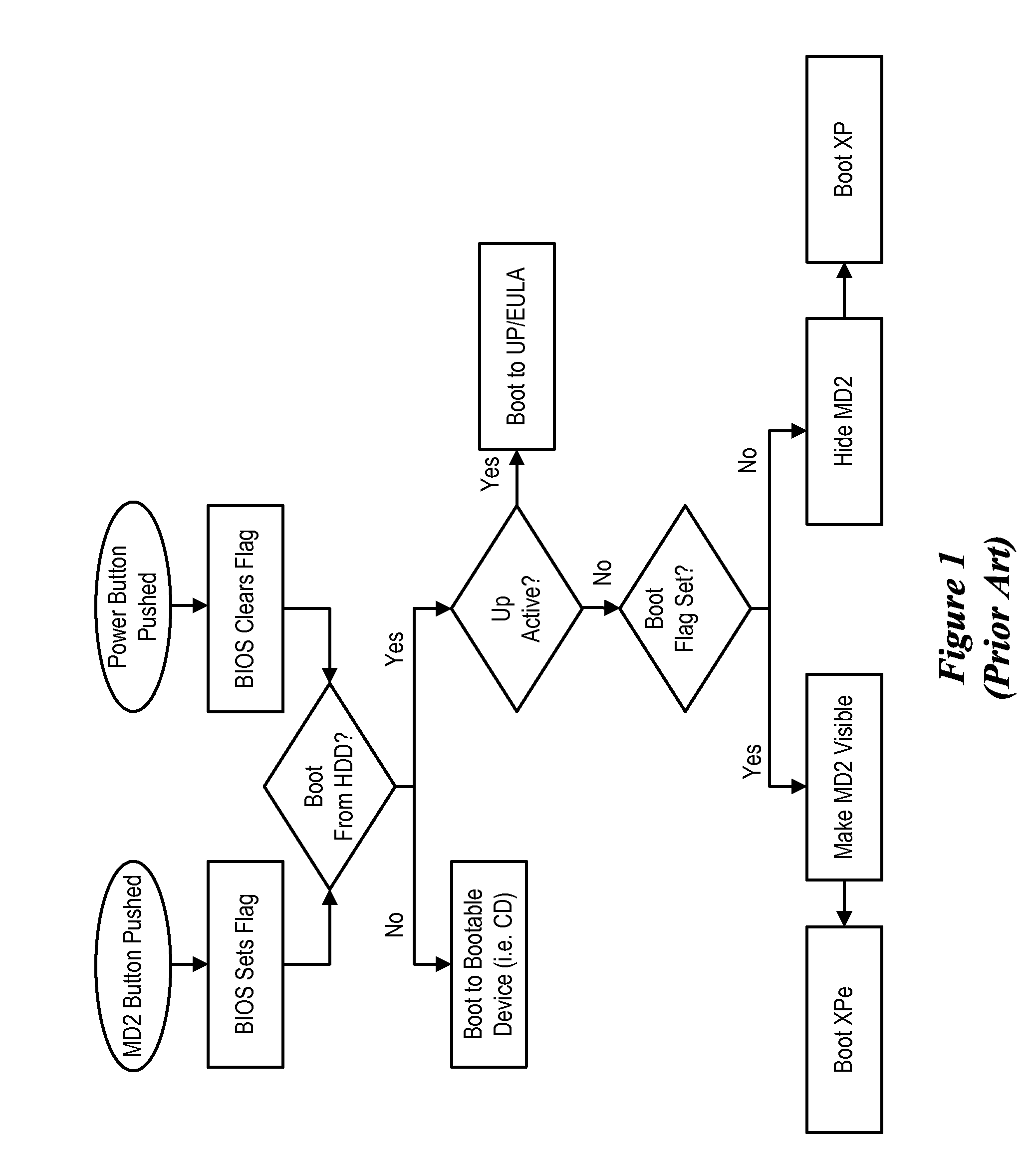
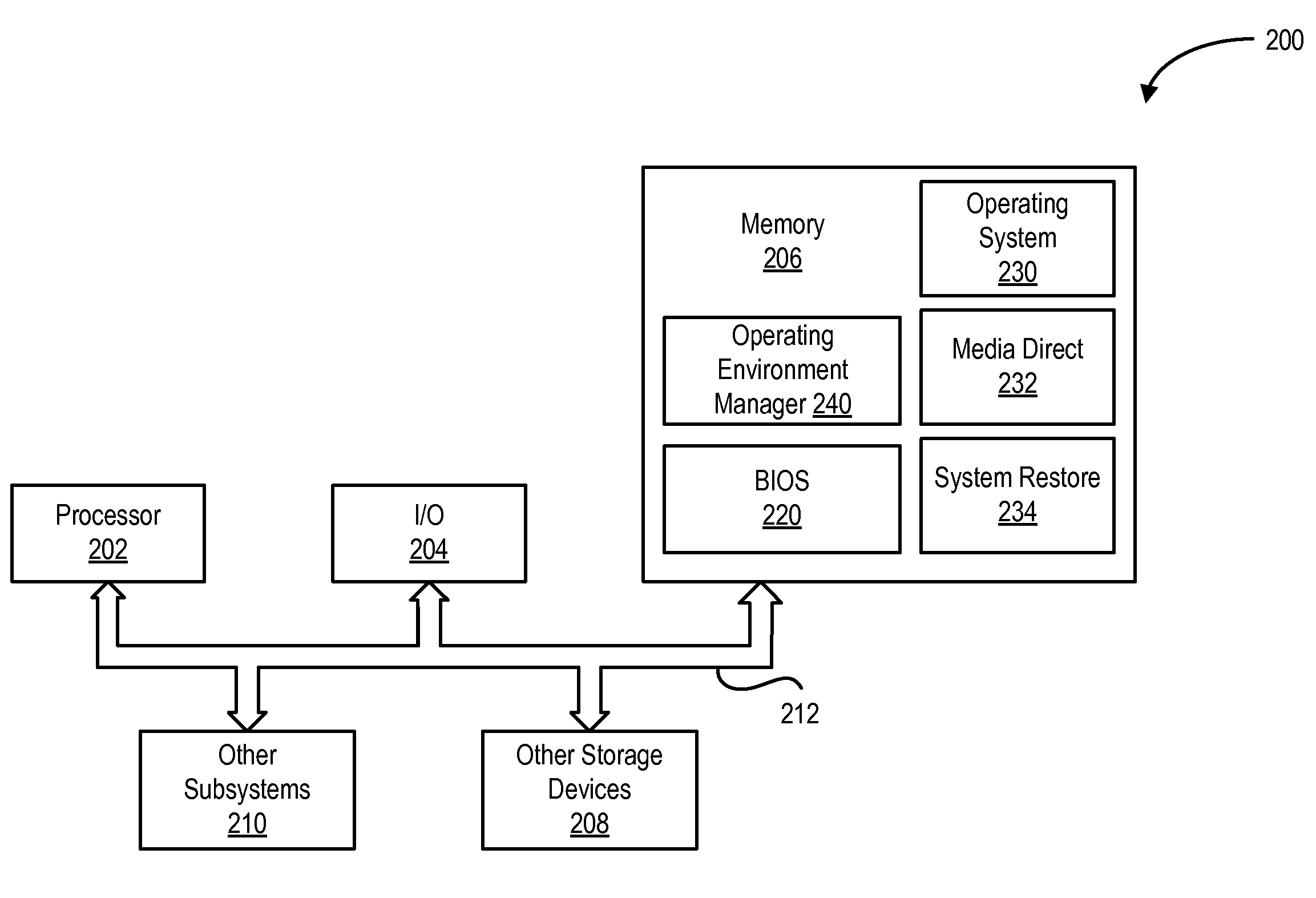
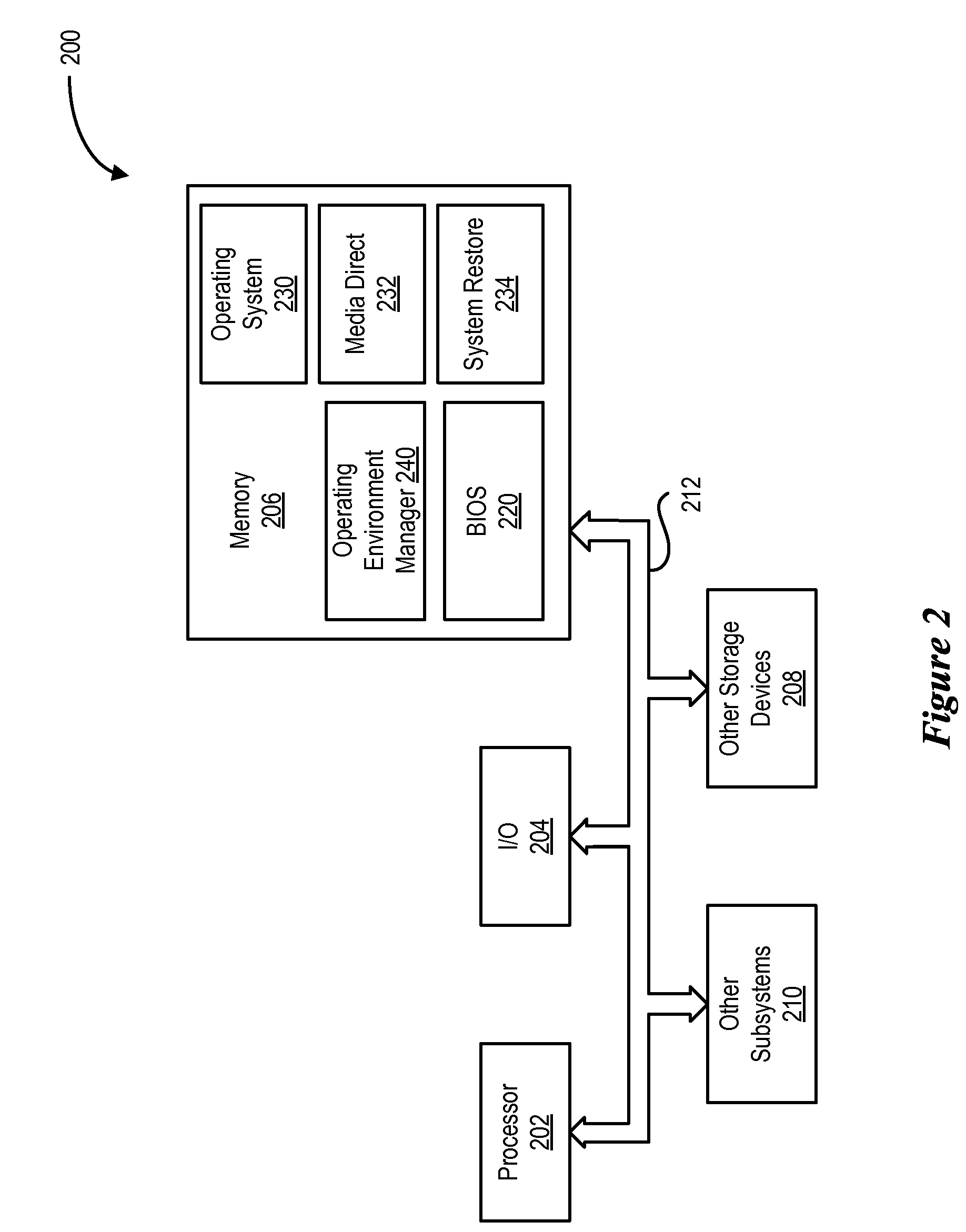
System for Registering and Initiating Pre-Boot Environment for Enabling Partitions
ActiveUS20080114976A1Self containedDigital computer detailsBootstrappingLogical clockApplication software
Owner:DELL PROD LP
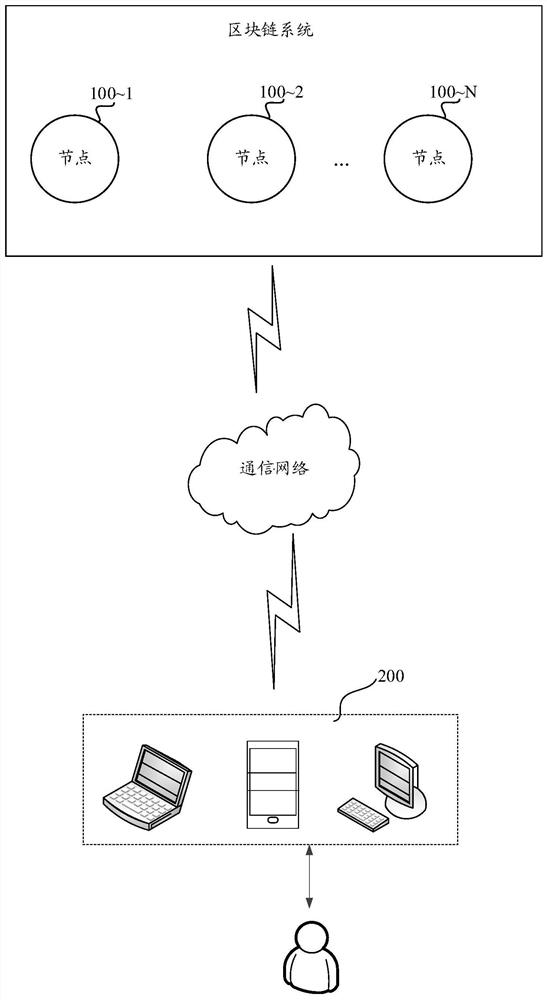
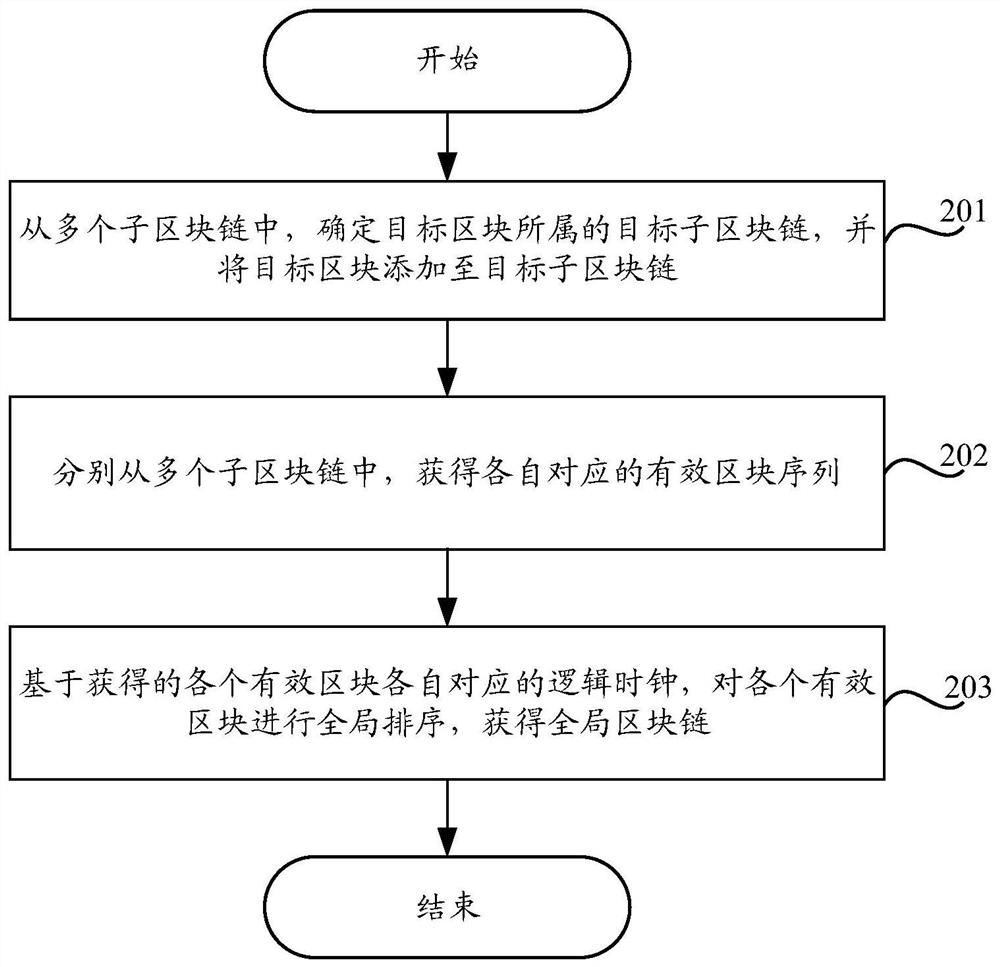
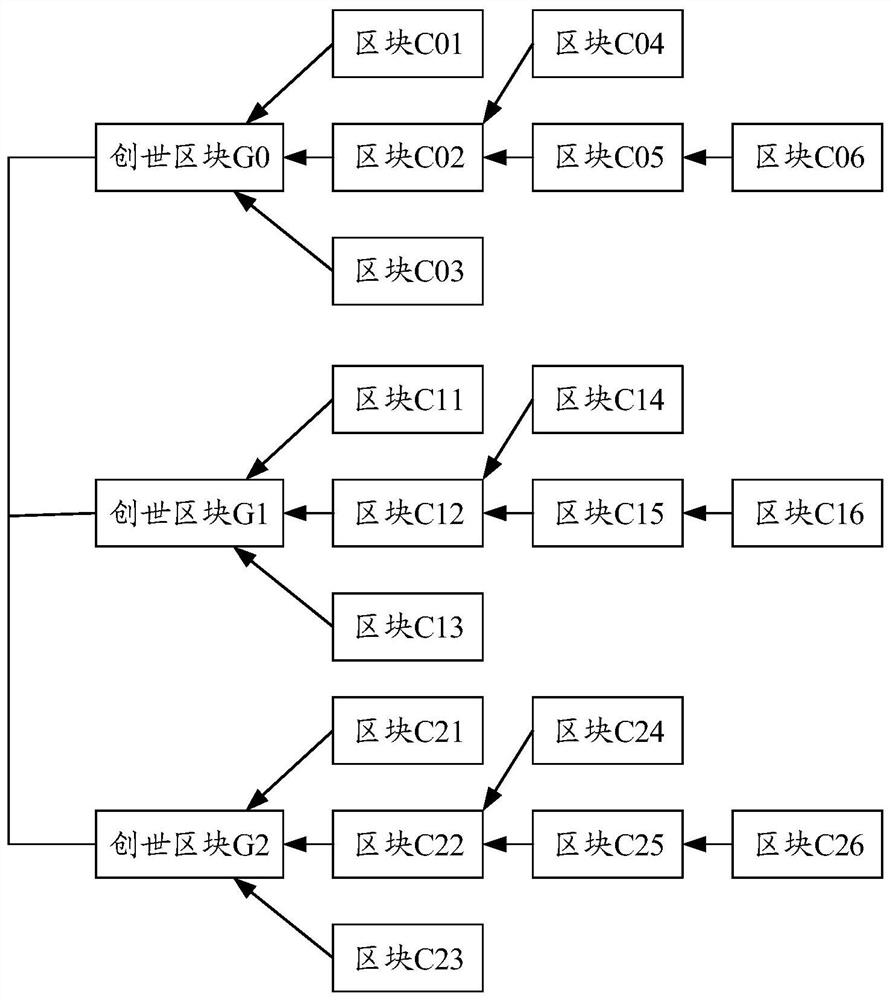
Block chain consensus method and device, equipment and storage medium
PendingCN114281888AImprove acceleration performanceImprove transaction throughputDatabase distribution/replicationSpecial data processing applicationsLogical clockTransaction data
The embodiment of the invention provides a block chain consensus method and device, equipment and a storage medium, and relates to the technical field of block chains, and the method comprises the steps that a node generates a target block based on transaction data and a verifiable delay function, or synchronously obtains the target block from other nodes. And determining a target sub-block chain to which the target block belongs from the plurality of sub-block chains, and adding the target block to the target sub-block chain. Then, respectively obtaining respective corresponding effective block sequences from the plurality of sub-block chains; and on the basis of the obtained logic clocks corresponding to all the effective blocks, all the effective blocks are globally sorted, and a global block chain is obtained. The global block chain is obtained in a multi-chain consensus mode, and the expandability and transaction throughput of the block chain system in a large-scale open network environment are improved. Based on the logic clocks corresponding to all the effective blocks, when all the effective blocks are globally sorted to obtain the global block chain, the security of the multi-chain system can be better improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIONPAY
Real time correlation of parallel charging events
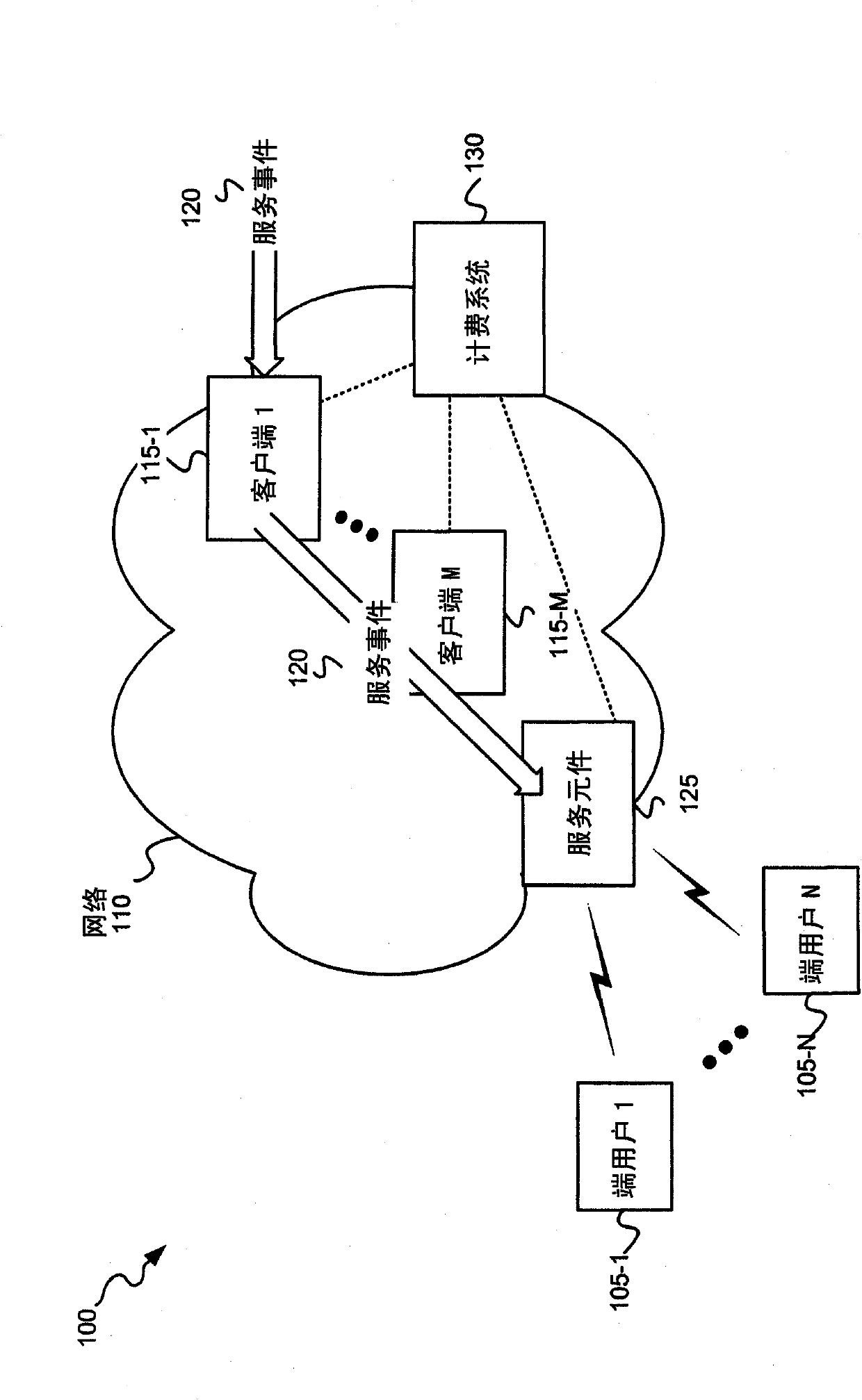
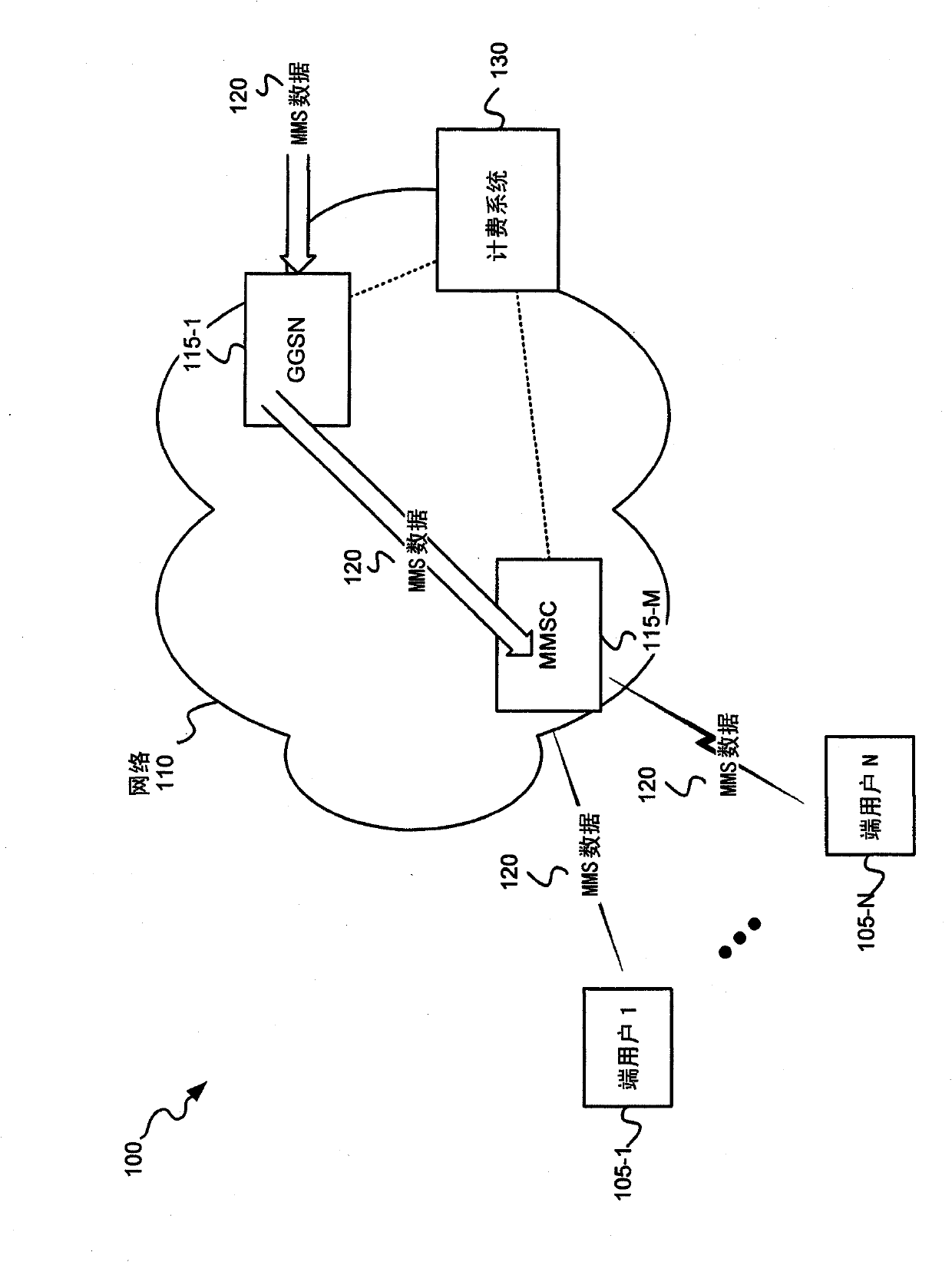
ActiveCN102090050AMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccounting/billing servicesGeneral Packet Radio ServiceSession Initiation Protocol
A method is implemented in a network (110) that provides a service to an end user, the network including a first client (115-1), a second client (115 -M) and a charging system (130). The method includes the first client (115-1) receiving (900) a service event (120) that is destined for an end user (105) and retrieving (915) a first logical clock value from memory, where the first logical clock value specifies a number of service events received at the second client (115- M). The method further includes the first client (115-1) incrementing (920) a second logical clock value based on receipt of the service event (120) and constructing (920) a first time stamp parameter based on the first logical clock value and the second logical clock value. The method also includes the first client (115-1) sending (925) a charging request to a charging system, where the charging request includes the first time stamp parameter and where the charging request requests credit authorization associated with providing the service event (120) to the end user (105). The service event may be associated with one of Multimedia messaging service (MMS) data, a Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) signaling message, or a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) message received at the first client. In one exemplary embodiment, the first client includes a Gateway General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Support Node (GGSN) and the second client includes a MultiMedia Messaging Service Center (MMSC). In a second exemplary embodiment, the first client includes a GGSN and the second client comprises a Serving Call Session Control Function (S-CSCF). In a third exemplary embodiment, the first client includes a router and the second client includes a S-CSCF.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Secure logical vector clocks
ActiveUS8533487B2Improve security levelEasy to implementPublic key for secure communicationUnauthorized memory use protectionCommunication unitLogical clock
Embodiments include a system for processing logical clock values according to a secure maximum operation. The system may include a communication unit and a processing unit. The communication unit may be configured to receive an encrypted first value of a logical clock, send an encrypted blinded difference, receive an encrypted blinded maximum value, and receive a maximum value. The processing unit may be configured to access an encrypted second value of the logical clock, generate the encrypted blinded difference between the first value and the second value, provide an encrypted blinded first value and an encrypted blinded second value in an oblivious transfer protocol, and generate an encrypted maximum value from the encrypted blinded maximum value.
Owner:SAP AG
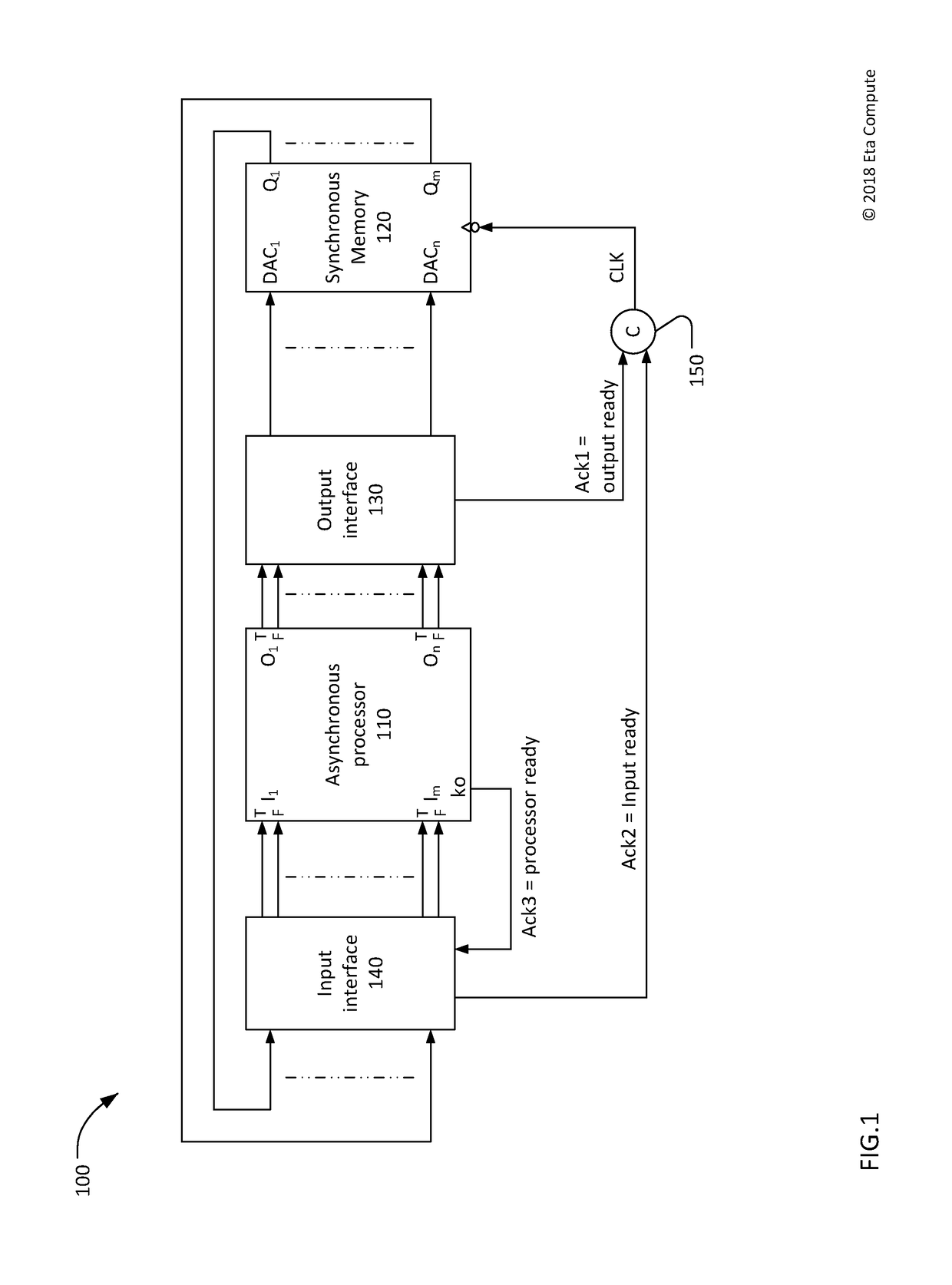
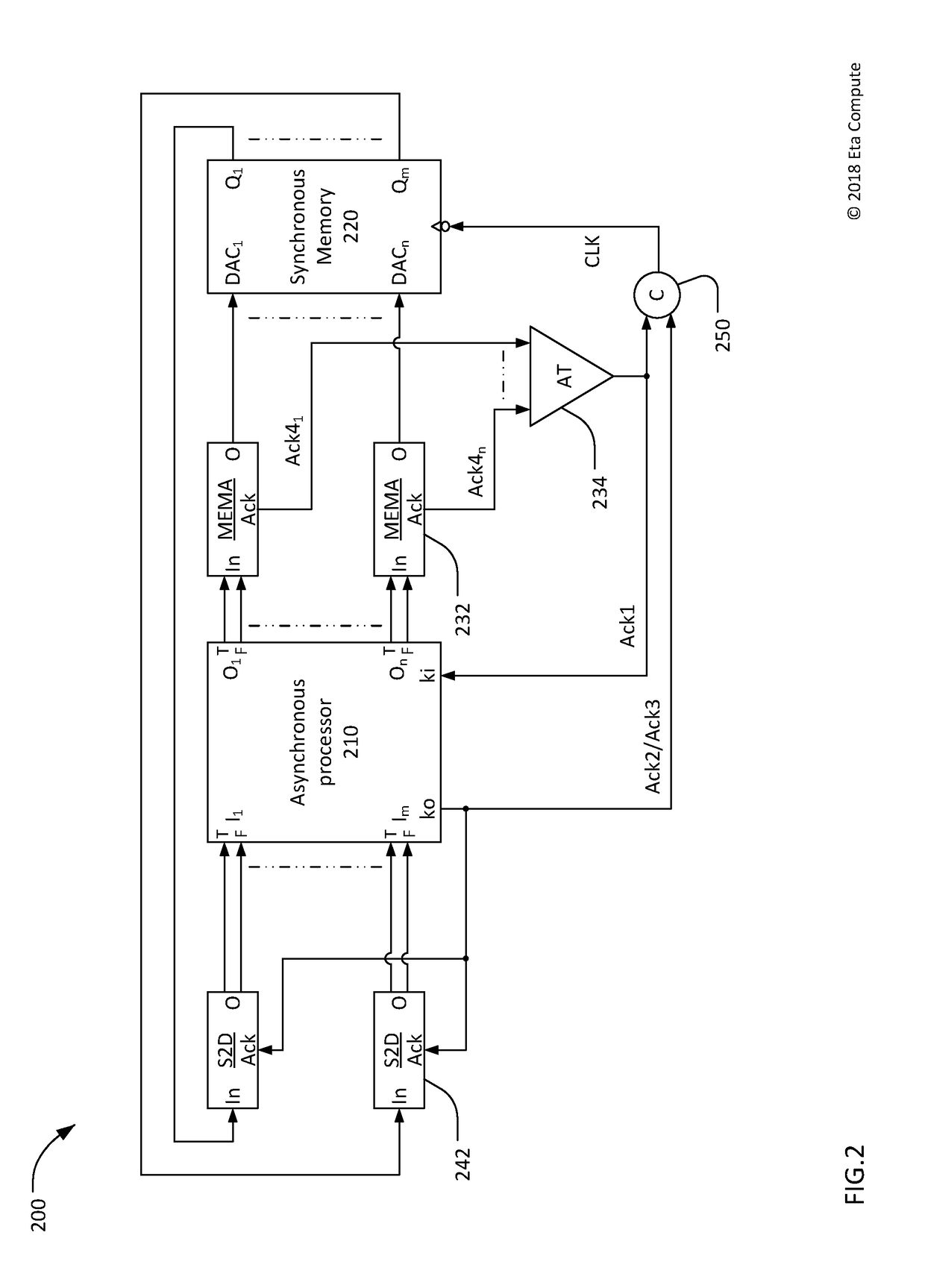
Interface from null convention logic to synchronous memory
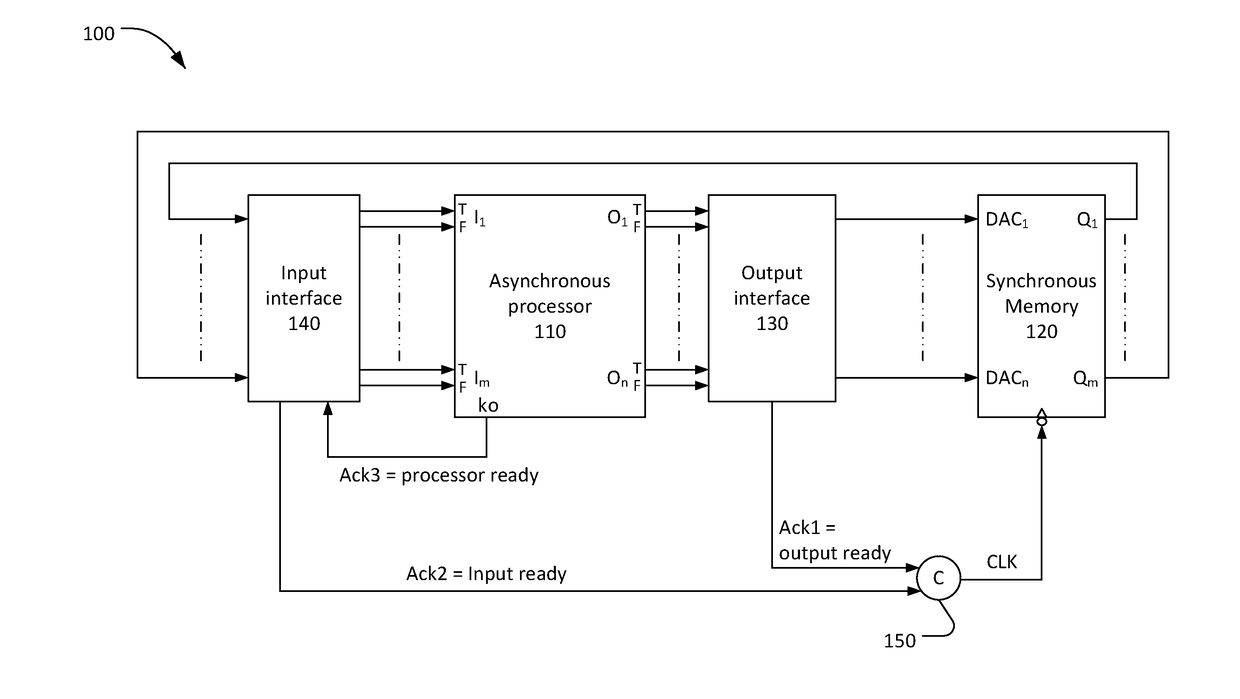
ActiveUS20180300263A1Power supply for data processingGenerating/distributing signalsActive edgeSignal on
Self-timed processing systems and methods of operating self-timed processing systems are disclosed. A self-timed processing system includes an asynchronous null convention logic (NCL) processor, a memory that accepts input signals on an active edge of a memory clock signal, and logic to combine a first acknowledge signal and a second acknowledge signal to generate the memory clock signal. The first acknowledge signal indicates input signals are ready to be accepted by the memory. The second acknowledge signal indicates data signals previously output from the memory have been accepted by the processor.
Owner:ETA COMPUTE INC
Consistent clock synchronization frequency offset estimation method based on sequence least square
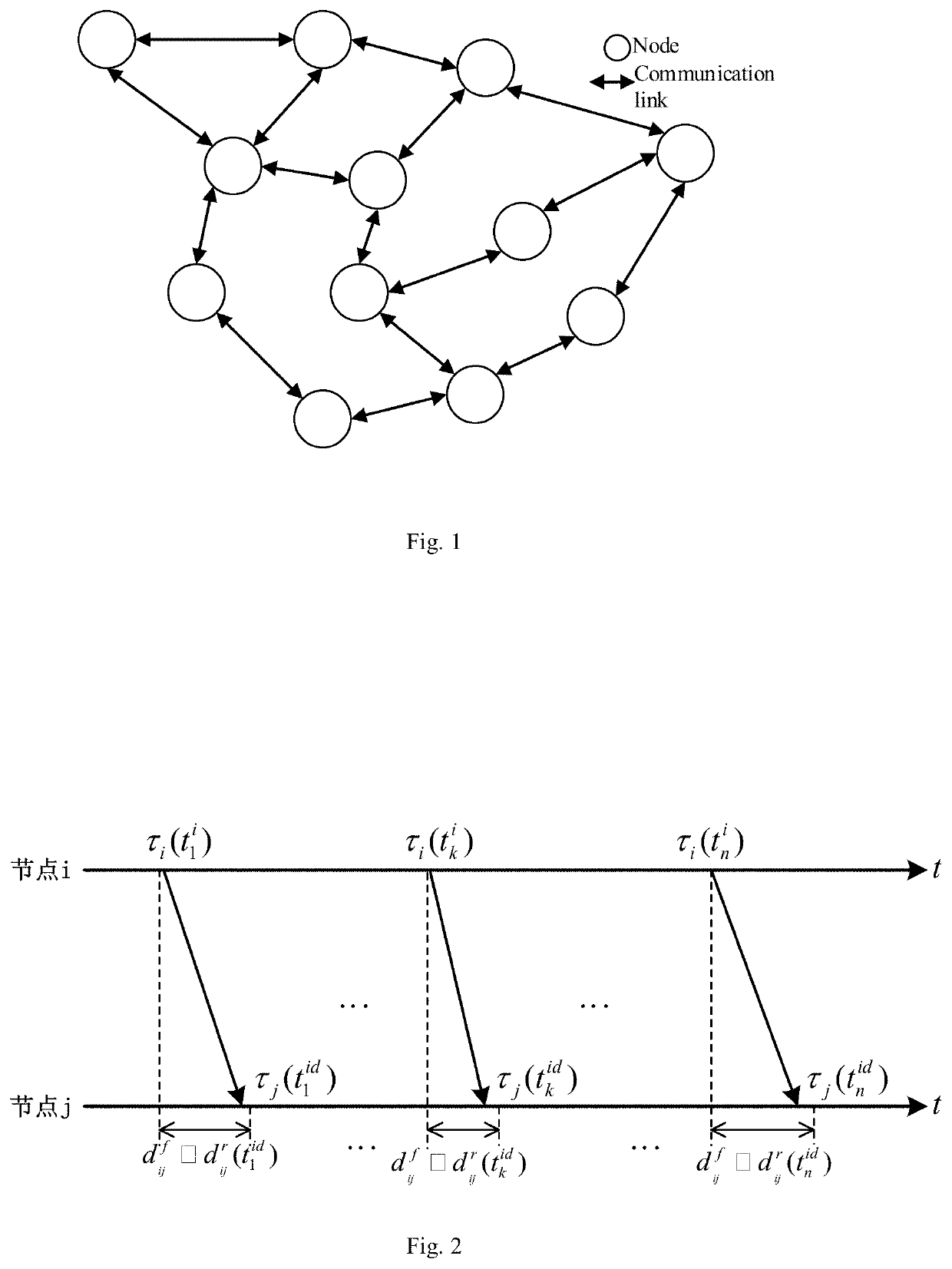
ActiveCN113207167AImprove robustnessHigh precisionSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesLine sensorAlgorithm
The invention relates to a consistent clock synchronization frequency offset estimation method based on sequence least square, and belongs to the technical field of wireless sensor networks. According to the method, for a bounded random communication time delay scene obeying arbitrary distribution, a relation model of clock information and time delay between nodes is established, all clock information from neighbors received by the nodes is fully considered, a clock parameter estimation model and a cost function based on the least square principle are constructed, relative clock frequency offset between nodes is iteratively estimated by adopting a sequence least square method, and logic clock parameters of the nodes are updated by utilizing a consistent clock synchronization method, so that all the nodes in the network realize global clock consistency in a completely distributed manner. According to the method, the precision of relative frequency offset estimation is improved, the storage overhead of the nodes is effectively reduced, and the robustness of a consistency synchronization algorithm to communication delay is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
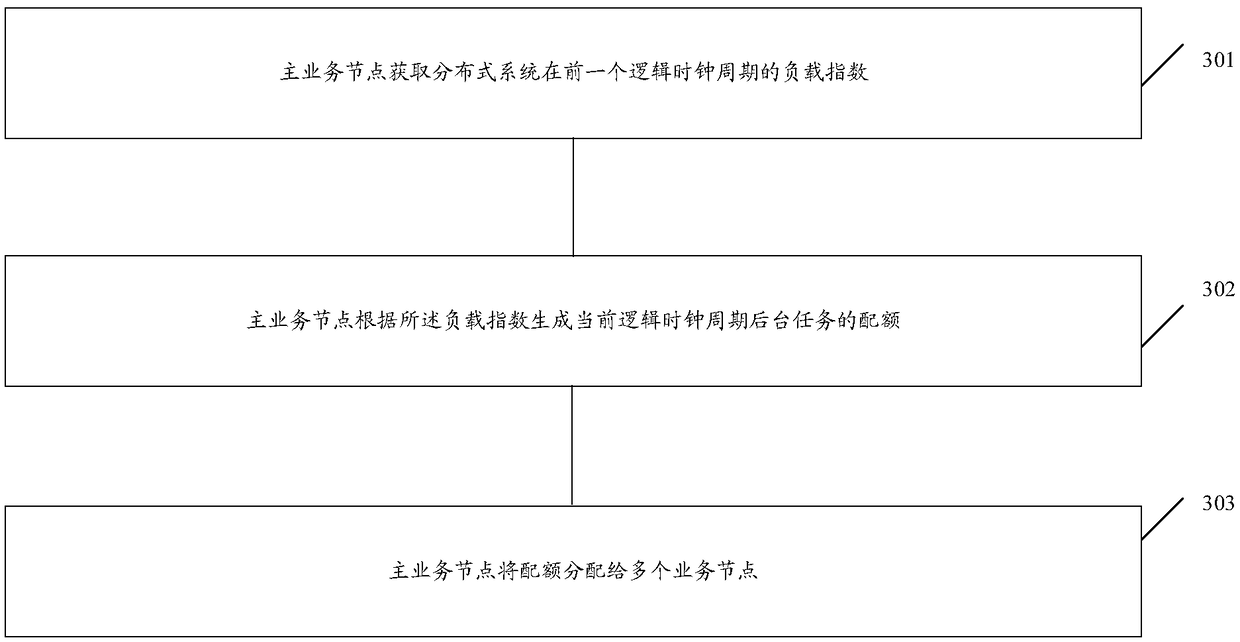
Task scheduling method, device and computer program product
A Task Scheduling Scheme, Quotas for background tasks are generated based on logical clocks and load indices of the distributed system, Quotas are allocated to multiple business nodes for processing,so as to realize flexible scheduling of background tasks based on distributed system load in logical clock cycle, improve the flexibility and real-time of background task scheduling, and ensure the accuracy of background task scheduling.
Owner:HUAWEI CLOUD COMPUTING TECH CO LTD
System for registering and initiating pre-boot environment for enabling partitions
A method for registering and initiating a pre-boot environment for enabling partitions. The method provides a basic input output system (CIOS) with an application program interface (API) that accesses a Logical Clock Address (LCA) sector number when a boot configuration flag is set, the LCA sector number stores an operating environment manager which then boots the information handling system to an appropriate partition.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Time sequence management method and device of server cluster and electronic equipment
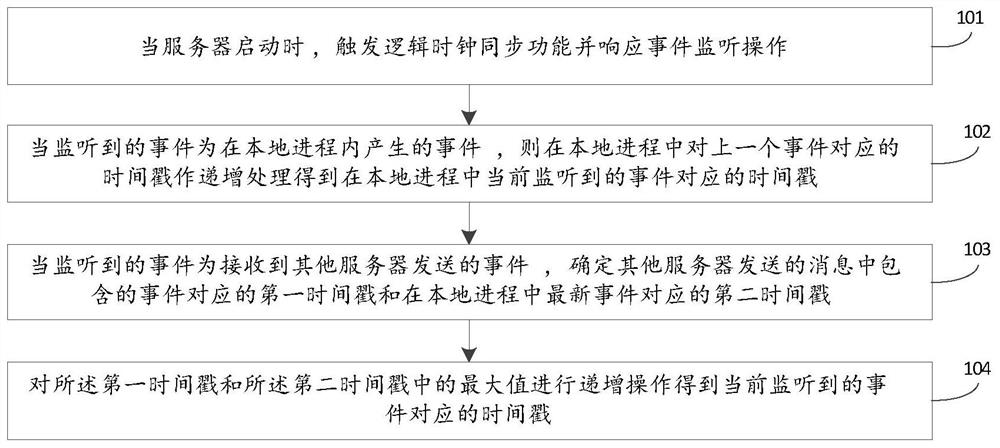
PendingCN113946448AAvoid influenceResource allocationInterprogram communicationLogical clockTimestamping
The invention discloses a time sequence management method and device for a server cluster and electronic equipment, and the method comprises the steps: triggering a logic clock synchronization function and responding to an event monitoring operation when a server is started; when the monitored event is the event generated in the local process, progressively increasing the timestamp corresponding to the previous event in the local process to obtain the timestamp corresponding to the currently monitored event in the local process; when the monitored event is the event sent by the other server, determining a first timestamp corresponding to the event contained in the message sent by the other server and a second timestamp corresponding to the latest event in the local process; and performing progressive increase operation on the maximum value in the first timestamp and the second timestamp to obtain a timestamp corresponding to the currently monitored event. By starting a logic clock synchronization function and performing timestamp marking on the event in the local process according to the event generation mode, the accuracy of event time sequence recording is ensured.
Owner:SUZHOU LANGCHAO INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
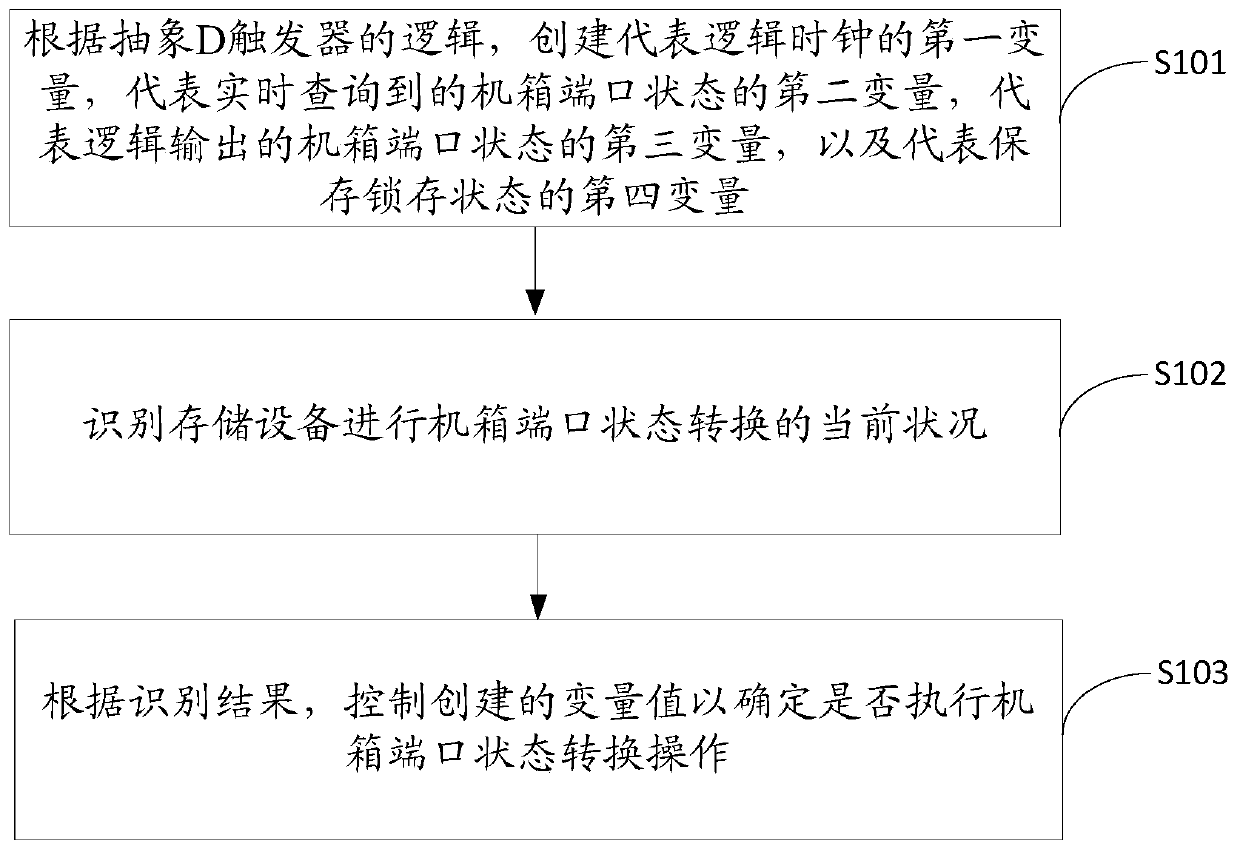
Case port state conversion method, device and equipment, and storage medium
ActiveCN111309253AReduce executionReduce the impactInput/output to record carriersLogical clockFlip-flop
The invention discloses a case port state conversion method, device and equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: according to logic of an abstract D trigger, creatinga first variable representing a logic clock, a second variable representing a case port state inquired in real time, a third variable representing a case port state output by logic, and a fourth variable representing a storage latch state; identifying a current state of the storage device for carrying out case port state conversion; and according to the identification result, controlling the created variable value to determine whether to execute a case port state conversion operation or not. According to the method and the device, the case port state conversion is realized by utilizing the algorithm principle of the D trigger, so that the case port state conversion time can be shortened, the discovery frequency can be reduced, the unnecessary case port state conversion logic execution is reduced, the influence on the user service performance is reduced as much as possible, and the resource utilization rate of the storage equipment is improved.
Owner:INSPUR SUZHOU INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Average consistency time synchronization method based on event triggering
ActiveCN114423073AReduce overheadHigh synchronization accuracySynchronisation arrangementHigh level techniquesClock timeTime delays
The invention relates to an average consistency time synchronization method based on event triggering, and belongs to the technical field of wireless networks. The method comprises the following steps of: aiming at the condition that communication time delay and clock time frequency offset exist in a wireless network, setting an updating period and an initial relative frequency offset estimation value and a logic clock compensation value of each node in the network, and updating a logic frequency offset estimation value step by step according to the period; judging whether the node meets a broadcast triggering condition or not according to the difference between the latest updated logic frequency offset value and the last broadcast logic frequency offset value; if the trigger condition is met, the node broadcasts relevant parameters of the hardware clock and the logic clock at the moment to other neighbor nodes; and relative frequency offset estimation is carried out by using a sequence least square method, and global consistency of a network clock is realized by using a proportional-integral estimator. According to the method, the influence of transmission time delay and clock time frequency offset in a wireless network is considered, compromise is achieved between communication overhead and synchronization precision, and high synchronization precision is achieved with appropriate communication overhead.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
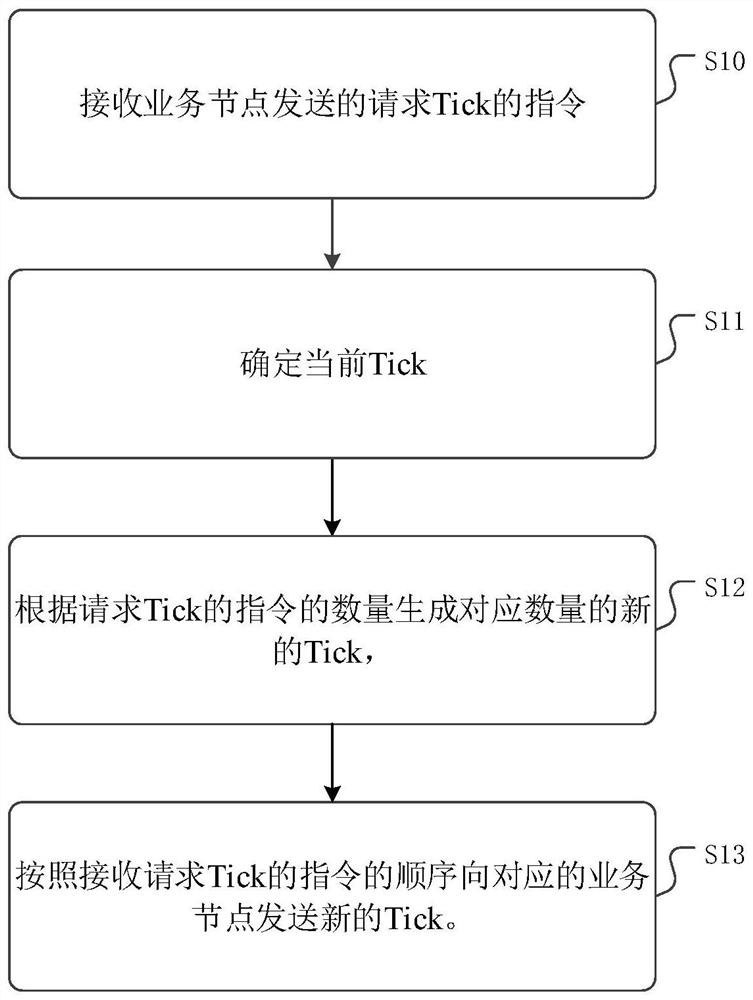
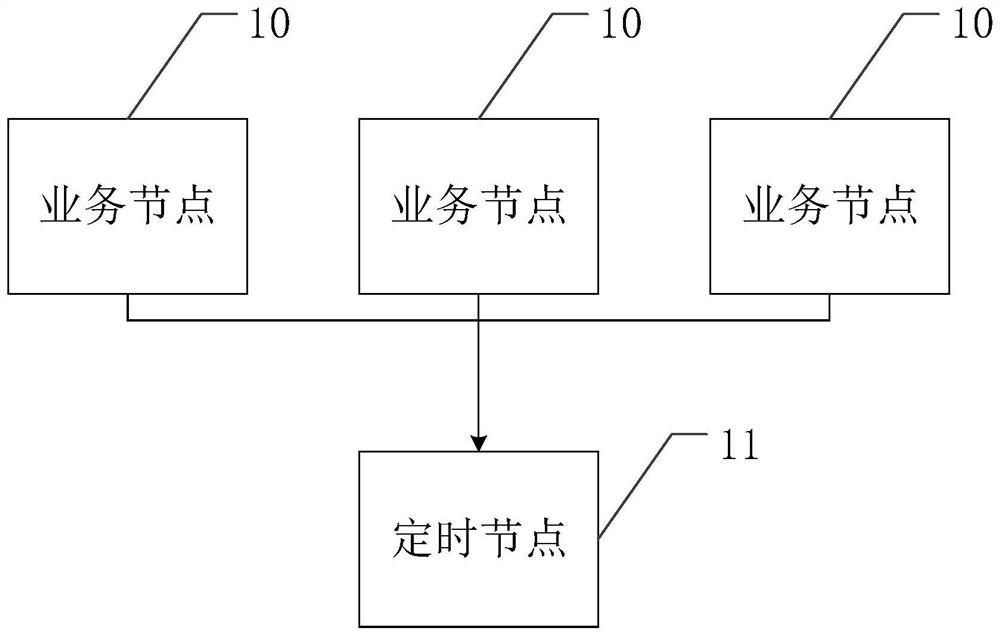
Distributed cluster time synchronization method and device and computer readable storage medium
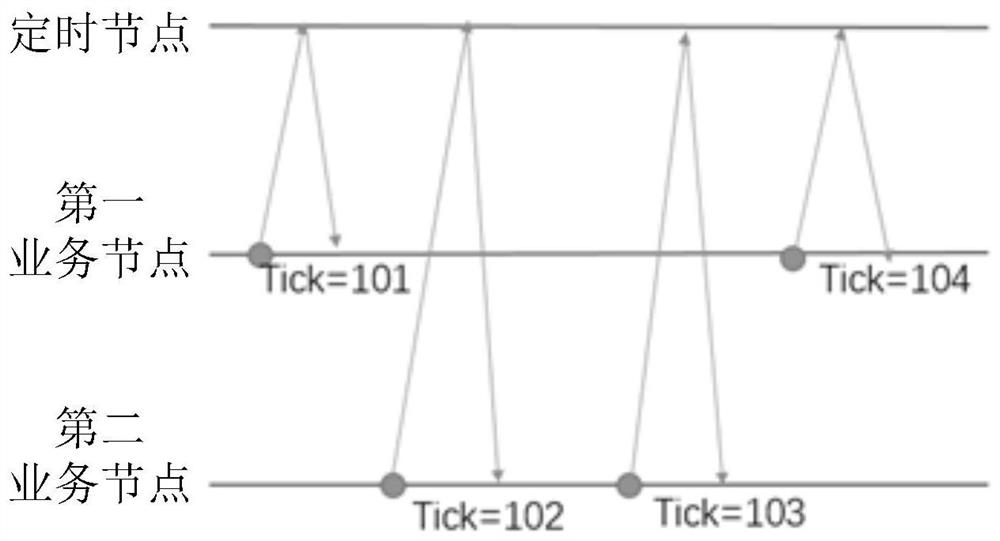
InactiveCN114666346ASynchronous Interaction Achievement TimeAvoid out-of-sync problemsTransmissionComputer networkLogical clock
The invention discloses a distributed cluster time synchronization method and device and a computer readable storage medium, and relates to the field of computers. The method comprises the following steps: receiving a Tick request instruction sent by a service node and determining a current Tick; new Ticks with the corresponding number are generated according to the number of the instructions for requesting the Tick, and 1 is sequentially added to the new Ticks on the basis of the current Tick; and sending the new Tick to the corresponding service node according to the order of receiving the instruction for requesting the Tick. Through adoption of a logic clock mode, time synchronization of interaction of each service node is achieved, and the problem of data asynchronization in a cluster is avoided.
Owner:INSPUR SUZHOU INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Frequency Offset Estimation Method For Average Consistency Clock Synchronization
PendingUS20220369258A1Accurate frequencyImprove clock synchronization performanceSynchronisation arrangementCarrier regulationLine sensorLogical clock
The present invention relates to a frequency offset estimation method for average consensus-based clock synchronization, and belongs to the technical field of wireless sensor networks. According to the method, in combination with distributed one-way broadcast characteristics, solving of maximum likelihood estimation is converted into a linear optimization problem, and a relative frequency offset estimation value is obtained by adopting an iterative method. By applying the estimation value to the compensation of logic clock parameter between nodes, an effect of keeping logic clocks of network nodes consistent can be achieved. According to the present invention, distribution characteristics of communication time delay are fully considered, accurate relative frequency offset estimation can be implemented, so the synchronization precision of average consensus-based clock synchronization is effectively improved, the maximum likelihood estimation solving is performed by adopting the iterative method, an estimation algorithm is simplified, and storage overhead is reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and apparatus for securing and authenticating encoded data and documents containing such data
InactiveUS7543151B2Accurate detectionUser identity/authority verificationCard-like record carriersComputer hardwareLogical clock
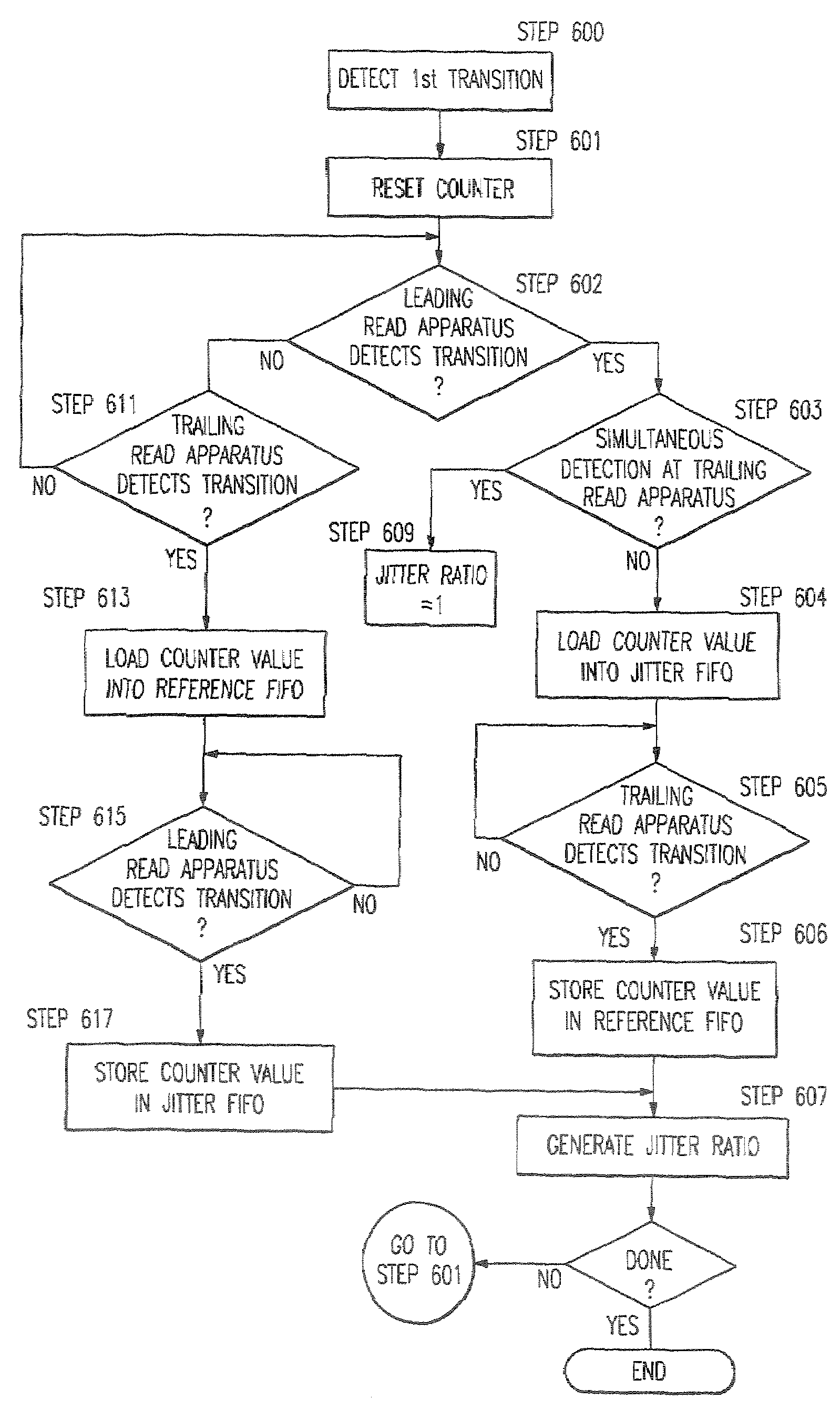
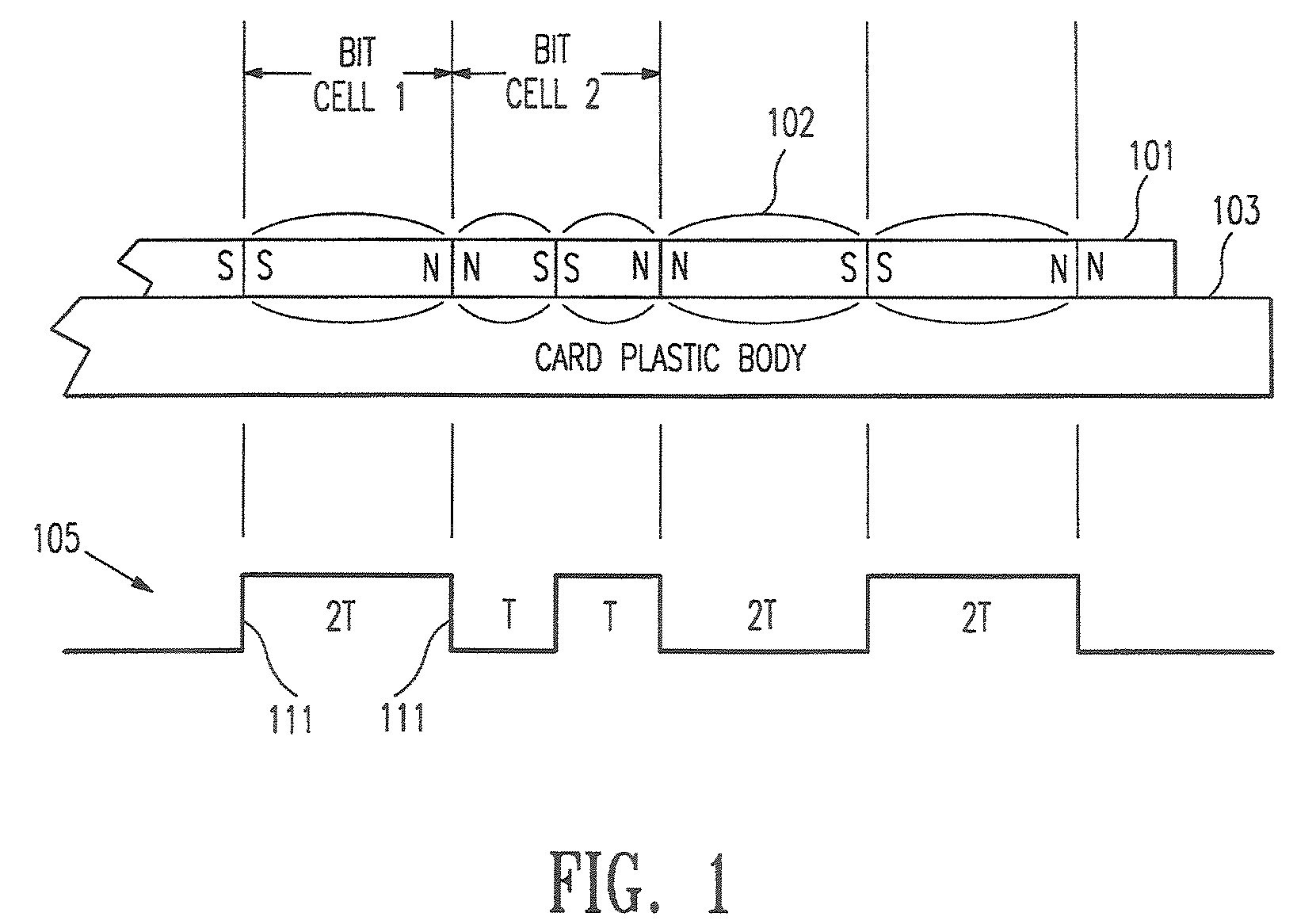
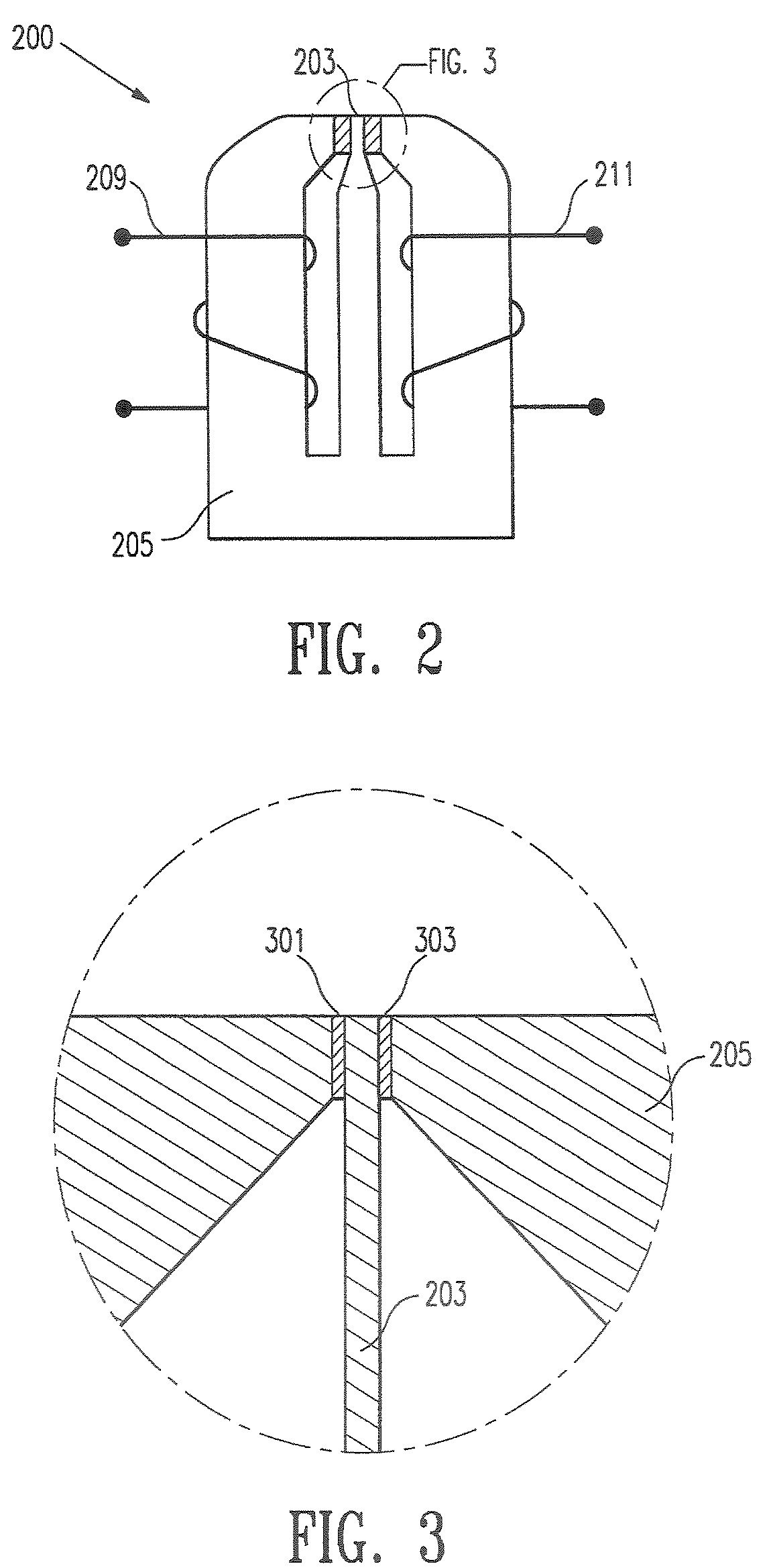
A method and apparatus for determining the distance between transitions from a first logical state to a second logical state stored on a medium (i.e., a document). This determination is used to precisely characterize the information pattern in order to authenticate the information and the medium on which the information is stored. The invention uses a reader having a leading and trailing read apparatus which allow information to be read simultaneously from two or more locations spaced a known distance apart. The distance between the centerlines of each read apparatus is preferably an odd integer multiple of one half the distance between logical clock transitions. The distance between a first transition at the leading read apparatus and a next transition at the trailing read apparatus is used as a reference (i.e., the “Reference Value”). The Reference Value is compared with the distance between the first transition and the next transition on the medium (i.e., the “Jitter Value”). Detection of an deviations in spacing between transitions is unaffected by variations in the velocity of the medium with respect to the reader.
Owner:SEMTEK INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com