Detection method for single nucleotide polymorphism
A single nucleotide polymorphism and detection method technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of detection equipment, isotope pollution, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
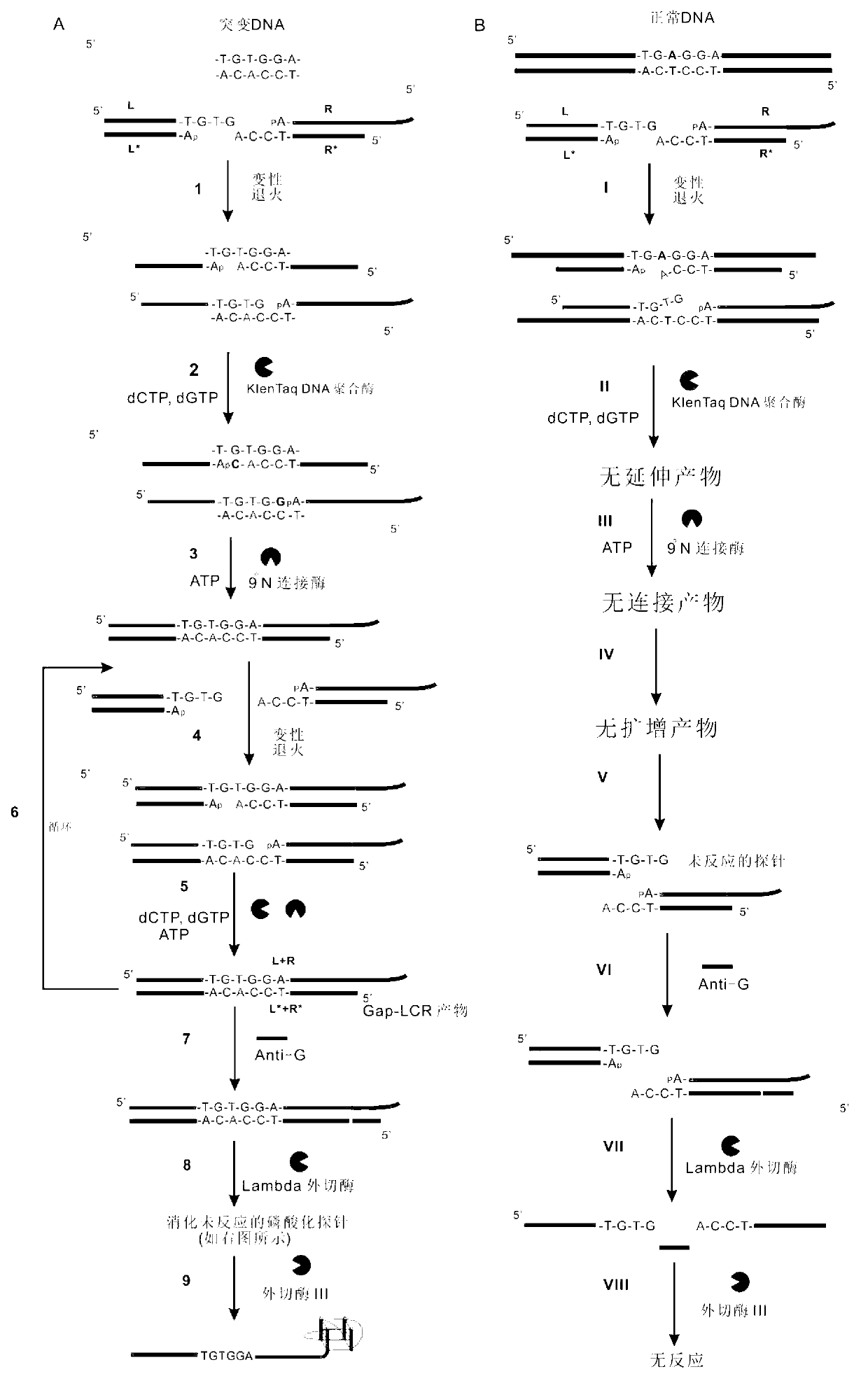
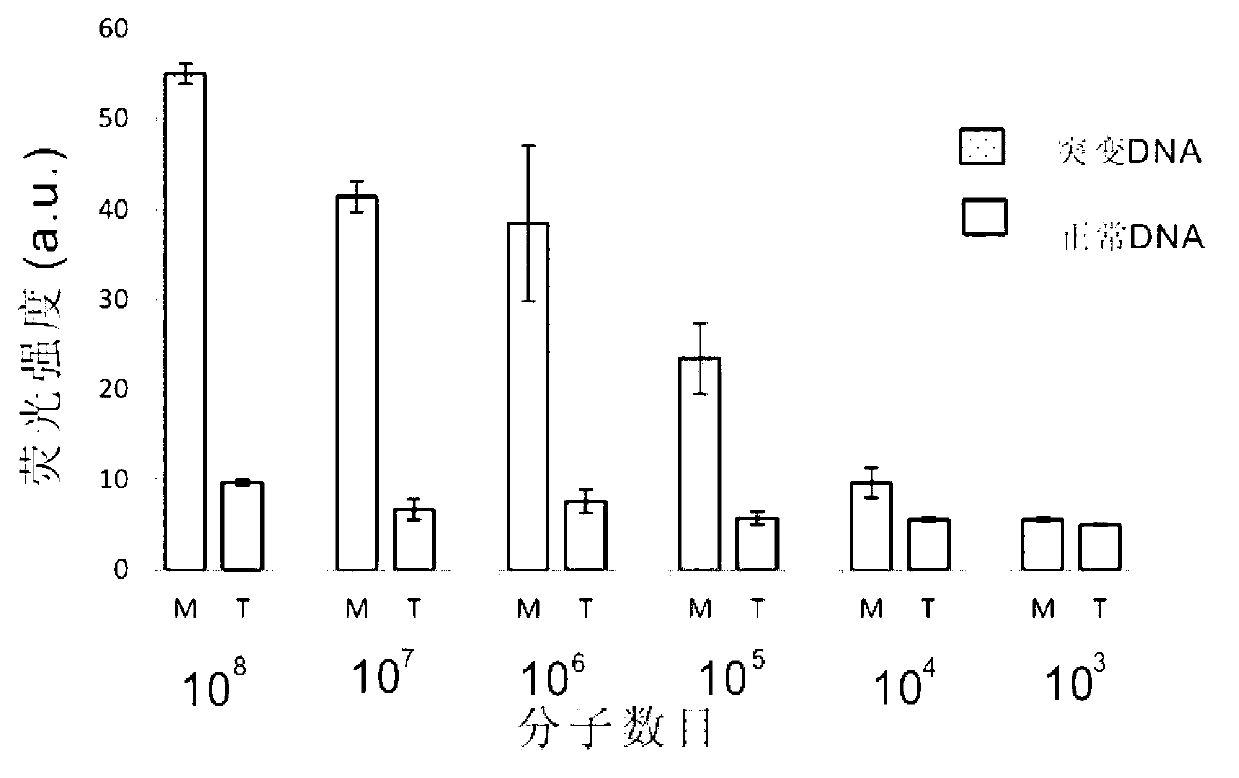
[0038] Example 1. Detection of sickle cell anemia gene DNAT-1 with group A (Probe L, ProbeL*, Probe R, Probe R*) oligonucleotide probes (mutant DNAT-1 is mutant DNA, normal DNAT-1 is normal DNA).
[0039] For the reaction steps to detect the sickle cell anemia gene, see figure 1 . Group A (Probe L, ProbeL*, Probe R, Probe R*) oligonucleotide probes are designed to detect the sickle cell anemia gene, in which the 3' end of the oligonucleotide probe Probe R is labeled with a porphyrin The DNAzyme sequence with peroxidase activity is used for signal detection; the sequence at the 5' end is a sequence that can form a complementarity with the sequence near the mutation site of the target gene to be detected, and is used for Gap-LCR amplification.
[0040] After adding group A oligonucleotide probes Probe L, ProbeL*, Probe R, Probe R* into the Gap-LCR system, under denaturing conditions, the double strand of the DNA T-1 to be tested and the probe (Probe L, ProbeL* , Probe R, Prob...
Embodiment 2
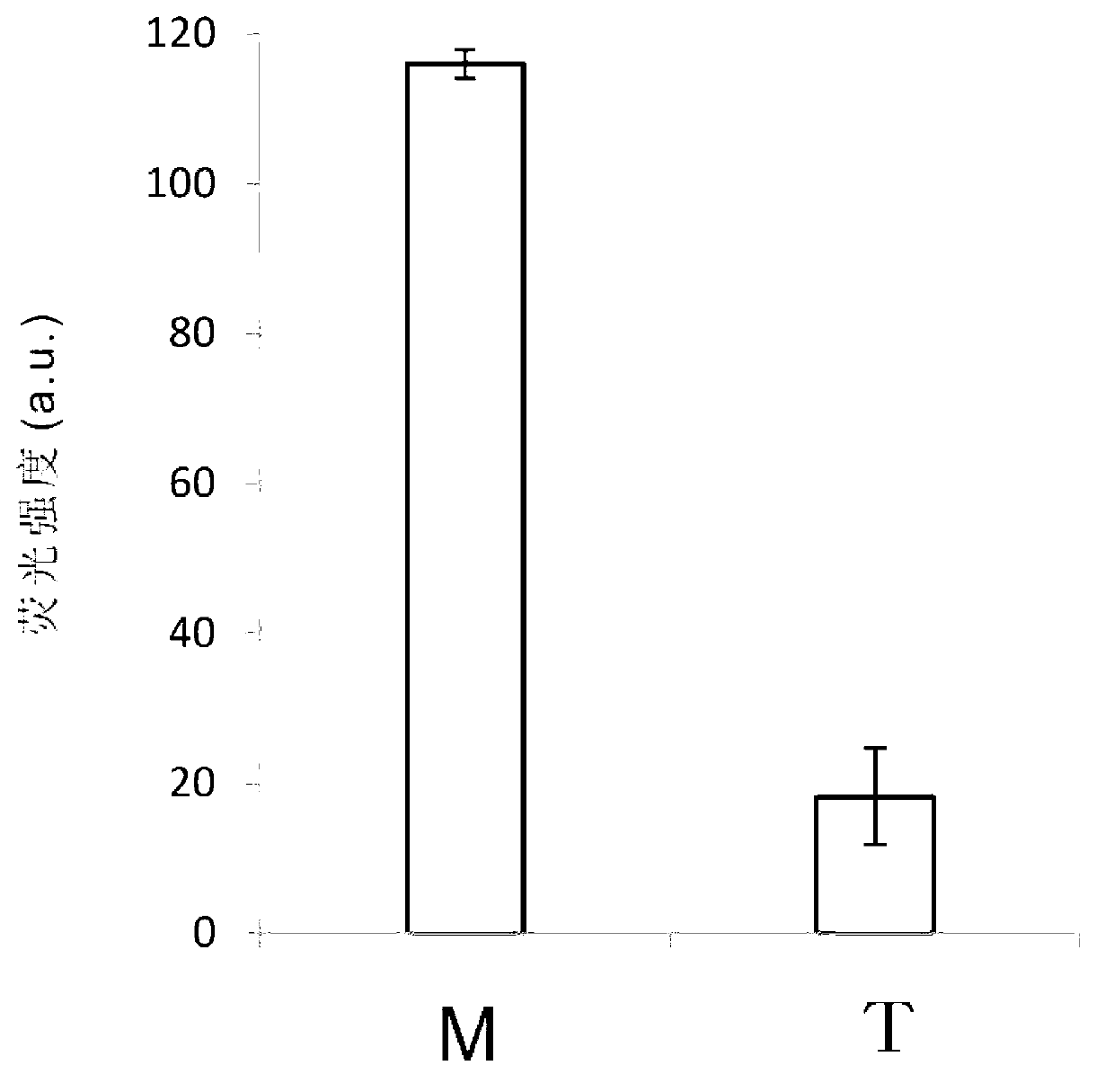
[0058] Example 2. Using group B (B1-B4) oligonucleotide probes to detect the mutation site 235delC in the neonatal deafness gene.
[0059] For the detection results of the mutation site 235delC in the neonatal deafness gene, see image 3 . Group B (B1-B4) oligonucleotide probes are designed to detect the mutation site 235delC in the neonatal deafness gene, in which the 3' end of the oligonucleotide probe B4 is labeled with a compound that can bind to porphyrin iron, etc. The DNAzyme sequence with peroxidase activity is used for signal detection; the sequence at the 5' end is a sequence that can form a complementary sequence with the sequence near the mutation site of the target gene to be detected, and is used for Gap-LCR amplification.
[0060] After adding group B oligonucleotide probes (B1-B4) into the Gap-LCR system, under denaturing conditions, the double-strand structure of the DNA T-1 to be tested and the double-strand structure of probe 1 are opened; Under the condit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com