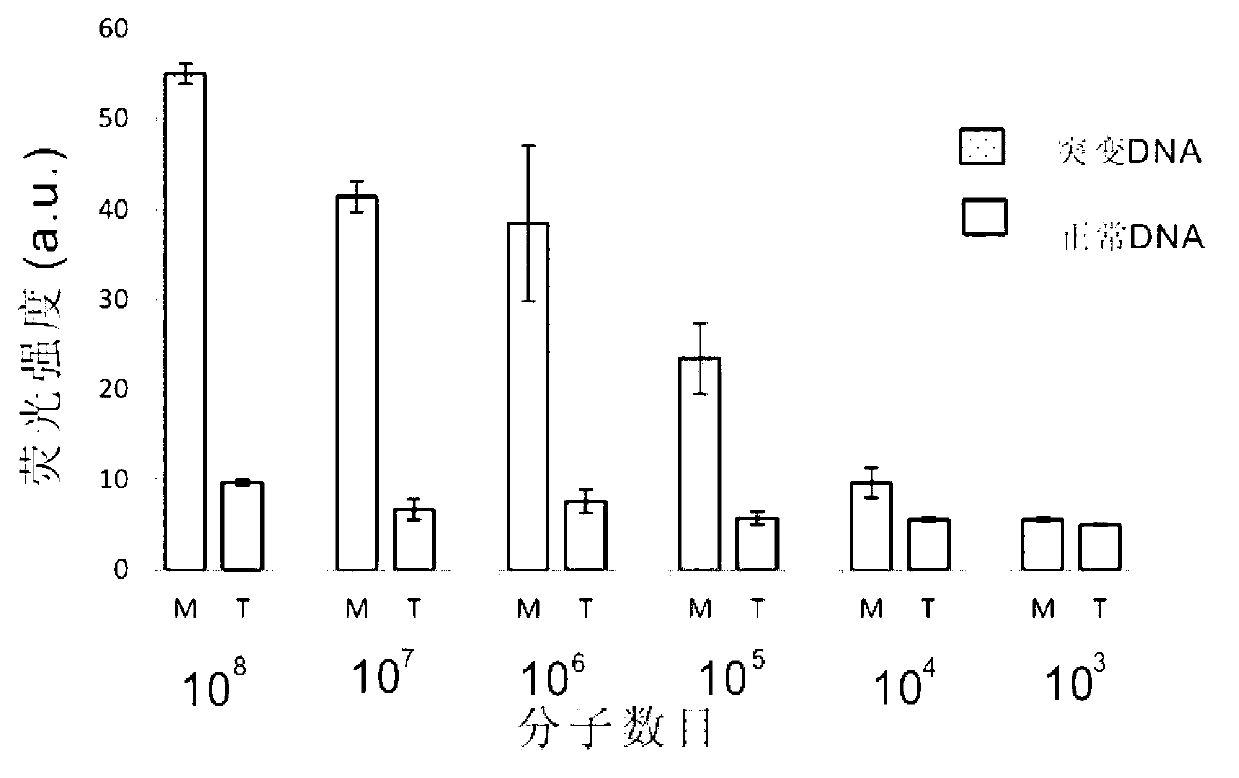
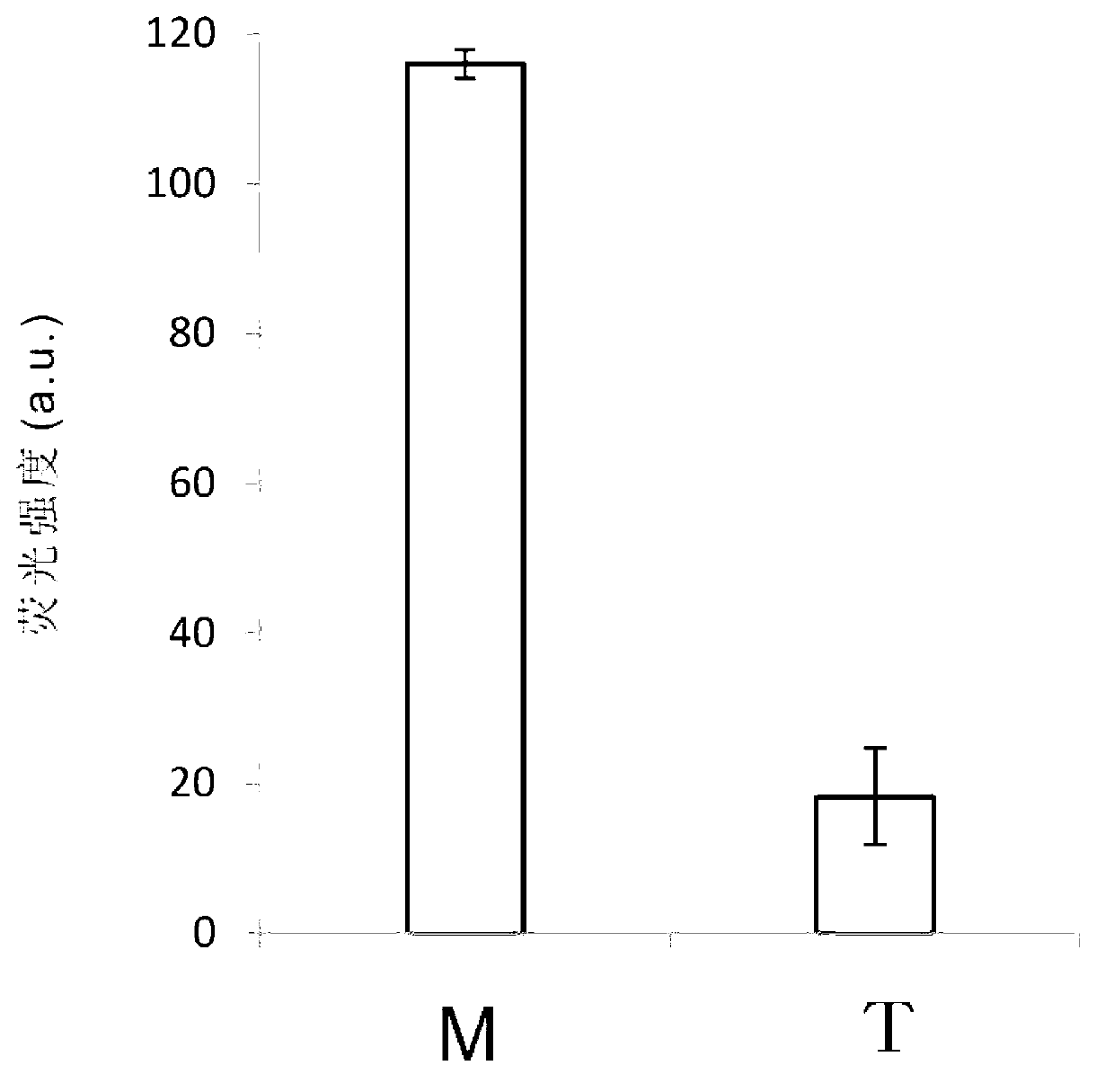
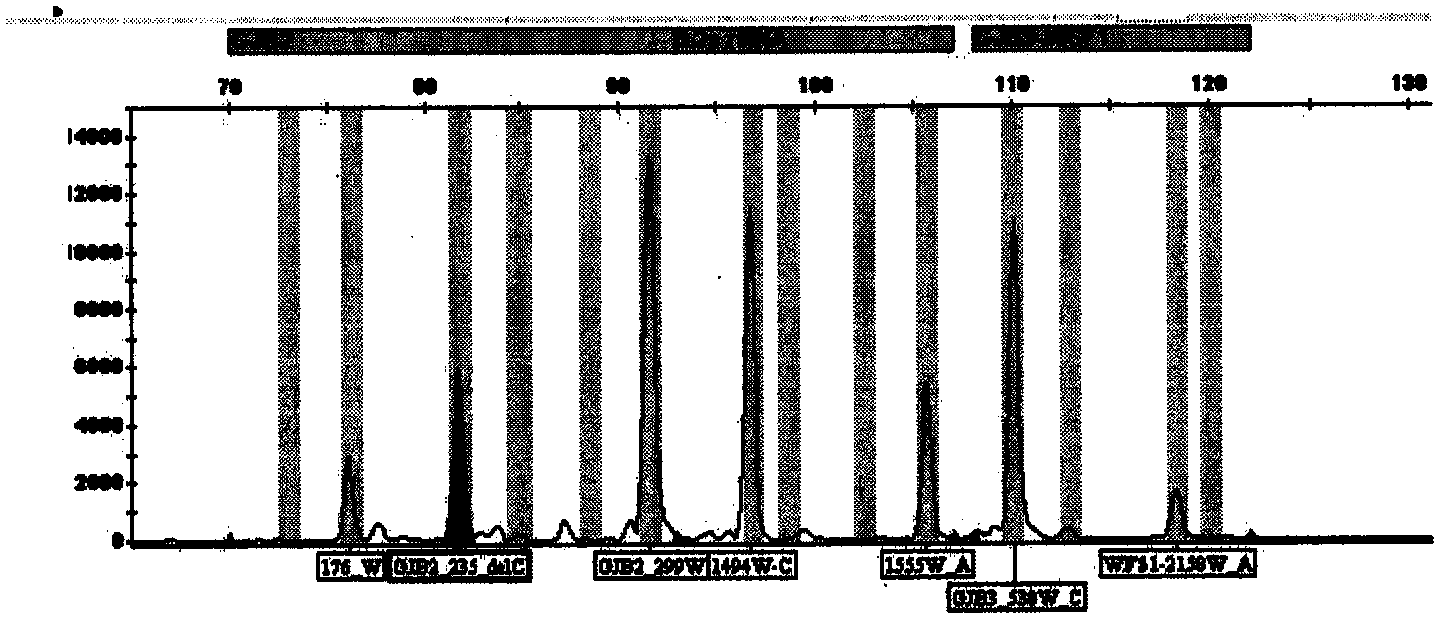
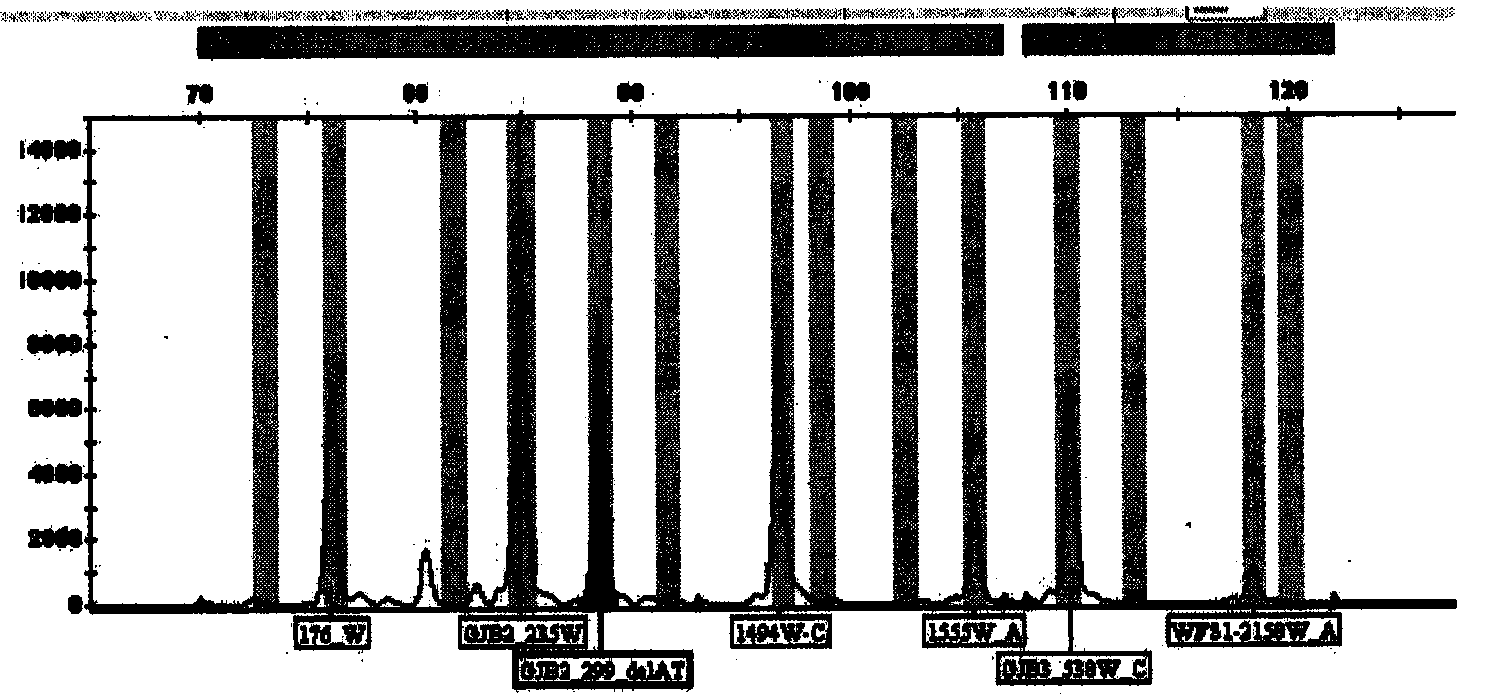
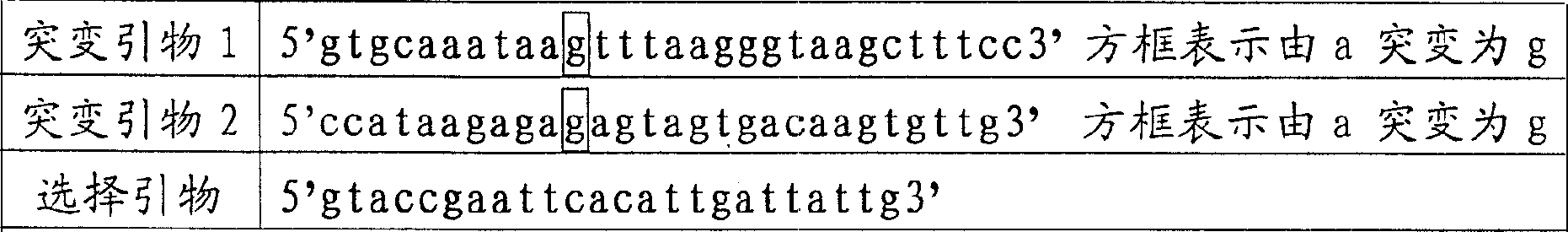Patents
Literature
30 results about "Ligase chain reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
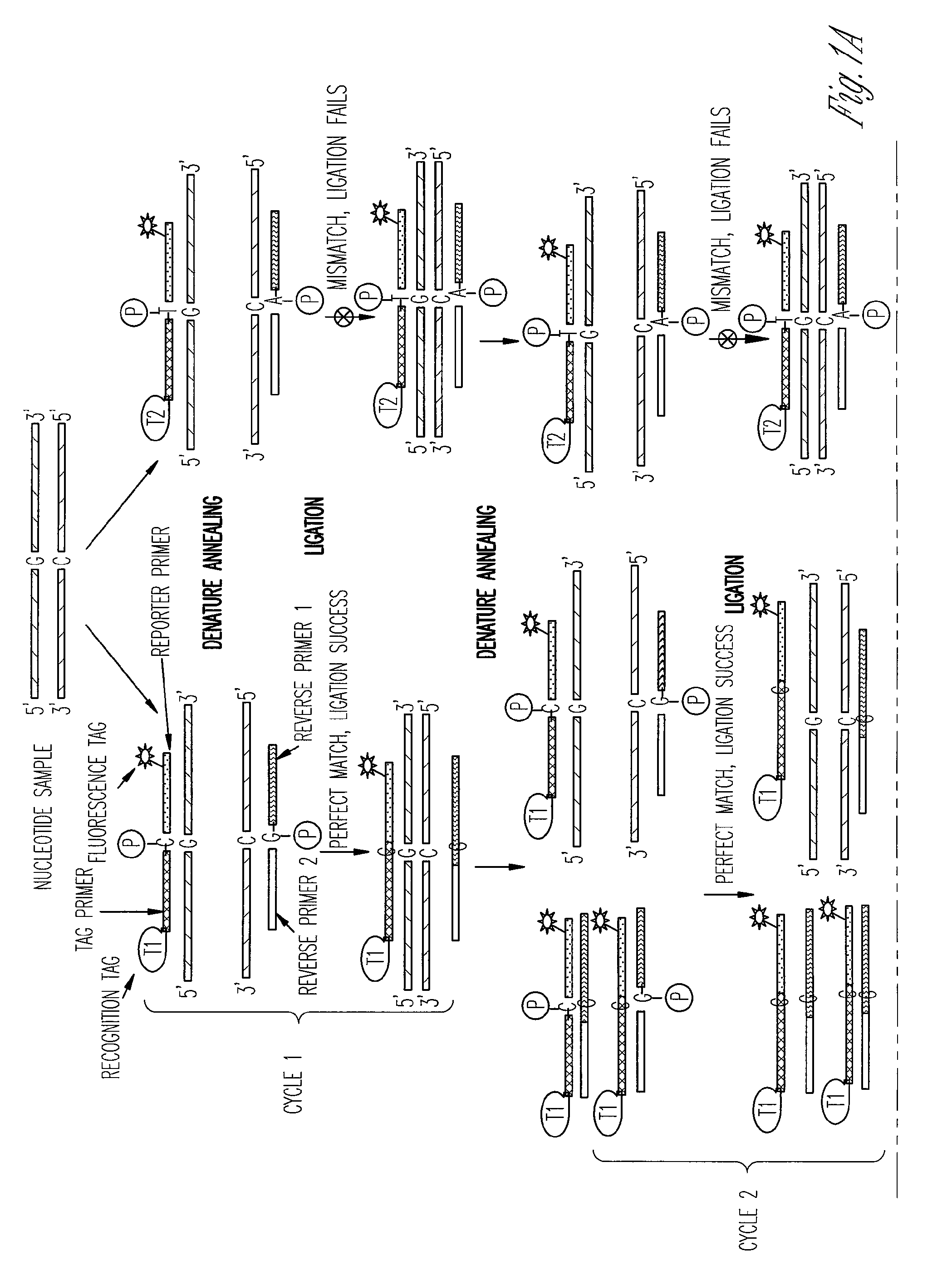
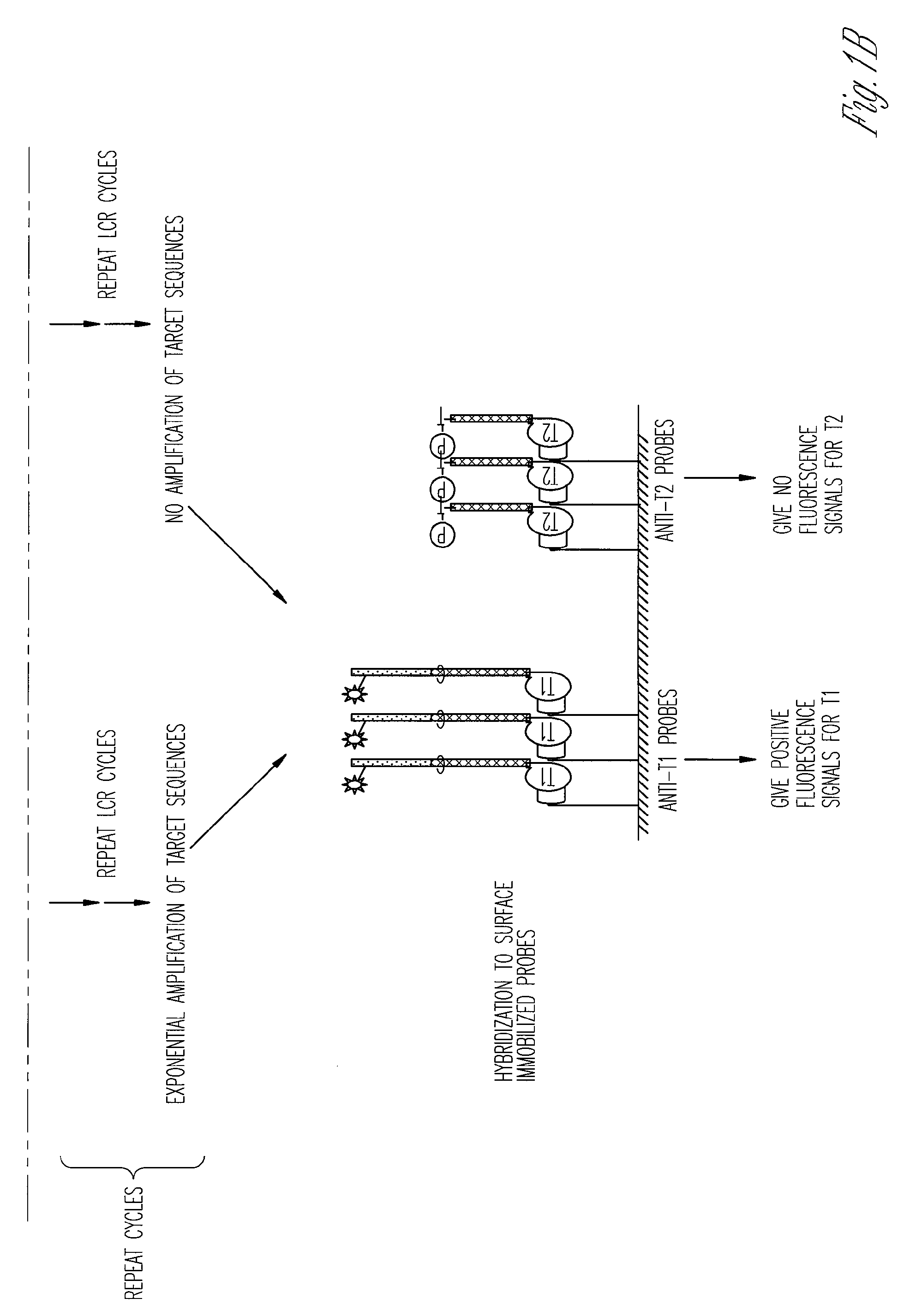
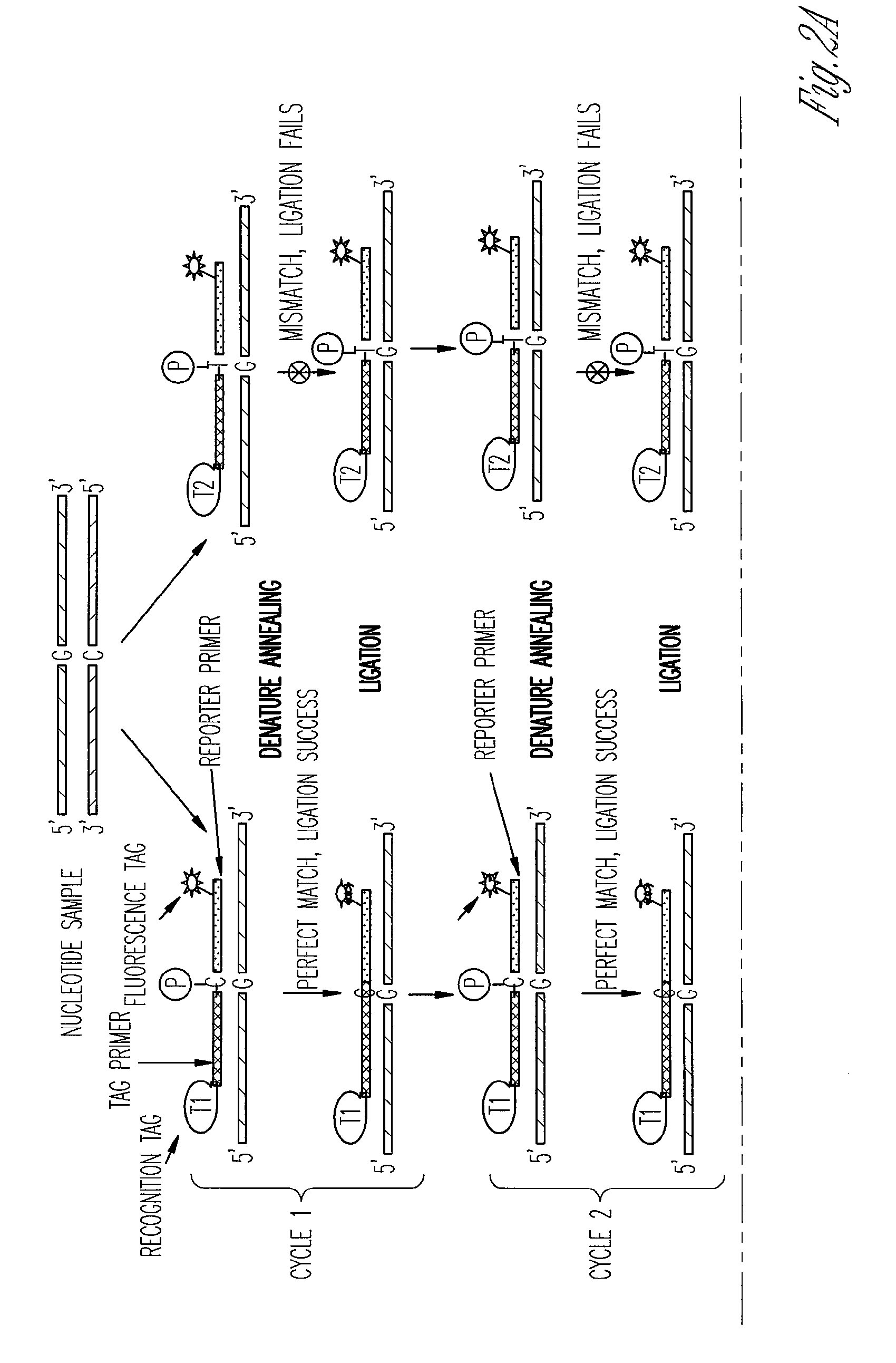
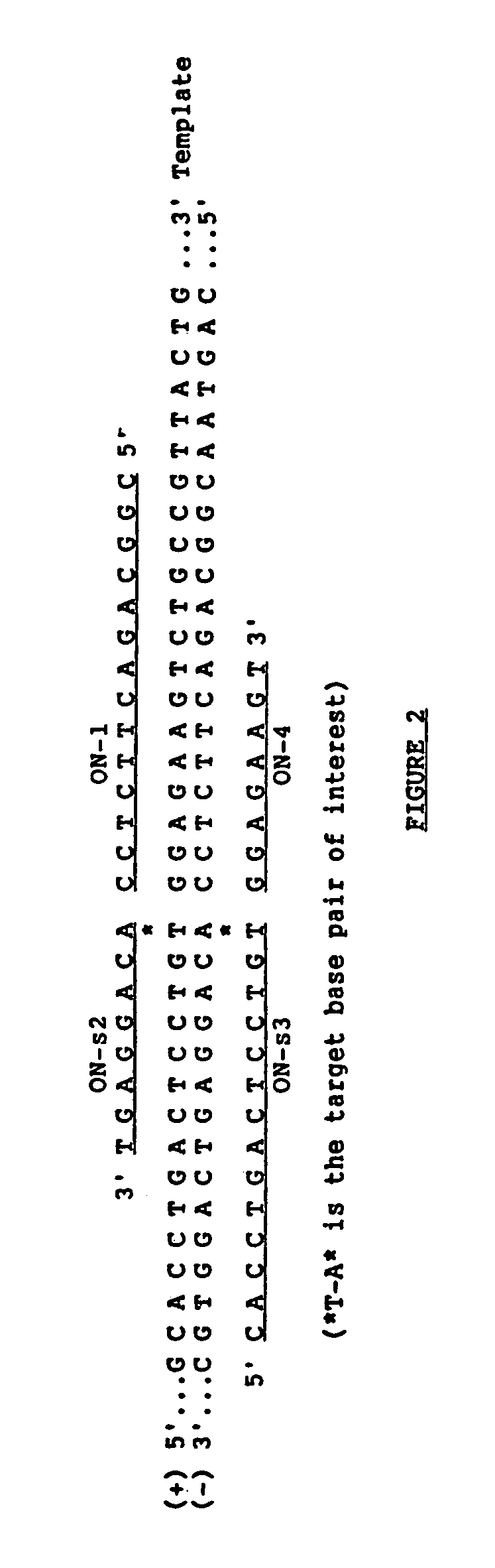
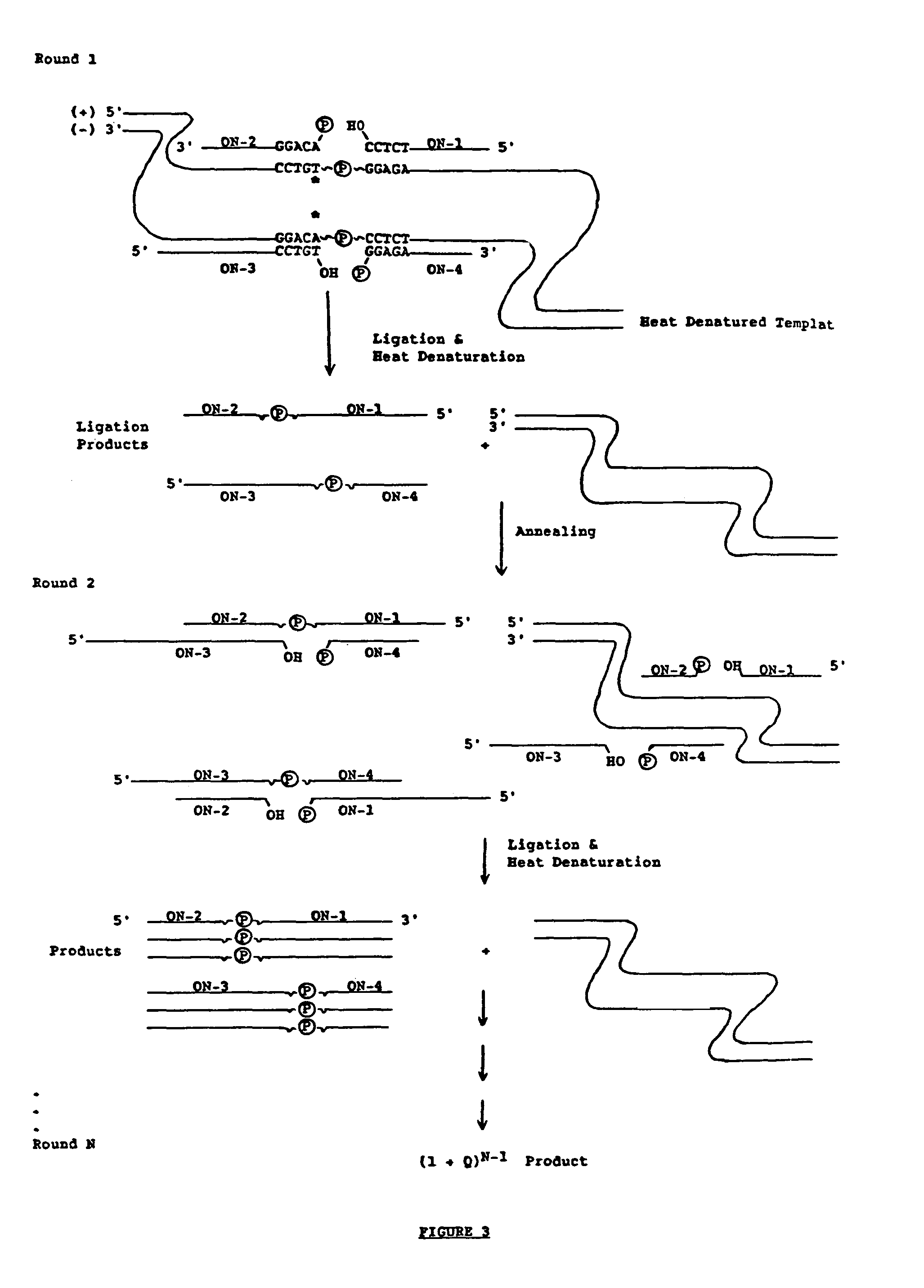
The ligase chain reaction (LCR) is a method of DNA amplification. The ligase chain reaction (LCR) is an amplification process that differs from PCR in that it involves a thermostable ligase to join two probes or other molecules together which can then be amplified by standard PCR cycling (Barany, 1991). Each cycle results in a doubling of the target nucleic acid molecule. A key advantage of LCR is greater specificity as compared to PCR.Thus, LCR requires two completely different enzymes to operate properly: ligase, to join probe molecules together, and a thermostable polymerase (e.g., Taq polymerase) to amplify those molecules involved in successful ligation. The probes involved in the ligation are designed such that the 5′ end of one probe is directly adjacent to the 3′ end of the other probe, thereby providing the requisite 3′-OH and 5′-PO4 group substrates for the ligase.
Digital microfluidics based apparatus for heat-exchanging chemical processes
ActiveUS20110048951A1Low costEasy to detectTelevision system detailsSludge treatmentElectricityEngineering
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for performing heat-exchanging reactions on an electro wetting-based micro fluidic device. The apparatus provides one or multiple thermal contacts to an electro wetting-based device, where each thermal contact controls the part of the electro wetting-based device it communicates with to a designed temperature. The electrowetting-based device can be used to create, merge and mix liquids in the format of droplets and transport them to different temperature zones on the micro fluidic device. The apparatus and methods of the invention can be used for heat-exchanging chemical processes such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and other DNA reactions, such as ligase chain reactions, for DNA amplification and synthesis, and for real-time PCR.
Owner:DIGITAL BIOSYST
Electrochemical denaturation and annealing of nucleic acid
InactiveUS6197508B1Ensure sufficient separationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMethyl ViologenDouble stranded
A process is described for denaturing native double-stranded nucleic acid material into its individual strands in an electrochemical cell. The process disclosed is an electrical treatment of the nucleic acid with a voltage applied to the nucleic acid material by an electrode. The process may also employ a promoter compound such as methyl viologen to speed denaturation. The process may be used in the detection of nucleic acid by hybridizing with a labelled probe or in the amplification of DNA by a polymerase chain reaction or ligase chain reaction. A process is described for annealing complementary strands of nucleic acid by application of an electrical voltage.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
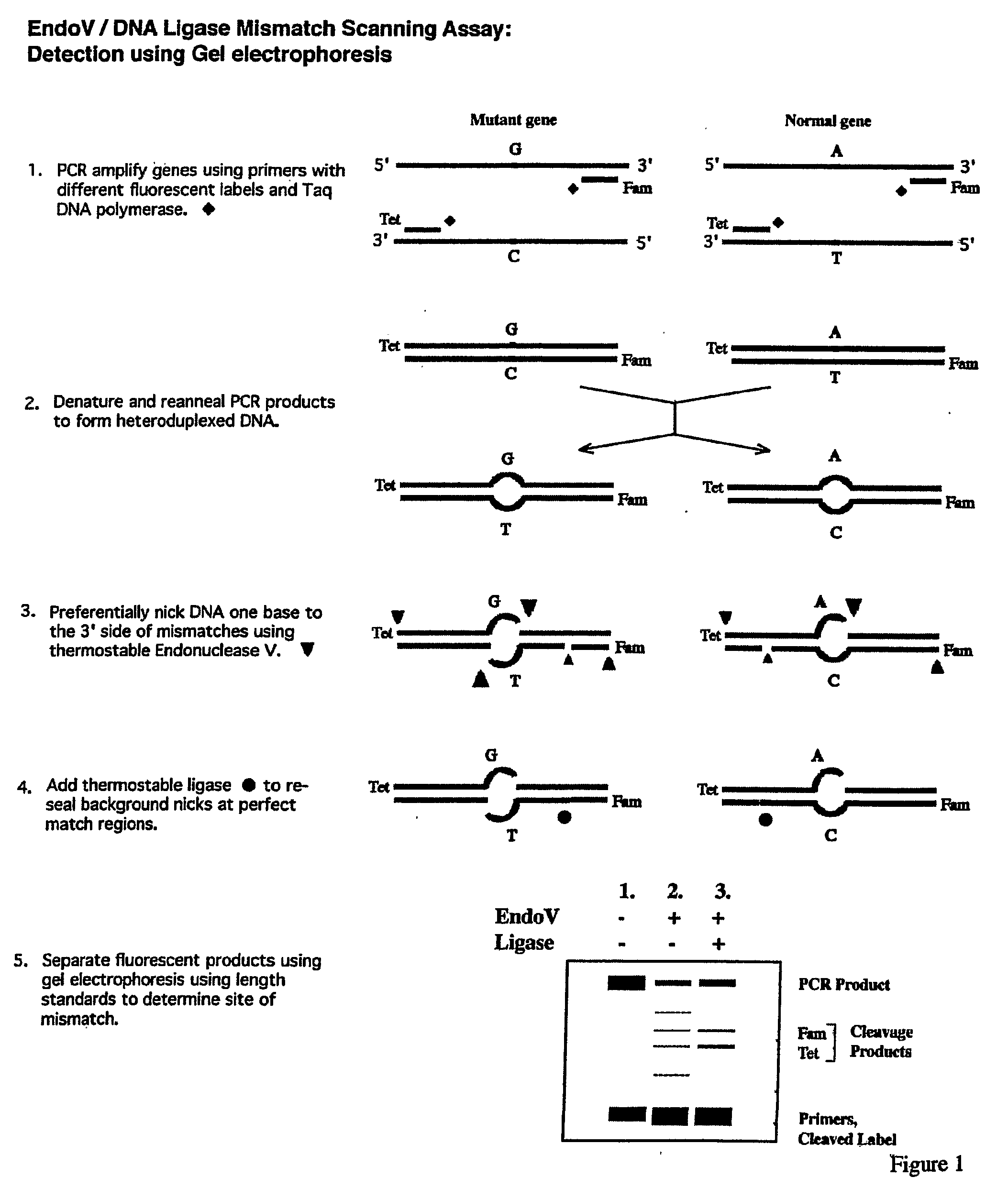
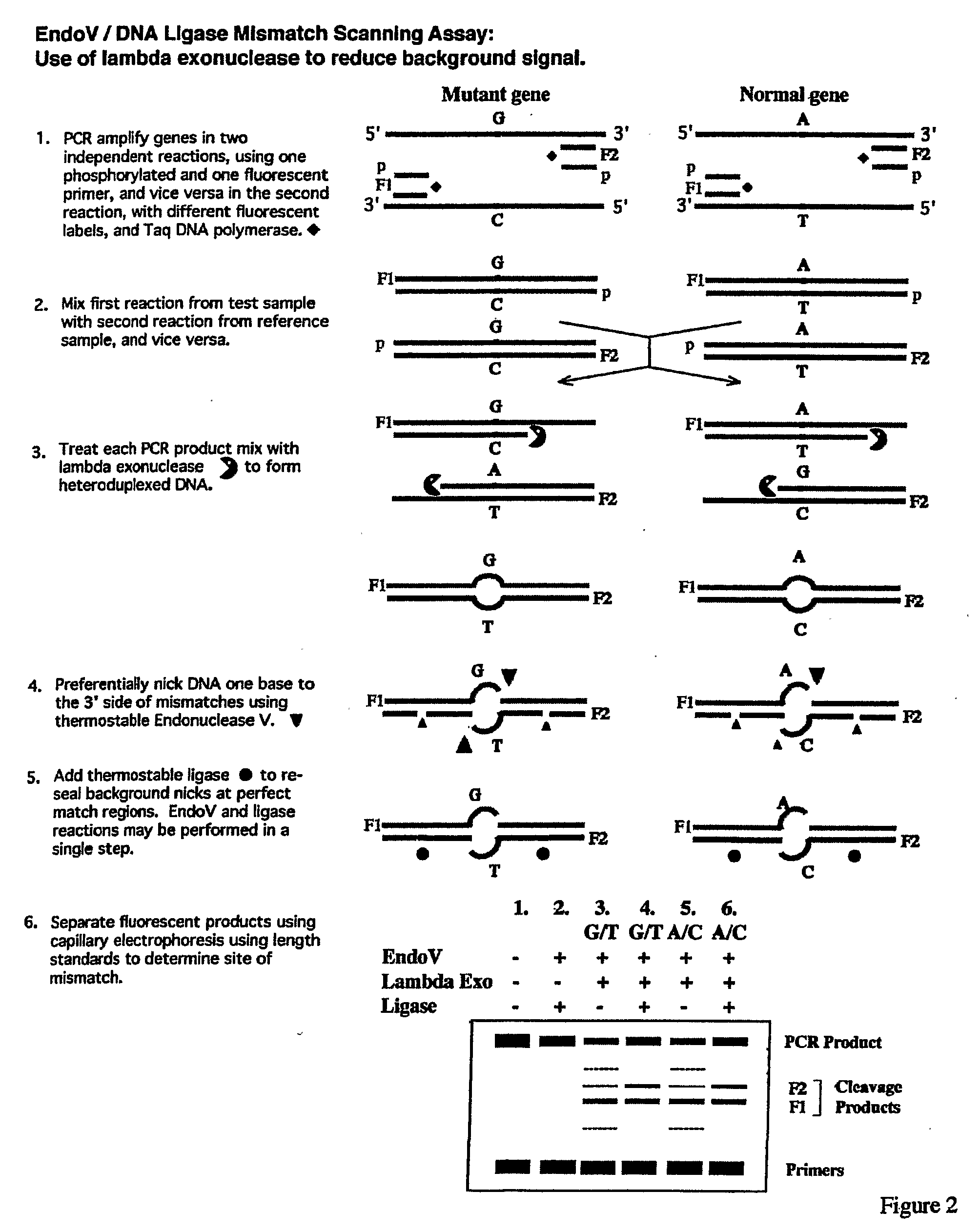
Detection of nucleic acid differences using endonuclease cleavage/ligase resealing reactions and capillary electrophoresis or microarrays
InactiveUS20090123913A1Reduce noiseObstruction is producedMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsHeteroduplexA-DNA
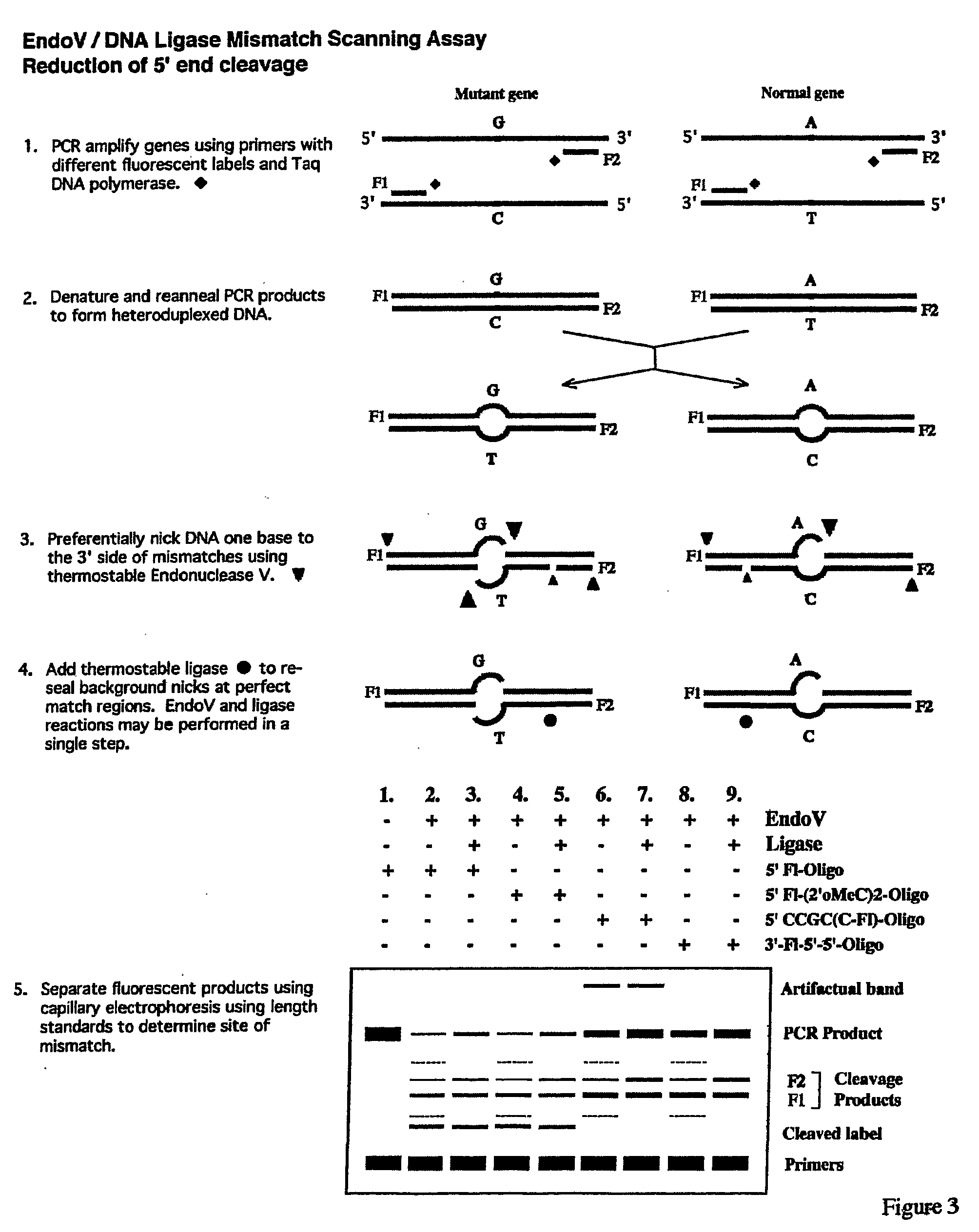
The present invention is directed to various methods for detecting DNA sequence differences, including single nucleotide mutations or polymorphisms, one or more nucleotide insertions, and one or more nucleotide deletions. Labeled heteroduplex PCR fragments containing base mismatches are prepared. Endonuclease cleaves the heteroduplex PCR fragments both at the position containing the variation (one or more mismatched bases) and, to a lesser extent, at non-variant (perfectly matched) positions. Ligation of the cleavage products with a DNA ligase corrects non-variant cleavages and thus substantially reduces background. This is then followed by a detection step in which the reaction products are detected, and the position of the sequence variations are determined.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Method for Stabilizing Assay Reagents, Reagent Container with Stabilized Assay Reagents and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20070243601A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReverse transcriptasePolymerase L
This invention relates to a reagent container for detection and / or quantitation of at least one biological or chemical analyte from a sample, said reagent container comprising an inner surface enclosing a volume, wherein volume analytical reactions of at least one analysis for detection and / or quantitation of at least one analyte take place, and at least two reagents of an analysis of an analyte have been dried onto said inner surface and at least a first said reagent has been dried onto a first area of the inner surface distinctly separate, i.e. without any overlap, from a second area of the inner surface onto which at least a second said reagent has been dried. Characteristic for the reagent container is that the first reagent and the second reagent form a pair wherein the first reagent is an enzyme and the second reagent is a substrate of said enzyme, and said pair consists of a nucleic acid polymerase and substrate thereof. This invention also relates to a method for stabilising onto an inner surface of a reagent container dried assay reagents for the detection and / or quantitation of a biological or chemical analyte from a sample, said method comprising the steps of dispensing at least two reagents, a first reagent and a second reagent, needed in the detection of the analyte onto the inner surface of the reagent container; and removing excess water from the reagents, wherein first reagent is dispensed onto a first area of the inner surface distinctly separate, i.e. without any overlap, from a second area of the inner surface onto which the second reagent is dispensed. Characteristic for the method is that the first reagent and the second reagent form a pair wherein the first reagent is an enzyme and the second reagent is a substrate of said enzyme, and said pair consist of a nucleic acid polymerase and substrate thereof. This invention further relates to the use of the reagent container to perform an assay selected from the group consisting of a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay, an assay that utilizes a reverse transcriptase, a reverse transriptase polymerase chain reaction, an immuno-PCR assay, a nucleic acid sequence based assay (NASBA), a proximity ligation assay, a ligase chain reaction (LCR) assay, a rolling circle amplification (RCA) assay, and a strand displacement amplification (SDA) assay.
Owner:UNIOGEN OY
Digital microfluidics based apparatus for heat-exchanging chemical processes
InactiveCN101679932AImprove scalabilityEasy to detectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityEngineering
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for performing heat-exchanging reactions on an electro wetting-based micro fluidic device. The apparatus provides one or multiple thermal contacts to an electro wetting-based device, where each thermal contact controls the part of the electro wetting-based device it communicates with to a designed temperature. The electrowetting-based device can be used to create, merge and mix liquids in the format of droplets and transport them to different temperature zones on the micro fluidic device. The apparatus and methods of the invention can be used for heat-exchanging chemical processes such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and other DNA reactions, such as ligase chain reactions, for DNA amplification and synthesis, and for real-time PCR.
Owner:DIGITAL BIOSYST
Detection method for single nucleotide polymorphism
InactiveCN103103283AHas a catalytic functionHas peroxidase activityMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePhosphorylation
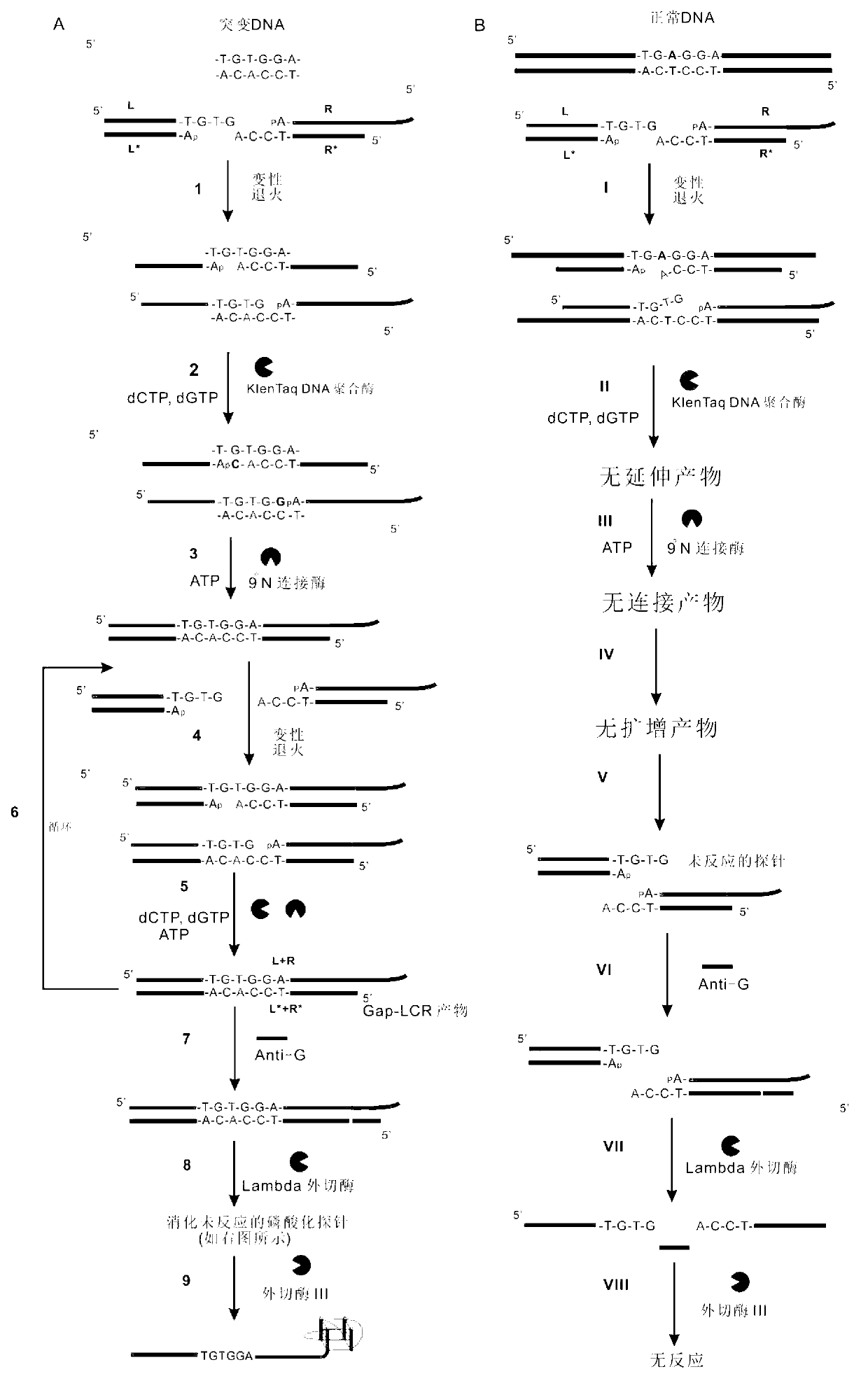
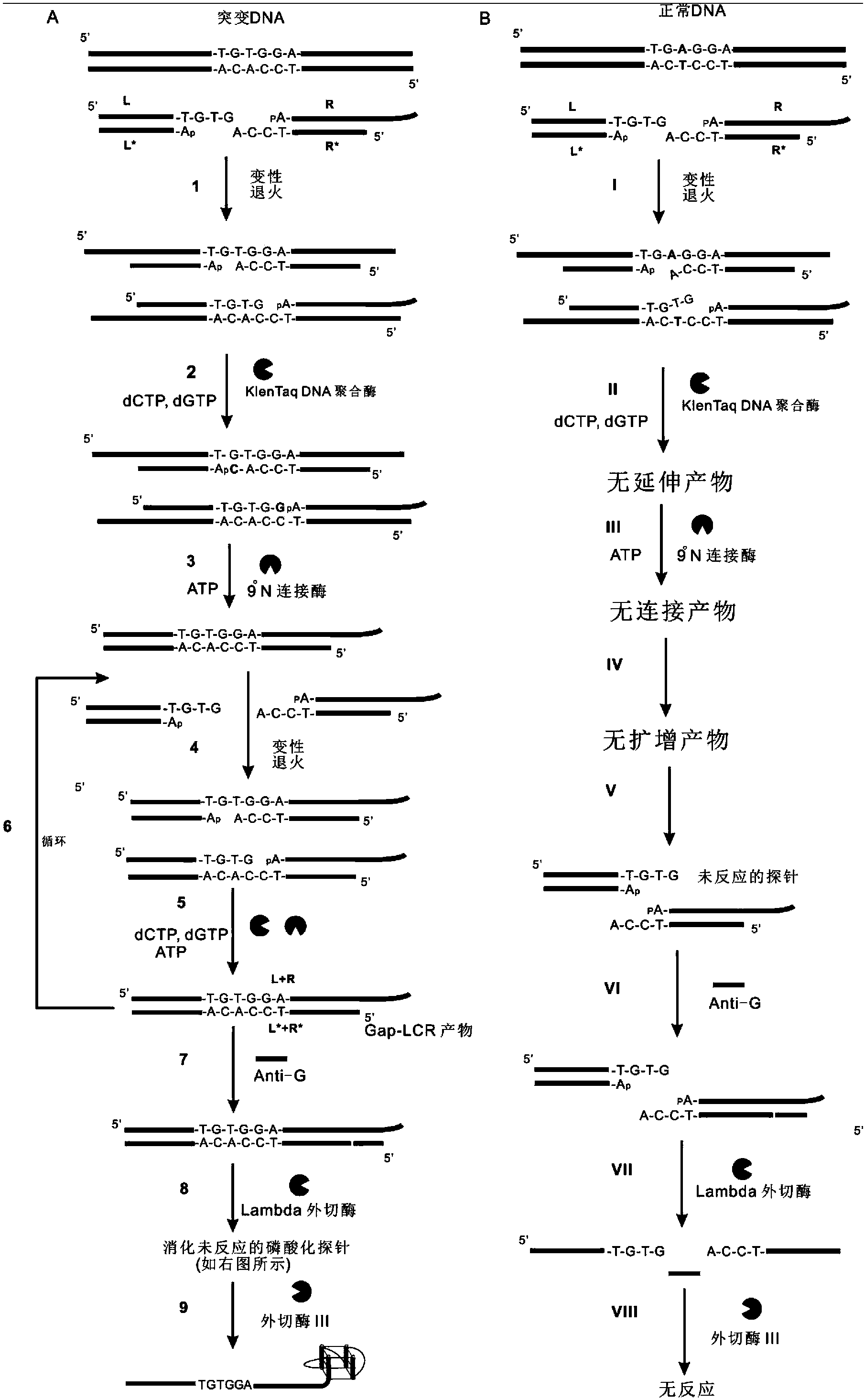
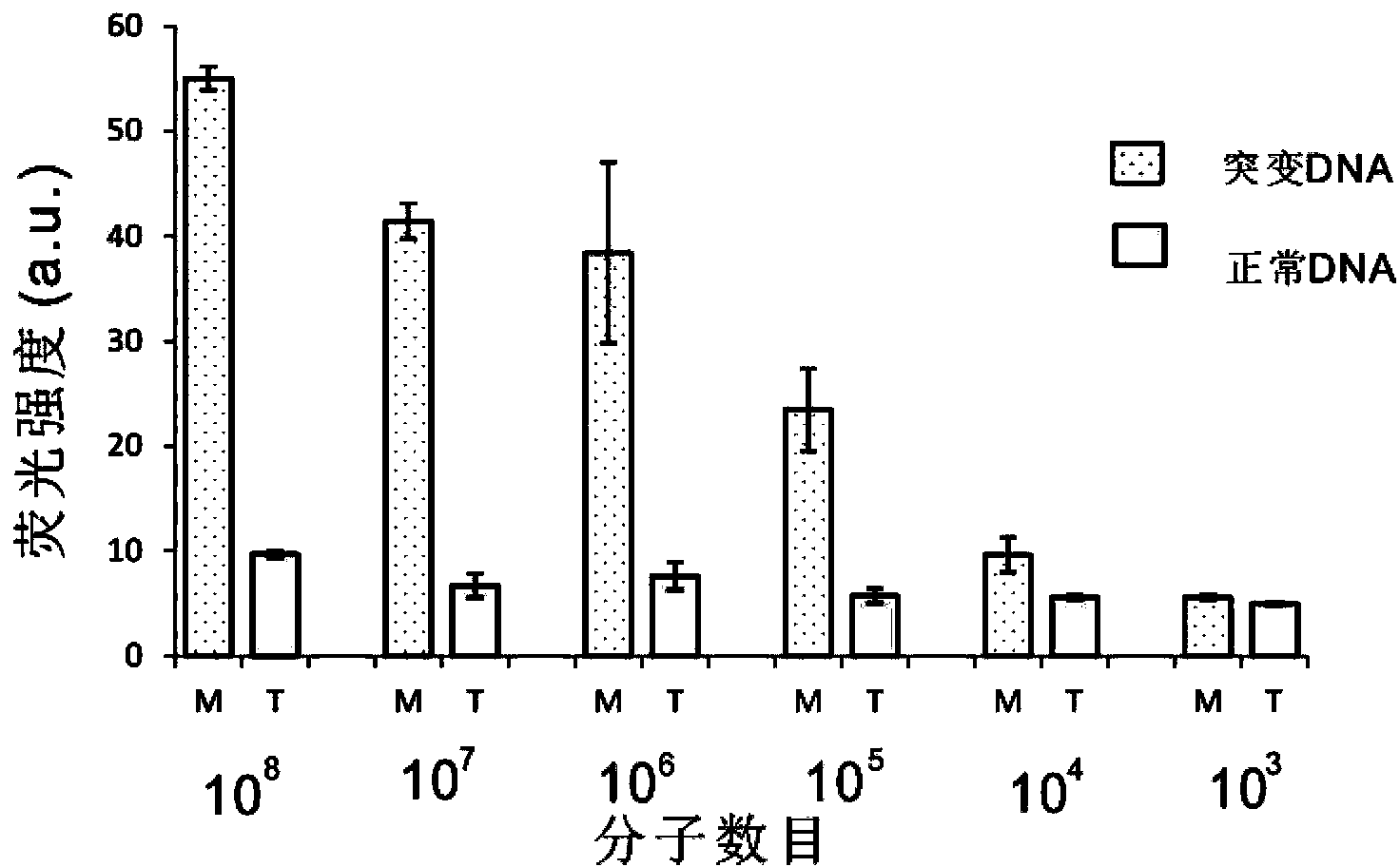
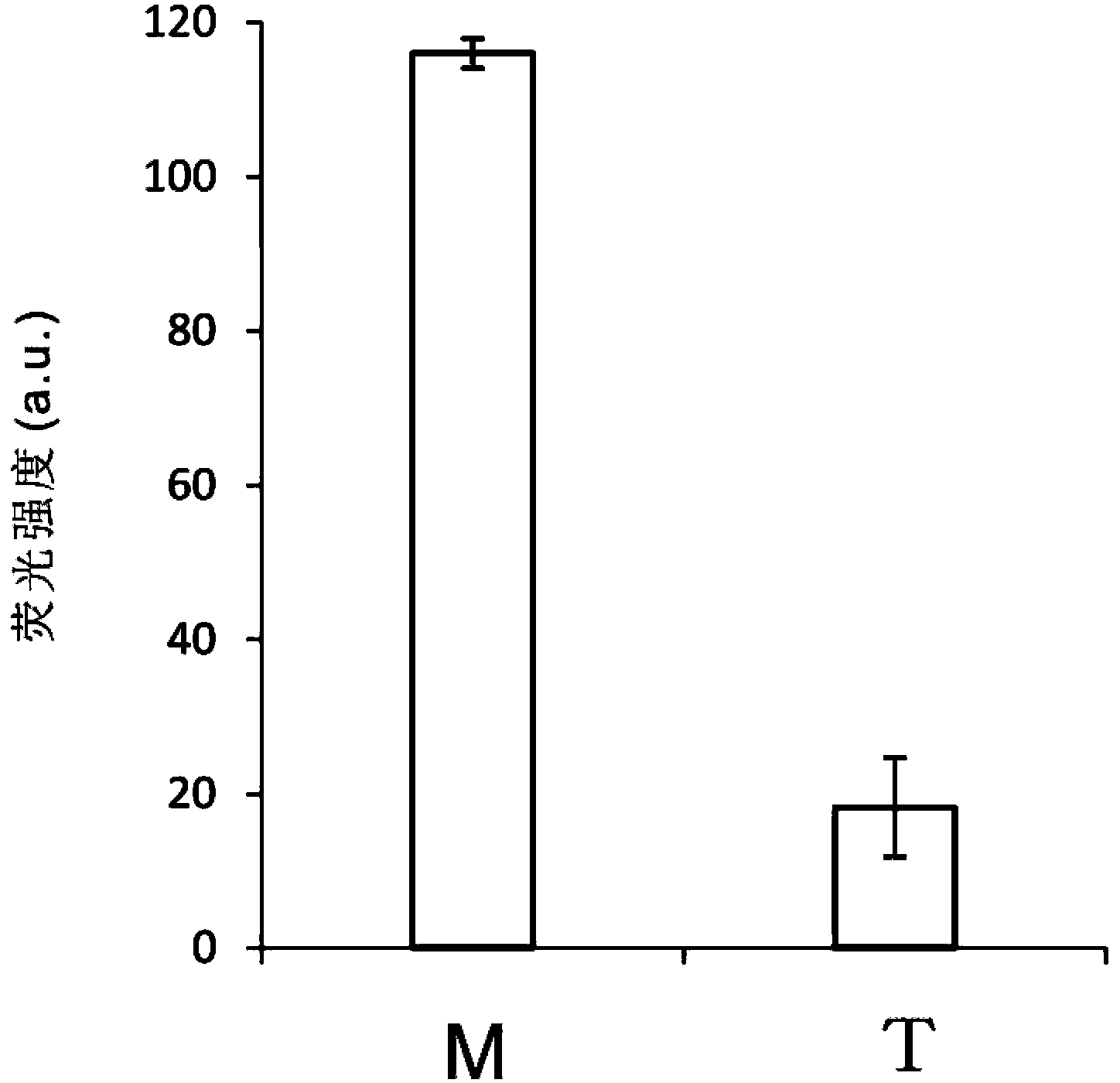
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, relates to analysis and detection for single nucleotide polymorphism, and in particular relates to a universal detection method. The detection method comprises the steps of amplifying target DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) by gap-ligase chain reaction, introducing a DNAzyme sequence into a ligation product, degrading a phosphorylated probe which does not participate in the ligation reaction by Lambda excision enzyme, and releasing DNAzyme by excision enzyme III. The detection method is characterized in that a DNAzyme probe is combined with a Gap-LCR (ligase chain reaction) probe, and is characterized by comprising the following steps of: adding a section of DNAzyme sequence into a phosphorylated probe to be connected in an LCR system, adding an Anti-G sequence into a system (in complementary pairing with a DNAzyme sequence part in the probe) after the Gap-LCR amplification reaction stops, degrading a 5-end phosphorylated DNA probe by the Lambda excision enzyme, and releasing the DNAzyme in the ligation product by the excision enzyme III, thereby qualitatively and quantitatively detecting the SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) due to the characteristics of the DNAzyme. The method is simple, convenient, practical and economical, and is widely applicable to the detection of various single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
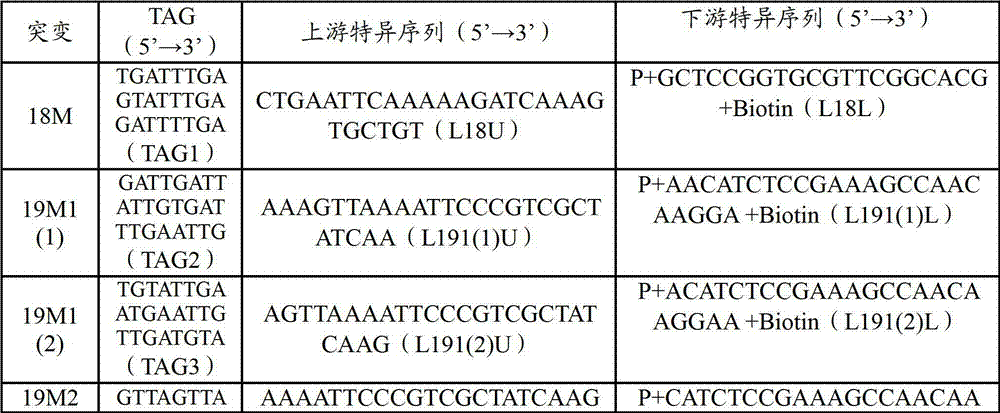
Multiple PCR-LDR (polymerase chain reaction-ligase detection reaction) detection kit for multiple deaf susceptibility genes with high specificity at 14 sites
ActiveCN104313159AAchieving Simultaneous DetectionRealize identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsGene Mutant
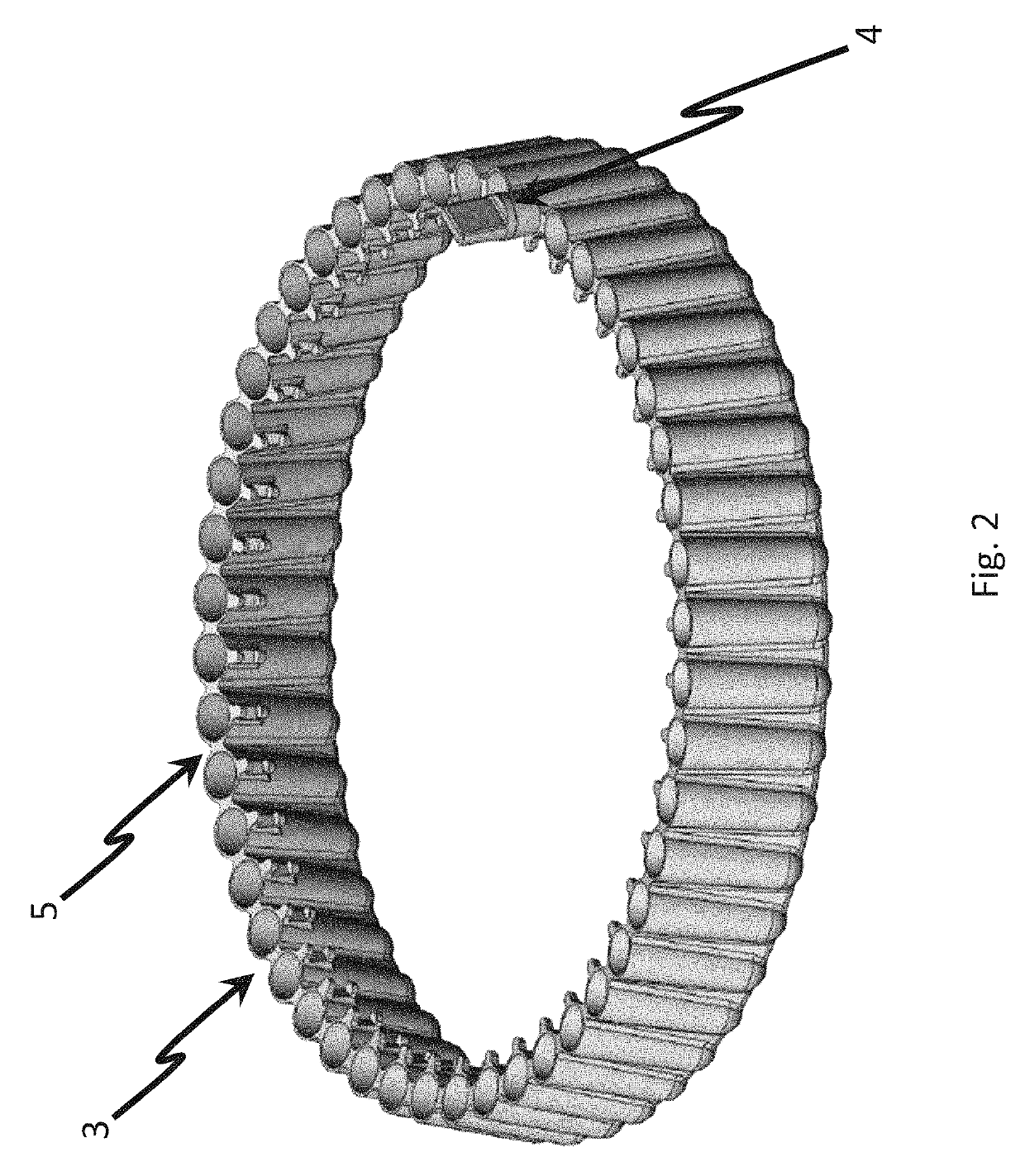
The invention provides a PCR-LDR (polymerase chain reaction-ligase detection reaction) detection kit for simultaneously detecting 14 deaf susceptibility genes. The kit comprises a packaging box body (1) and PCR amplification and LDR reaction reagents (2)-(5), wherein eight pairs of PCR primers and 16 groups of probes are contained, wherein two groups of universal probes and 14 groups of detection probes are contained. The method is high in sensitivity and clear and accurate to judge. Compared with the conventional sequencing technique, the kit can realize high throughput screening of 14 key deaf gene mutant diagnosing results at one time, so that the kit has the advantages of being economical, efficient, high in accuracy and the like.
Owner:步迅
A kind of detection method of telomerase activity
ActiveCN102260739AAvoid False Positive ResultsEasy to expandMicrobiological testing/measurementTelomeraseFluorescence
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, specifically to a telomerase activity detection method. The detection method comprises the following steps of: acquiring active telomerase from a sample to be measured, extending TS primers to obtain a telomerase extension product, using the telomerase extension product as a template, carrying out gap-ligase chain reaction amplification in the presence of four primers to obtain an amplification product, mixing the amplification product and a molecular beacon to react, and carrying out a fluorescence detection to obtain the telomerase activity. The detection method provided by the invention has high sensitivity and good specificity, and can be used to effectively detect the activity of telomerase in the sample to be measured.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Ultrasensitive colorimetric sensing detection method for determining ochratoxin A
InactiveCN107723347ARealize detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMagnetite NanoparticlesA-DNA
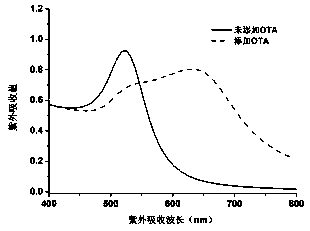
The invention relates to an ultrasensitive colorimetric sensing detection method for determining ochratoxin A, belonging to the field of biological detection. The method comprises the steps of modifying an ochratoxin A aptamer by virtue of magnetic nanoparticles, forming a partially hybridized DNA double-chain structure by virtue of the magnetic nanoparticles modified aptamer and partially complementary DNA molecules, preparing a DNA modified gold nanoparticle probe, and constructing an ochratoxin A colorimetric sensor. According to the method, by virtue of a specific recognition function of the ochratoxin A aptamer to ochratoxin A molecules, and the assembling degrees of gold nanoparticles are differentiated through ligase chain reaction when ochratoxins A with different concentrations exist, so that different color gradients are formed, and the target ochratoxin A is detected by determining the change of an ultraviolet absorption value after the reaction. The method is high in detection sensitivity, low in detection limit and good in specificity, a detection method is easy to observe, and the effective method is provided for the trace detection of the ochratoxin A.
Owner:樊之雄
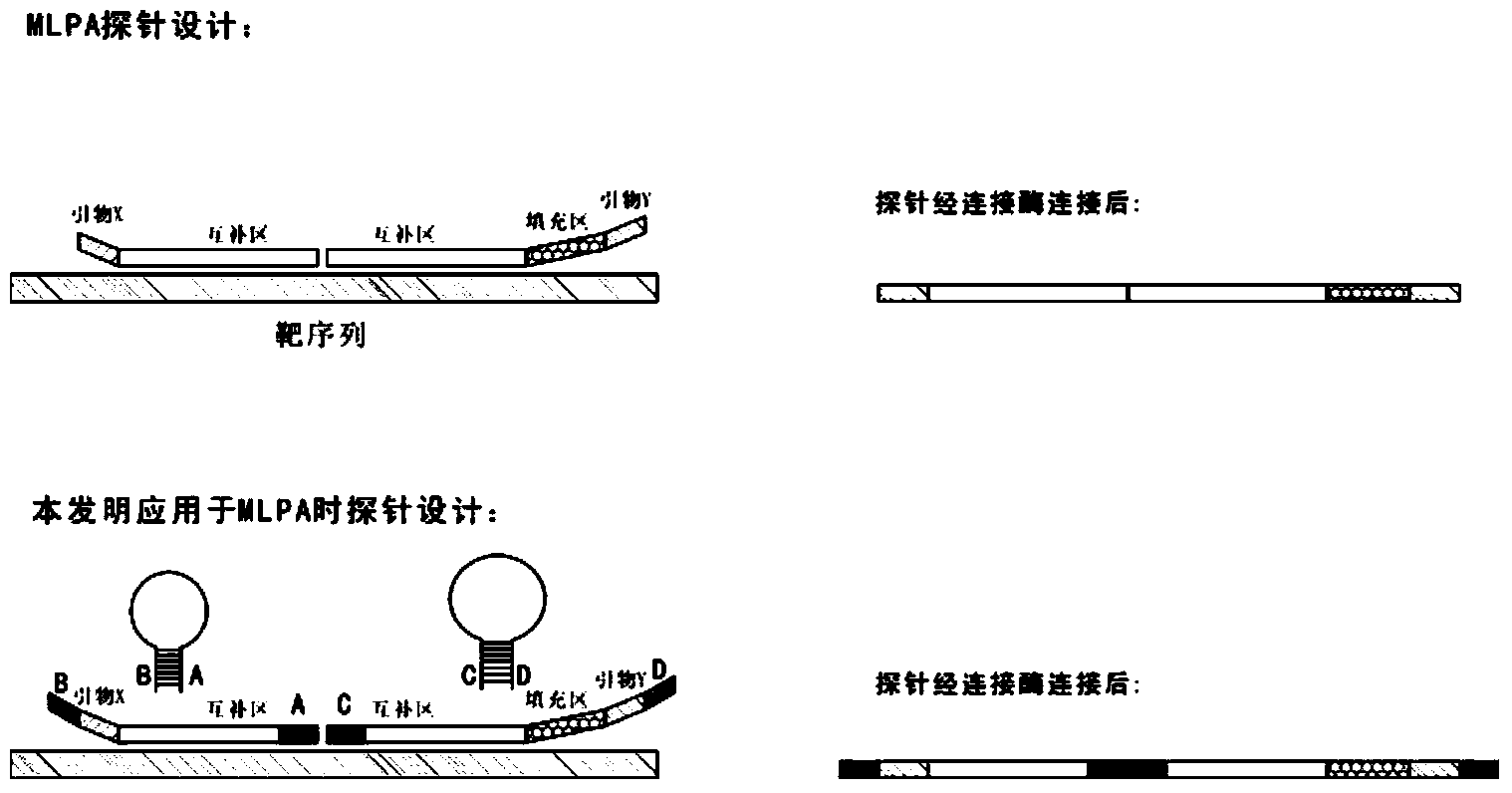
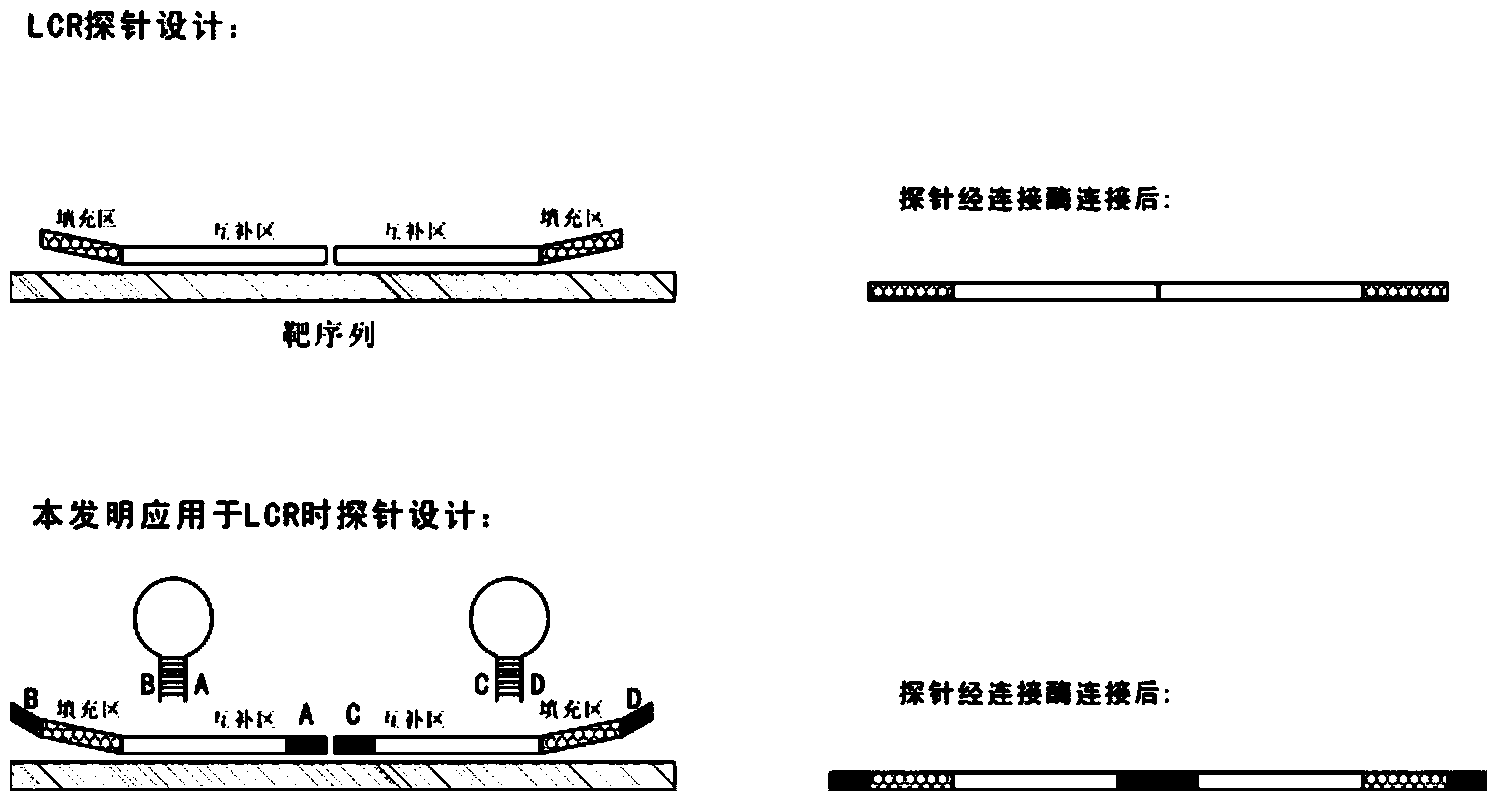
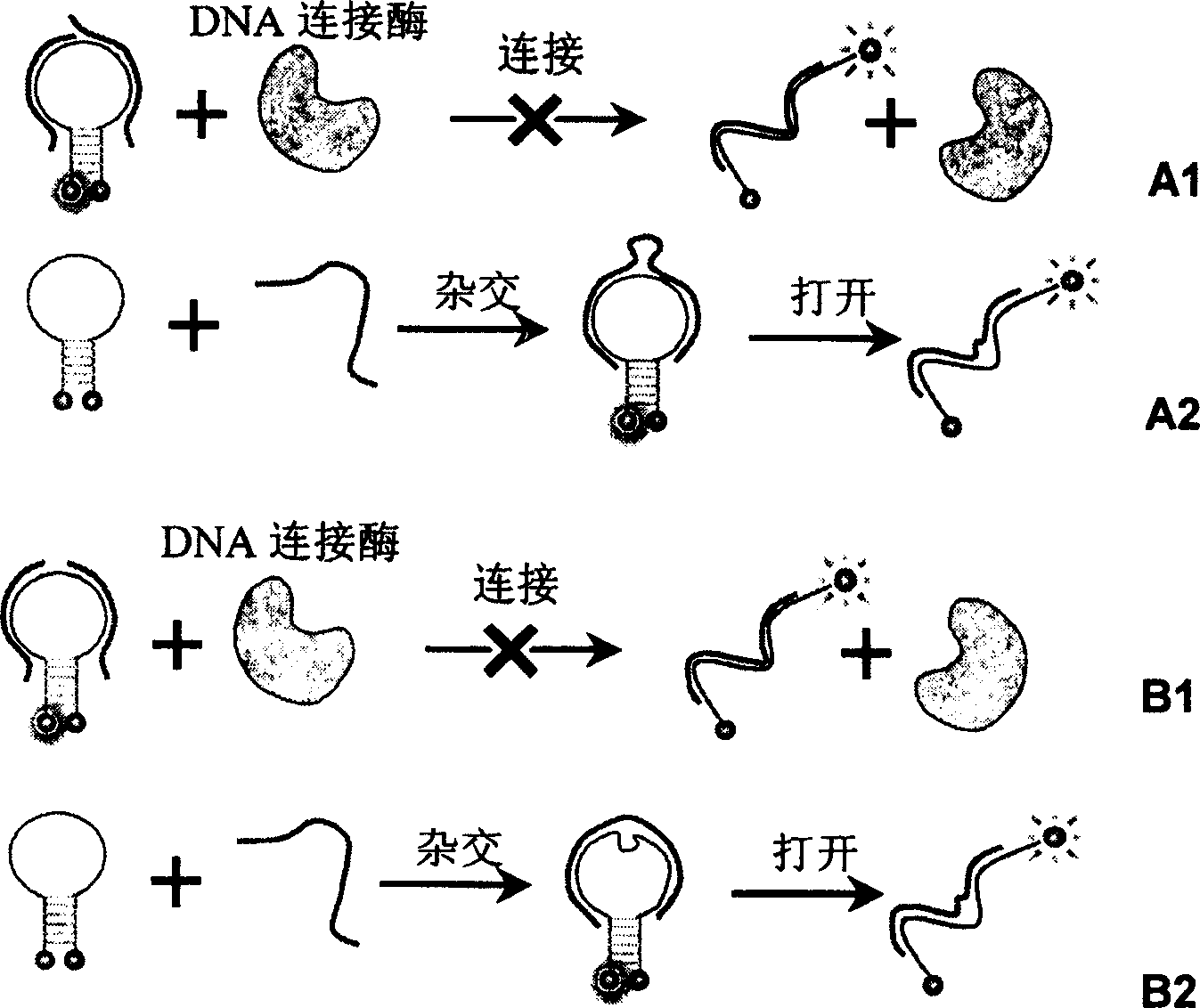
Novel probe design method for ligase reaction
InactiveCN104263827AAvoid it happening againMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotide sequencingDesign methods
The invention relates to a probe design method and application in ligase-mediated nucleic acid amplification reaction. In the ligase-mediated nucleic acid amplification reaction, one target sequence can be amplified by using 1-2 pairs of probes, and each probe is characterized by comprising a complementary area which is strictly complementary to the target sequence, a filling area (optional) for adjusting the length of each probe, a primer area (optional) used as a PCR primer and an extension area, wherein the length of the extension area is 5-20bp, and the extension area is complementary to a nucleotide sequence of the front end or tail end of the complementary area, namely, the nucleotide sequence of the extension area is determined by the target sequence; when each probe is not combined with the target sequence, the probe is of a stem-and-loop structure; and under a certain condition, a pair of the probes are combined with the target sequence and are connected with the target sequence to form a complete oligonucleotide chain by virtue of the ligase. The probe design method disclosed by the invention can be used for reducing non-specific amplification and avoiding false positive, and is particularly suitable for multiple detection of nucleic acids.
Owner:宁波有成生物医药科技有限公司
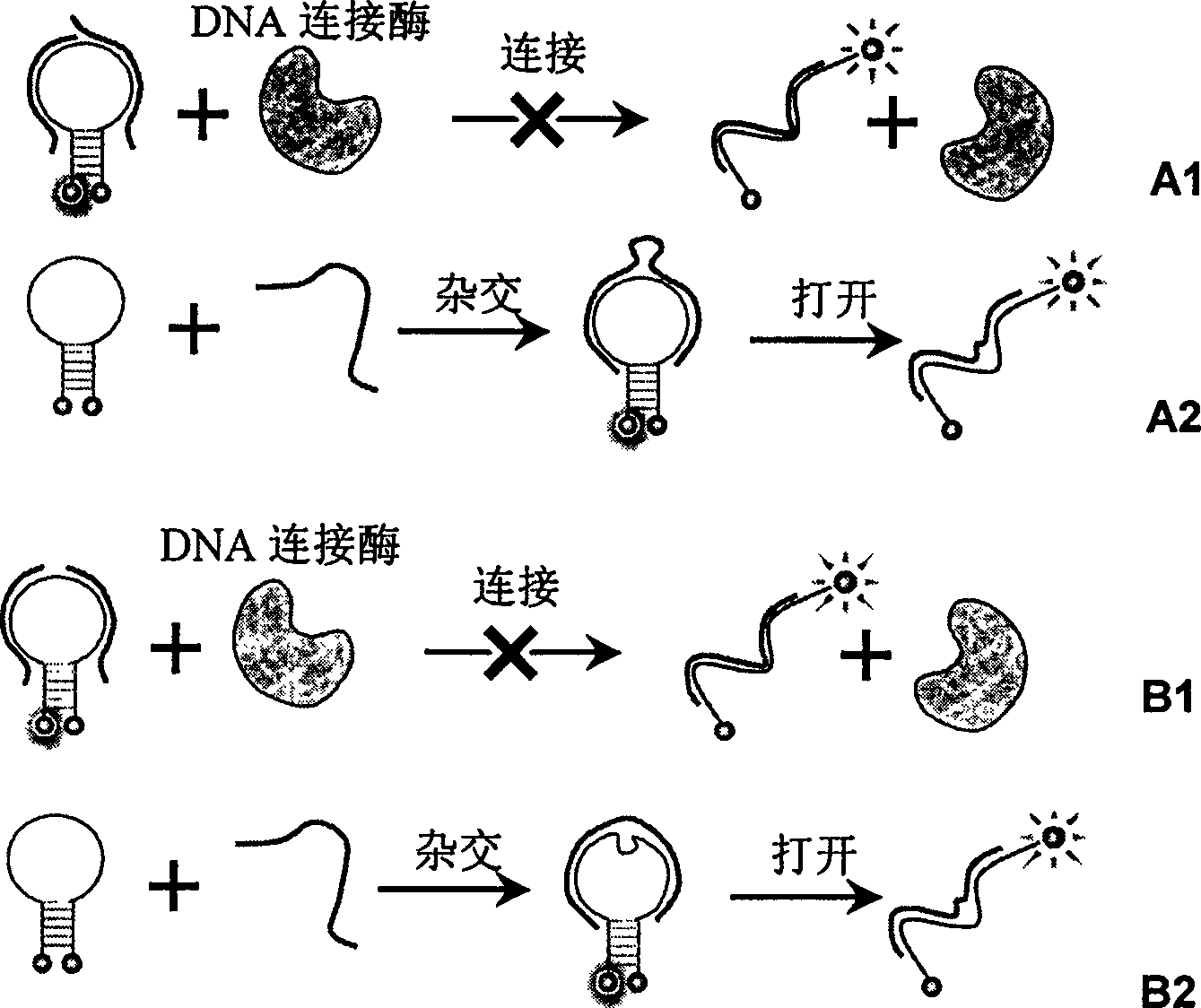
Real time method for detecting nucleic acid ligase reaction and nucleic acid ligase chain reaction
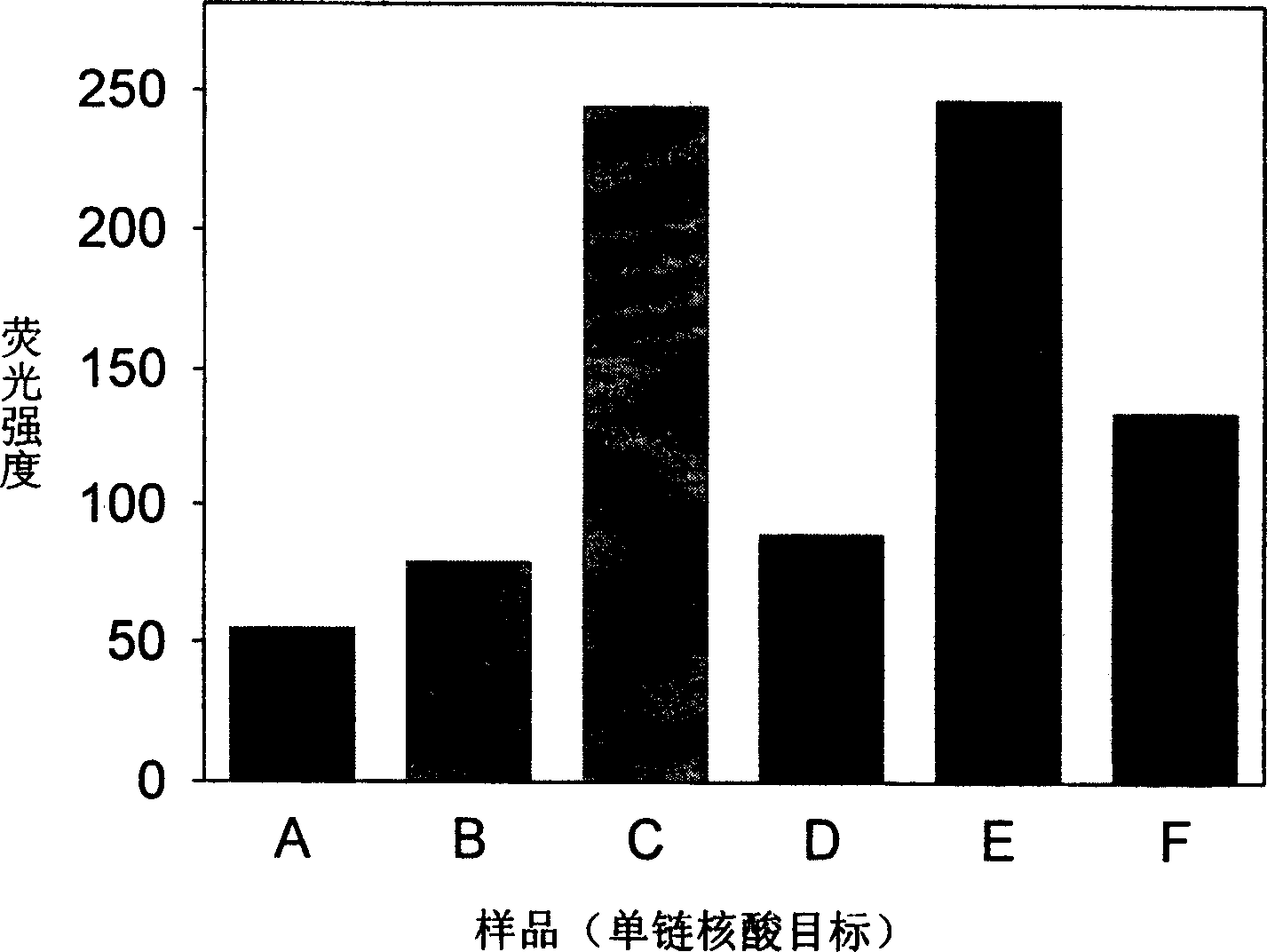
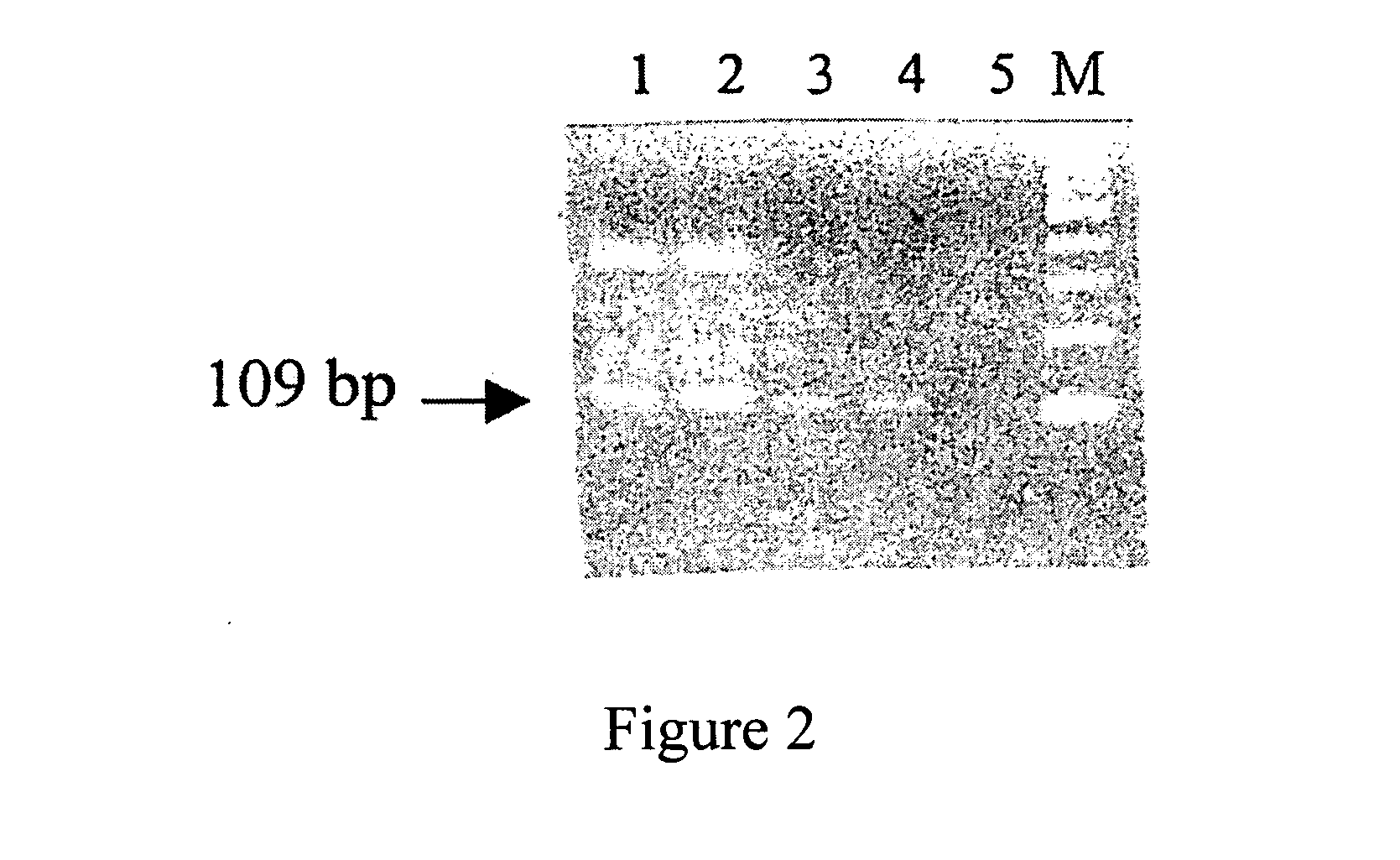
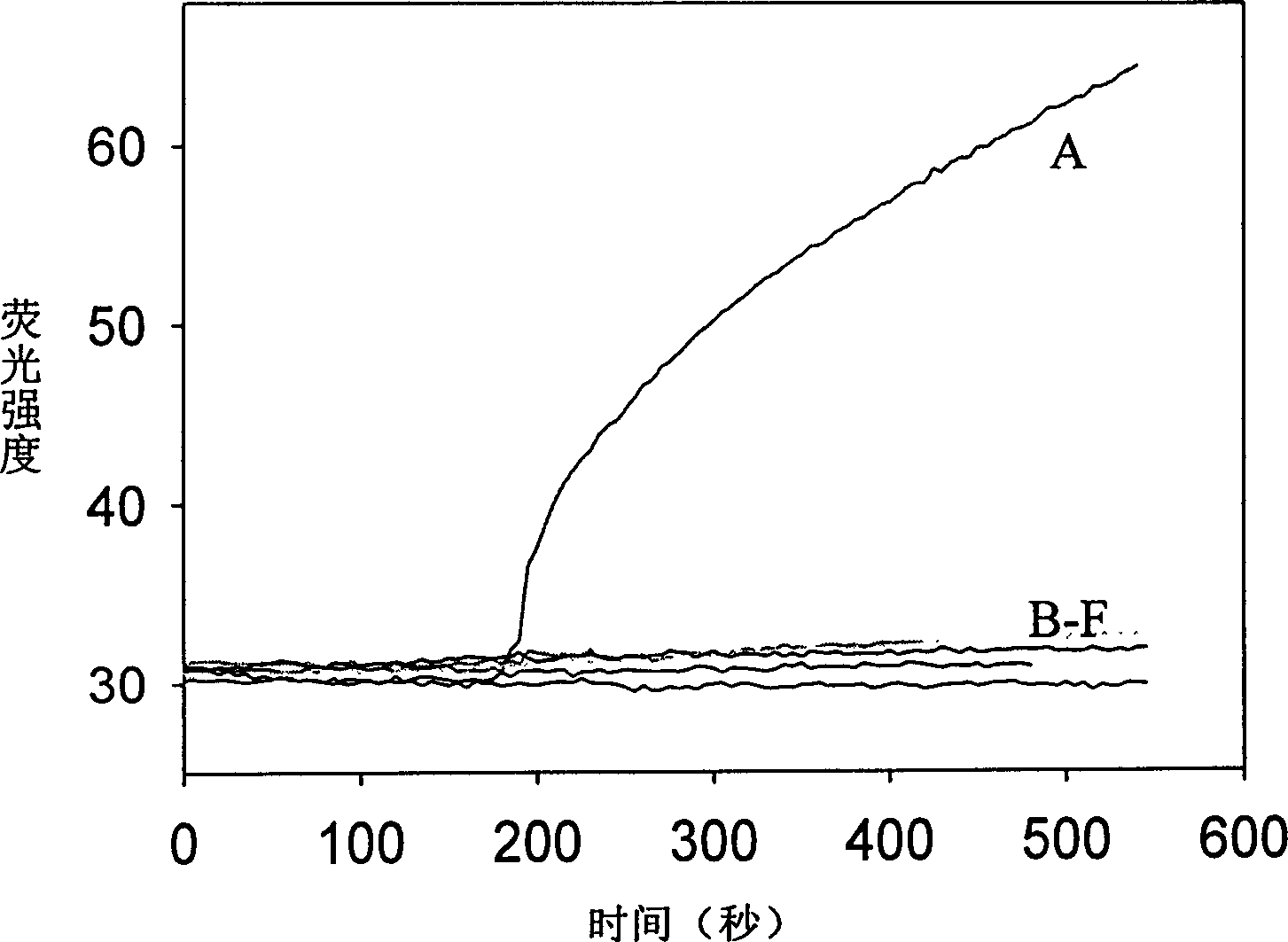
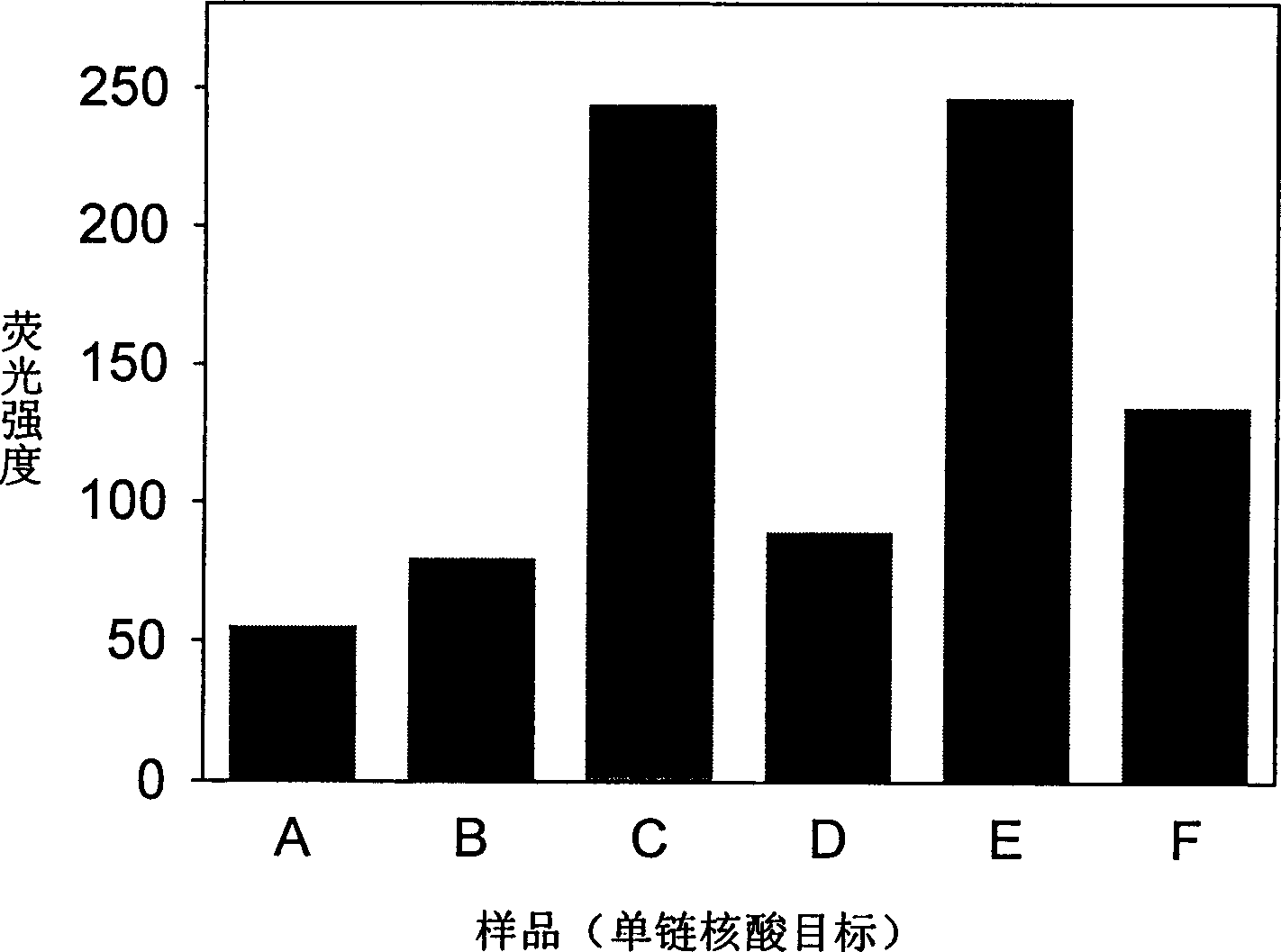
A system for detecting the ligase reaction of nucleic acid and the ligase chain reaction of nucleic acid is compose dof the nucleic acid probes of molecular label, amplified nucleic fragrance, Taq ligase and buffer solution. Its real-time analysis method includes such steps as adding molecular label, Taq ligase, amplifying primer, and single-chain or dual-chain target nucleic acid to the buffer solution, LDR or LCR temp cycle, and detecting the fluorescent intensity of specimen in low-temp cycle.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Helicobacter pylori antigens in blood
The present invention provides methods for detecting Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) DNA and / or fragments thereof in blood. The first method involves extracting DNA from a blood sample, preferably plasma, by amplifying the DNA using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or a ligase chain reaction (LCR) method, and detecting a target DNA sequence in the amplified DNA. The preferred target DNA sequence comprises a Mr26 or a 16S rRNA gene or fragments thereof specific to H. pylori. The second method involves extracting DNA from a blood sample, preferably serum, by hybridizing the extracted DNA with a radioisotope or fluorescence labeled H. pylori DNA probe.
Owner:JOY BIOMEDICAL
Highly sensitive multiplex single nucleotide polymorphism and mutation detection using real time ligase chain reaction microarray
InactiveUS20100105032A1Maximum efficiencyHigh strengthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMutation detectionNucleotide
A method and apparatus for real-time, simultaneous, quantitative measurement of one or more single nucleotide polymorphisms in one or more target nucleic acids is provided. This method involves combining a ligase chain reaction (LCR), a ligase detection reaction (LDR), and / or a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique with an evanescent wave technique.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
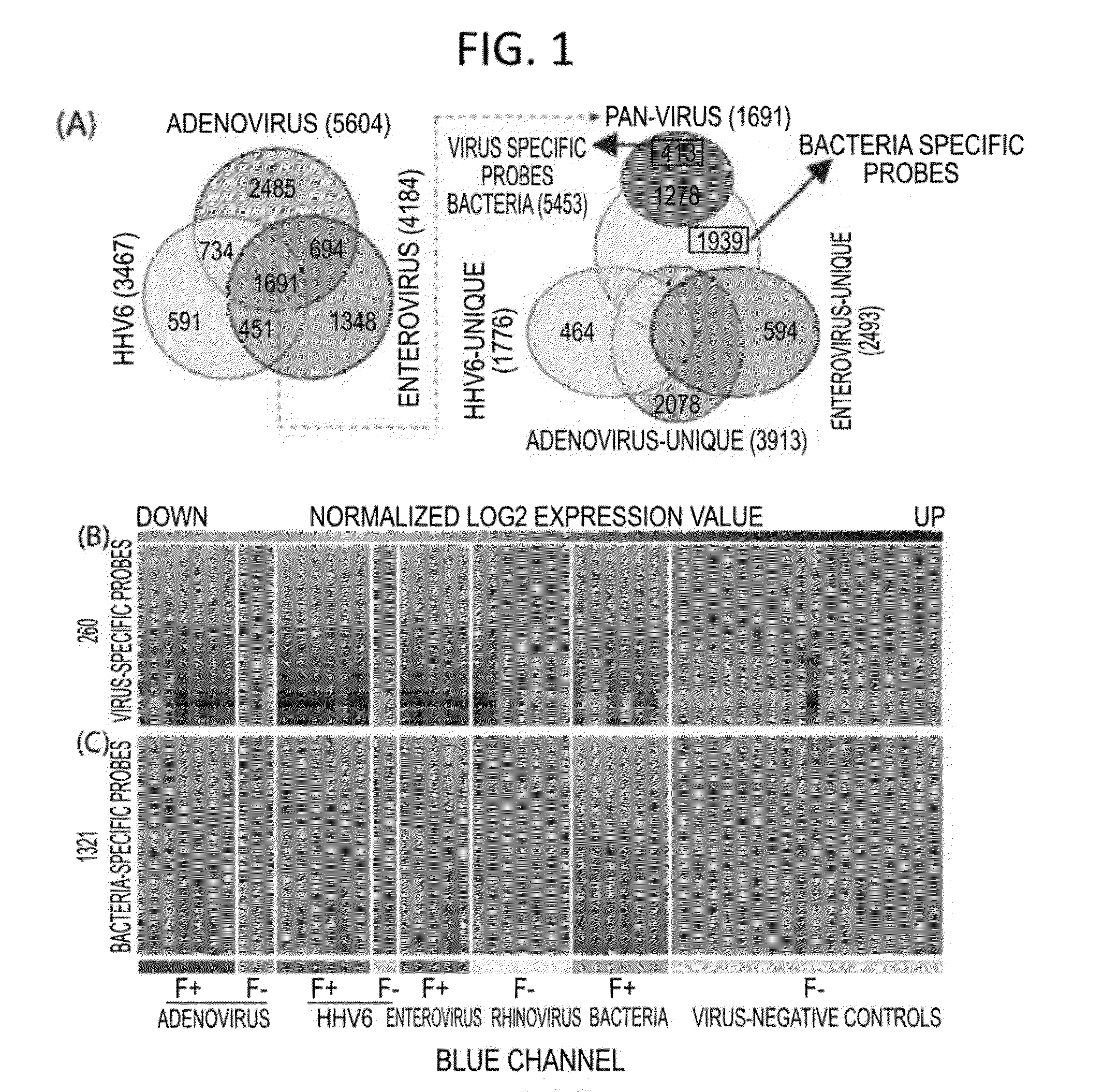
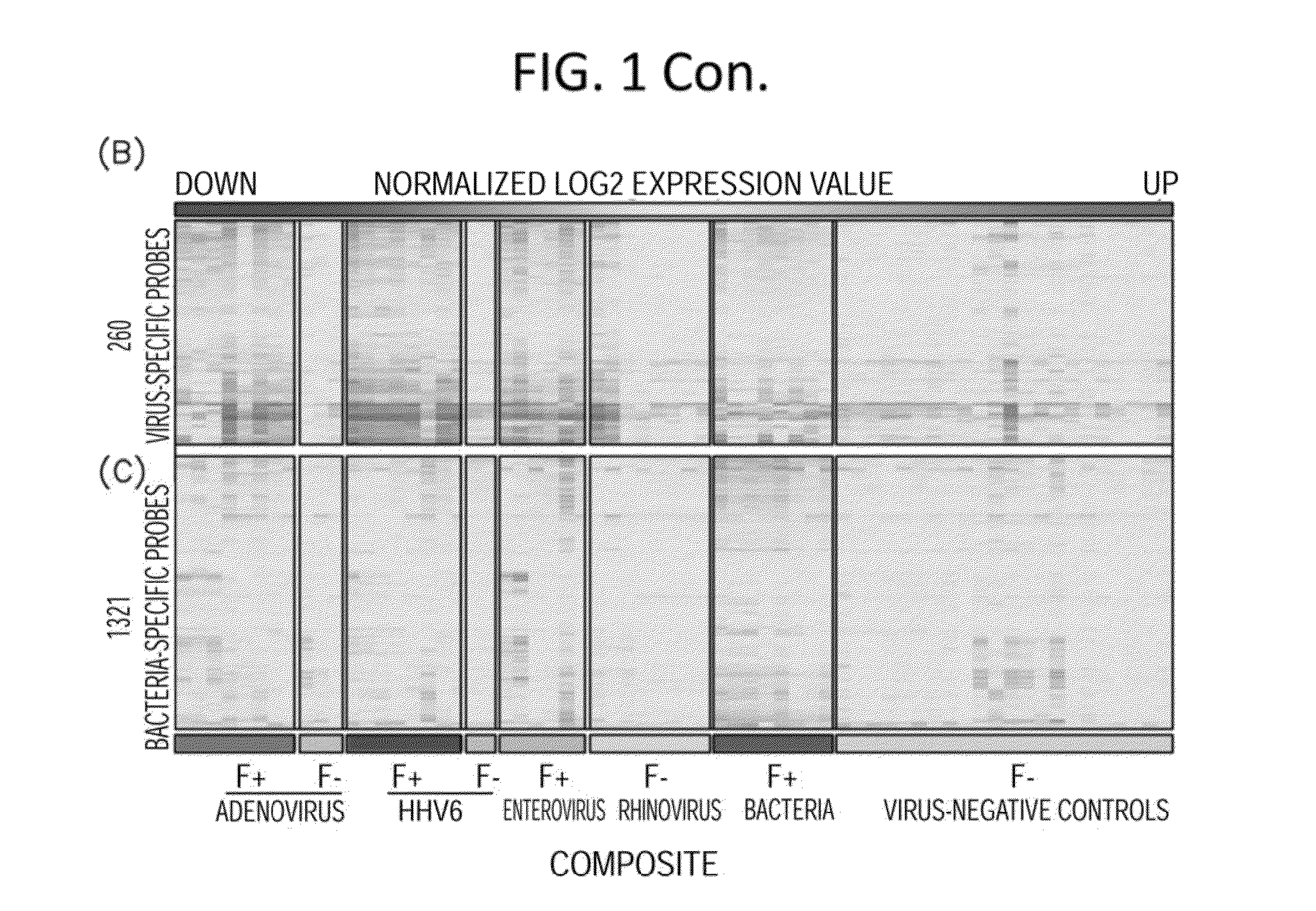
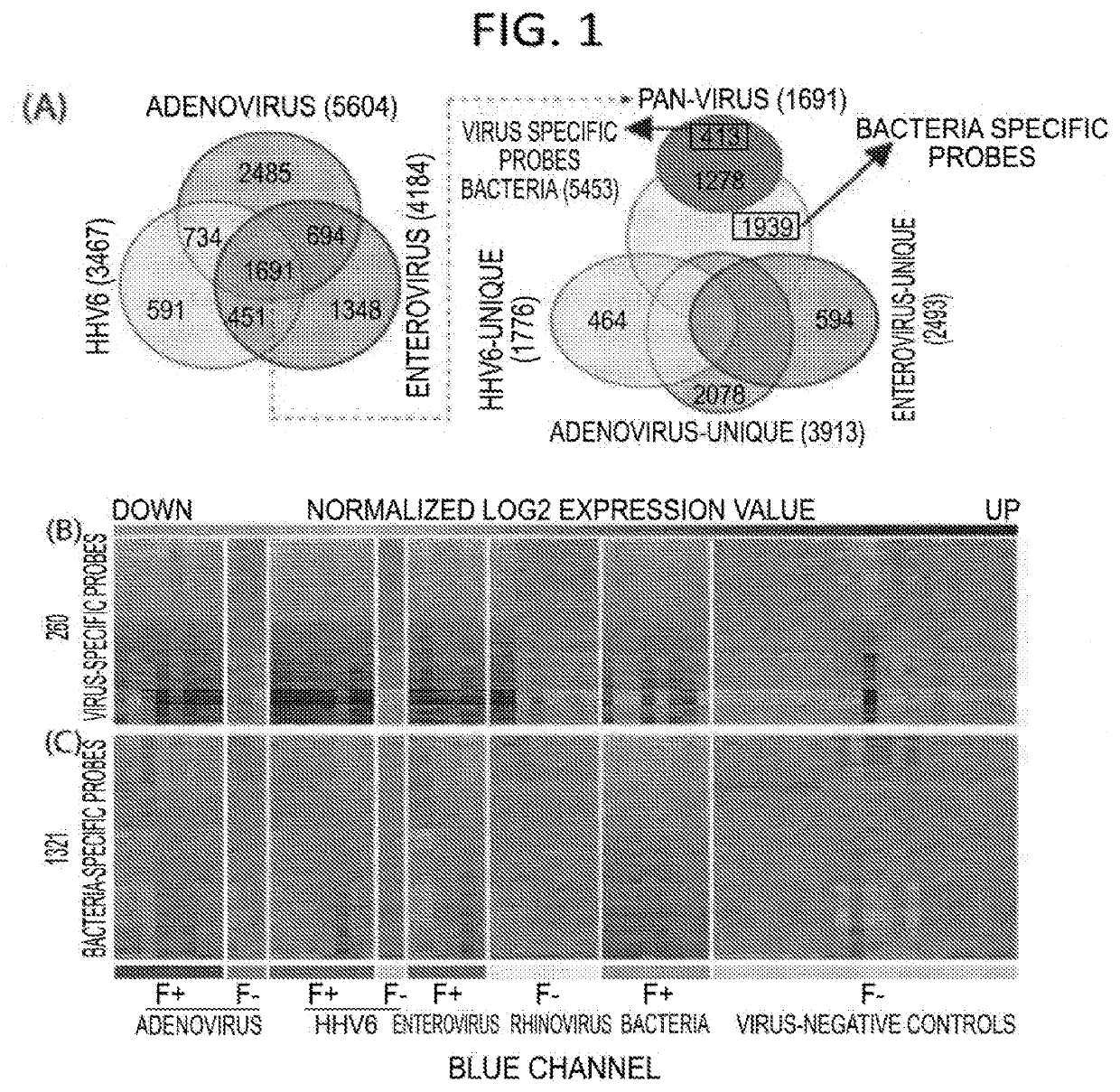
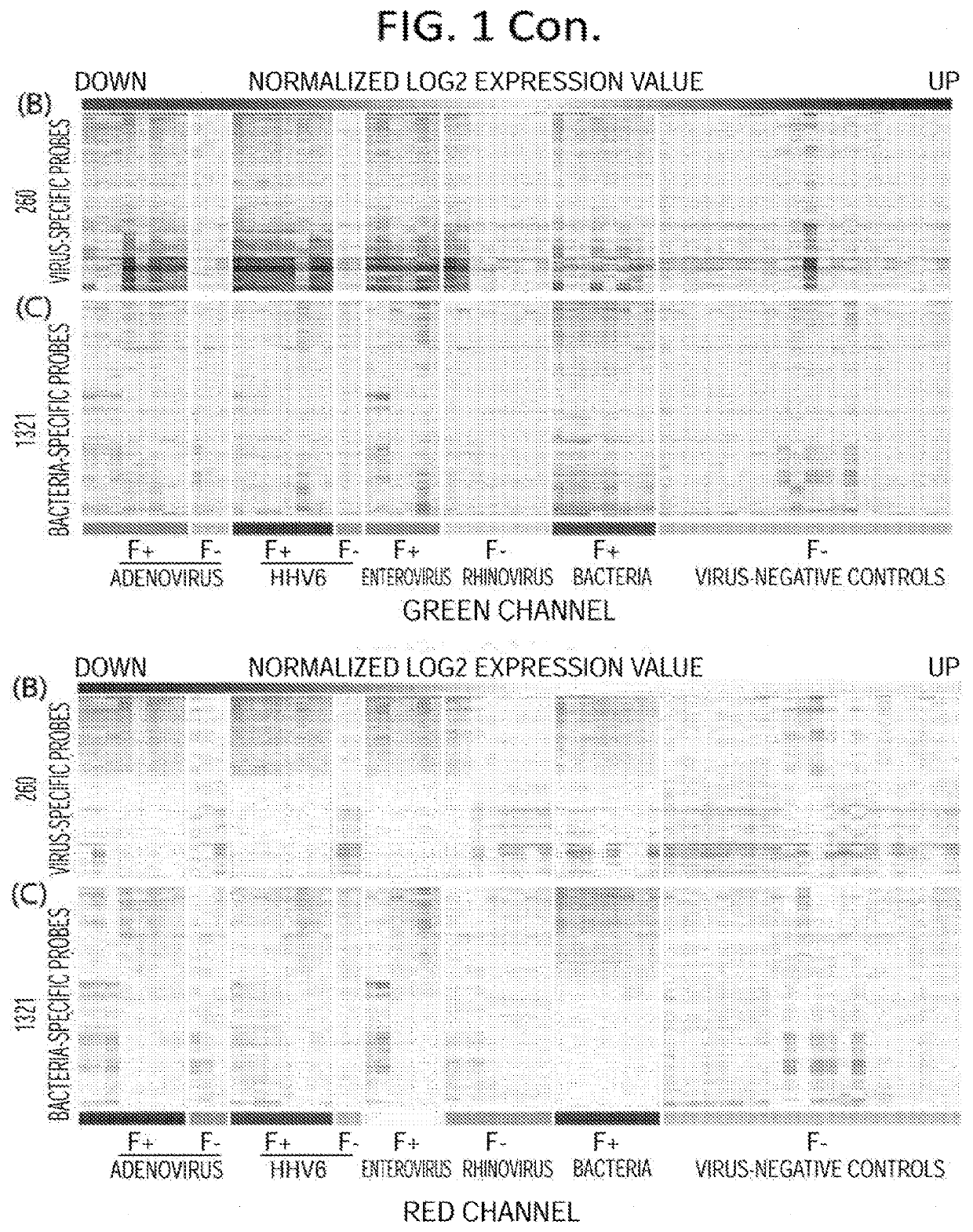
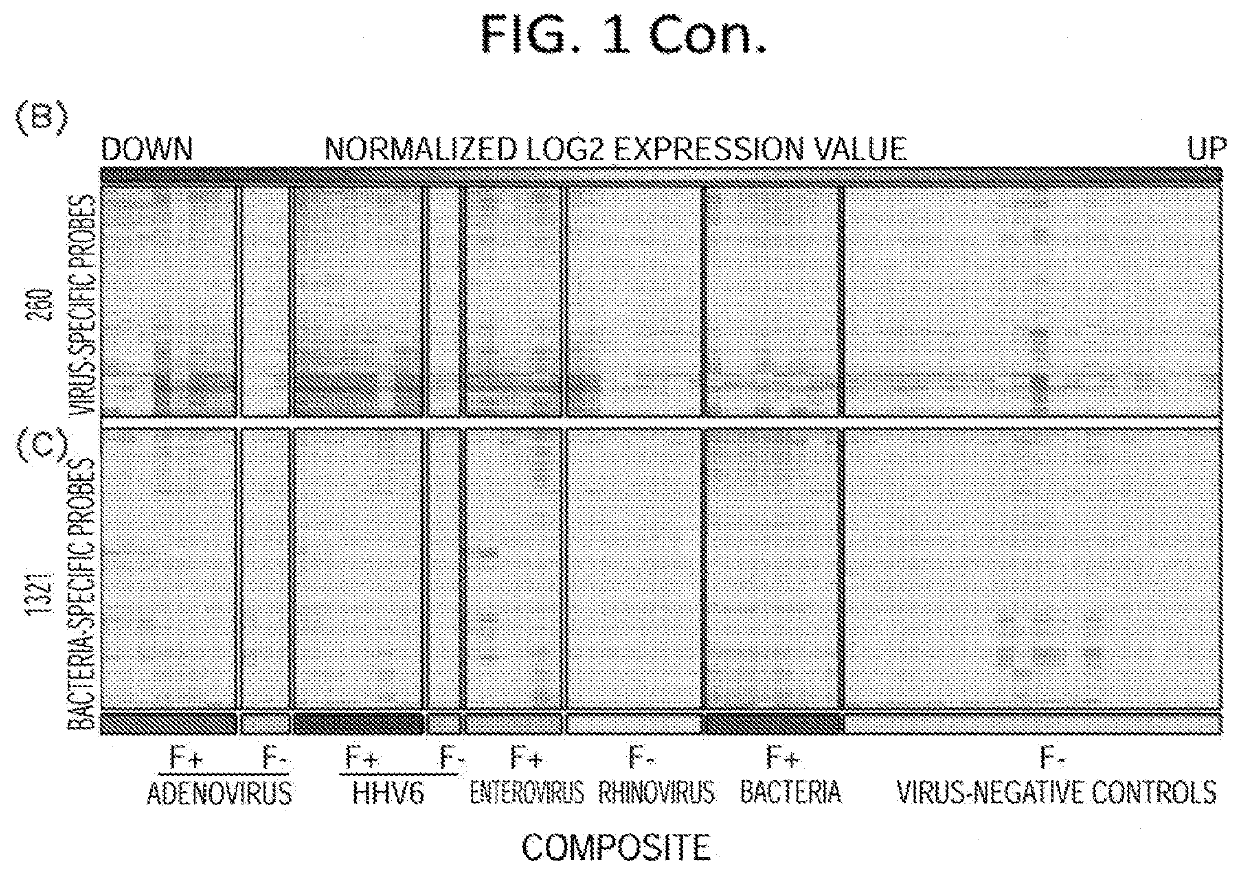
Diagnostic methods for infectious disease using endogenous gene expression
Disclosed are methods of diagnosis of a pathogen-associated disease. These methods comprise: providing a biological sample from a human subject; determining presence, absence and / or quantity of a bacterial pathogen, a viral pathogen, or a combination thereof, by a pathogen culture, a serum antibody detection test, a pathogen antigen detection test, a pathogen DNA and / or RNA detection test, or a combination thereof; determining in the sample, expression levels of at least one endogenous gene in which aberrant expression levels are associated with infection with a pathogen, by a microarray hybridization assay, RNA-seq assay, polymerase chain reaction assay, a LAMP assay, a ligase chain reaction assay, a Southern, Northern, or Western blot assay, an ELISA or a combination thereof. The subject can be diagnosed with the disease if the subject comprises the pathogen and an aberrant level of expression of an endogenous gene.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Thermocycler
ActiveUS20160263579A1Easy temperature controlHeating or cooling apparatusSamplingEngineeringElectromagnetic shielding
The present invention provides a thermocycler comprising: a rotatable platform having a plurality of reaction wells or being adapted to receive a plurality of reaction containers, wherein the rotatable platform and / or the reaction wells are formed, at least in part, of a material which is adapted to be inductively heated by exposure to electromagnetic energy. An electromagnetic energy source is provided and is configured to direct electromagnetic energy at the rotatable platform, wherein the electromagnetic energy source surrounds a sufficient amount of the rotatable platform in order to heat the entire platform substantially simultaneously. In preferred embodiments, the electromagnetic energy source completely surrounds the rotatable platform. The invention further comprises a method of cycling a reaction mixture between predetermined temperatures utilising the novel thermocycler apparatus of the invention. The invention also comprises use of the novel thermocycler apparatus of the invention for conducting a nucleic acid amplification reaction such as the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and the ligase chain reaction (LCR).
Owner:BIO MOLECULAR SYST
Method for stabilizing assay reagents, reagent container with stabilized assay reagents and use thereof
A reagent container having an inner surface upon which at least two reagents are dried, with the first reagent dried on a first area separate from a second area where the second reagent is dried. The first and second reagents are a nucleic acid polymerase and its substrate. A method is disclosed which includes dispensing at least the first and second reagents onto separate areas of the inner surface of the reagent container, and removing excess water from the reagents. The reagent container can be used in a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay, an assay that utilizes a reverse transcriptase, a reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction, an immuno-PCR assay, a nucleic acid sequence based assay, a proximity ligation assay, a ligase chain reaction assay, a rolling circle amplification assay, and a strand displacement amplification assay.
Owner:UNIOGEN OY
Monitoring DNA amplification
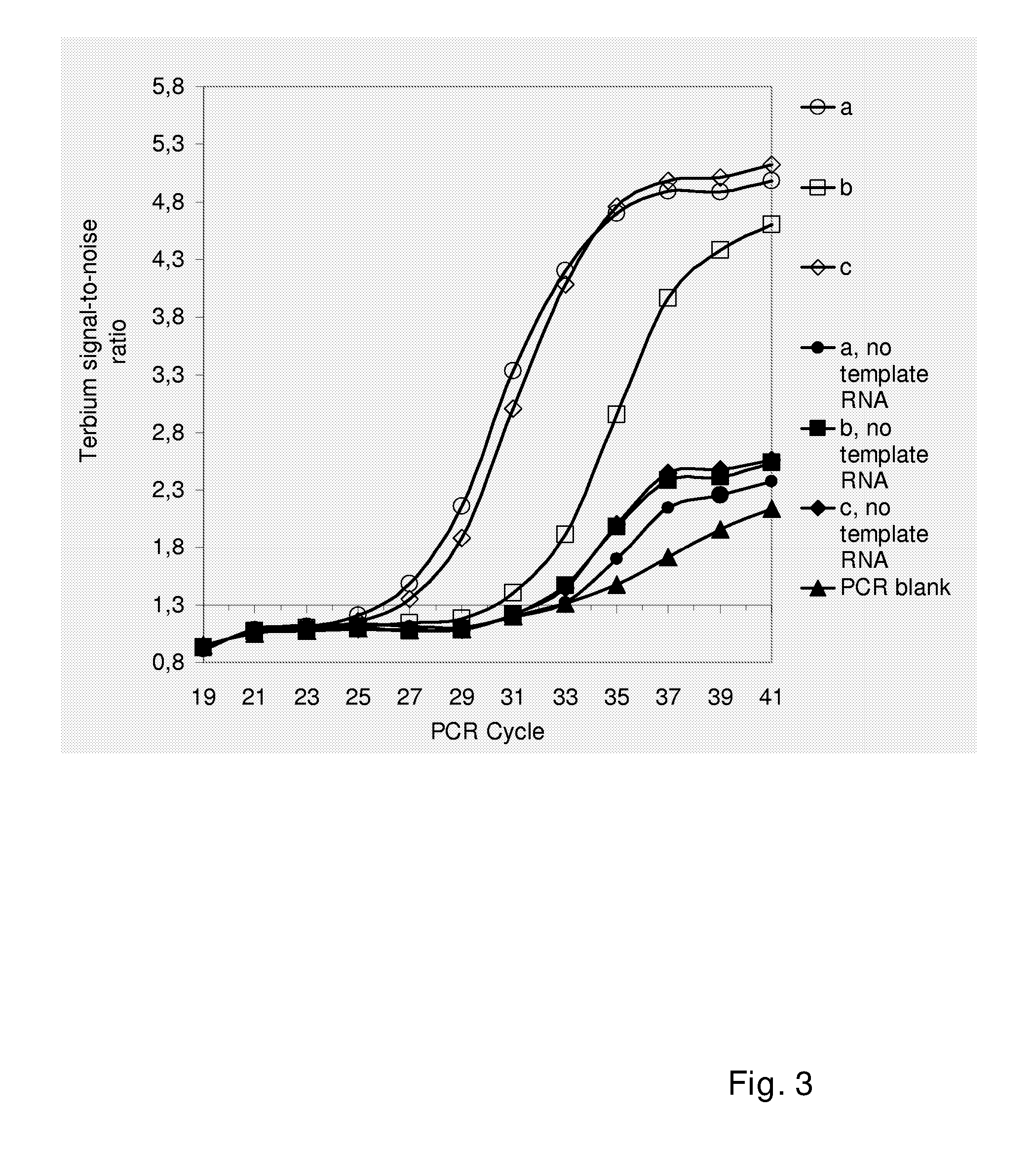
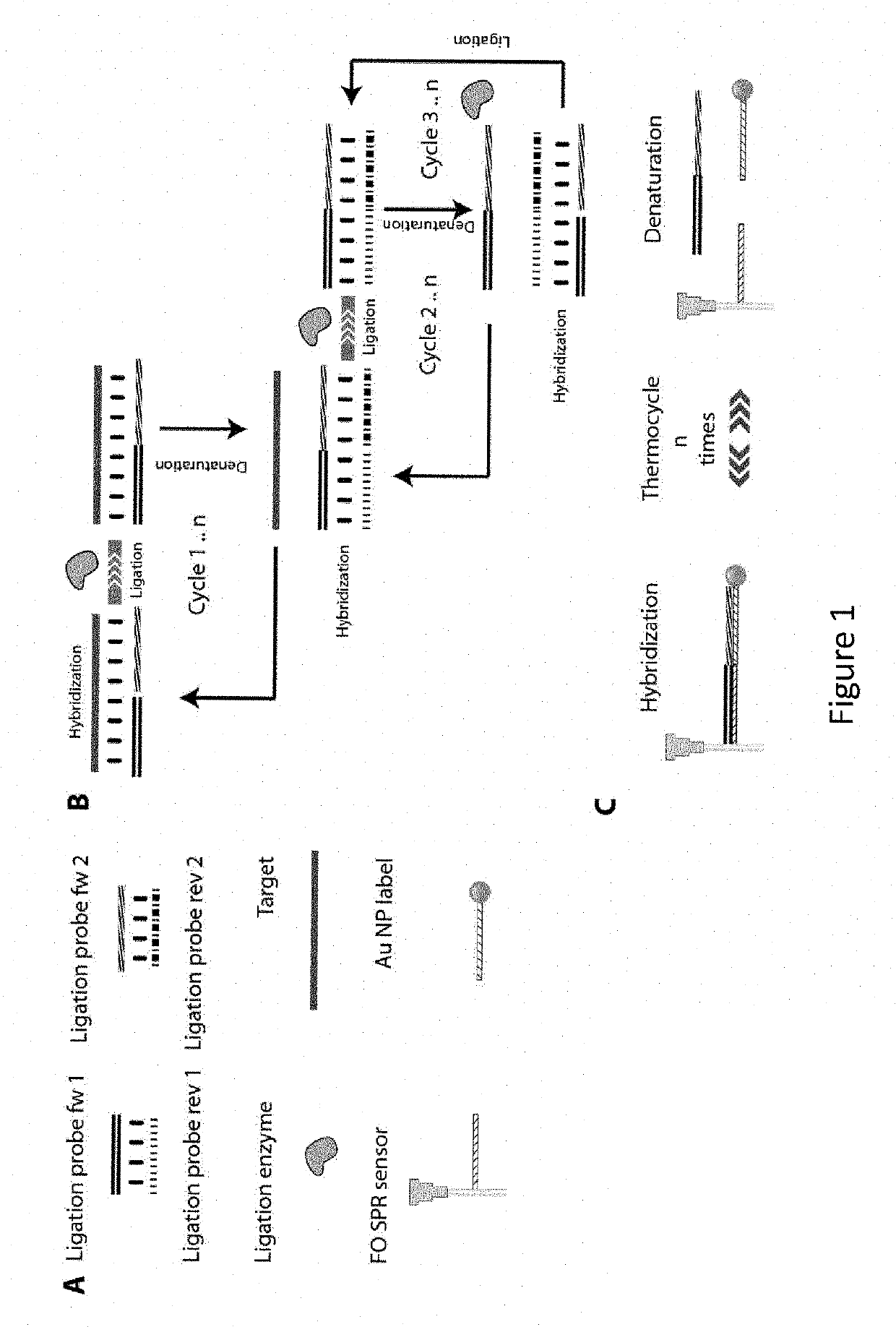
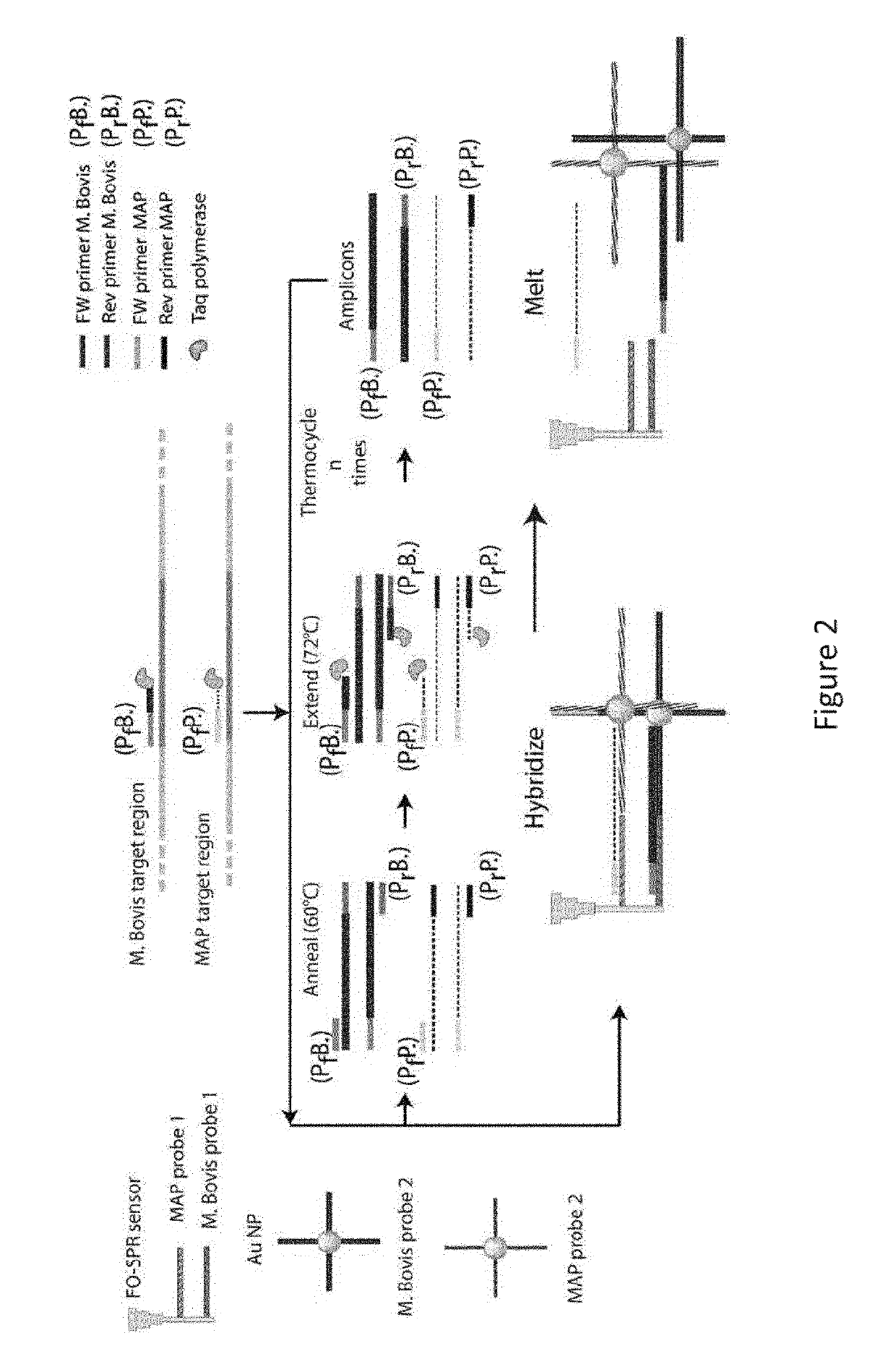
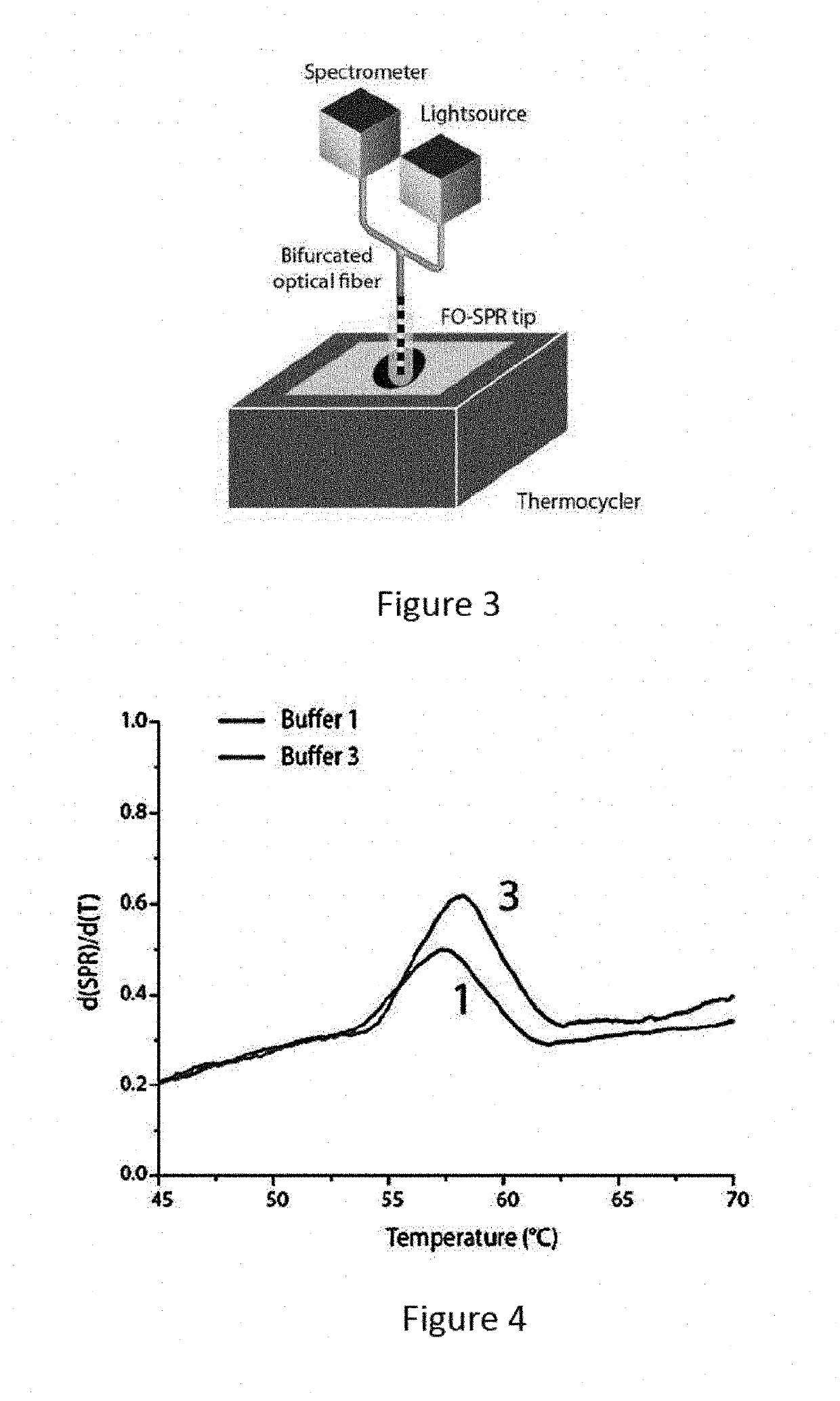
A method and kits are provided for nucleic acid quantification and discrimination using surface plasmon resonance (SPR). The method provided is able to significantly enhance the detection limit and multiplex the discrimination assay using the melting properties of the target DNA on top of standard PCR reaction. By using the heating and cooling cycles of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or Ligation chain reaction (LCR), DNA is melted and hybridized onto the SPR sensor surface together with a nanoparticle label. Thus, during every cycle of DNA amplification, the quantity and type of target DNA can be monitored.
Owner:FOX BIOSYST NV
Methods for assembling nucleic acids
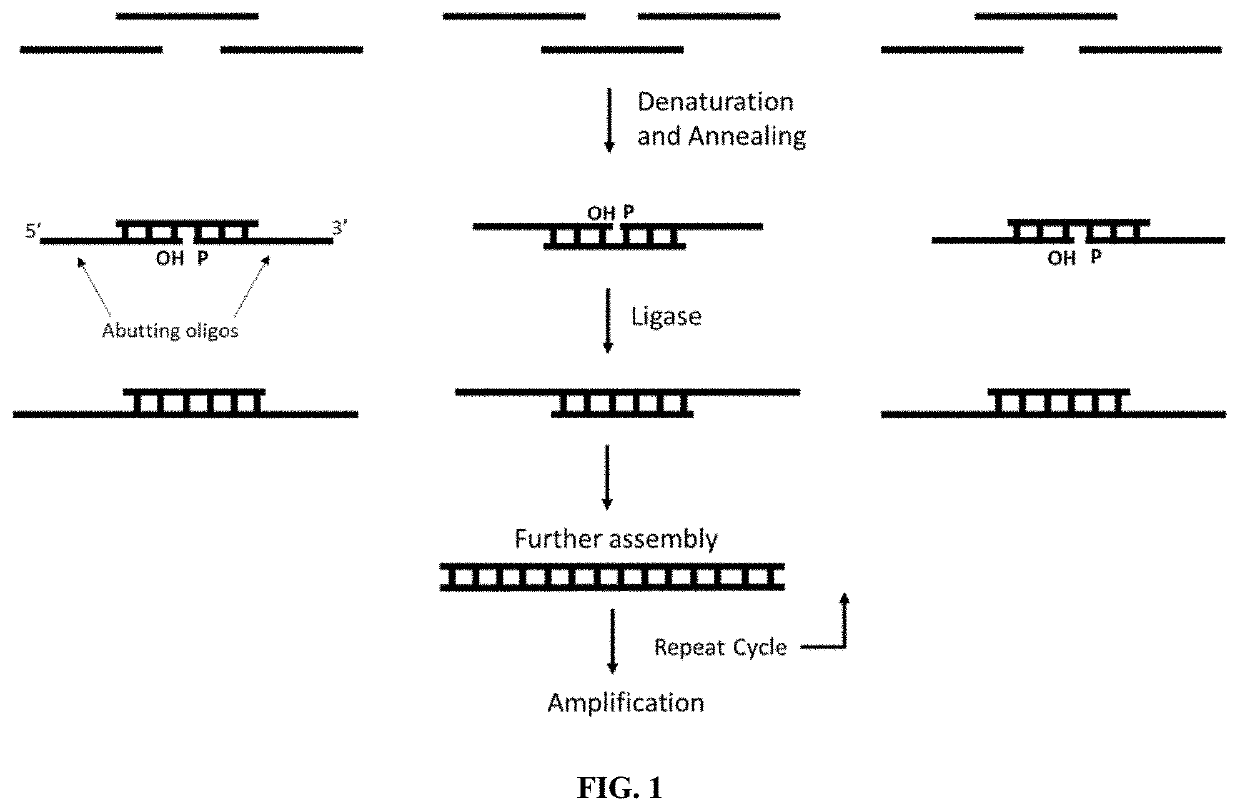
The invention provides methods of assembling a DNA molecule having a desired sequence. The methods involve contacting a DNA ligase with a plurality of short oligonucleotides to be assembled and performing the ligase chain reaction to thereby generate a set of polynucleotides. Oligonucleotides in the plurality overlap with and are complementary to a sequence of at least one other oligonucleotide in the plurality, and at least 50% of the oligonucleotides in the plurality are 6-30 nucleotides in length. The set of polynucleotides produced are contacted with a DNA polymerase and dNTPs in a mixture to join the set of polynucleotides and thereby create a DNA molecule having a desired sequence by polymerase chain assembly. The method allows for production of oligonucleotides of any length having very high sequence fidelity to a desired sequence.
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
Ligation amplification of nucleic acid sequences
ActiveUS8148065B1Convenient ligationMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
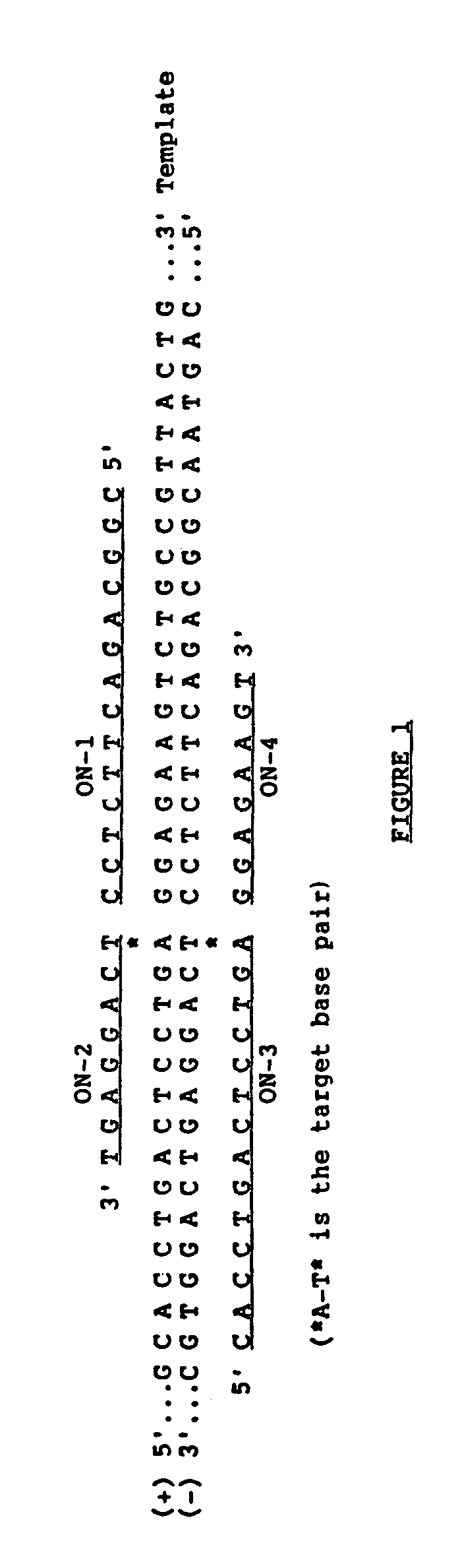
A method is described for the identification of point mutations by a template-dependent ligation procedure. Also described is a template-dependent ligase chain reaction procedure for the amplification and detection of nucleic acid sequences.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Amplification primer, detection probe and liquid phase chip for EGFR gene mutation detection
InactiveCN103045746AAccurate analysisMake up detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicrosphereEGFR Gene Mutation
The invention belongs to the technology of medical IVD (in vitro diagnosis) and particularly relates to an amplification primer, a detection probe and a liquid phase chip for EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) gene mutation detection. The liquid phase chip for EGFR gene mutation detection comprises PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification primers, LDR (ligase detection reaction) connection probes and Anti-Tag sequence coated microspheres, wherein the amplification probes comprise four pairs of primers for exons 18, 19, 20 and 21; and the connection probes comprise eight pairs of connection probes for eight primary mutation sites related with drug therapeutic effect of a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI). The liquid phase chip can be used for carrying out joint detection on mutation of eight EGFR genes and accurately analyzing the eight mutation sites at the same time by single reaction, and has the characteristics of low price and suitability for parallel detection of a large amount of samples.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHEST HOSPITAL +1
Diagnostic methods for infectious disease using endogenous gene expression
ActiveUS20200216904A1Organic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigenInfectious Disorder
Disclosed are methods of diagnosis of a pathogen-associated disease. These methods comprise: providing a biological sample from a human subject; determining presence, absence and / or quantity of a bacterial pathogen, a viral pathogen, or a combination thereof, by a pathogen culture, a serum antibody detection test, a pathogen antigen detection test, a pathogen DNA and / or RNA detection test, or a combination thereof; determining in the sample, expression levels of at least one endogenous gene in which aberrant expression levels are associated with infection with a pathogen, by a microarray hybridization assay, RNA-seq assay, polymerase chain reaction assay, a LAMP assay, a ligase chain reaction assay, a Southern, Northern, or Western blot assay, an ELISA or a combination thereof. The subject can be diagnosed with the disease if the subject comprises the pathogen and an aberrant level of expression of an endogenous gene.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Helicobacter pylori antigens in blood
The present invention provides methods for detecting Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) DNA and / or fragments thereof in blood. The first method involves extracting DNA from a blood sample, preferably plasma, by amplifying the DNA using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or a ligase chain reaction (LCR) method, and detecting a target DNA sequence in the amplified DNA. The preferred target DNA sequence comprises a Mr26 or a 16S rRNA gene or fragments thereof specific to H. pylori. The second method involves extracting DNA from a blood sample, preferably serum, by hybridizing the extracted DNA with a radioisotope or fluorescence labeled H. pylori DNA probe.
Owner:JOY BIOMEDICAL
Real time method for detecting nucleic acid ligase reaction and nucleic acid ligase chain reaction
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Telomerase activity detection method
ActiveCN102260739BHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementTelomeraseFluorescence
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, specifically to a telomerase activity detection method. The detection method comprises the following steps of: acquiring active telomerase from a sample to be measured, extending TS primers to obtain a telomerase extension product, using the telomerase extension product as a template, carrying out gap-ligase chain reaction amplification in the presence of four primers to obtain an amplification product, mixing the amplification product and a molecular beacon to react, and carrying out a fluorescence detection to obtain the telomerase activity. The detection method provided by the invention has high sensitivity and good specificity, and can be used to effectively detect the activity of telomerase in the sample to be measured.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Method of point mutation without need of chain reaction of polymerase and the kit
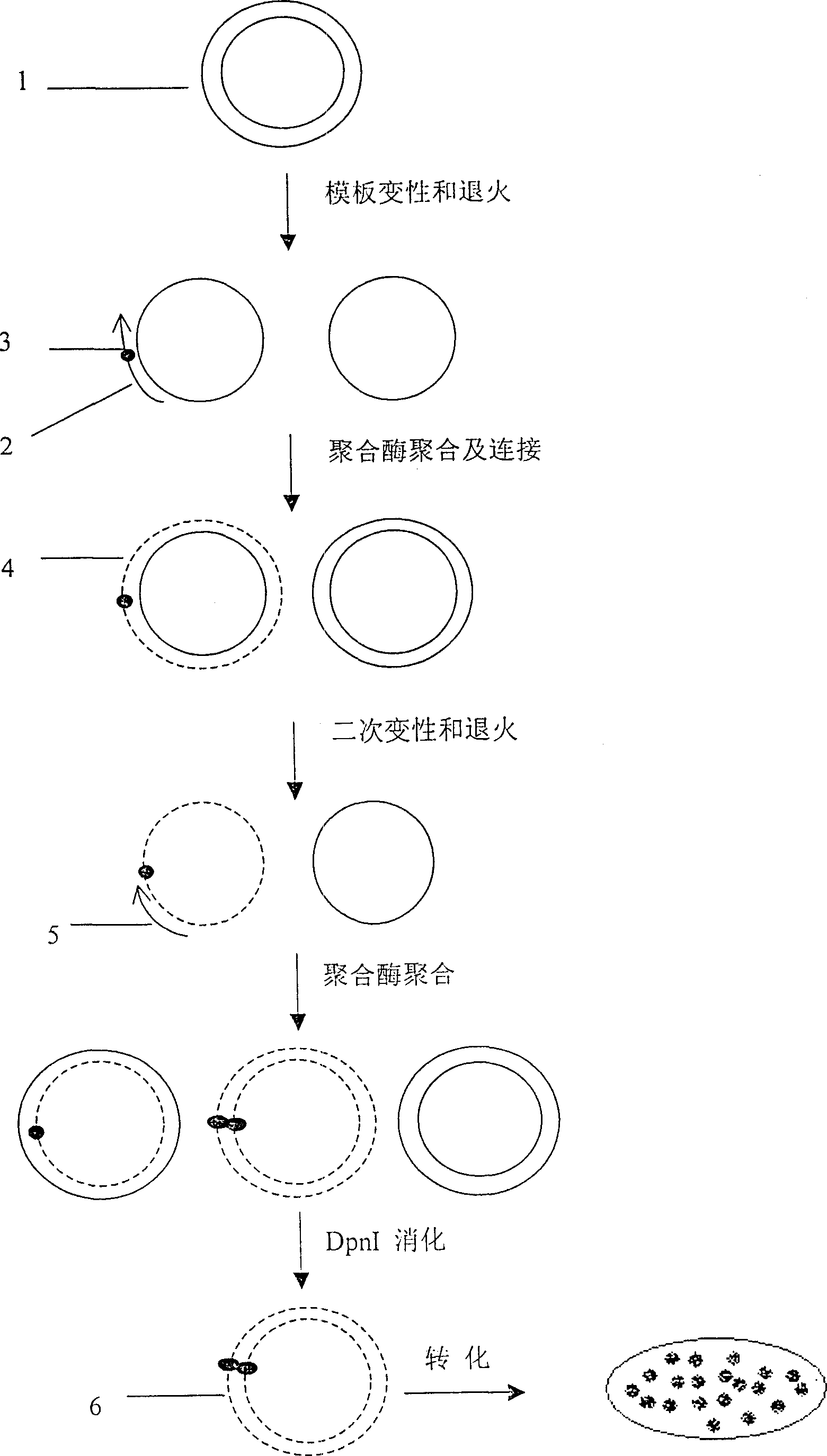
InactiveCN1233827CLow priceEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMutant preparationDpnI restriction endonucleaseGenetics
The invention relates to a point mutation method without polymerase chain reaction and its kit. In this method, the plasmid template is first denatured, and the primer containing the point mutation is annealed to the template; then DNA polymerase and DNA ligase are added to synthesize the mutant chain and the nick is closed; then the second step of denaturation is performed, and the selection primer is added and combined with the mutation Chain annealing; use polymerase to polymerize to synthesize another mutant chain; finally add DpnI restriction endonuclease to the product to digest and remove the non-mutated template. Since the method does not require PCR, the mutation process is high-fidelity and does not introduce other additional mutations; and the method is cheap, time-saving, fast and easy to operate.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Determination of variants produced upon replication or transcription of nucleic acid sequences
ActiveUS9150906B2Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationReverse transcriptaseReverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
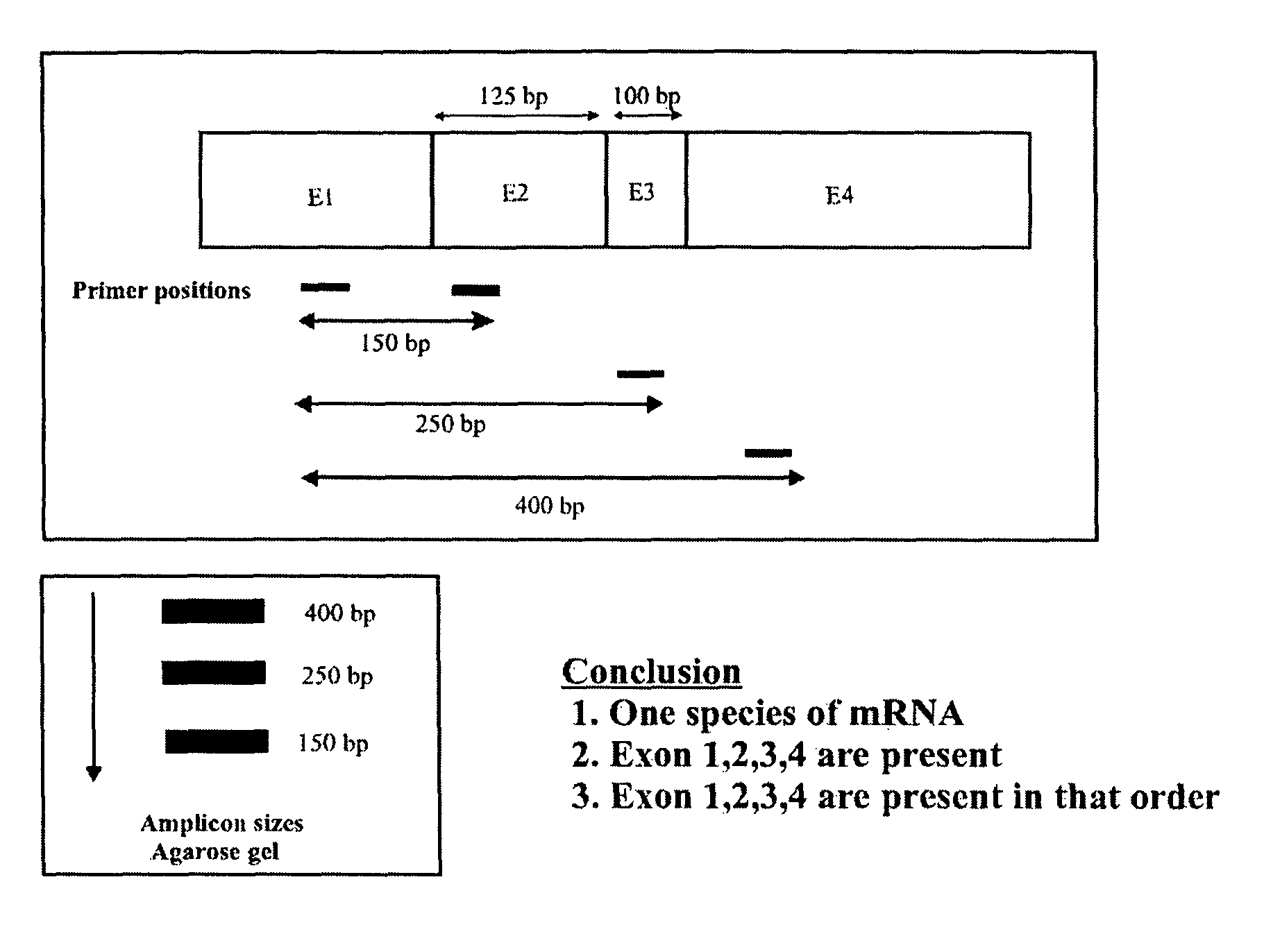
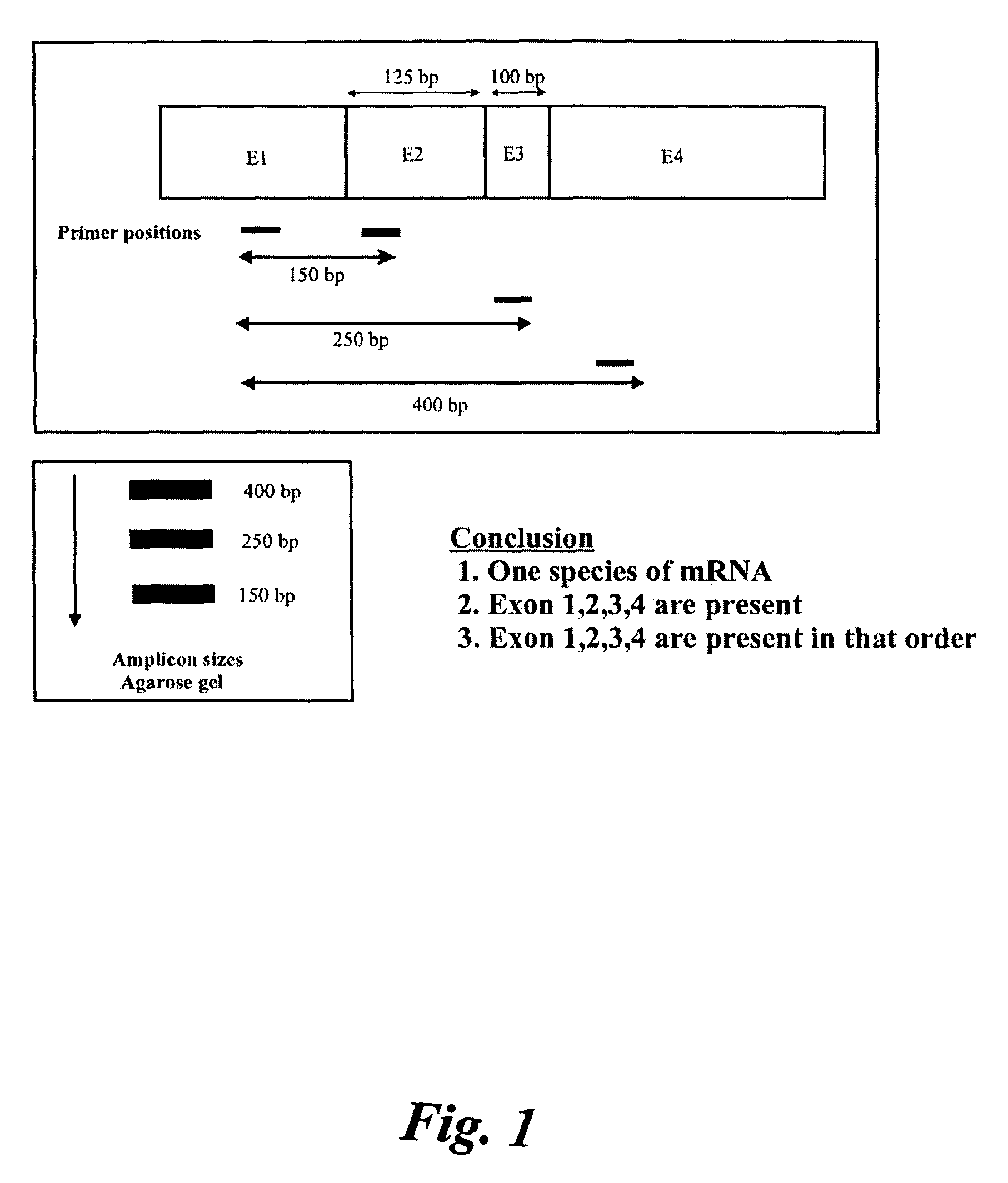
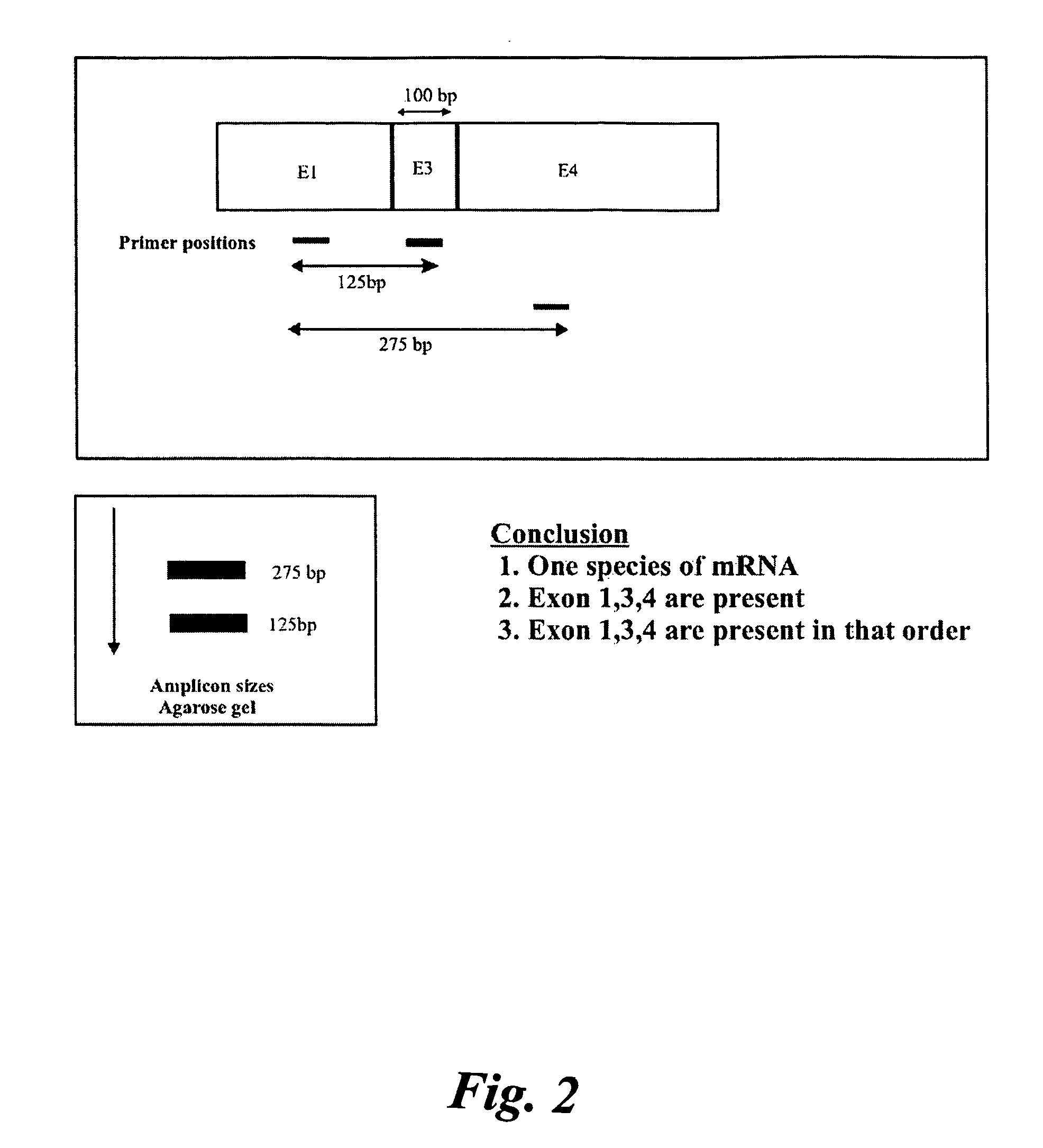
A method of determining whether or not a nucleic acid having an expected sequence or one or more variants of the expected sequence are present in a sample containing nucleic acids after replication, transcription or editing (or other transformation) of a substrate nucleic acid. The method involves deciding an expected sequence likely to be formed in the sample upon the replication, transcription or editing of the substrate nucleic acid, and possible variants of the expected sequence, providing primer pairs for a polymerase chain reaction, reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction or ligase chain reaction, carrying out the polymerase chain reaction or reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction in one or more steps to form amplicons, and analyzing the amplicons to determining whether or not a nucleic acid having the expected sequence and / or variants are present in the sample. The primers of the primer pairs are designed to anneal to regions of the nucleic acid of the expected sequence and the variants, the regions being selected to reveal unambiguously the presence or absence in the sample of the nucleic acid of the expected sequence or the variants thereof according to the presence or absence of specific amplicons amplified by the primers.
Owner:BIO ID DIAGNOSTIC
Detection method for single nucleotide polymorphism
InactiveCN103103283BSensitive methodAccurate methodMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePhosphorylation
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, relates to analysis and detection for single nucleotide polymorphism, and in particular relates to a universal detection method. The detection method comprises the steps of amplifying target DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) by gap-ligase chain reaction, introducing a DNAzyme sequence into a ligation product, degrading a phosphorylated probe which does not participate in the ligation reaction by Lambda excision enzyme, and releasing DNAzyme by excision enzyme III. The detection method is characterized in that a DNAzyme probe is combined with a Gap-LCR (ligase chain reaction) probe, and is characterized by comprising the following steps of: adding a section of DNAzyme sequence into a phosphorylated probe to be connected in an LCR system, adding an Anti-G sequence into a system (in complementary pairing with a DNAzyme sequence part in the probe) after the Gap-LCR amplification reaction stops, degrading a 5-end phosphorylated DNA probe by the Lambda excision enzyme, and releasing the DNAzyme in the ligation product by the excision enzyme III, thereby qualitatively and quantitatively detecting the SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) due to the characteristics of the DNAzyme. The method is simple, convenient, practical and economical, and is widely applicable to the detection of various single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Thermocycler
ActiveUS10406527B2Easy temperature controlHeating or cooling apparatusSamplingEngineeringElectromagnetic shielding
The present invention provides a thermocycler comprising: a rotatable platform having a plurality of reaction wells or being adapted to receive a plurality of reaction containers, wherein the rotatable platform and / or the reaction wells are formed, at least in part, of a material which is adapted to be inductively heated by exposure to electromagnetic energy. An electromagnetic energy source is provided and is configured to direct electromagnetic energy at the rotatable platform, wherein the electromagnetic energy source surrounds a sufficient amount of the rotatable platform in order to heat the entire platform substantially simultaneously. In preferred embodiments, the electromagnetic energy source completely surrounds the rotatable platform. The invention further comprises a method of cycling a reaction mixture between predetermined temperatures utilising the novel thermocycler apparatus of the invention. The invention also comprises use of the novel thermocycler apparatus of the invention for conducting a nucleic acid amplification reaction such as the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and the ligase chain reaction (LCR).
Owner:BIO MOLECULAR SYST
Multi-component chromatography single nucleotide polymorphism detection method for biologically coding based on general PCR amplification
InactiveCN102586462AReduce dosageSimple and fast operationComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction enzyme digestionNucleotide
The invention discloses a multi-component chromatography single nucleotide polymorphism detection method for biologically coding based on general PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification. The multi-component chromatography single nucleotide polymorphism detection method comprises an allele specific ligase chain reaction, a general PCR amplification reaction, a restriction enzyme digestion reaction, and multi-component quantitative detection for a target gene specific biological coding length fluorescent marker nucleic acid fragment by using liquid chromatography. According to the detection method disclosed by the invention, a connecting product matched with the type of a target gene is generated by using an allele specific ligase chain reaction; a fluorescent marker amplified product of the connecting product is generated by the general PCR amplification reaction; the amplified product is converted into the target gene specific length coding fluorescent marker nucleic acid fragment by using the restriction enzyme digestion reaction; and the multi-component quantitative detection is carried out by the liquid chromatography. The method is less in sample consumption, simple and convenient in operation and lower in cost; and in addition, the method can be used for simultaneously determining multiple components, so that a general technical platform can be provided for biological research on mass screening and antepartum biological research.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for detecting fetal patrilineal DNA point mutation from pregnancy plasma
InactiveCN1975389AHigh sensitivityAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceRelationship - FatherBlood plasma
A method to detect the father DNA dot mutation of the fetus from the gravida plasma includes three processes: the sample treatment, recognizing the dot mutation by the space-connecting enzyme reaction, detecting the connecting product by the fluorescent quantitative PCR. The method is reliable and has the high sensitivity, so it can detect the father DNA dot mutation of the fetus from the gravida plasma accurately.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com