Unmanned aerial vehicle obstacle avoidance controlling method
A control method and unmanned aerial vehicle technology, applied in three-dimensional position/channel control, etc., to achieve good environmental adaptability, simple method, and improved safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
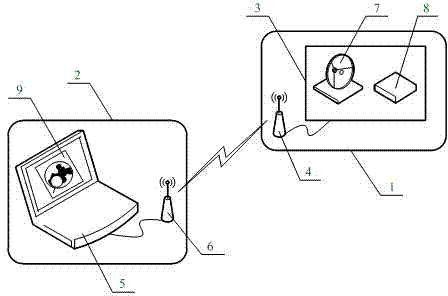
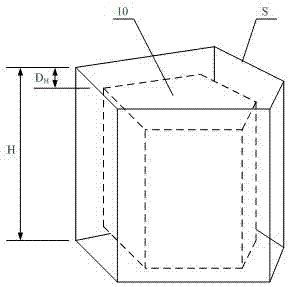
[0042] Example 1: Such as figure 1 , UAV obstacle avoidance control system based on columnar space planning constraints, with UAV subsystem 1 and ground station subsystem 2; UAV subsystem 1 includes embedded flight controller 3 and airborne terminal 4 of wireless data link , The embedded flight controller 3 has a built-in satellite positioning receiver 7 and an altitude sensor 8; the ground station subsystem 2 includes an embedded monitoring computer 5 and the ground terminal 6 of the wireless data link, and the embedded monitoring computer 5 has a built-in computer that contains obstacle geographic information Electronically Picture 9 ; The embedded flight controller 3 is connected with the airborne terminal 4 of the wireless data link through a serial bus, the embedded monitoring computer 5 is connected with the ground terminal 6 of the wireless data link through a serial bus, and the airborne terminal 4 of the wireless data link is connected with The ground end 6 of the wire...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Example 2: Such as Figure 4 As shown, for an obstacle with an arc-shaped boundary, N straight line segments are used to surround the two-dimensional geographic boundary of the obstacle to form a closed boundary contour line 14, as follows:
[0052] ① The operator in the built-in two-dimensional ground of the monitoring computer 5 Picture 9 Manual operation above, for the straight line boundary, directly take the straight line segment corresponding to the boundary;
[0053] ② For the convex arc boundary, select multiple characteristic points on the arc boundary including the starting and ending points of the arc boundary. The number and position of the points are selected by the ground operator according to the size of the arc. Generally, the number of points ≥ 3. The positions are evenly distributed, and the greater the radian, the more points; this embodiment takes 5 characteristic points, namely X 1 ~X 5 ; Draw arc-shaped tangents along each characteristic point, and two ...
Embodiment 3
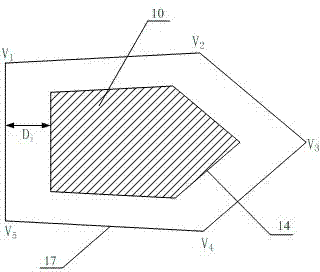
[0057] Example 3: Such as Figure 5 As shown, for an annular obstacle, obstacle avoidance boundaries are respectively set on the outer boundary and the inner boundary of the annular obstacle. Figure 5 The middle 10 is the obstacle, 15 is the inner boundary contour, 16 is the outer boundary contour, and the obstacle avoidance boundary 19 of the outer boundary is set in the same way as in the first and second embodiments. V 1 ~V 16 Is the vertex.
[0058] The method for determining the obstacle avoidance boundary of the inner boundary is as follows: for the straight line boundary, directly take the straight line segment corresponding to the boundary; for the convex arc boundary, select multiple arc boundaries including the start and end points of the arc boundary The feature points, the number of points, and the location are selected by the ground operator according to the radian. In general, the number of points is ≥3, and the location is evenly distributed. The larger the arc, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com