Method, system and apparatus for multi-level processing
A processor and data processing technology, applied in data processing power supply, electrical digital data processing, program control design, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing bandwidth requirements, simplifying parallel programming, and reducing power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
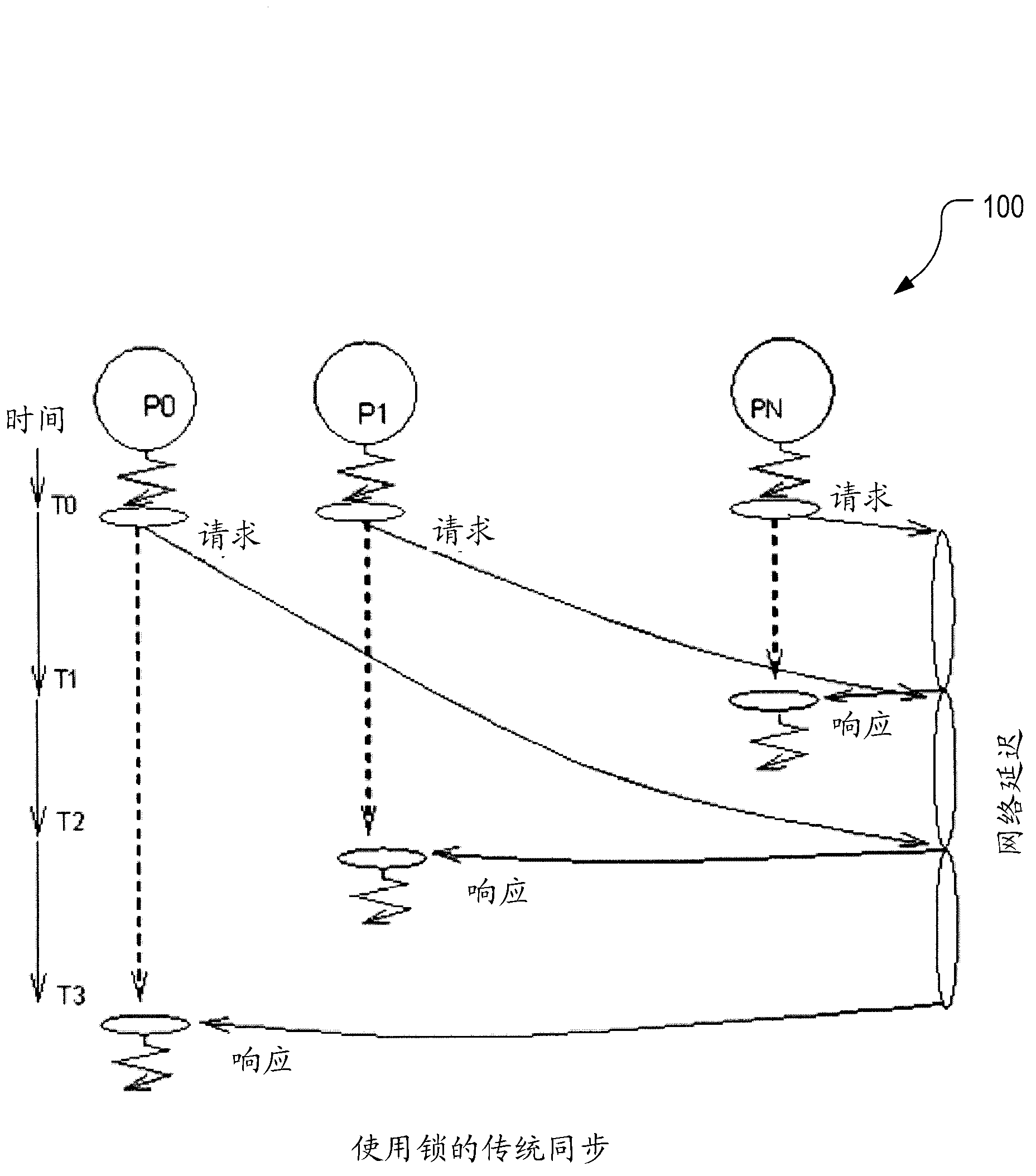
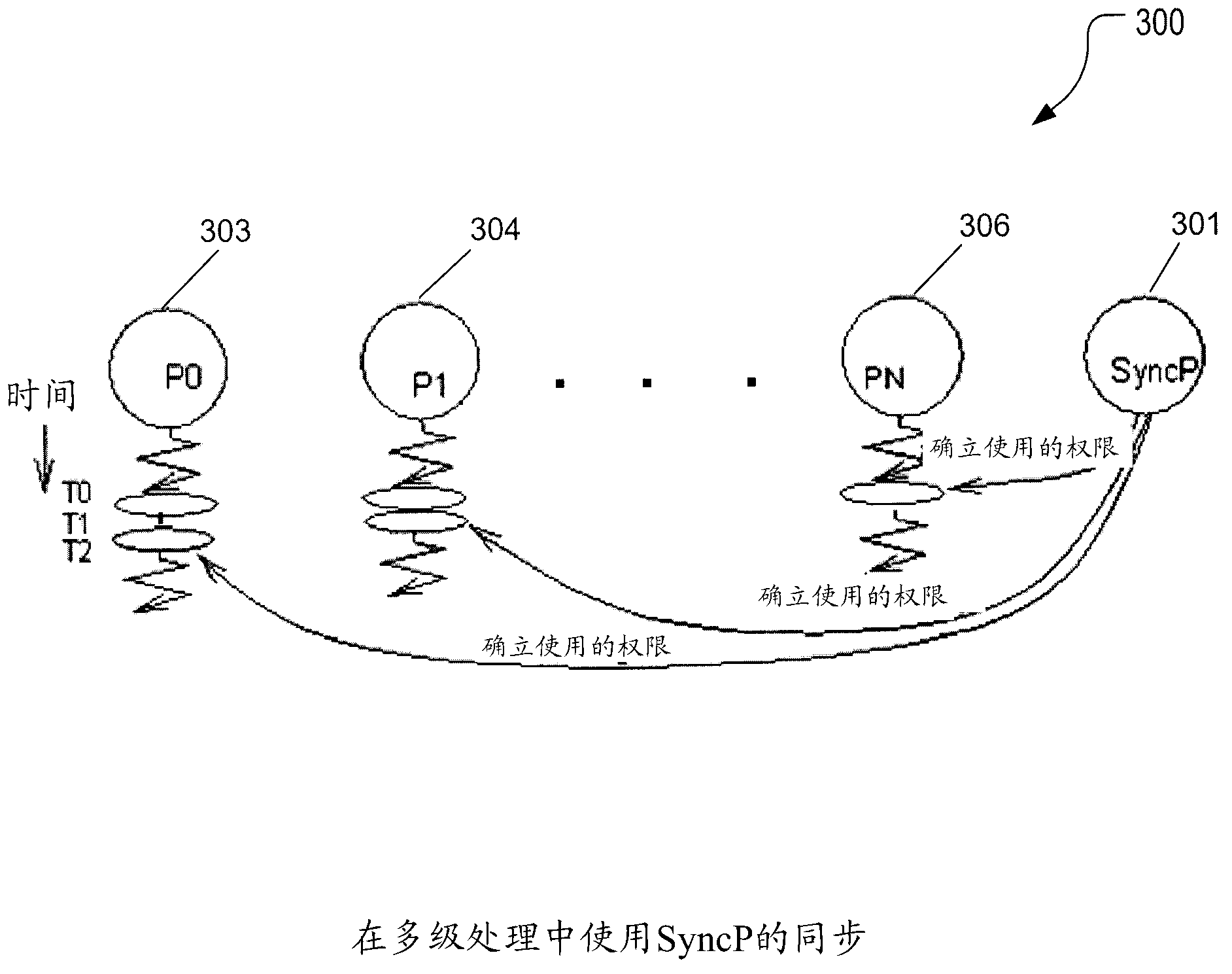
[0044] The following embodiments focus on addressing fundamental issues of parallel processing including synchronization. A solution suitable for current and future massively parallel systems is desired. This embodiment eliminates the need for locks and provides synchronization through the upper-level processor. Upper-level processor control issues permissions to use shared data or access critical sections directly to each processor at processor speed without requiring each processor to contend for a lock. Synchronization overhead is reduced to one clock for access to shared data. Traditional synchronization using locks costs N 2 bus cycles, compared to N processor cycles for synchronization in the multi-stage processing of the present invention. For a 32 conventional multiprocessor system using a 100-cycle bus, synchronization takes 32 x 32 x 100 cycles, compared to only 32 x 1 cycles for multi-stage processing, providing a gain of 3200 times.
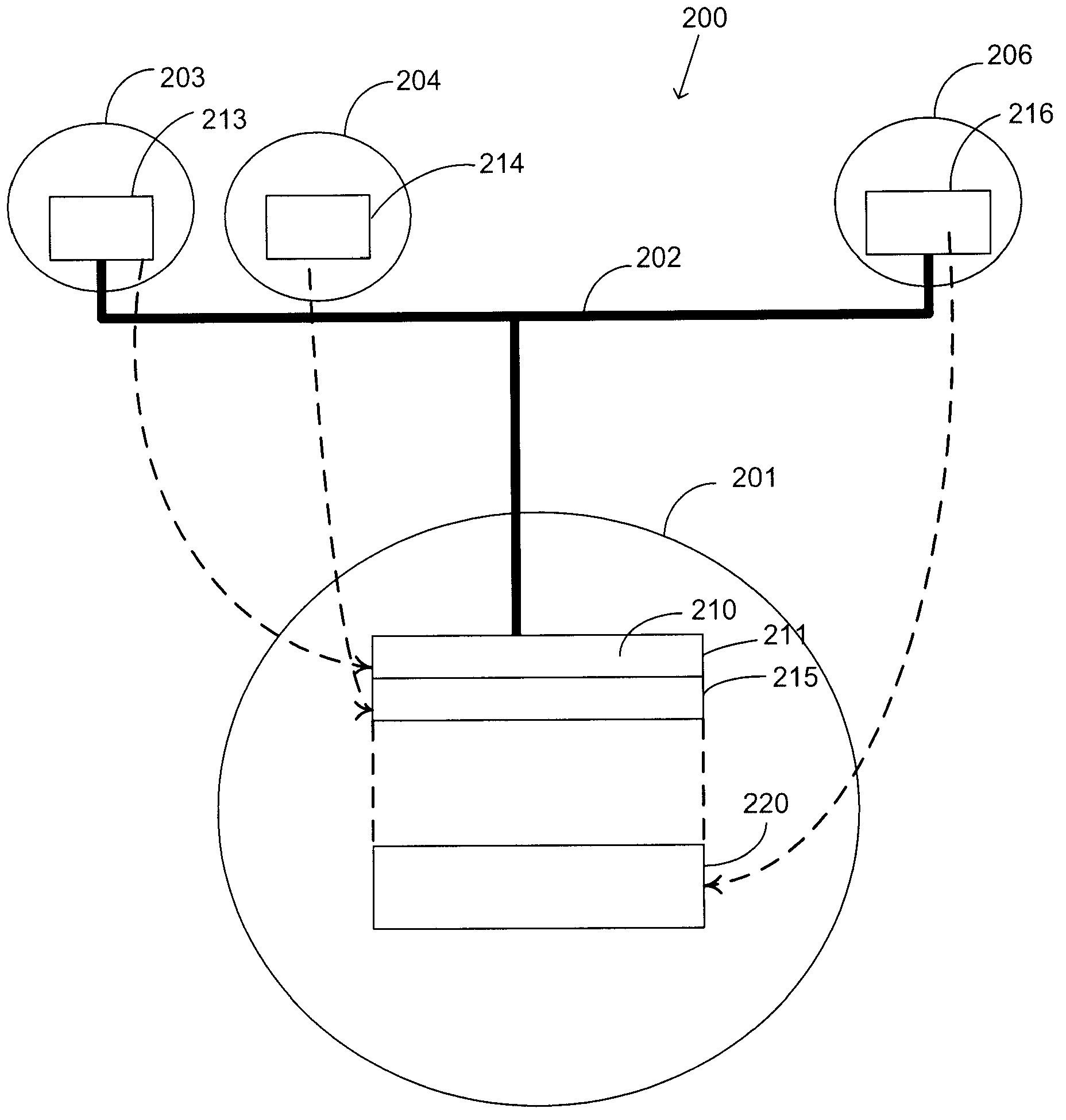
[0045] figure 2 is a bloc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com