A method for detecting the ability of plants to resist phosphorus deficiency stress by using the characteristics of root organic acid secretion
A feature detection and root exudation technology, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, material separation, and material analysis, can solve the problems of many parameters, great influence from the external environment, and high instrument cost, and achieve strong plant adaptability, short experiment period, and good quality. The effect of controllability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
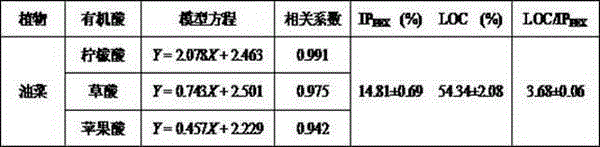
Embodiment 1
[0043] The mulberry seedlings were placed in a tray with a bottom, cultured with normal formula Hoagland (Hoagland) nutrient solution for 30 days, and then randomly divided into groups. 12 plants in each group. Different phosphorus treatments were set up, one group was cultured with normal formula (control group, normal phosphorus concentration in Hoagland’s nutrient solution), and the other group was cultured with phosphorus deficiency adversity stress treatment (phosphorus deficiency group, Hoagland’s nutrient solution). No phosphorus in the nutrient solution).
[0044] After culturing for 30 days, the root exudates of two groups of mulberry trees were collected at the same time. Add 200mL, 1mmol / LCaCl 2 The solution is collected in the bottom of the hole tray for 4 hours from 10:00 am to 14:00 pm. The solution in the hole plate is collected and the filtrate obtained by washing the roots of the plants with deionized water is the root exudation of the mulberry tree. Save, ...
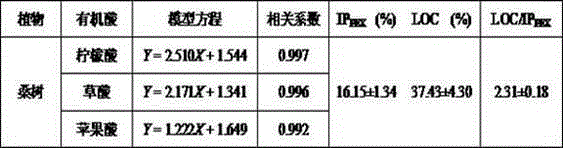
Embodiment 2
[0052] The mulberry seedlings were placed in a tray with a bottom, cultured with Hoagland nutrient solution of normal formula for 30 days, and then randomly divided into groups. 12 plants in each group. Different phosphorus treatments were set up, one group was cultured with normal formula (control group, normal phosphorus concentration in Hoagland’s nutrient solution), and the other group was cultured with phosphorus deficiency adversity stress treatment (phosphorus deficiency group, Hoagland’s nutrient solution). No phosphorus in the nutrient solution).
[0053] After culturing for 30 days, the root exudates of two groups of mulberry trees were collected at the same time. Add 200mL, 1mmol / LCaCl 2 The solution is collected in the bottom of the plug tray for 4 hours from 10:00 am to 14:00 pm, the solution in the plug tray is collected and the filtrate obtained by washing the roots of the plants with deionized water is the root exudation of the mulberry tree and stored at low...
Embodiment 3
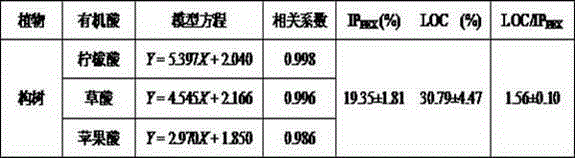
[0061] The Zhugecai seedlings were placed in a hole tray with a bottom, cultured with a normal formula of Hoagland nutrient solution for 30 days, and then randomly divided into groups. 12 plants in each group. Different phosphorus treatments were set up, one group was cultured with normal formula (control group, normal phosphorus concentration in Hoagland’s nutrient solution), and the other group was cultured with phosphorus deficiency adversity stress treatment (phosphorus deficiency group, Hoagland’s nutrient solution). No phosphorus in the nutrient solution).
[0062] After culturing for 30 days, the root exudates of the two groups of Zhuge Cai were collected at the same time. Add 200mL, 1mmol / LCaCl 2 The solution is placed in the bottom of the plug tray, collected for 4 hours from 10:00 am to 14:00 pm, the solution in the plug tray is collected and the filtrate obtained by rinsing the roots of the plants with deionized water is the root exudate of Zhuge vegetable. Prese...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com