Optical fiber splicer
A technology of optical fiber splices and optical fibers, which is applied in the field of optical fiber connection devices, can solve the problems of long-term reliability decline, failure of optical fiber docking, and easy breakage of bare fibers, etc., and achieve the effect of simple structure, high quality of docking, and low price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
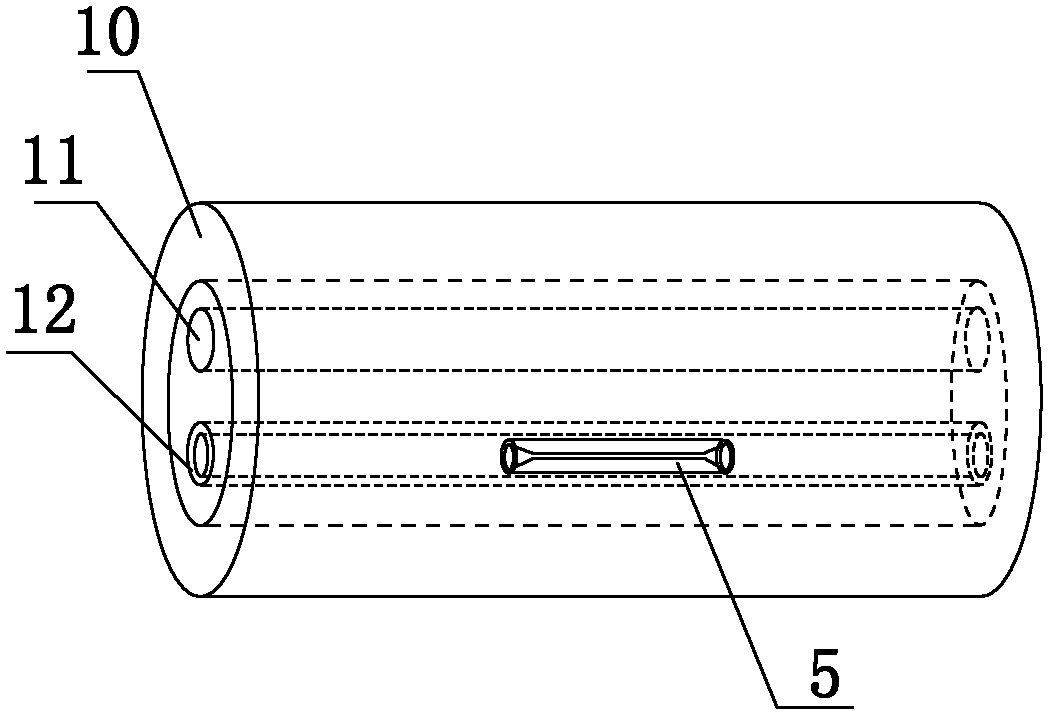
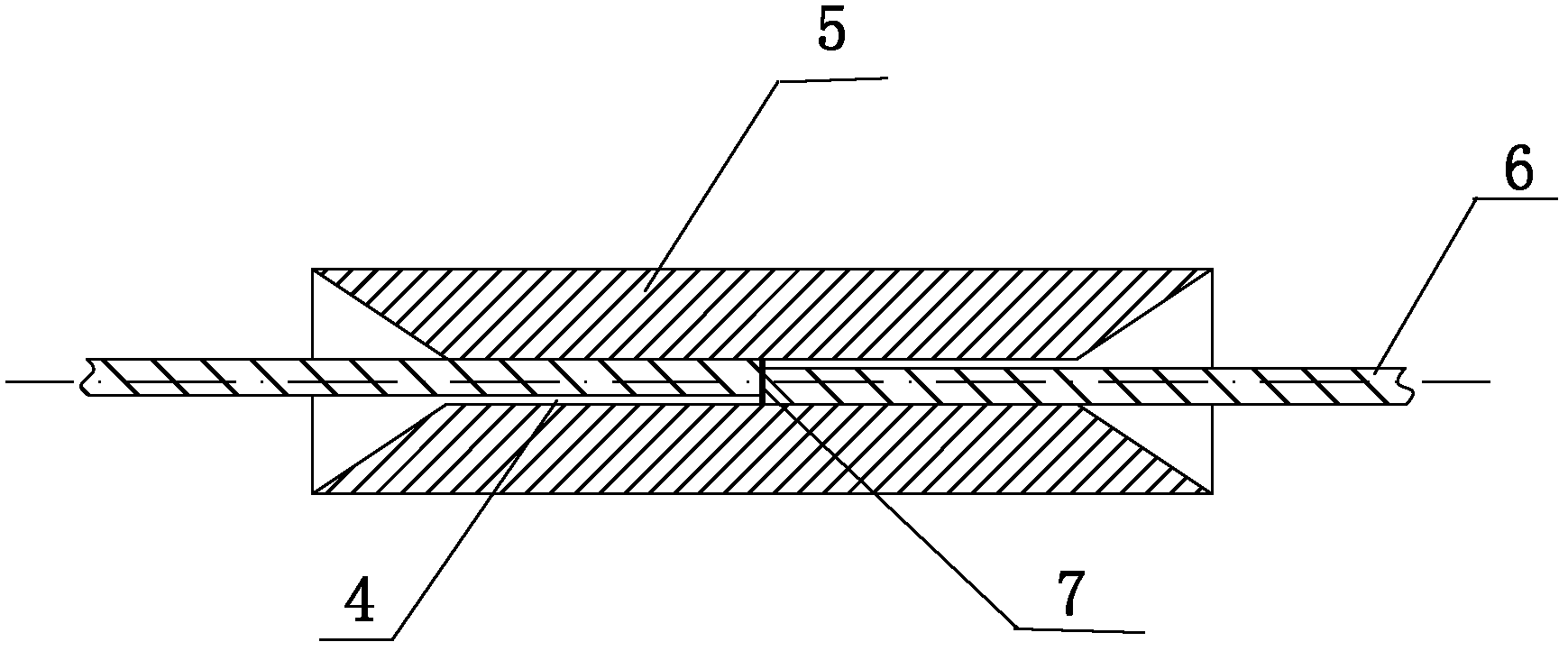
[0035] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 with image 3 As shown, a fiber optic connector includes an alignment tube 5 made of a memory alloy material. The two ends of the alignment tube 5 are tapered optical fiber 6 inlets, and the initial inner diameter of the inner hole of the alignment tube 5 is D. T1 Inner diameter D after low temperature expansion T2 The relationship with fiber 6 is:
[0036] [1-(1-S)×K]×D F T1 F (1)
[0037] D. F T2 F ×(1+S×K) (2)
[0038] D. F is the outer diameter of the optical fiber at the time of docking, K is the shape memory gauge factor of the alignment tube 5 made of memory alloy material, S is a selected proportional coefficient, the preferred K value is 8%, and the S value is selected as 0.5, which also includes thermal shrinkage The sleeve 10, inside the heat-shrinkable sleeve 10 is arranged a heat-melt pipe 12 and a reinforcement 11 located outside the heat-melt pipe 12 and parallel to the heat-melt pipe 12, and the alignment pipe 5 ...
Embodiment 2
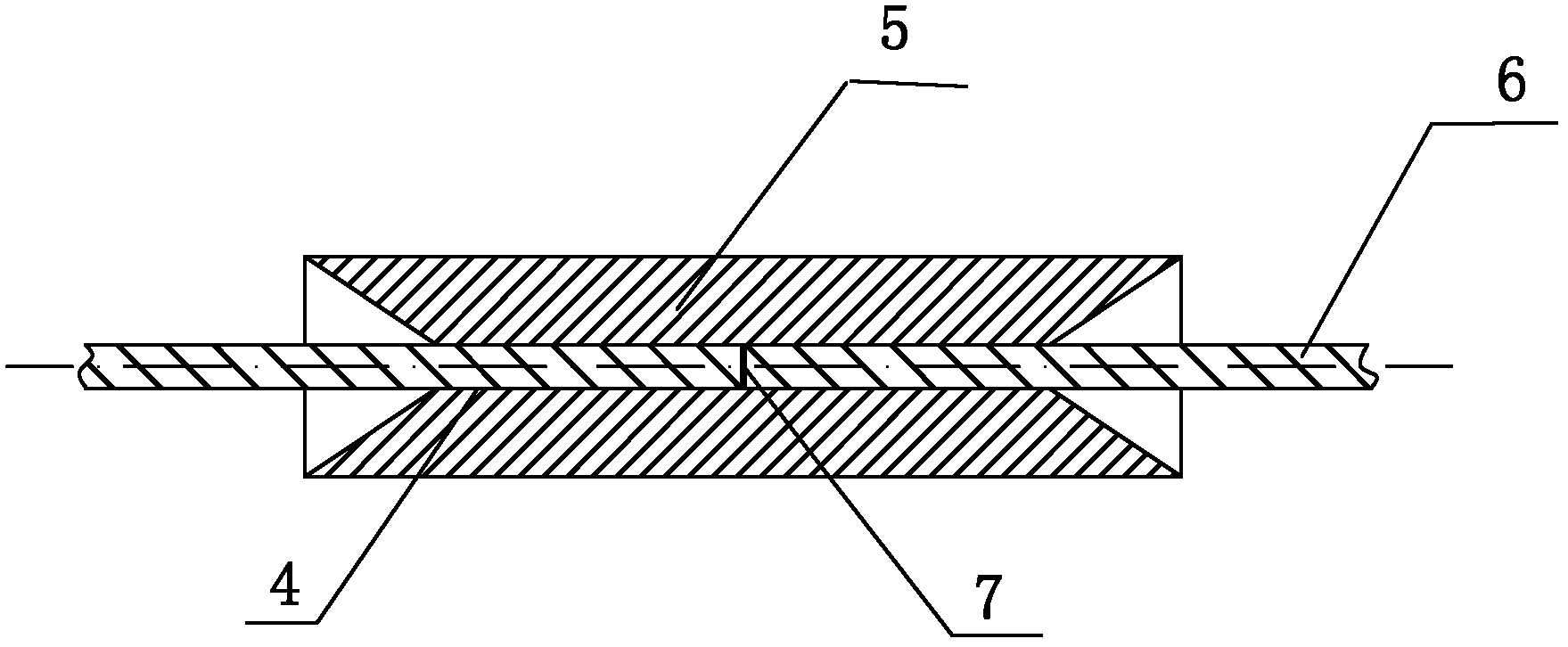
[0049] Such as Figure 4 , Figure 5 As shown, in this embodiment, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the alignment pipe 5 includes a circular pipe 1 in the middle and a semicircular pipe 2 extending to both sides with a radial opening not less than 120 degrees. and semicircular tube II 3. In this way, the first semicircular tube 2 and the second semicircular tube 3 can protect the uncoated bare optical fiber 6 and have good strength when the thermal fusion tube 12 is melted and cooled.
[0050] Preferably, the alignment tube 5 includes a circular tube 1 in the middle and flat plates extending to both sides.
[0051] In this embodiment, the structures, connections and working principles of other parts are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com