Pentose phosphate pathway upregulation to increase production of non-native products of interest in transgenic microorganisms
A transgenic and microbial technology, applied in the direction of microorganisms, microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems that hinder the function, toxicity, and acceleration of the PP pathway
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
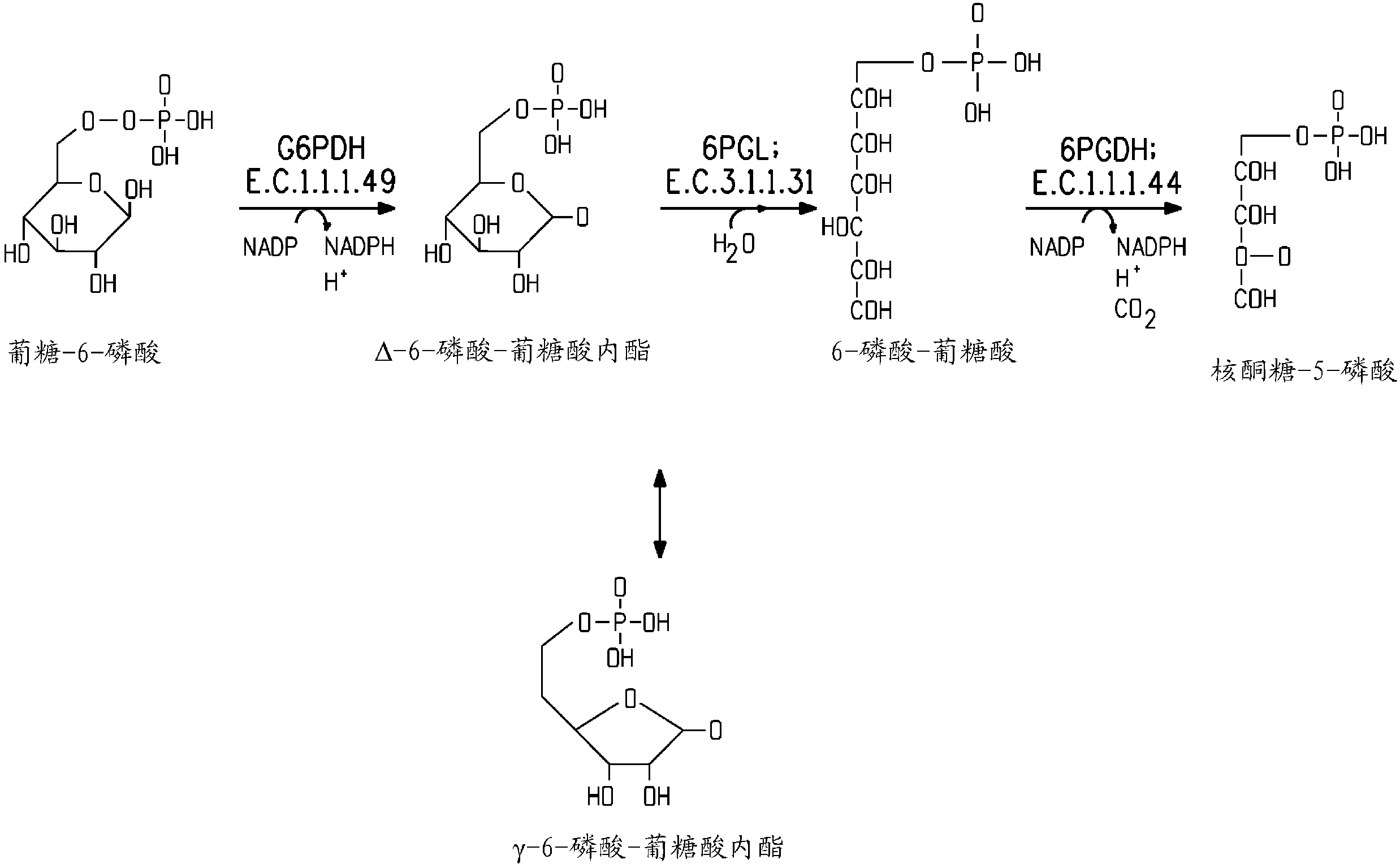
[0275] Overexpression of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in Yarrowia lipolytica strain Y2107U ("G6PDH")
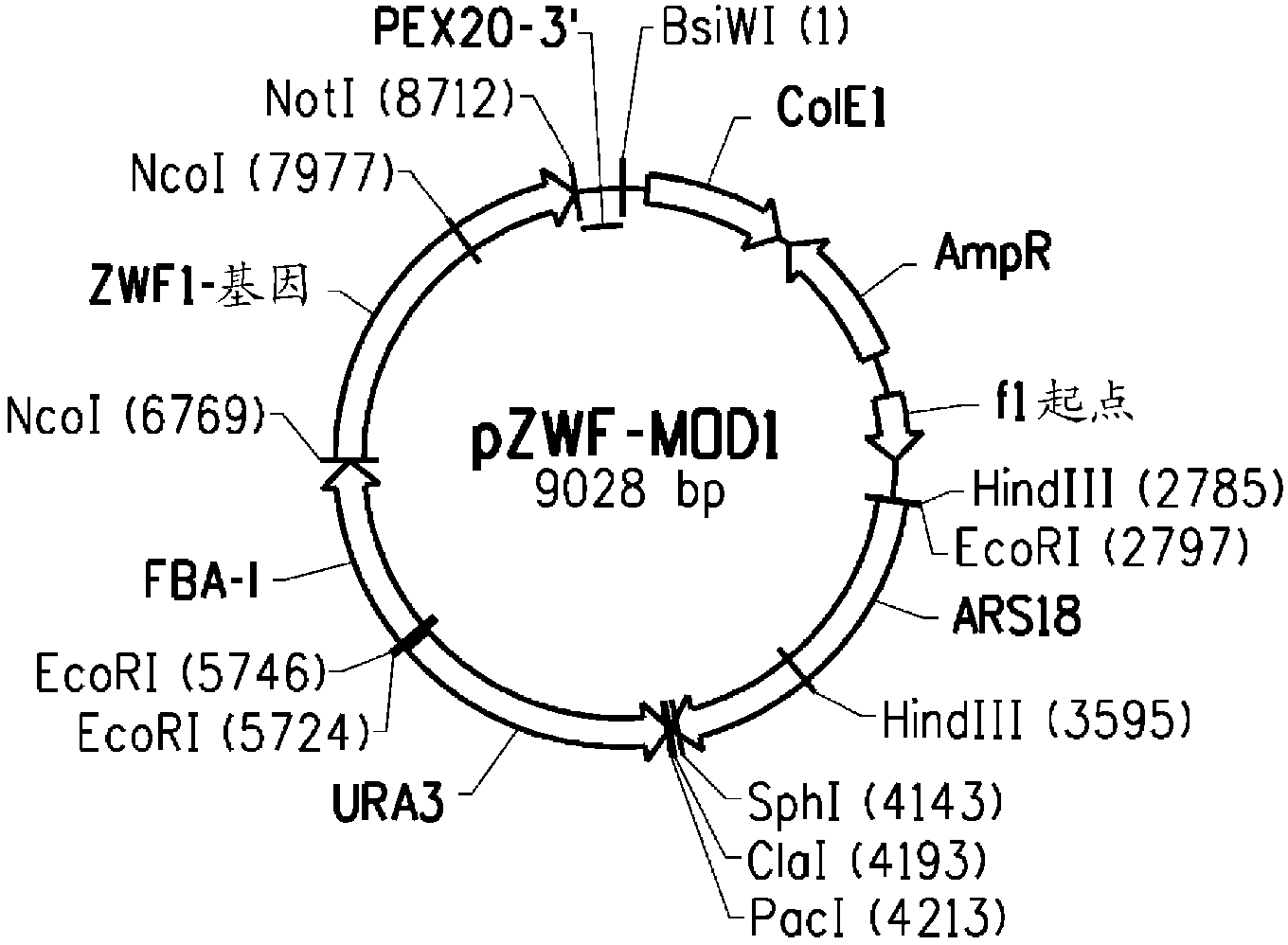
[0276] This example describes the construction of plasmid pZWF-MOD1 ( Figure 2A ; SEQ ID NO:7) to enable overexpression of the Yarrowia gene encoding glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase ["G6PDH"] under the control of the strong native Yarrowia promoter.
[0277] The PUFA-producing Yarrowia lipolytica strain Y2107U was transformed with the overexpression plasmid, and the effect of overexpression on cell growth and lipid synthesis was determined and compared. Specifically, overexpression of G6PDH caused decreased cell growth.
[0278] Construction of plasmid pZWF-MOD1 containing Yarrowia G6PDH
[0279] The Yarrowia lipolytica G6PDH ORF contains an intron near the 5' end (nucleotides 85-524 of SEQ ID NO: 10). The nucleotide sequence of the cDNA encoding G6PDH is shown in SEQ ID NO:1.
[0280] Primers YZWF-F1 (SEQ ID NO: 8) and YZWF-R (SEQ ID NO: 9) were designed to...
Embodiment 2
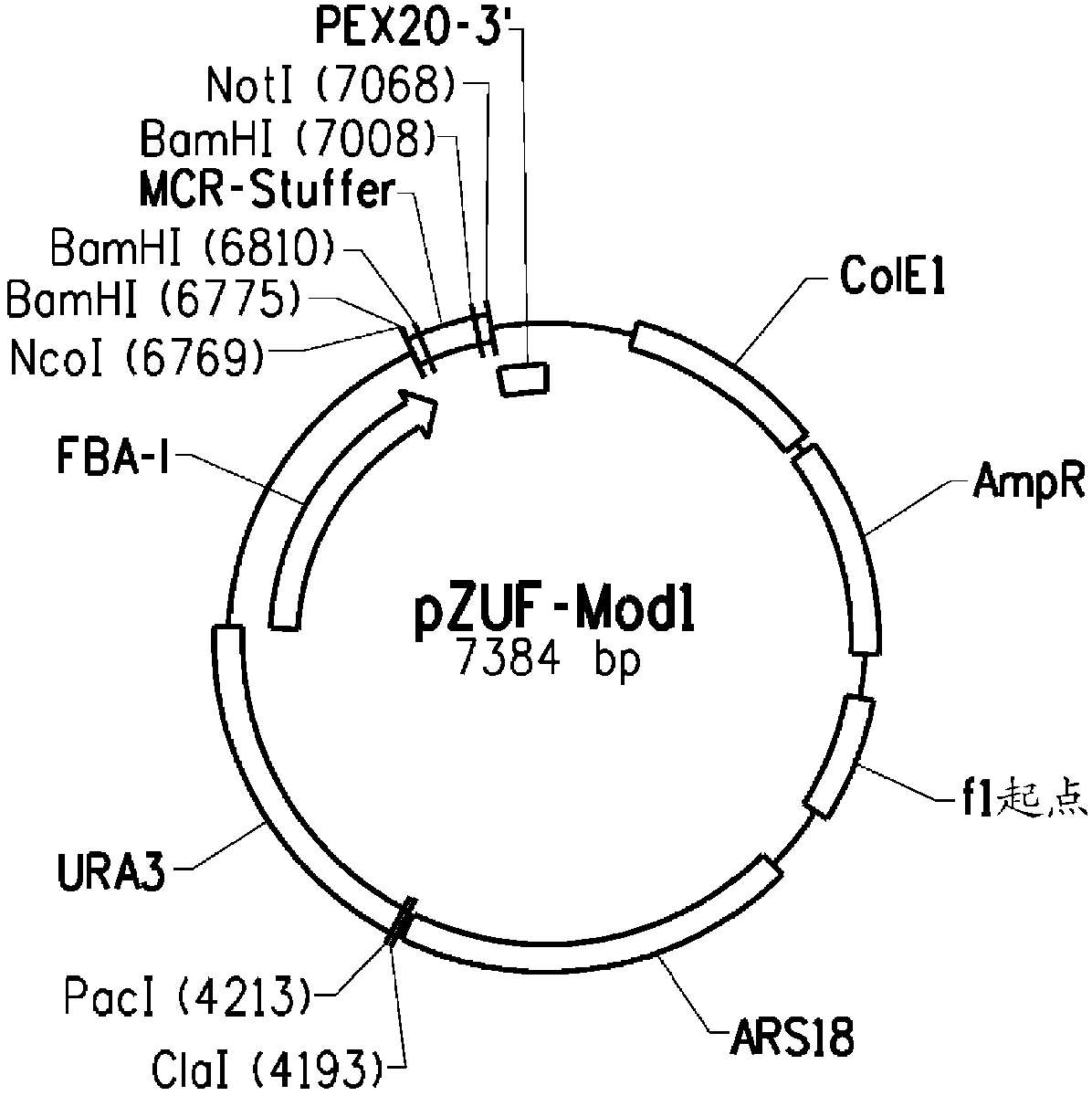
[0299] Construction of plasmid pZKLY-PP2 for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase ["G6PDH"] and glucose-6-phosphate Co-regulated overexpression of glycolactonase ["6PGL"]
[0300] This example describes the construction of plasmid pZKLY-PP2 ( Figure 3A ; SEQ ID NO: 15) Overexpression of Yarrowia encoding glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase ["G6PDH"] and 6-phosphogluconolactonase ["6PGL"] in a co-regulated manner Gene. Specifically, the weak native Yarrowia promoter was chosen to drive expression of G6PD, while the strong native Yarrowia promoter was operably linked to 6PGL. This process was designed to ensure rapid conversion of 6-phosphogluconolactone to 6-phosphogluconate and thereby avoid accumulation of toxic levels of 6-phosphogluconolactone.
[0301] Construction of plasmid pZKLY-PP2 to overexpress G6PDH and 6PGL
[0302] Construction of plasmid pZKLY-PP2 first required separate amplification of the Yarrowia 6PGL and G6PDH genes and ligation of each corresponding ge...
Embodiment 3
[0310] Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase ["G6PDH"] and 6- Co-regulated overexpression of phosphogluconolactonase ["6PGL"] increases accumulated total lipid
[0311] This example describes the transformation of PUFA producing Yarrowia lipolytica strain Y4305U with plasmid pZKLY-PP2 and the effect of co-regulated overexpression of G6PDH and 6PGL on cell growth and lipid synthesis. Specifically, co-regulated overexpression of G6PDH and 6PGL resulted in an increase in the total amount of lipids expressed as a percentage of DCW and the amount of PUFAs expressed as a percentage of TFA in transformed cells.
[0312] Y. lipolytica strain Y4305U (General Methods) was transformed with the 8.5 kB AscI / SphI fragment of pZKLY-PP2 (SEQ ID NO: 15; Example 2) (following General Methods). Transformants were selected on SD medium plates lacking uracil. The three pZKLY-PP2 transformants were referred to as strains PP12, PP13 and PP14.
[0313] For lipid analysis, pZKLY-PP2 transformants an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com