Optical waveguide device, and manufacturing method for optical waveguide device
A manufacturing method and technology for optical waveguides, applied in the directions of light guides, optics, optical components, etc., can solve the problems of no wavelength dependence of optical branches, interference resistance, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing wavelength dependence.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example )
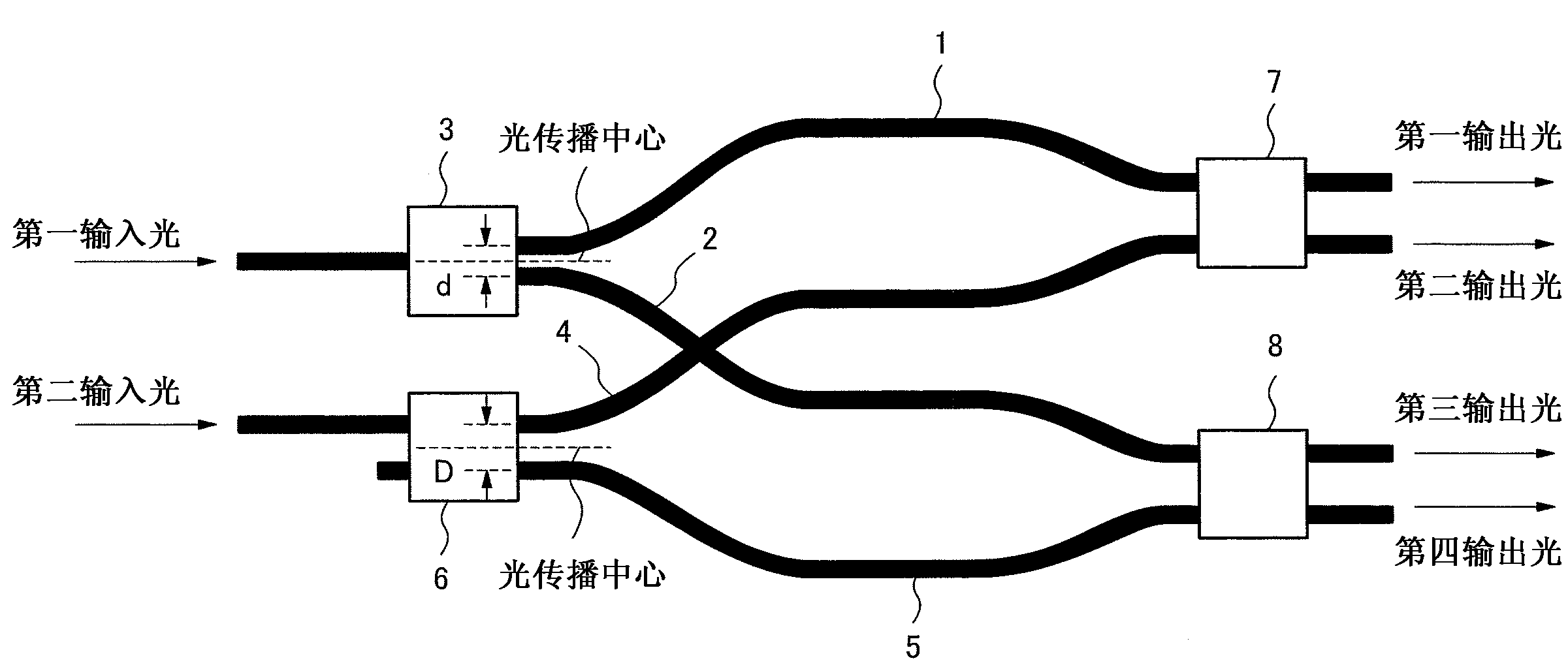
[0032] figure 1 is a schematic diagram showing the structure of the optical waveguide device according to the first embodiment of the present invention. figure 1 The optical waveguide device has: an optical branching device 3, which branches the first input light and outputs it to the optical waveguides 1 and 2; and an optical branching device 6, which branches the second input light and outputs it to the optical waveguides 4 and 5 . and figure 1The optical waveguide device has: an optical coupler 7 that mixes the light waves traveling through the optical waveguides 1 and 4, and then separates the mixed light waves to output first and second output lights; and an optical coupler 8 that mixes the light waves that pass through the optical waveguide 2 and 5 traveling light waves, and then separate and mix the light waves to output third and fourth output lights.
[0033] Each of the pair of optical waveguides 1 and 2 and the pair of optical waveguides 4 and 5 is equal in op...
no. 2 example )
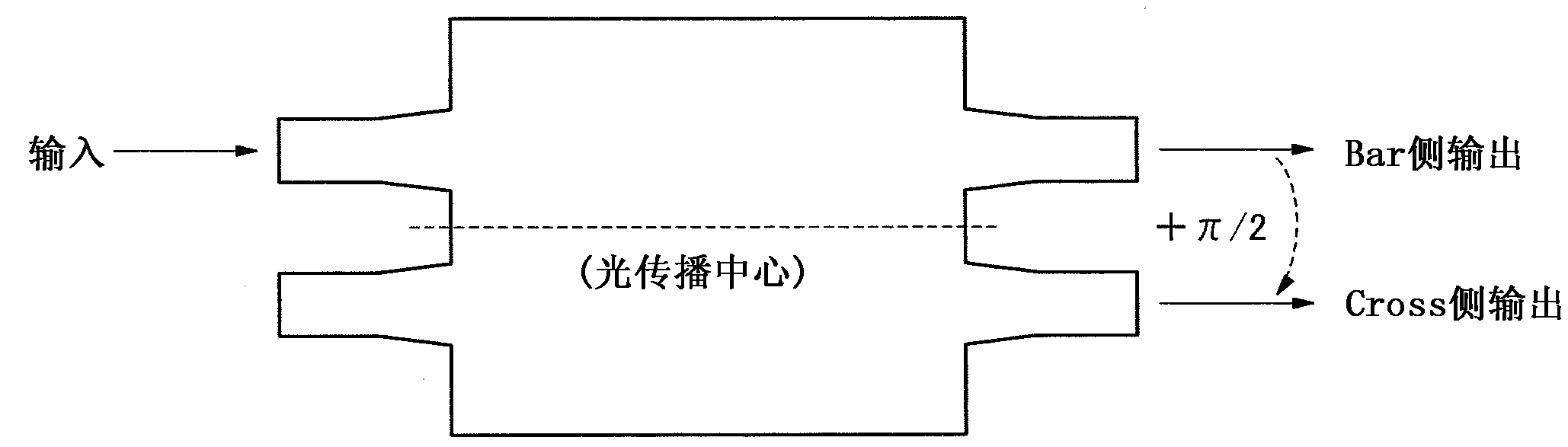
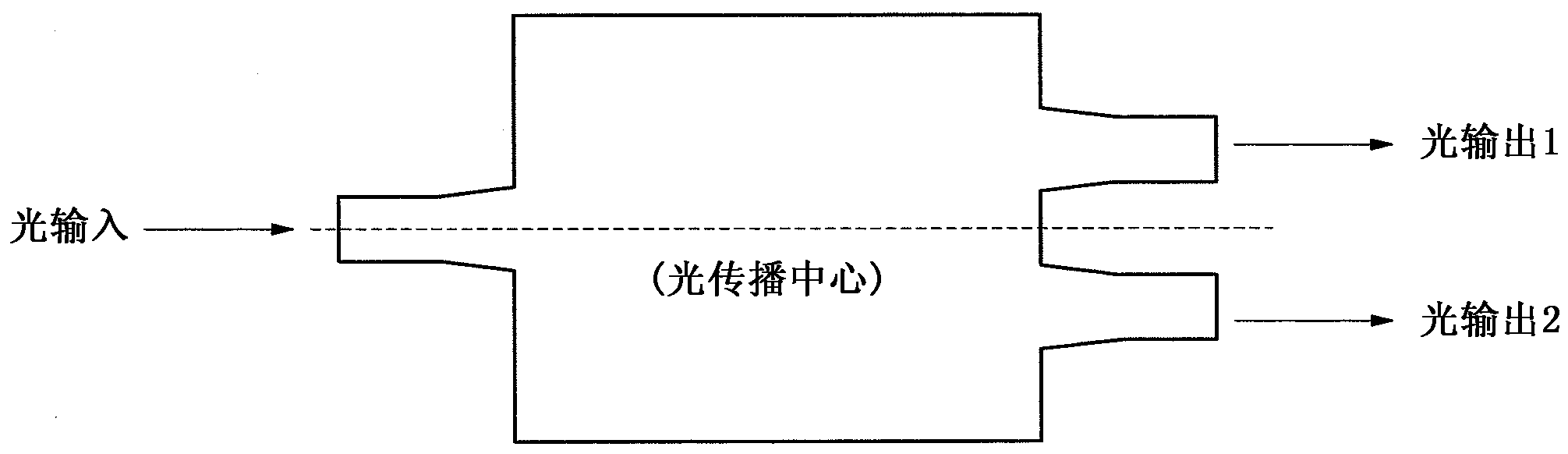
[0040] Next, a second embodiment of the present invention is described. The second embodiment uses the Y-branch structure type optical branching device as figure 1 Optical branching device 3 in. As the optical branching device 3, for example, even if using such as image 3 The shown multimode interferometer beam splitter with 1 input and 2 outputs having one input end performing light input from a position including the center of the light propagation direction can also perform the same light branching without causing a phase difference. However, the Y-branch structure type optical branching device has the characteristics that the structure is relatively simple, basically has no wavelength dependence, and is relatively resistant to interference in manufacture.
[0041] Also, as the optical couplers 7 and 8 , for example, Mach-Zehnder interferometers having the same characteristics can be used.
[0042] Furthermore, both the optical waveguide 1 and 2 pair, and the optical w...
no. 3 example )
[0053] Next, a third embodiment of the present invention is described. Figure 7 It is a schematic diagram showing an optical waveguide structure of a 90-degree optical mixing interferometer constituted by arranging two coherent mixers of the second embodiment in parallel.
[0054] However, in Figure 7 In , relative to the upper side coherent mixer, the lower side coherent mixer has an inverted positional relationship between the input ports of the optical signal and the local oscillator light. Therefore, the lower side coherent mixer switches the position of the input optical branching device, uses the Y-branch structure type optical branching device as the optical branching device 3b, and uses the 2-input and 2-output 3dB multimode interferometer beam splitter as the optical branching device 6b. In addition, the input side of the input light of the optical branching device 6b is also exchanged. Therefore, by configuring the lower side coherent mixer as described above, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com