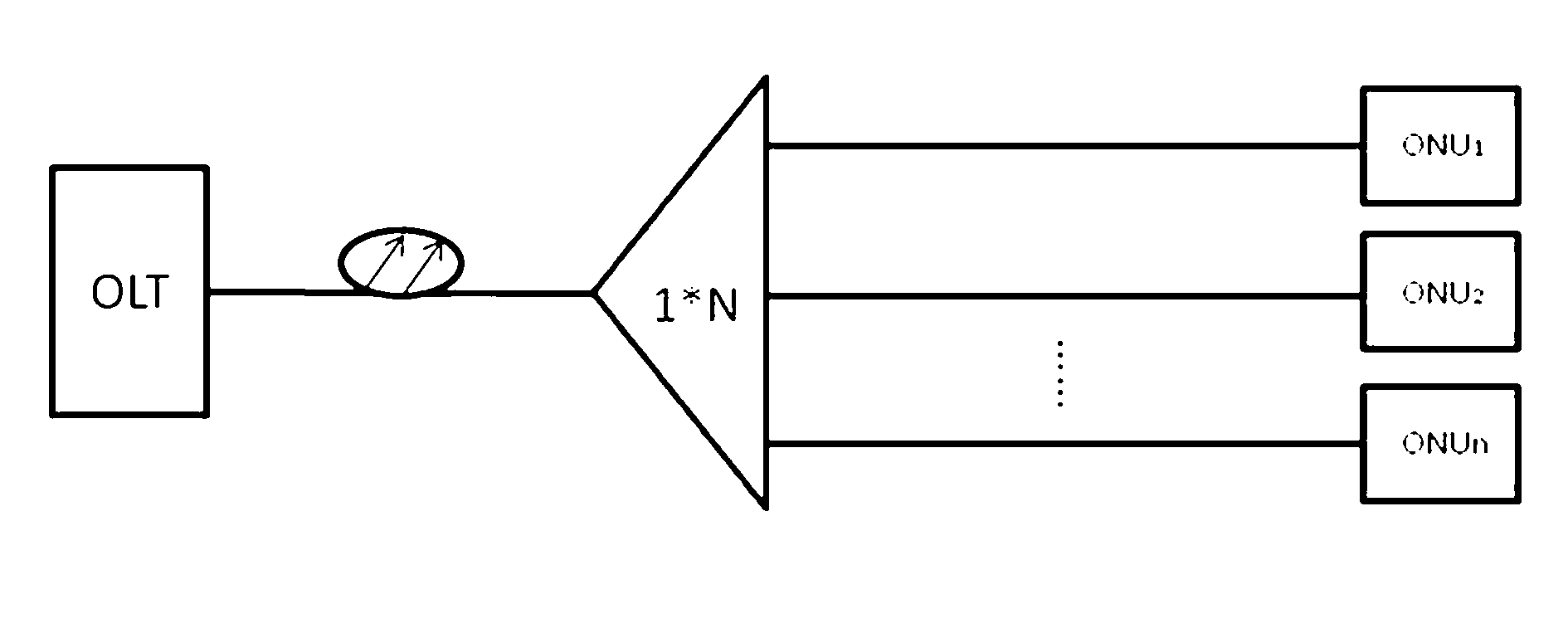
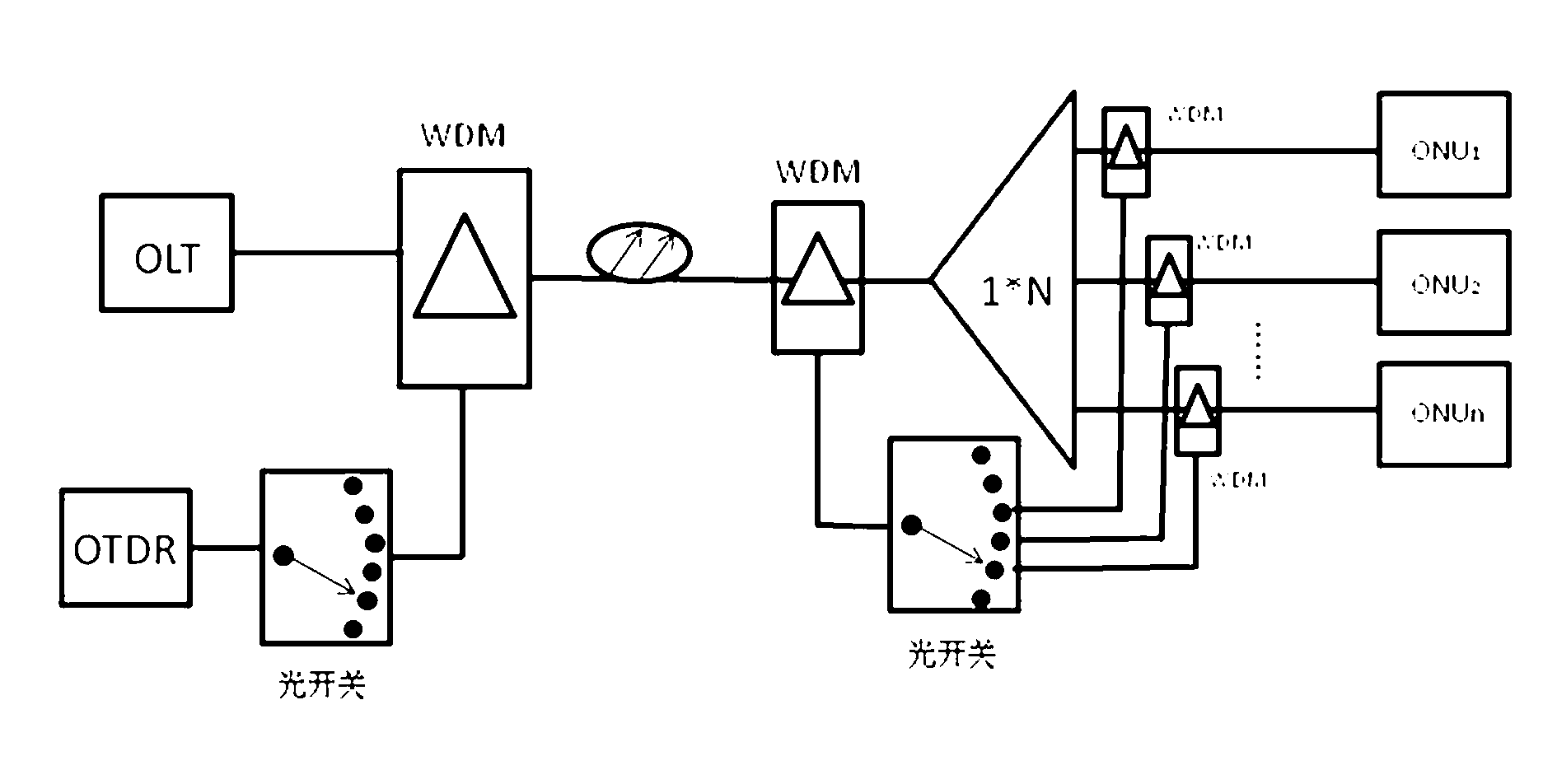
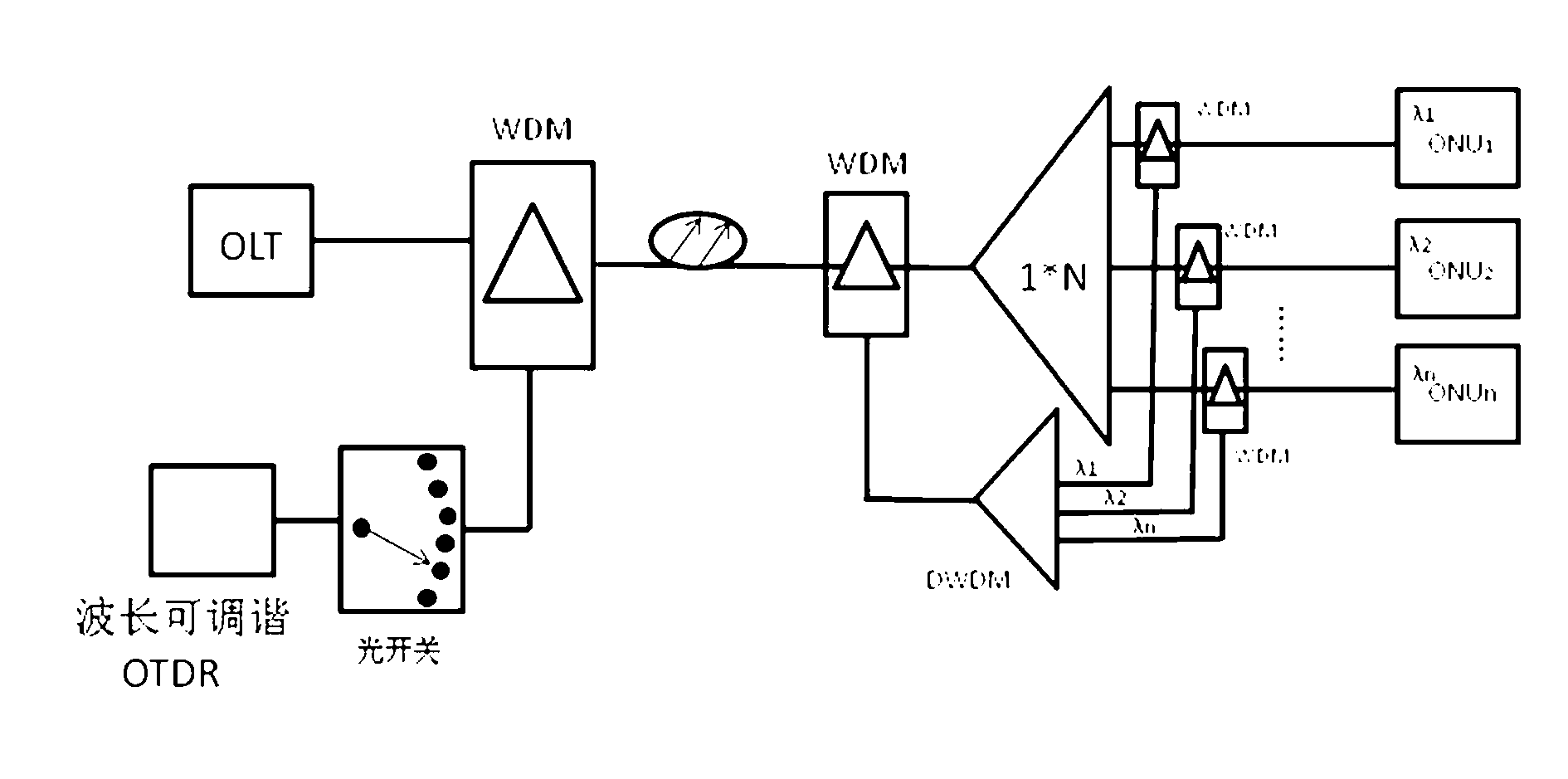
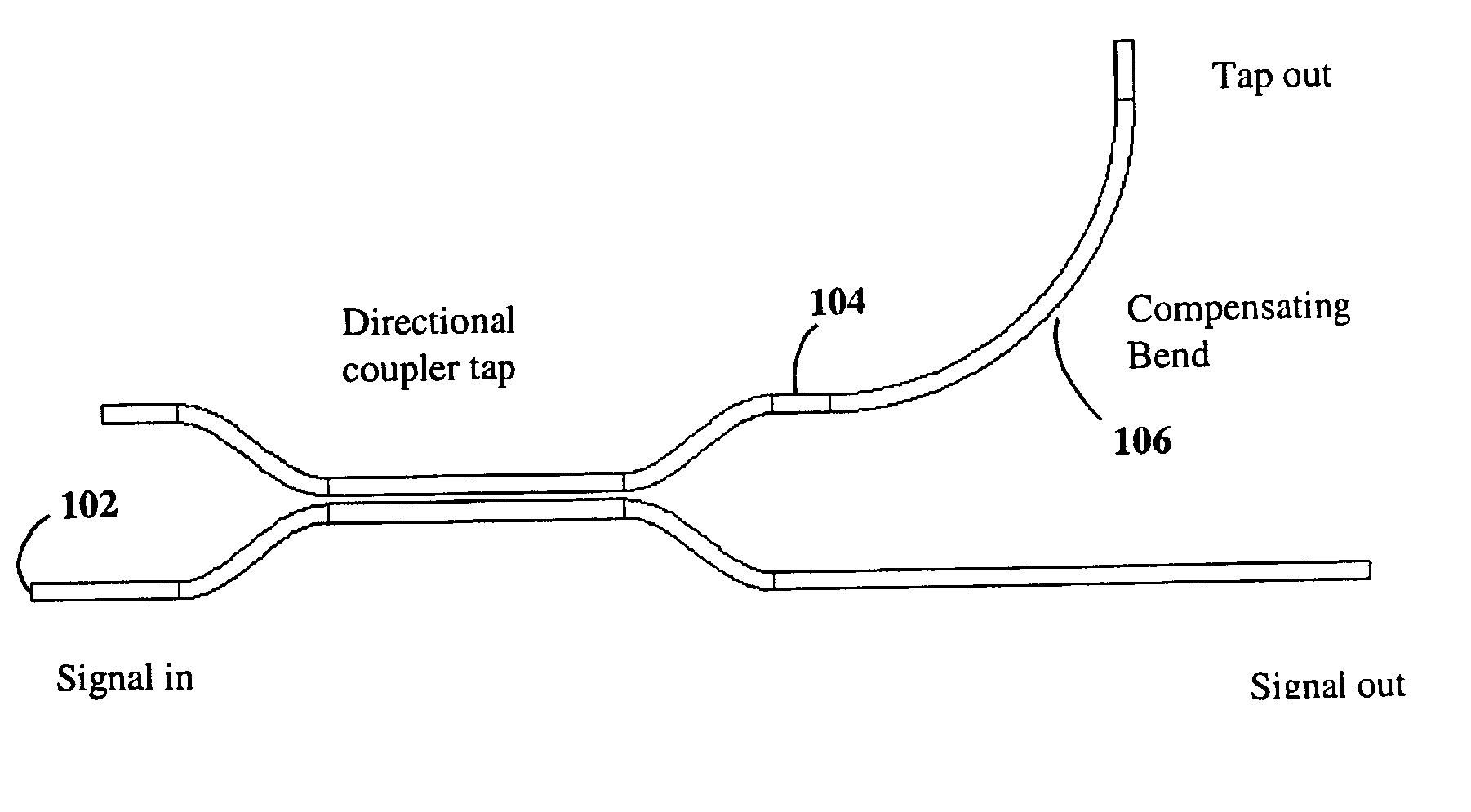
Patents
Literature
120 results about "Optical branch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
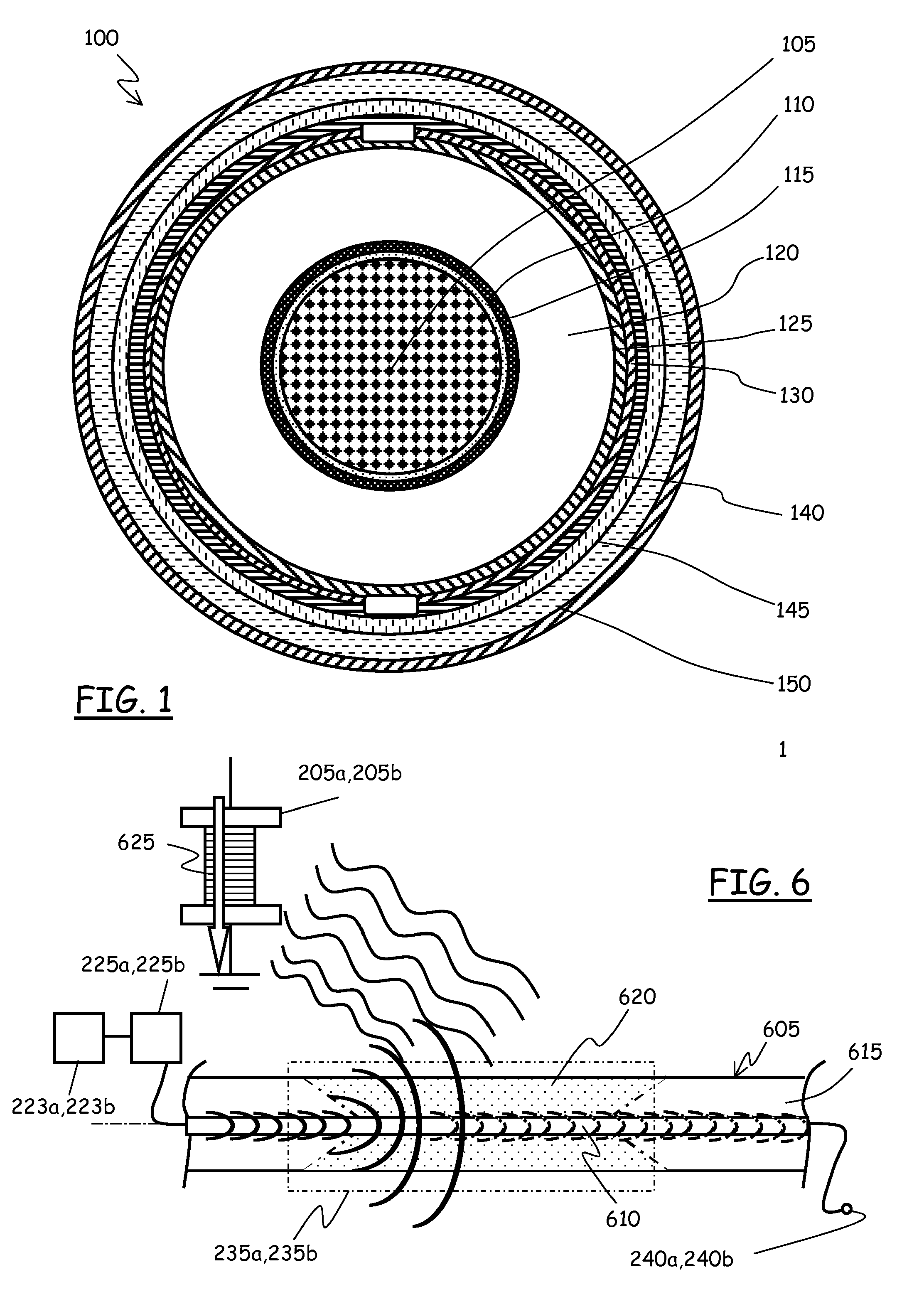
Seabed optical cable branch joint box and connection process thereof
ActiveCN1790078AAvoid excessive bendingSmall form factorOptical fibre/cable installationCoupling light guidesCommunications systemEngineering
The invention discloses a submarine optical branch connector box and connecting technology, which comprises the following parts: main cable bending limiter, external pyramid, middle pyramid, conical axle, bearing nut, pushing sleeve, O-shaped coil liner, sealing seat body, support ring, compression ring, locking axle, tray, sealing cylinder, branch line case, branch seat bearing nut, branch seat, locking nut, branch sealing seat and branch binding limiter, wherein the main cable bending limiter, bearing nut, pushing sleeve, sealing component, branch seat bearing nut and sealing seat pierce the main cable end sequently; branch one and two cables pierce the branch binding limiter, bearing nut, pushing sleeve and sealing component.
Owner:ZHONGTIAN TECH MARINE SYST CO LTD
Photonic filtering of electrical signals
InactiveUS20100230621A1Reliable and simple and widely tunable filterMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingPhotodetectorCarrier signal
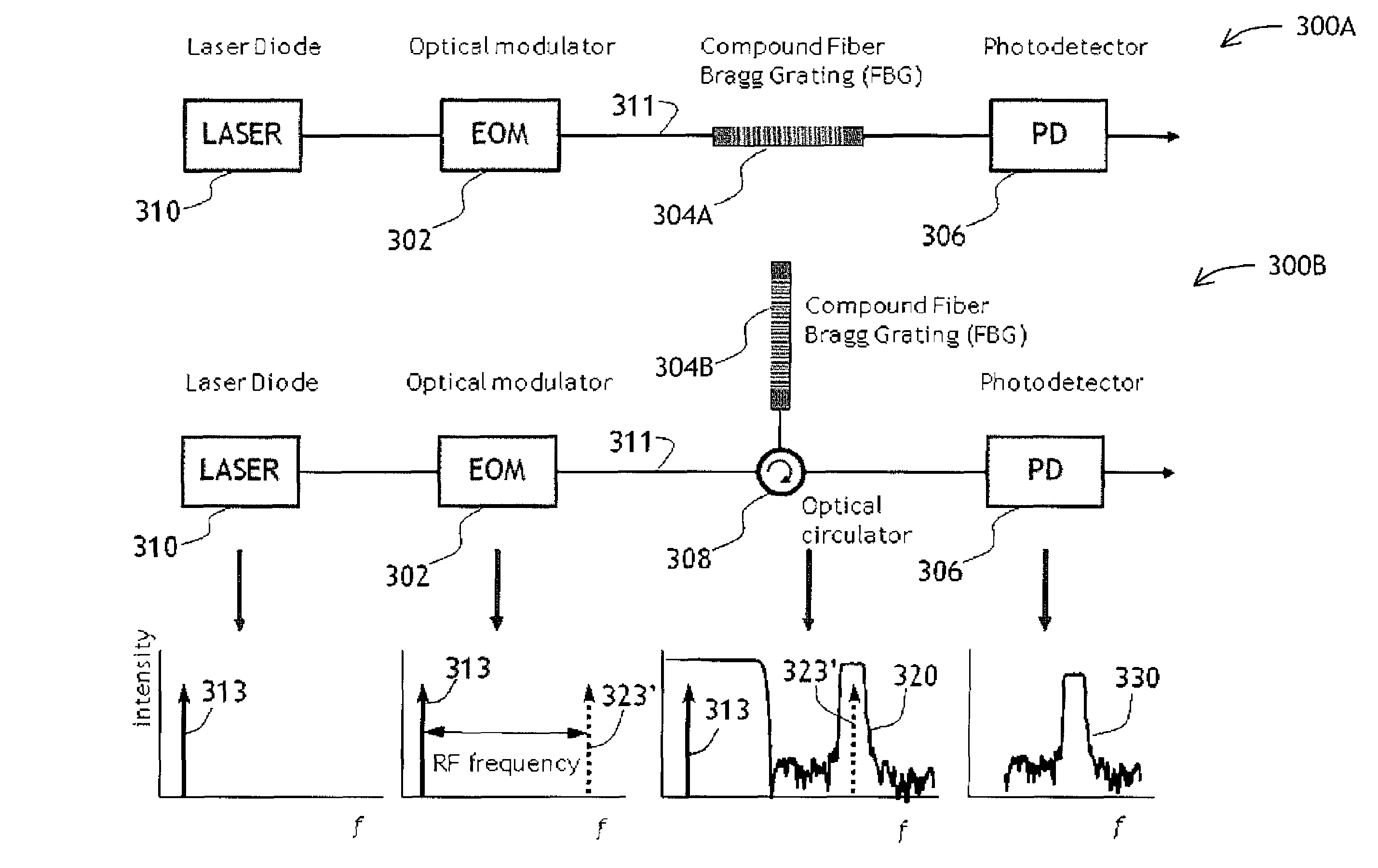
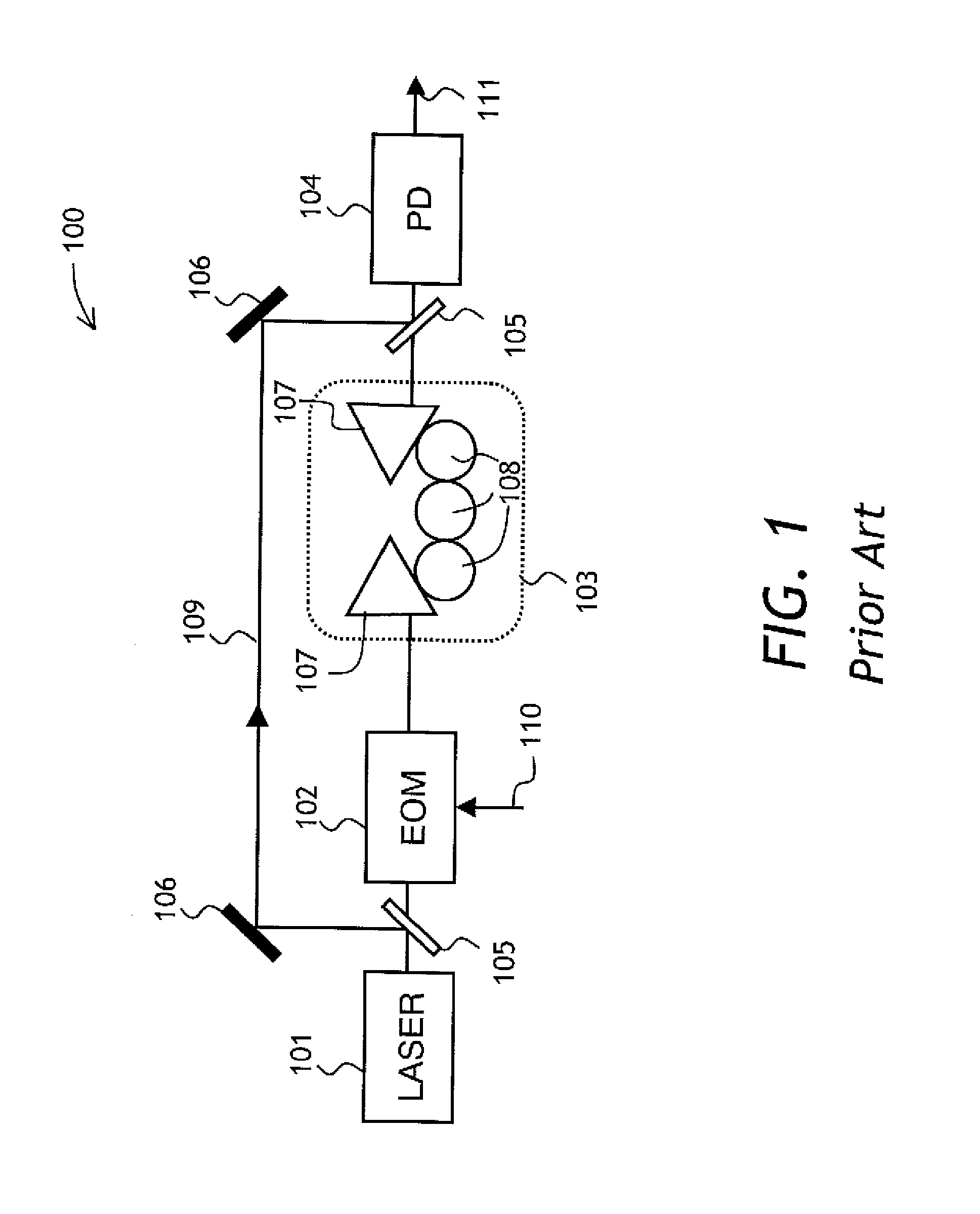
A filter and a method of filtering a high frequency electrical signal using photonic components is disclosed. The filter has a serially fiber-coupled laser source, a modulator, a filter, and a photodetector. The electrical signal is applied to the modulator. The modulated light propagates through the filter which is constructed to pass not only a modulated sideband, but also at least a fraction of light at the carrier frequency of the laser. The photodetector detects a signal at the beat frequency between the carrier and sideband signals, after both signals have propagated through the filter. As a result, a separate optical branch for light at the carrier frequency is not required, which considerably simplifies the filter construction and makes it more stable and reliable.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Optical add/drop multiplexer
InactiveUS20060023996A1Small and cheapTransmission distanceWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic network arrangementsAudio power amplifierMultiplexer
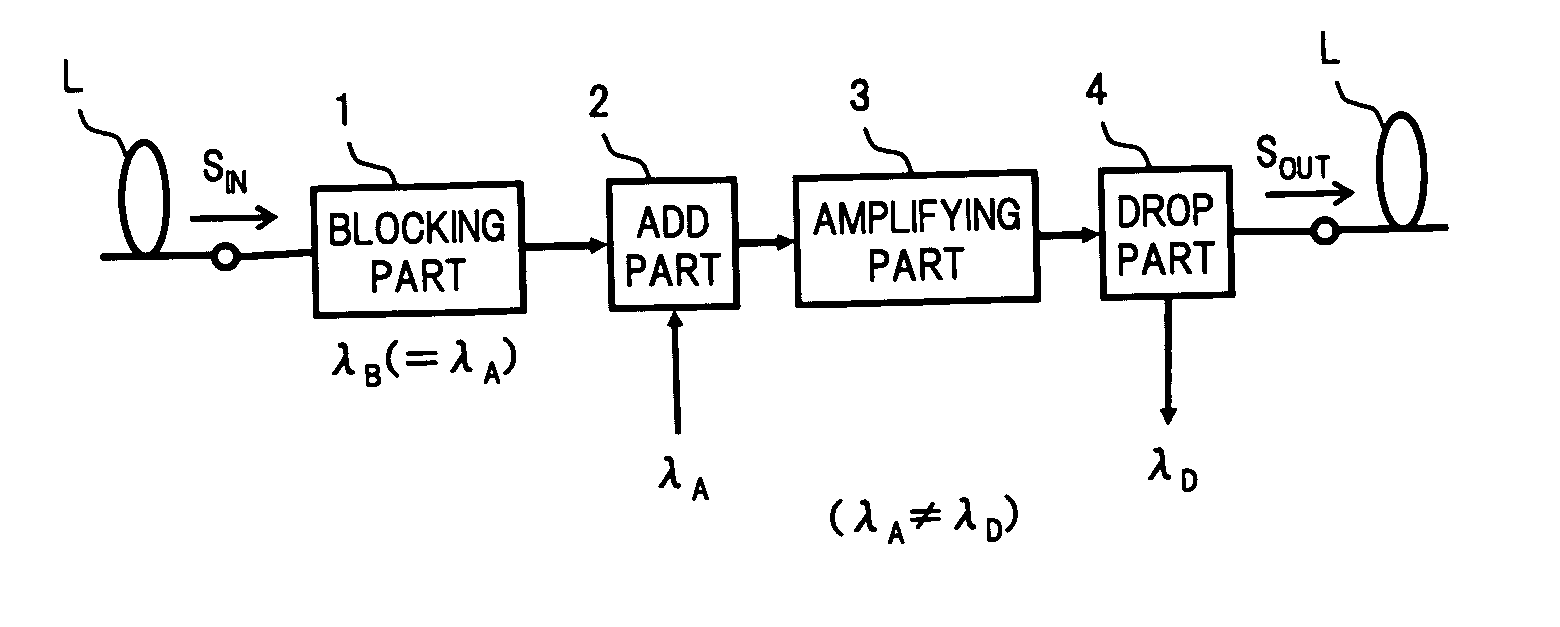
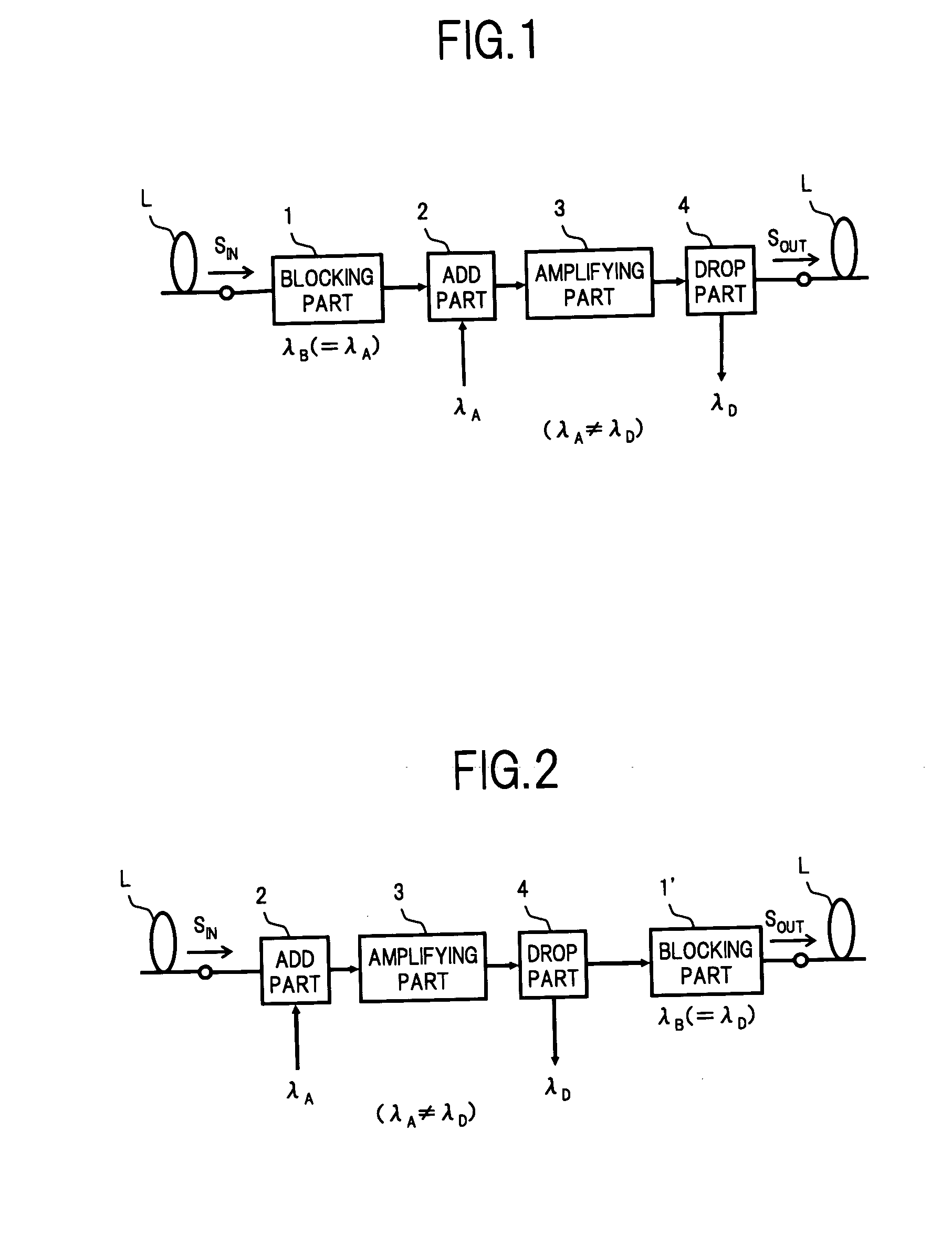
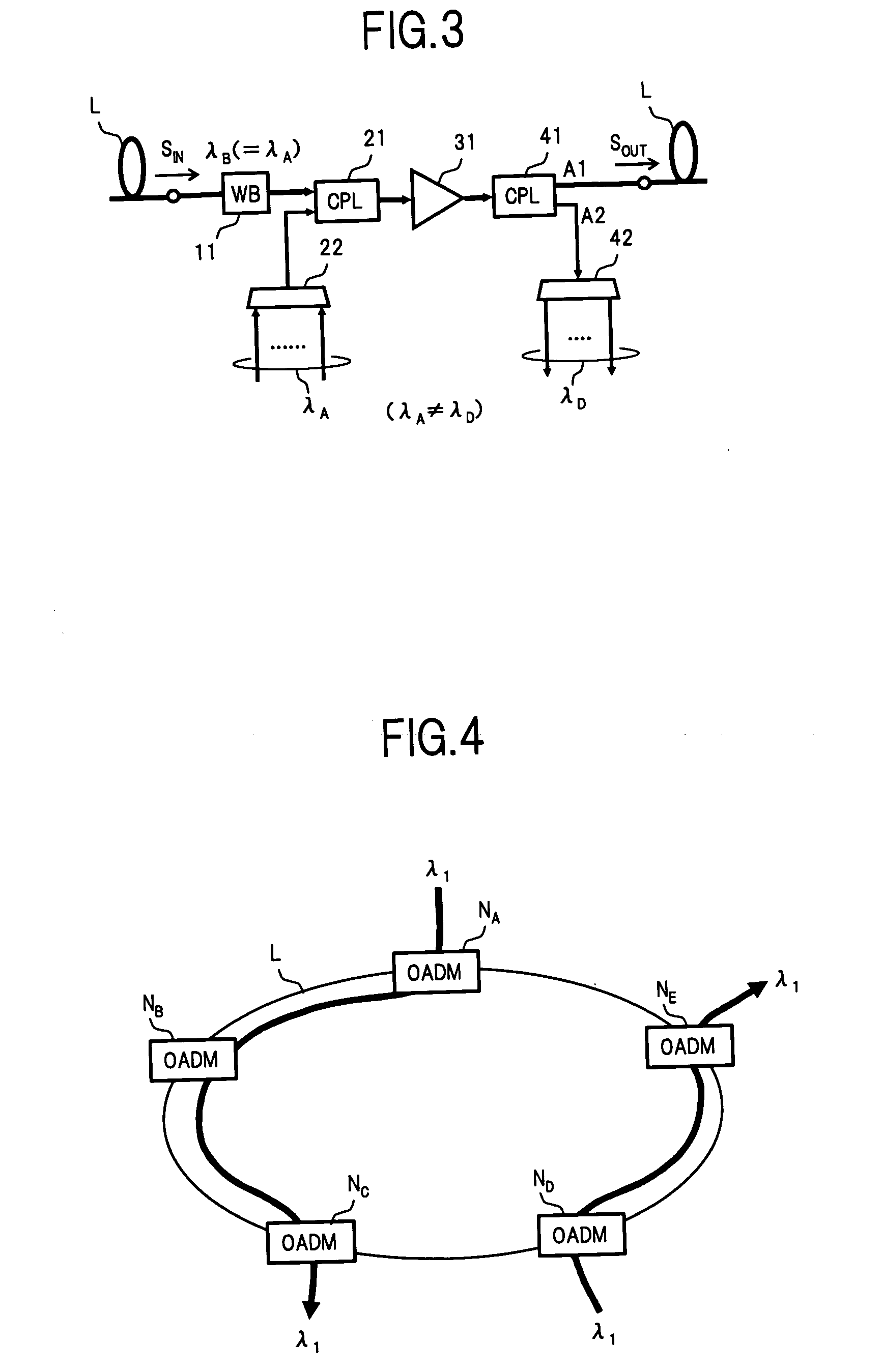
An optical add / drop multiplexer of the invention includes: a wavelength blocker for blocking signal light having at least one wavelength out of a plurality of signal lights included in WDM light supplied from a transmission line and passing the other signal light; an optical coupler for multiplexing signal light having the same wavelength as that of the signal light blocked by the wavelength blocker to signal light passed through the wavelength blocker; a WDM amplifier for amplifying the WDM light multiplexed by the optical coupler and outputting the amplified light; and an optical branch coupler for branching the WDM light output from the WDM amplifier into two lights, extracting signal light having at least one wavelength different from the wavelength of signal light multiplexed by the optical coupler from one of the branched lights, and outputting the other branched light to the transmission line. With the configuration, a small and cheap optical add / drop multiplexer as a flexible OADM node can be provided.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Sagnac interferometer type current sensor
InactiveCN1386199AFirmly connectedCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage/current isolationCurrent sensorDepolarizer
The depolarizer 11 is inserted between the light branching unit 2 and the polarization filter 3; the depolarizer 12 and the polarization filter 14 are inserted between the optical phase modulator 5 and the quarter-wave plate 16, and the depolarizer 13 and A polarizing filter 15 is inserted between the other branch end of the optical branching unit 4 and the quarter wave plate 17 . The optical branching element 2 and the optical phase modulator 5 are formed of a single-mode optical fiber, and the single-mode optical fiber is used for connection between optical devices, thereby providing an inexpensive device as a whole.
Owner:JAPAN AVIATION ELECTRONICS IND LTD +1
High resolution stereo mapping and reconnaissance integrated camera optical system
ActiveCN103345062AGood optical performanceImprove image qualityMirrorsPicture taking arrangementsLarge rangeFocal surface
A high resolution stereo mapping and reconnaissance integrated camera optical system comprises a high resolution stereo detection branch and a laser ranging branch, wherein the high resolution stereo detection branch and the laser ranging branch adopt a shared primary mirror and a shared secondary mirror, adopt independent subsequent optical paths and independent optical elements, and form two independent optical branches. The two branches are different in field angles of incident light rays, a field out of an axis is utilized by the high resolution stereo detection branch, a field on the axis is utilized by the laser ranging branch, the light rays in the field of the two branches simultaneously reach the primary mirror and the secondary mirror, a light beam of the high resolution stereo detection branch passes though four aspheric surface reflecting mirrors and then reach a high resolution stereo detection focal plane to be imaged, and a light beam of the laser ranging branch passes through the primary mirror and the secondary mirror, then passes through an optical filter and laser relay lens set and then is converged on a laser focal plane. The high resolution stereo mapping and reconnaissance integrated camera optical system has the advantages that resolution is high, distortion is zero, an optical-mechanical structure is high in integration level, the size is small and the weight is light. The high resolution stereo mapping and reconnaissance integrated camera optical system achieves high resolution, high precision detection and stereo ranging mapping functions for large-range surface features.
Owner:北京航天创智科技有限公司
Optical branching module and optical cable boot
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Optical fiber reflector and method of utilizing optical fiber reflector to achieve PON monitoring
InactiveCN103227677AMonitor working statusInformed statusElectromagnetic transmissionMonitoring systemSmall branch
The invention discloses an optical fiber reflector and a method of utilizing the optical fiber reflector to achieve PON (passive optical network) monitoring. The optical fiber reflector comprises an optical input interface (1), an optical branch device (2), a built-in extending optical fiber (3), a reflection port (4), an optical output interface (5) and a packaging implement (6), wherein the optical input interface and one end of the built-in extending optical fiber are connected with an input end of the optical branch device; the optical output interface is connected with a large-branch-ratio branch port of the optical branch device; the reflection port is connected with a small-branch-ratio branch port of the optical branch device; and the optical branch device, the built-in extending optical fiber and the reflection port are packaged in the packaging implement. According to a PON monitoring system achieved by utilizing the optical fiber reflector, a structure of a testing network can be simplified; the monitoring cost of the system can be lowered; and the low-cost PON network monitoring can be achieved.
Owner:GUILIN G LINK TECH
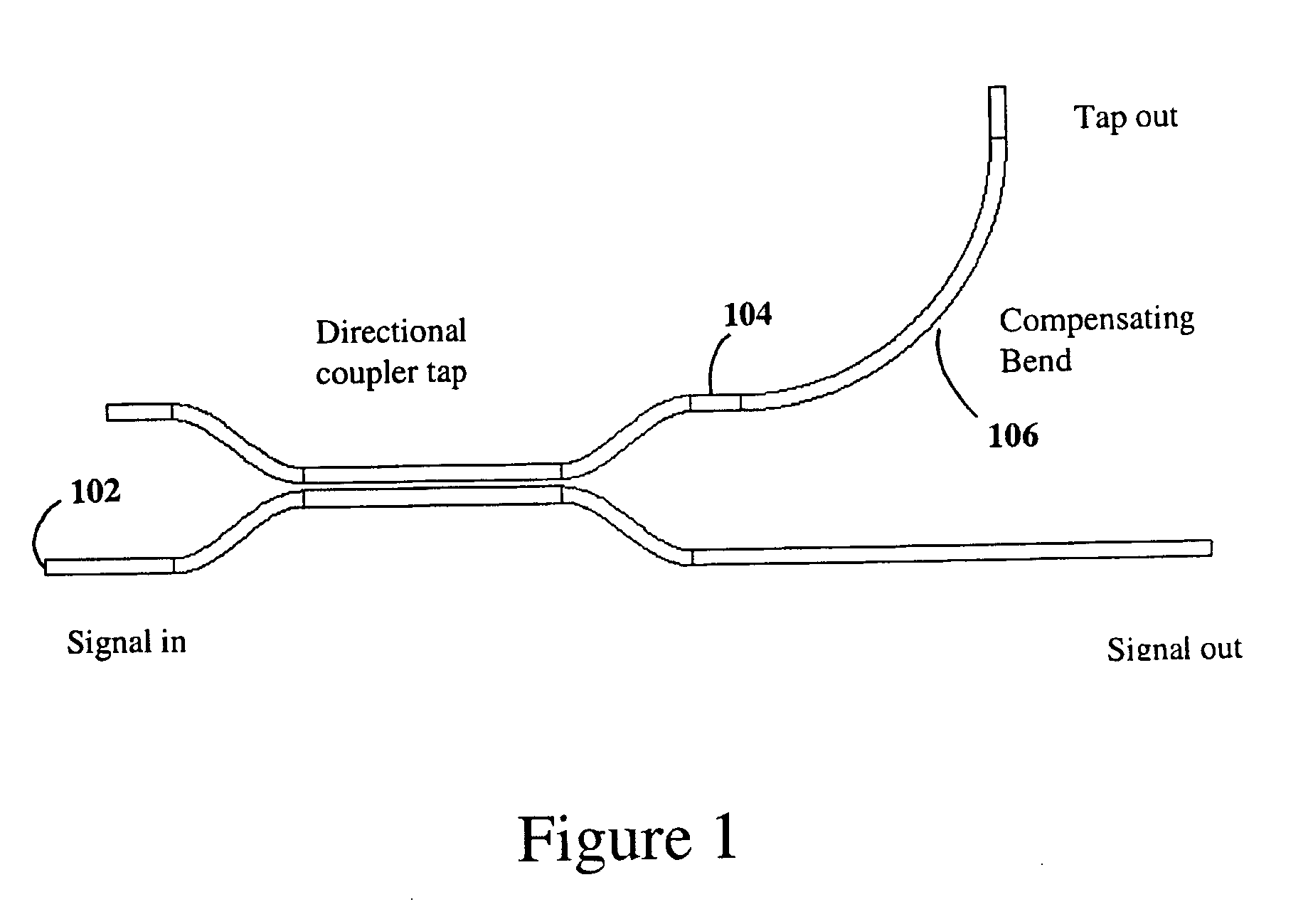
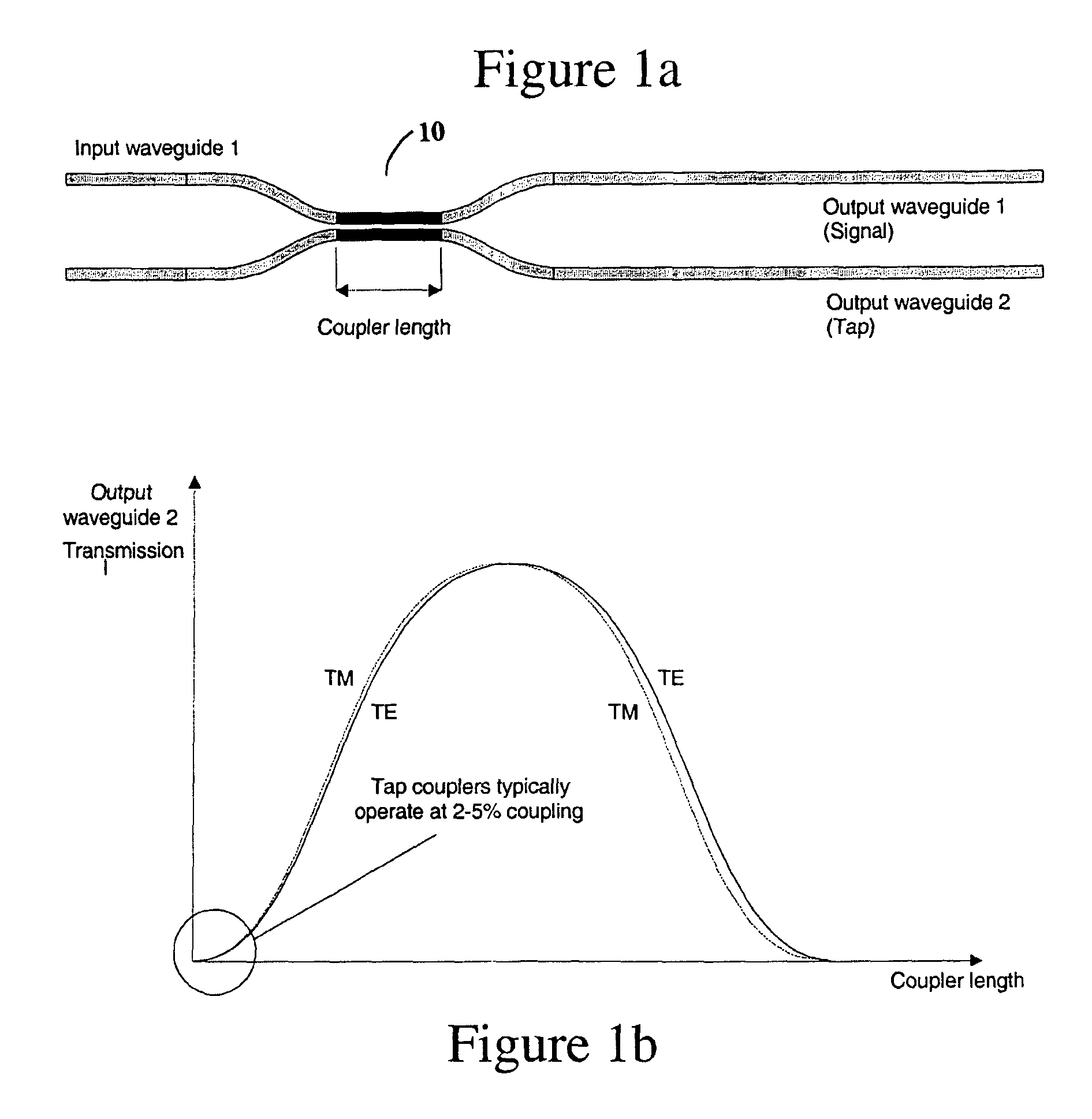
Polarization compensated optical tap
ActiveUS20050025427A1Improve efficiencyEffectively polarization dependenceCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideWaveguideLinearity
A polarization compensated planar waveguide branch is disclosed having a planar optical trunk waveguide for transporting a linearly un-polarized optical signal having TE and TM modes. A planar optical branch waveguide, capable of supporting TE and TM modes is optically coupled to the trunk waveguide such that at least a portion of an optical signal propagating within the trunk waveguide will couple into the branch waveguide with an undesired imbalance, having stronger TM mode coupling than TE mode coupling for the at least the portion of the optical signal which couples into the branch waveguide from the trunk waveguide. A portion of said branch waveguide downstream from a region where coupling takes place between the trunk and branch waveguides or a waveguide portion optically coupled thereto, receives the at least a portion of the optical signal, and has at least a predetermined bend with a predetermined radius for compensating for the unwanted imbalance in the TM and TE mode caused by light optically coupling into the branch from the trunk waveguide.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
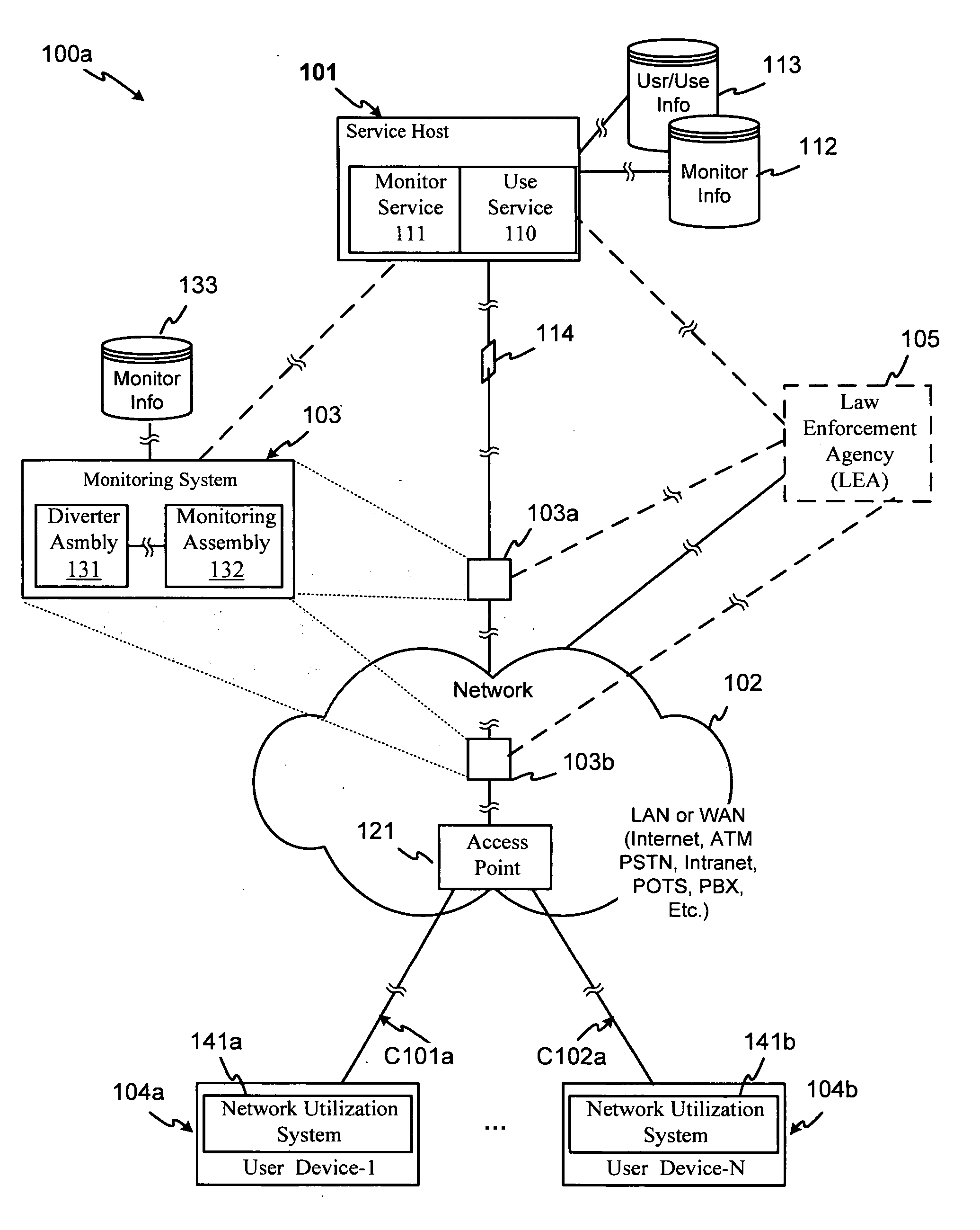
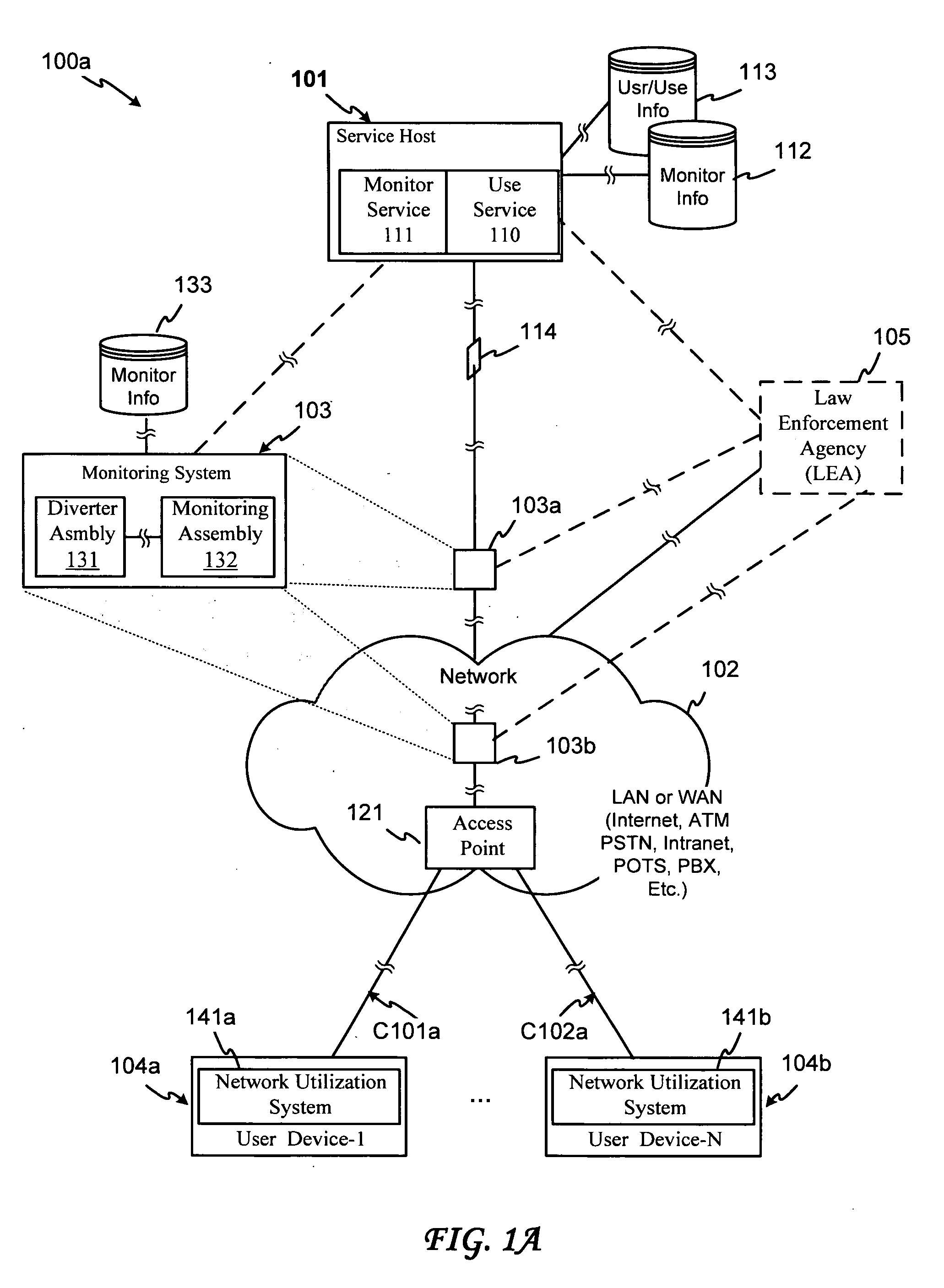
Optical network monitoring system and method
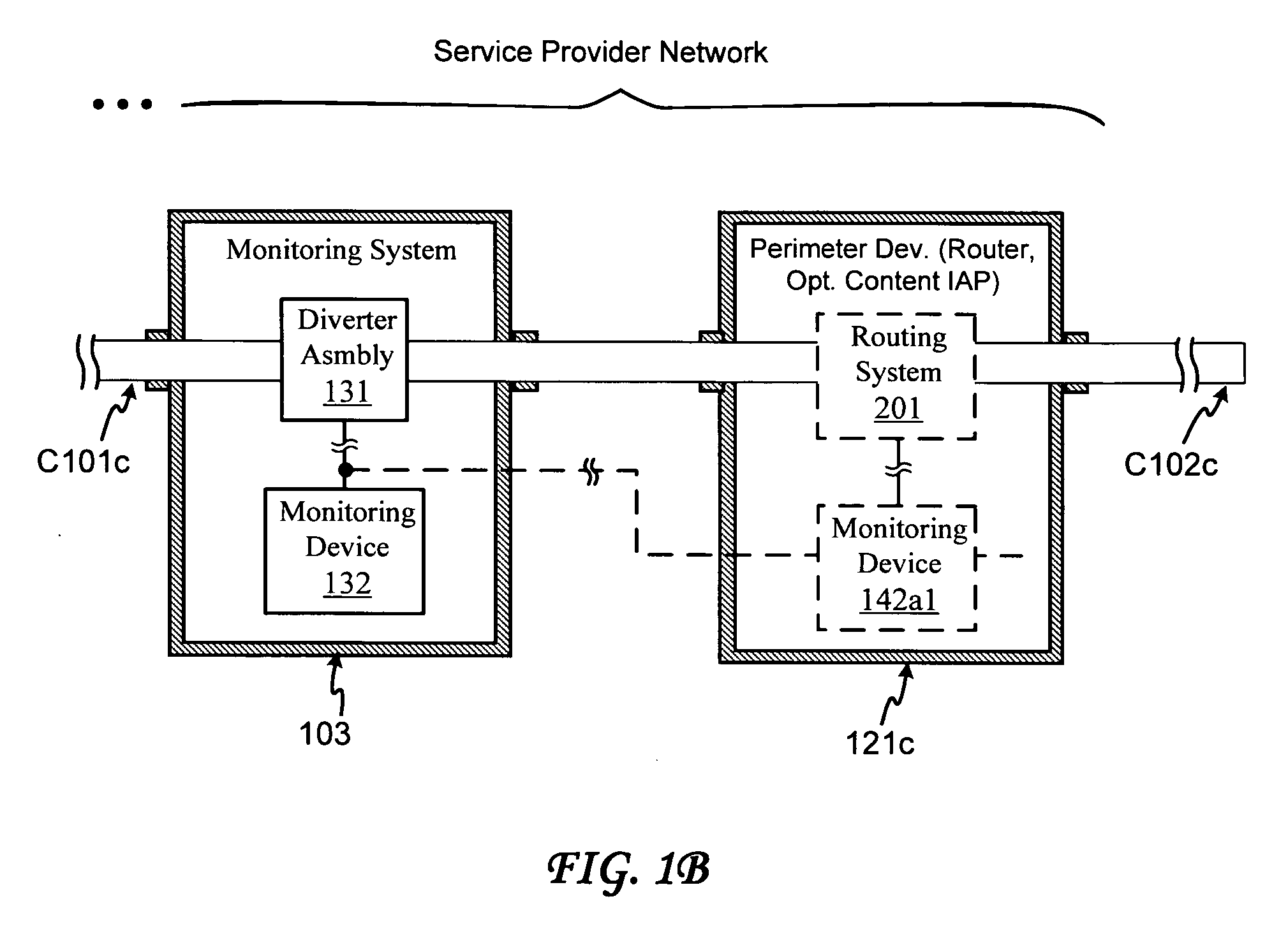
An optical network monitoring system and method provide for optical network diverting or further legal intercept, operational and / or other monitoring of general or specific transmission information that may be transmitted via a network optical branch. In one embodiment, a splitter within a diverter assembly diverts a portion of a received transmission signal (strength) to an optical receiver or re-transmitter, and outputs a further portion of the signal via a diverter assembly output or further via a re-transmitter or booster. In another embodiment, the splitter is generally matched to the receiver. A further embodiment provides for transferring the diverted portion to a monitoring assembly with which the diverting assembly may be matched, disposed or otherwise integrated, and which may provide for configuring the diverting assembly. The monitoring assembly may further provide for conducting monitoring processing, which may include receiving additional information from a service host or other system component, processing the diverted portion, additional information or both, and / or using the additional information for processing the diverted portion. The monitoring assembly may still further receive a monitoring request from a monitoring requester or other authorization authority that may include monitoring processing criteria, and may transfer designated content to a designated receiver.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
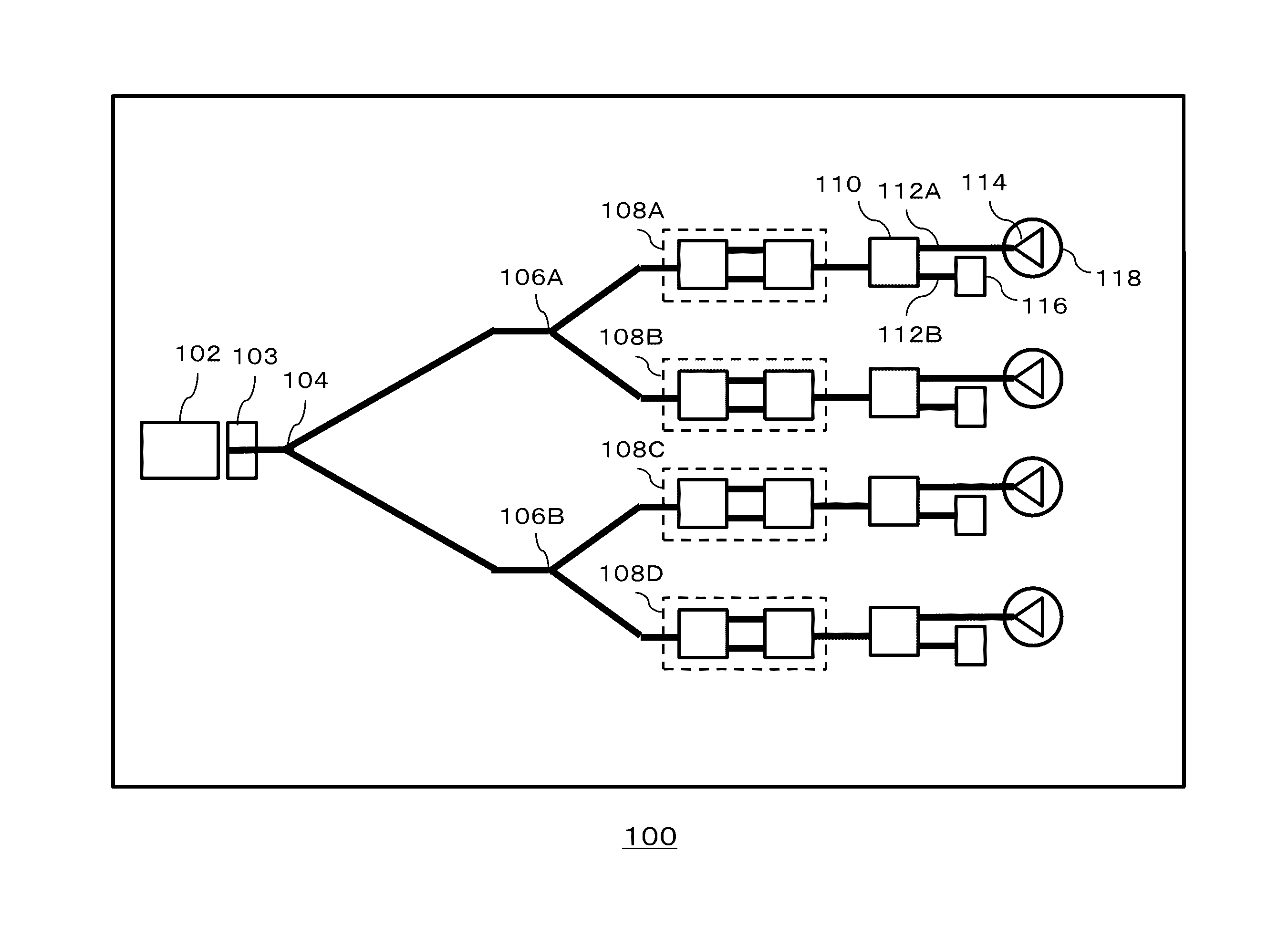
Optical couplers used in a downhole splitter assembly
Techniques and apparatus are provided for downhole sensing using optical couplers in a downhole splitter assembly to split interrogating light signals into multiple optical sensing branches. Each optical branch may then be coupled to an optical sensor (e.g., a pass-through or an optical single-ended transducer (OSET)) or to another optical coupler for additional branching. The sensors may be pressure / temperature (P / T) type transducers. Some systems may exclusively use OSETs as the optical sensors. In this manner, if one of the OSETs is damaged, it does not affect light traveling to any of the other sensors, and sensing information from remaining sensors is still returned.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
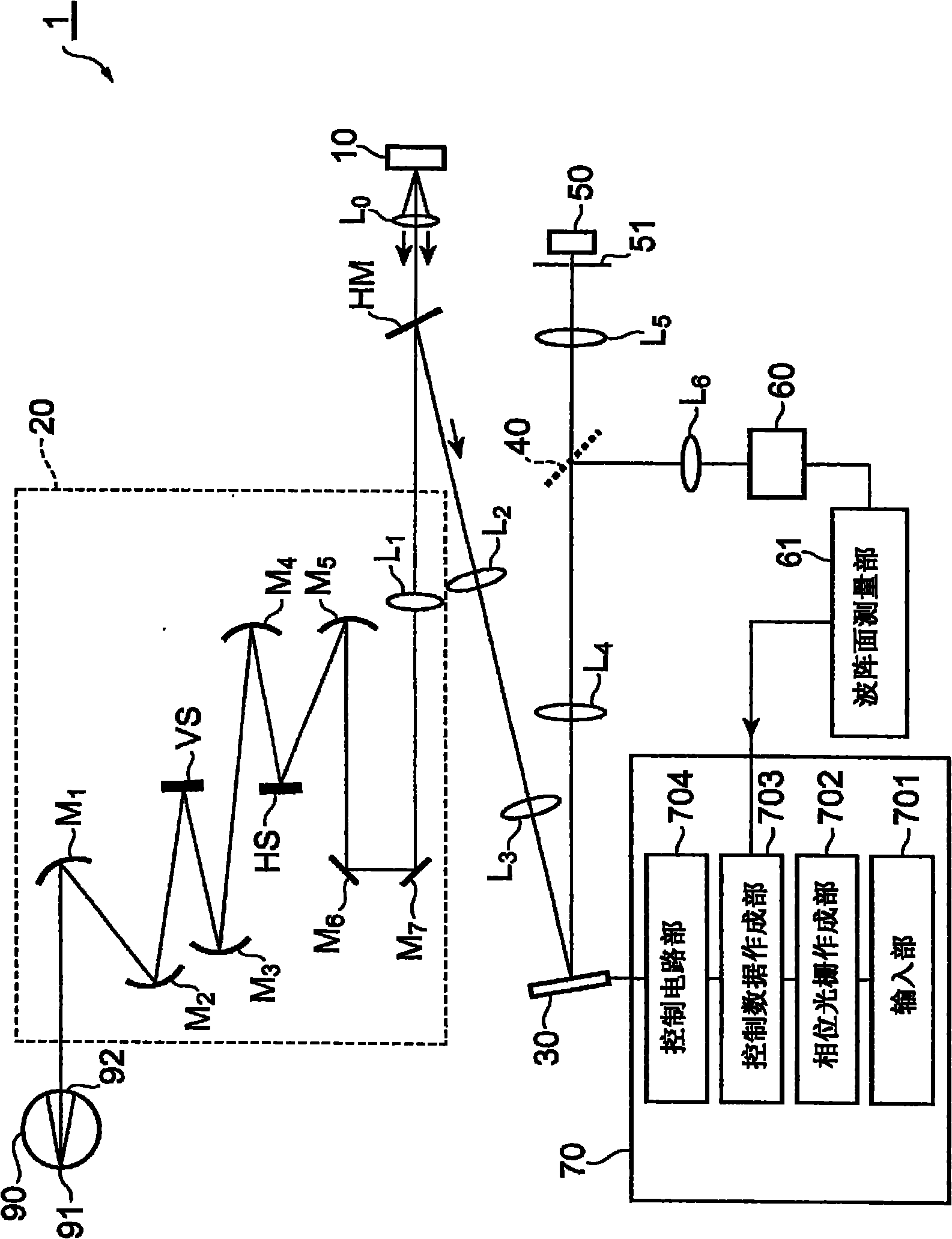
Observation device
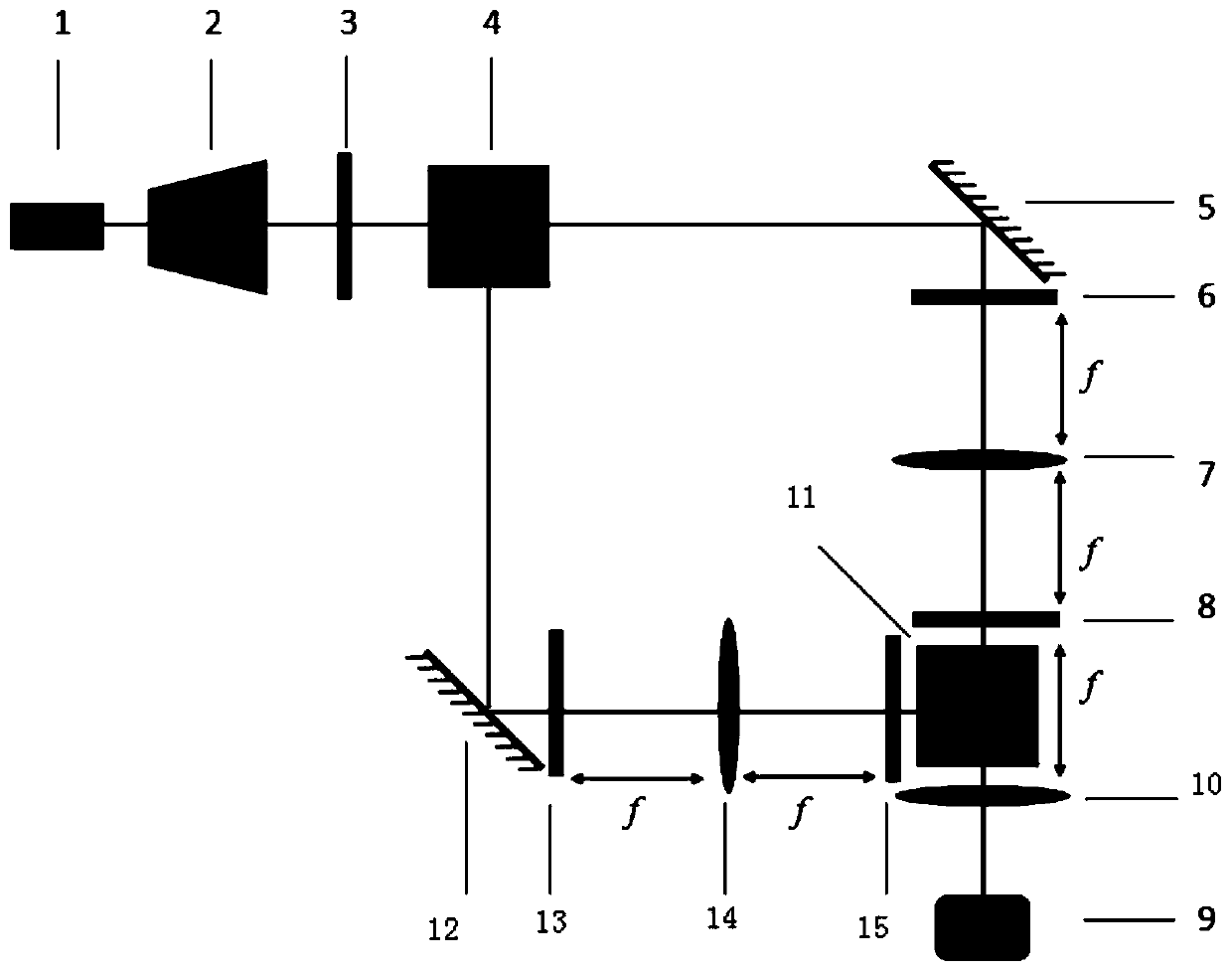
An observation device (1) is provided with a light source unit (10), a biaxial scanning system (20), a wavefront modulation unit (30), an optical branch unit (40), a light detection unit (50), a wavefront detection unit (60), a control unit (70) and the like. The wavefront modulation unit (30) presents a compensating phase pattern for the compensation of an aberration of input light and a branching phase pattern for the branch of the input light into first and second light. The wavefront detection unit (60) receives inputted light and detects a wavefront of the inputted light. The compensating phase pattern for the compensation of the wavefront aberration is feedback-controlled in loop processing that includes the detection of a distortion of the light wavefront by the wavefront detection unit (60), the adjustment of the phase pattern by the control unit (70) in accordance with the detection result of the distortion, and the presentation of the phase pattern by the wavefront modulation unit (30).
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Optical circuit
ActiveUS9519115B2Reduce impactLow costCoupling light guidesSemiconductor lasersOptical reflectionPhase difference
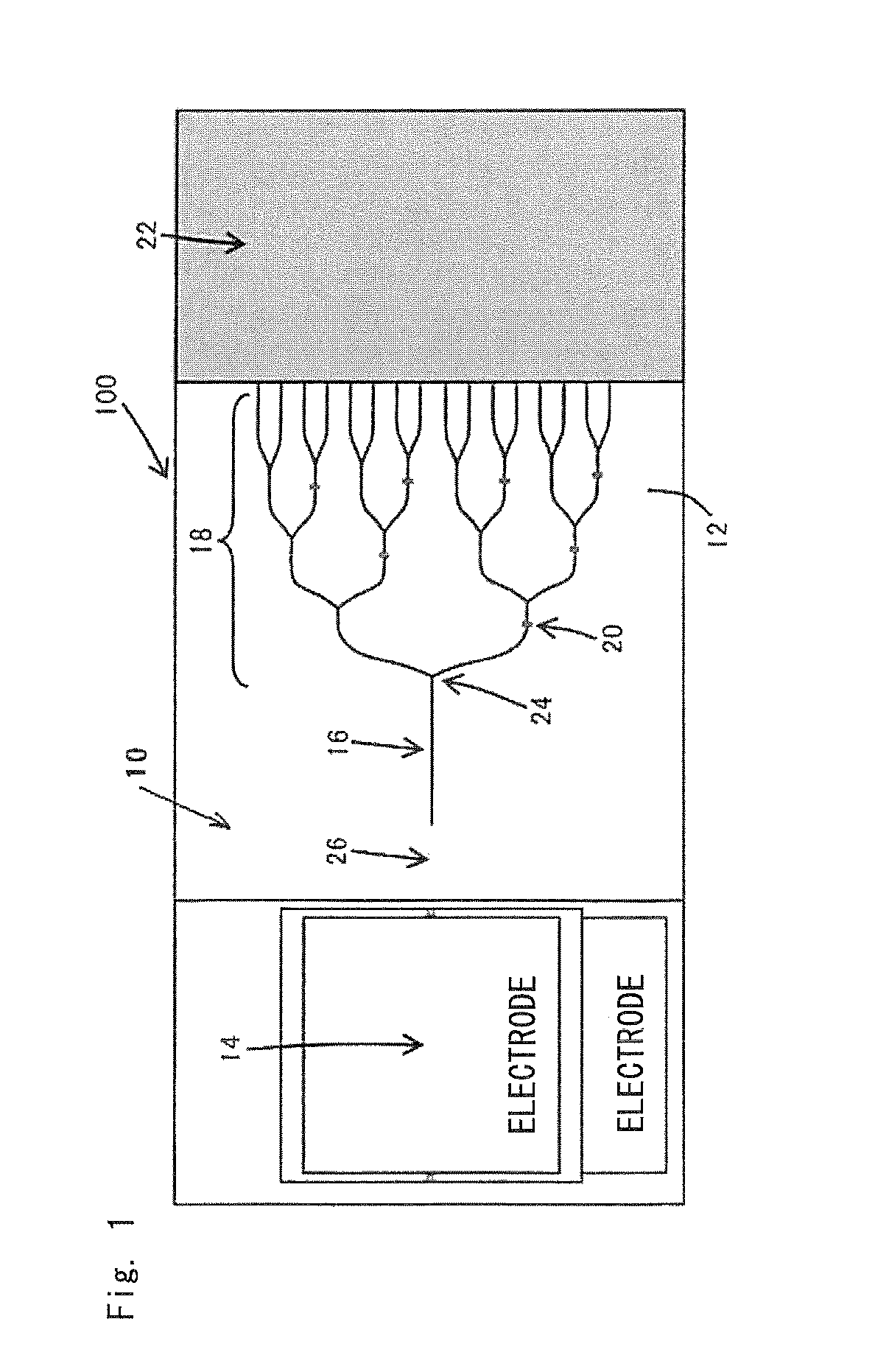
An optical circuit, wherein the effects of reflected light generated by an optical component are reduced. The optical circuit (100) is provided with an optical branching (110) for branching light, an optical coupler (114) for coupling a first portion of branched light to an optical waveguide (118) for transmission, and an optical reflecting unit (116) for reflecting a second portion of the branched light, the phase difference between the reflected light from the optical coupler (114) and the reflected light from the optical reflecting unit (116) being (2m−1)π (where m is an integer) on an input side of the optical branching (110).
Owner:PHOTONICS ELECTRONICS TECH RES ASSOC
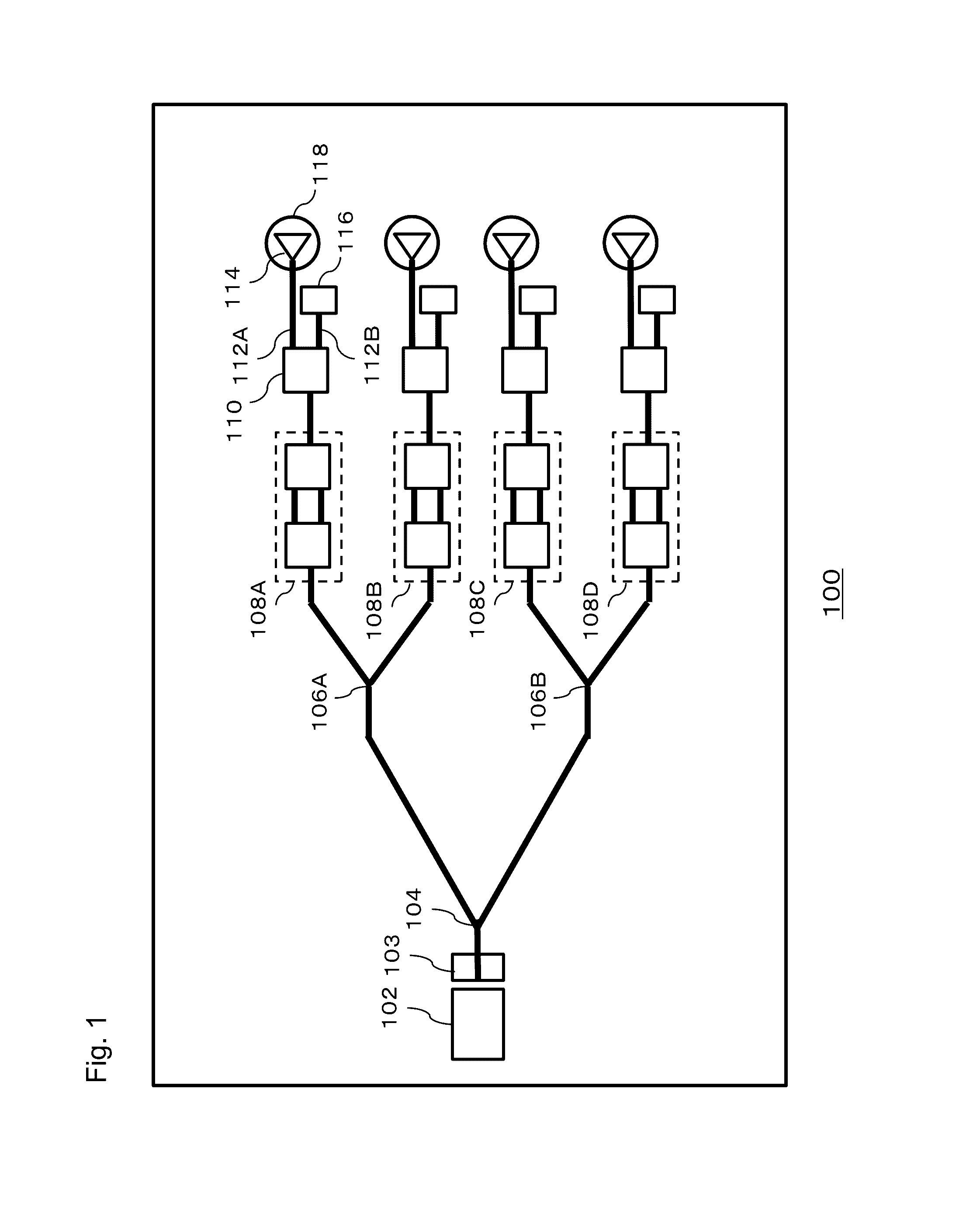
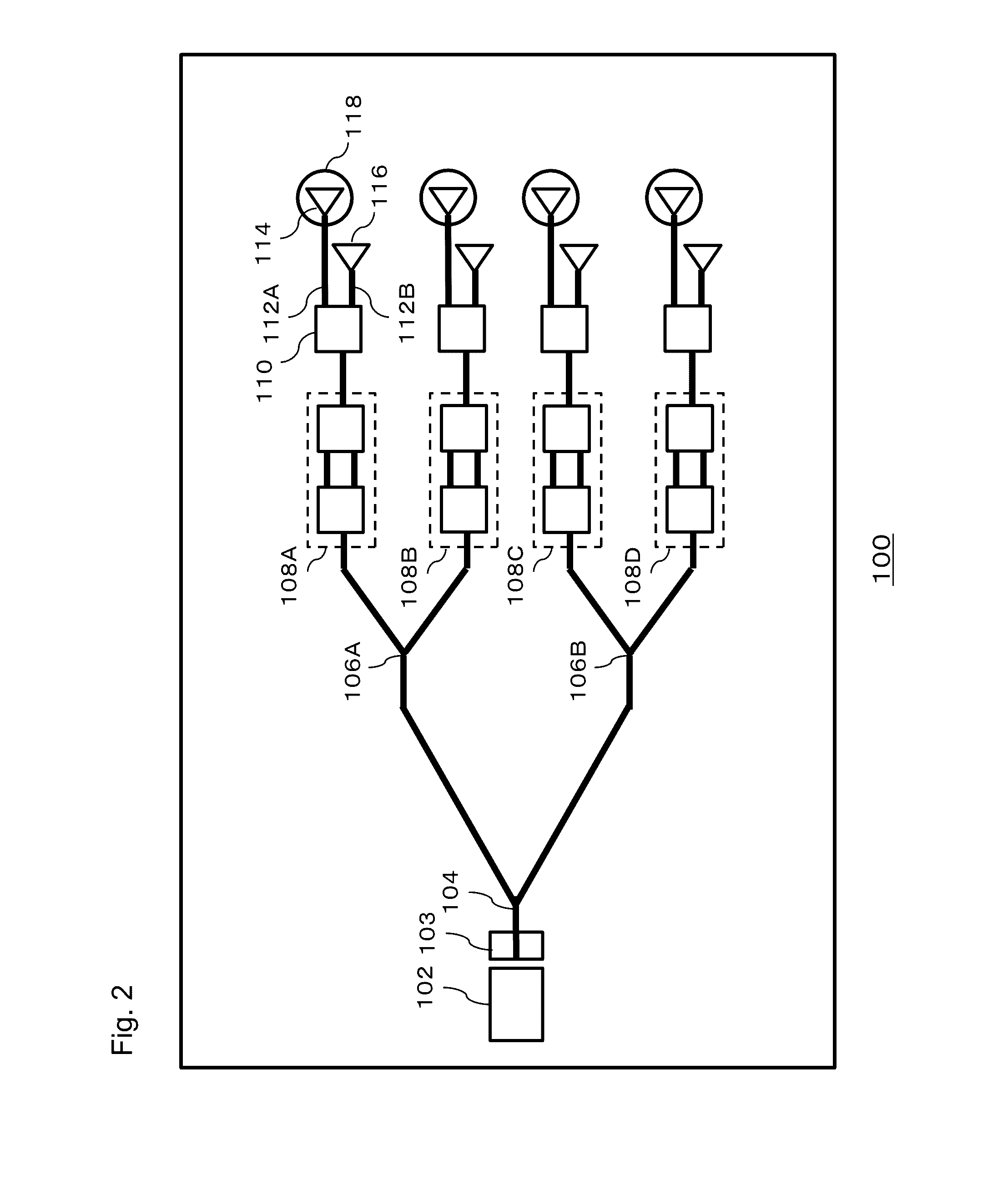
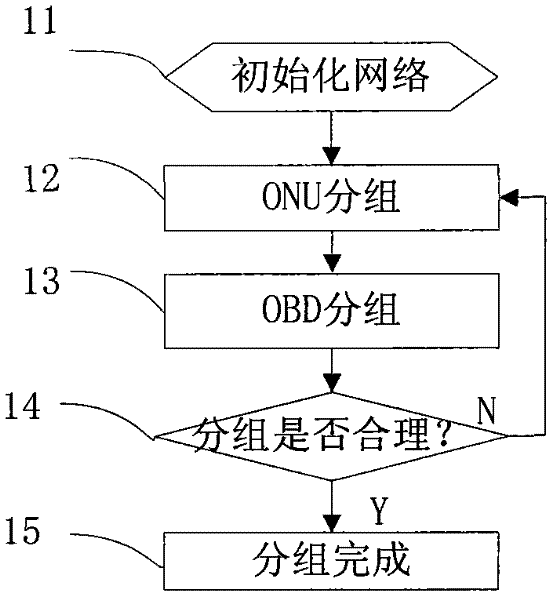
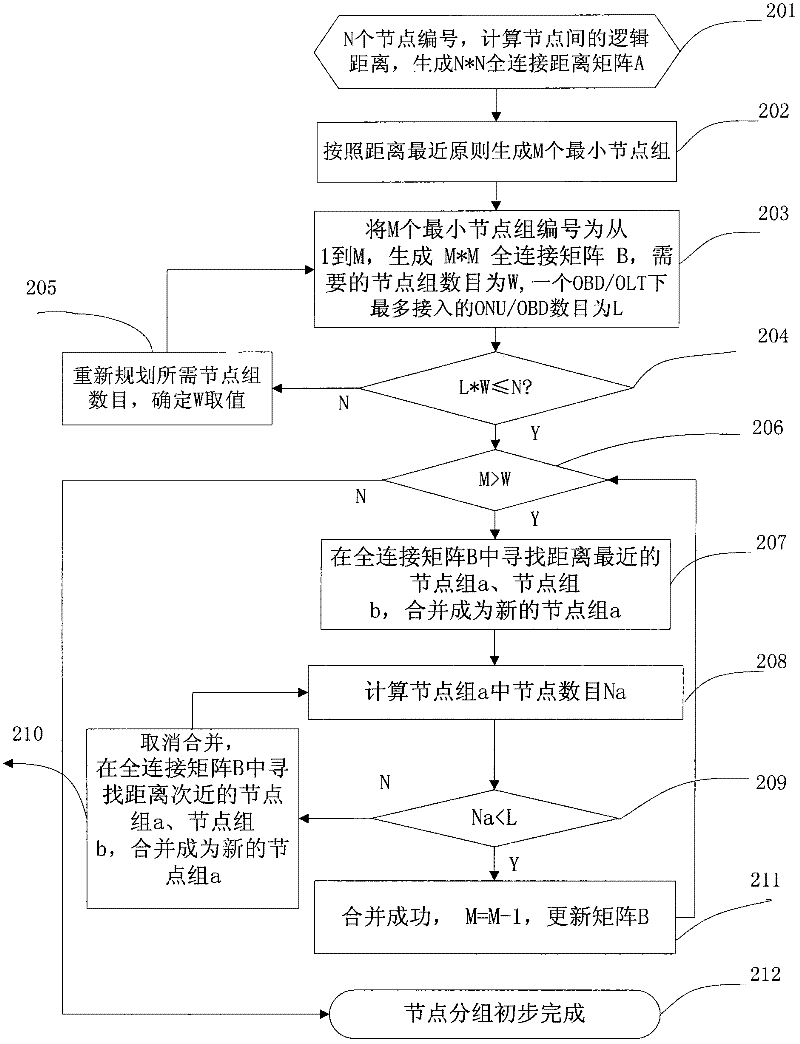
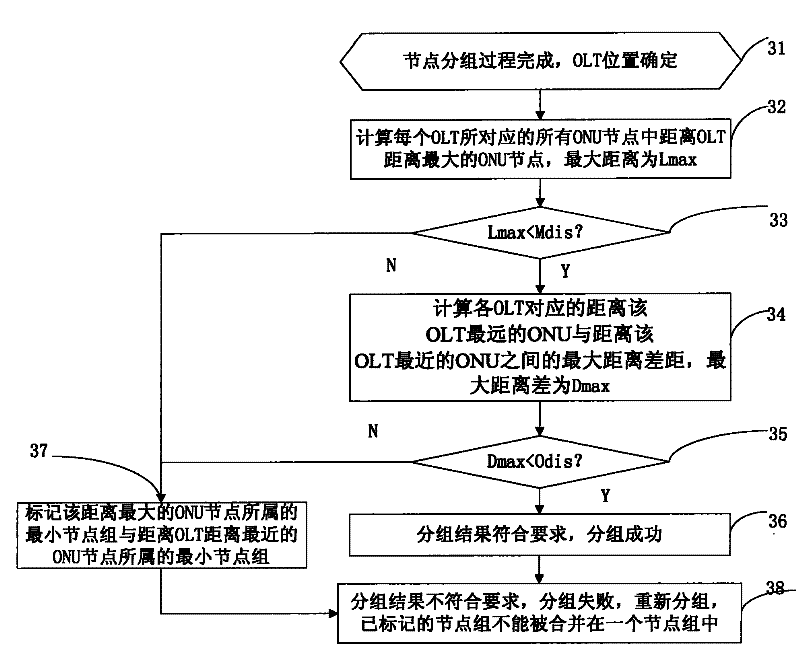
Node grouping algorithm applied in PON (Passive Optical Network) planning
InactiveCN102355301AElectromagnetic transmissionData switching networksAlgorithmOptical network unit
The invention discloses an application method of closest-distance node grouping algorithm in PON (Passive Optical Network) planning, which comprises the following steps: using a closest-distance grouping algorithm in the process of optical network unit grouping and an OBD (Optical Branch Device); and verifying a grouping result after the completion of the grouping. In the invention, the influence of the proximity relation of the nodes on the distance to an optical wiring network planning design is fully considered, by the method that the smallest node group is formed by a node closest distance, the condition that adjacent nodes are grouped in different node groups can be avoided, the combination problem of the node groups is solved, the result of the grouping algorithm can be used for directing the selection of the OBD and the optimal design of an optical wiring network, and the engineering applicability is improved by the algorithm through a series of verification conditions.
Owner:WUXI BUPT SENSING TECH & IND ACADEMY +1
Light source circuit and light source device equipped with same
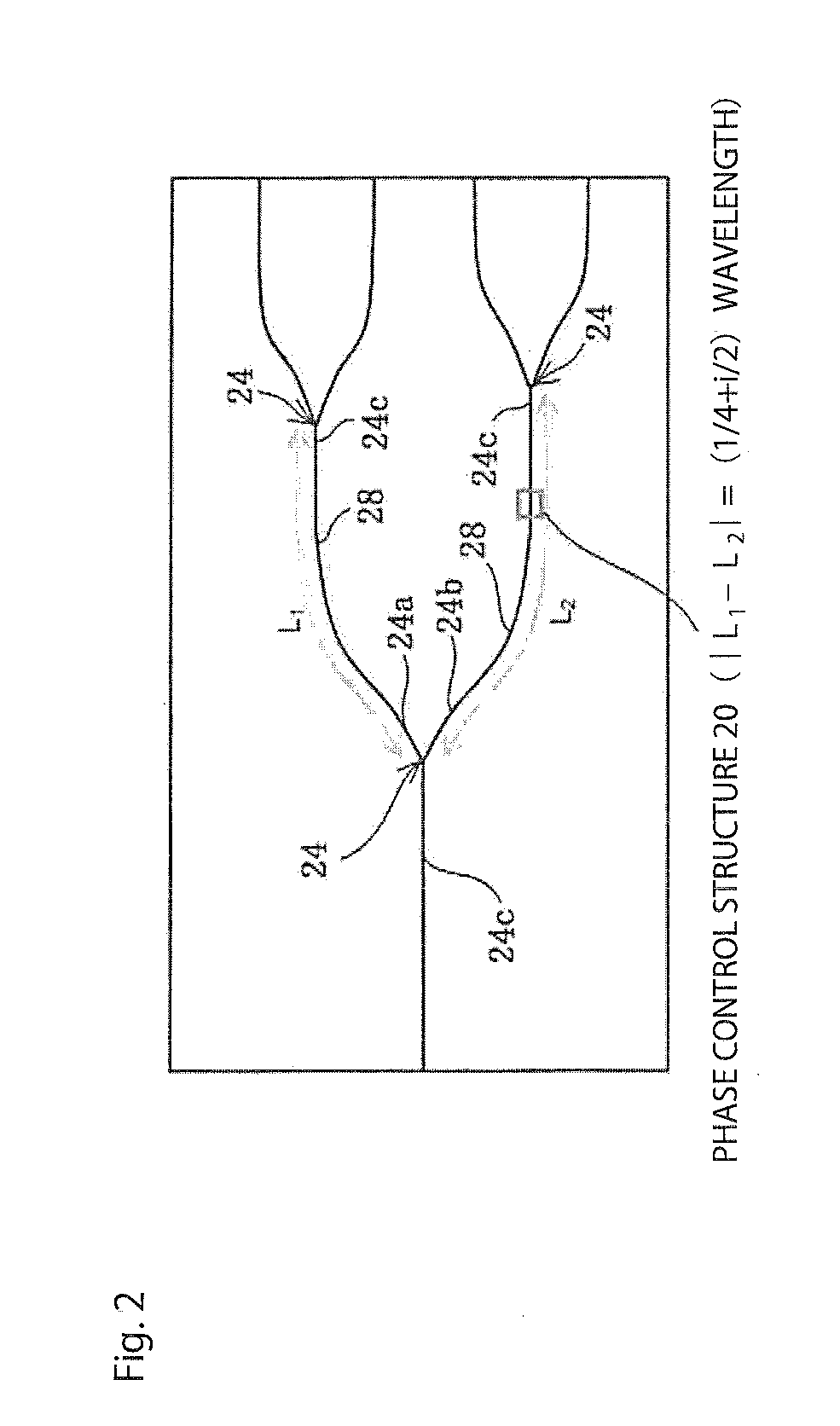
ActiveUS20150036964A1Effectively inhibit returning lightEffectively inhibit returning light in lightCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guidePath lengthWaveguide
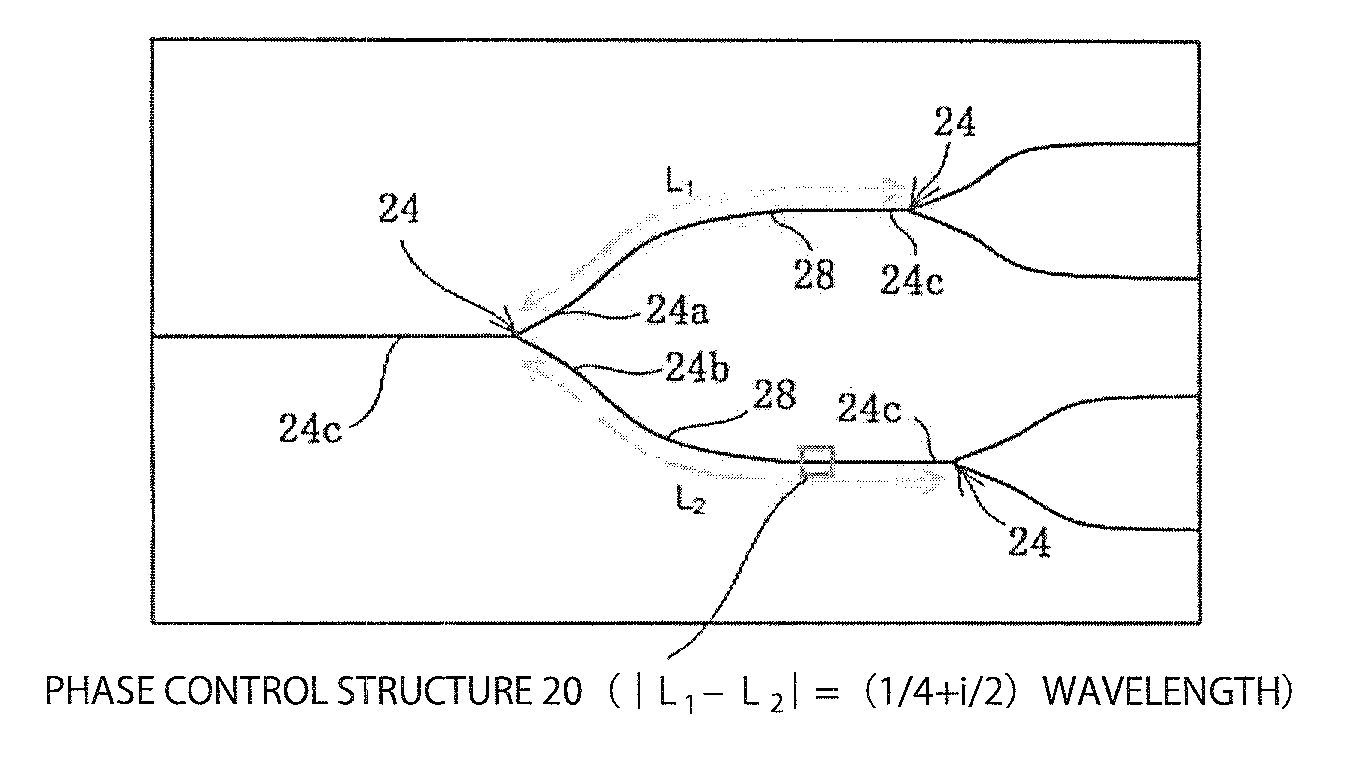
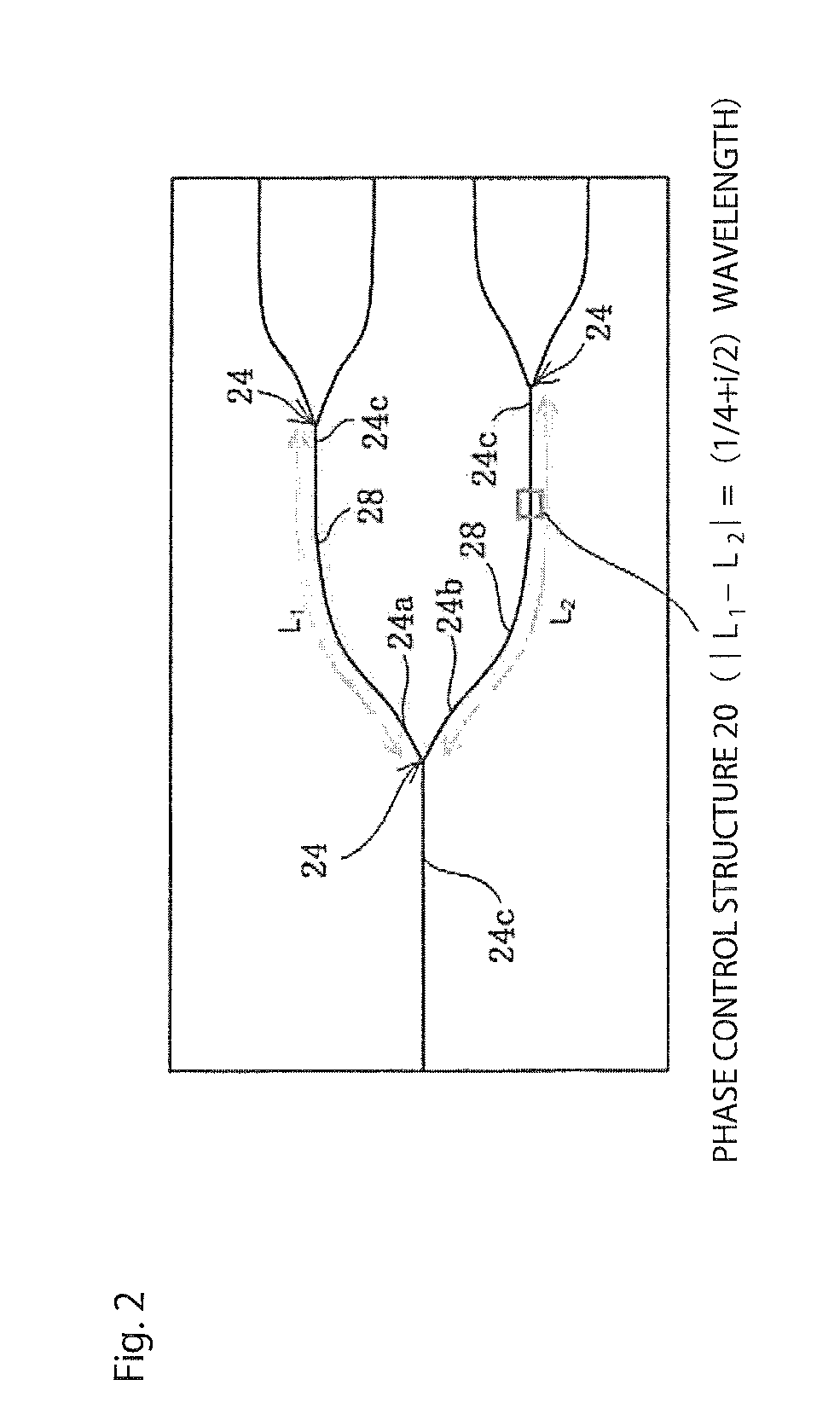
A light source circuit transmits light incident from a semiconductor laser source to a plurality of optical devices. At least one optical branch section is formed to branch one input-side optical waveguide at least into a first output-side optical waveguide terminal and a second output-side optical waveguide terminal. A light path length (L1) between the optical branch section and a next-stage optical branch section or the optical device is connected to the first output-side optical waveguide extending from the optical branch section and a light path length (L2) between the optical branch section and the next-stage optical branch section selected such that the absolute value of a difference between (L1) and (L2) is (¼+i / 2) times (i is zero or a positive integer) the wavelength of the light transmitted through the light source circuit.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Optical source concentrated wave division multiplexing passive optical network for simultaneously generating the DPSK and OOK signals
InactiveCN101056155ALow costMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistributed feedback laserFiber
The present invention discloses a wavelength division multiplex passive light network system that generates DPSK and OOK signals at the same time and centralizing the light sources in the field of wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network system (WDM-PON) and the technology of light network communication system. In the passive light network downlink center station, the optical lineterminal (OLT) is composed of N paths of light sources of distributed feedback laser and the N paths of light sources passes through a double-arm intensity modulator after passing through a wavelength division multiplexer to realize the optical carrier suppressing separation (OCSS) for forming nth-order optical signals; then the signals passes through an interleaver (IL) and the separated signalsare performed on-off keying (OOK) modulation and differential phase shift keying (DPSK) modulation; and the modulated signals of two paths are transmitted to the remote nodes of the passive light network from the optical fiber after being coupled. In the remote nodes, the downlink signals transmitted through a long-distance fiber line are separated through another interleaver (IL) and the intensity modulation signals are separated from the phase modulation signals; the intensity modulation signals and the phase modulation signals are routed through two demultiplexers (DeMux) to the corresponding passive optical network unit (ONU); in the passive optical network unit (ONU), 3R light receiving unit will detect the modulated on-off keying (OOK) modulation signals directly; the differential phase shift keying (DPSK) modulation signals are divided into two paths by the optical branch divider: one path of signals are modulated out the intensity signals directly through the MZ wave guide time delay interferometer; the other path of signals are modulated through reflecting type semiconductor optical amplifier (RSOA) for the recycle of wavelength.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Optical modulator and optical modulation device
ActiveUS20150277159A1Overall size miniaturizationReduce power consumptionNon-linear opticsLow voltageEngineering
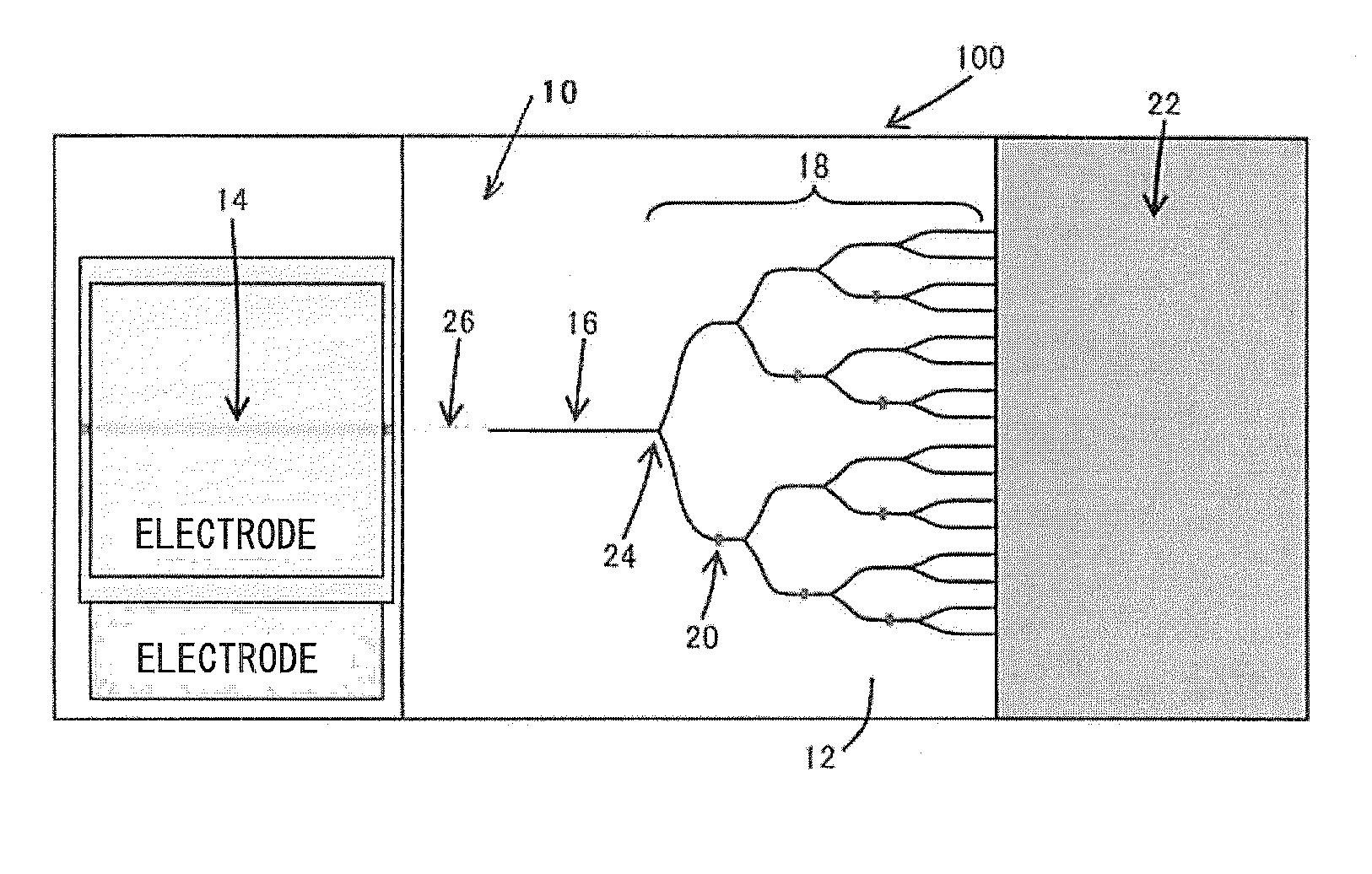
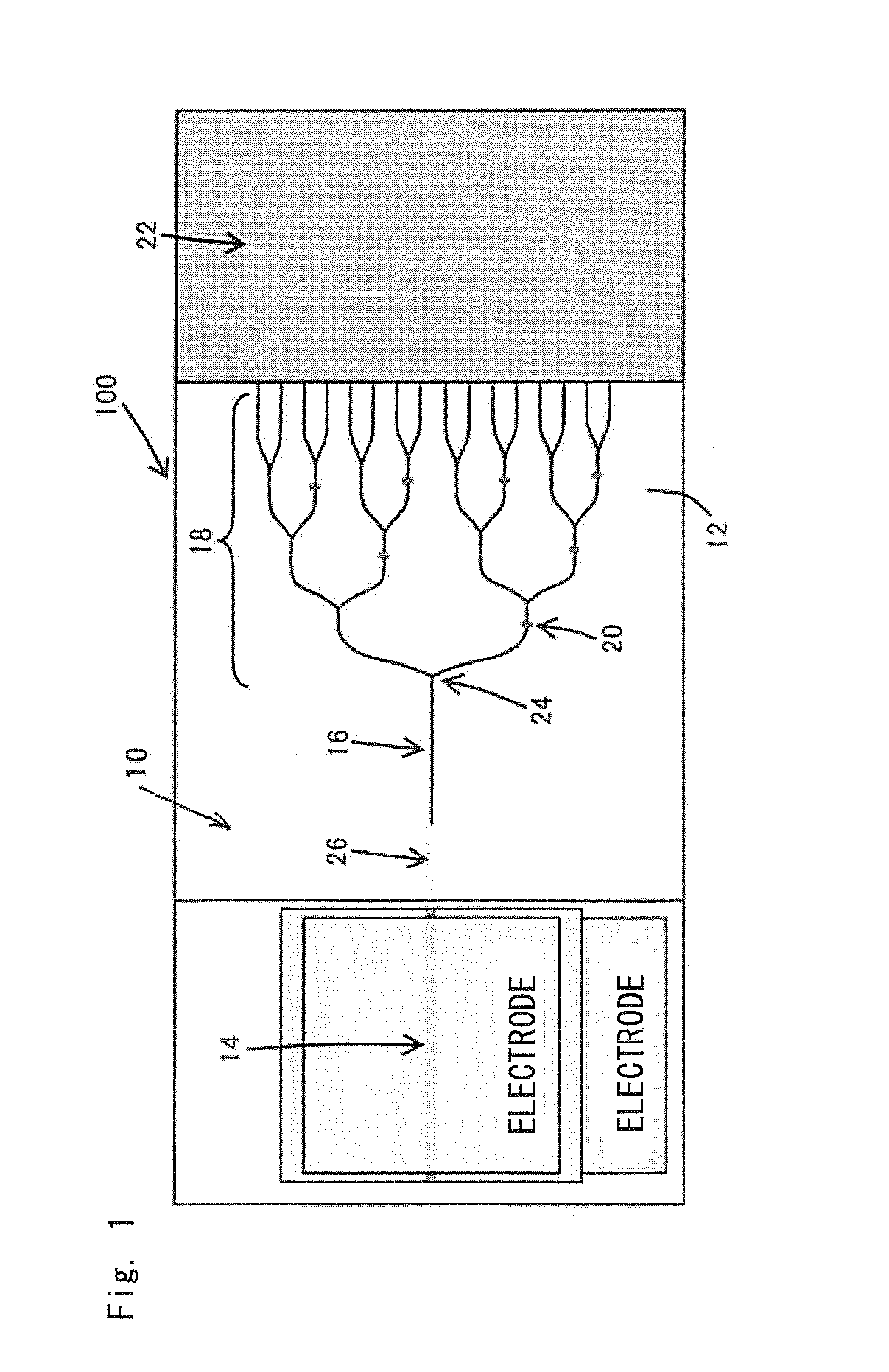
An optical modulator includes a plurality of electrode pads arranged in a zigzag alignment; two arms which are partially bent to circumvent the electrode pads so as to carry out optical phase modulation at various parts based on voltages input via the electrode pads; an optical branch structure branching the arms; and an optical coupling structure aggregating the arms together. Each arm is made of a silicon-base electro-optic element including a substrate; a first conductive semiconductor layer having a rib waveguide structure; a dielectric layer deposited on the rib waveguide structure; and a second conductive semiconductor layer deposited on the dielectric layer. The first conductive semiconductor layer is connected to first electrode wires via first contacts, while the second conductive semiconductor layer is connected to second electrode wires via second contacts. Thus, it is possible to miniaturize the optical modulator which can operate at a low voltage.
Owner:NEC CORP
Optical measuring apparatus and optical measuring method
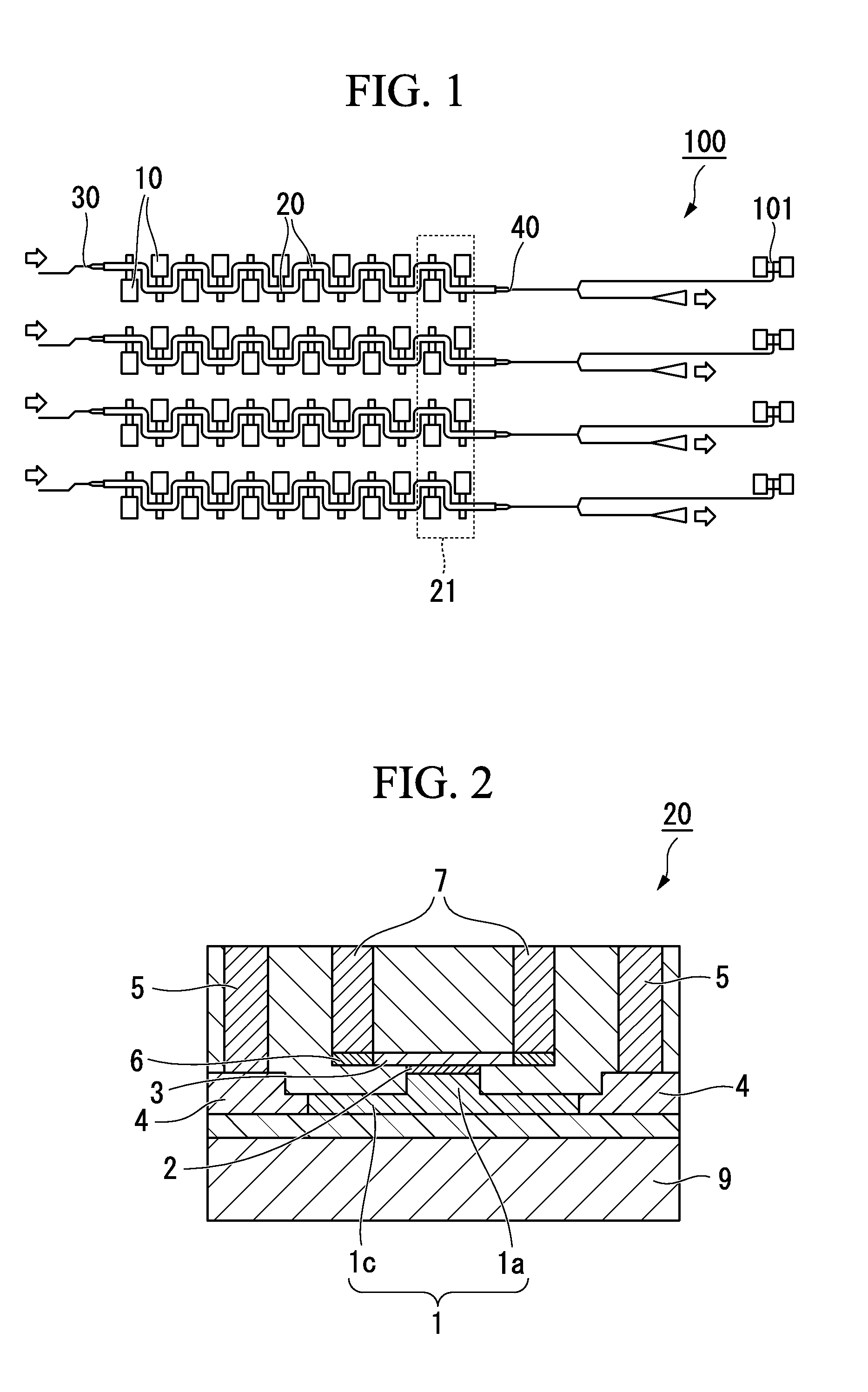
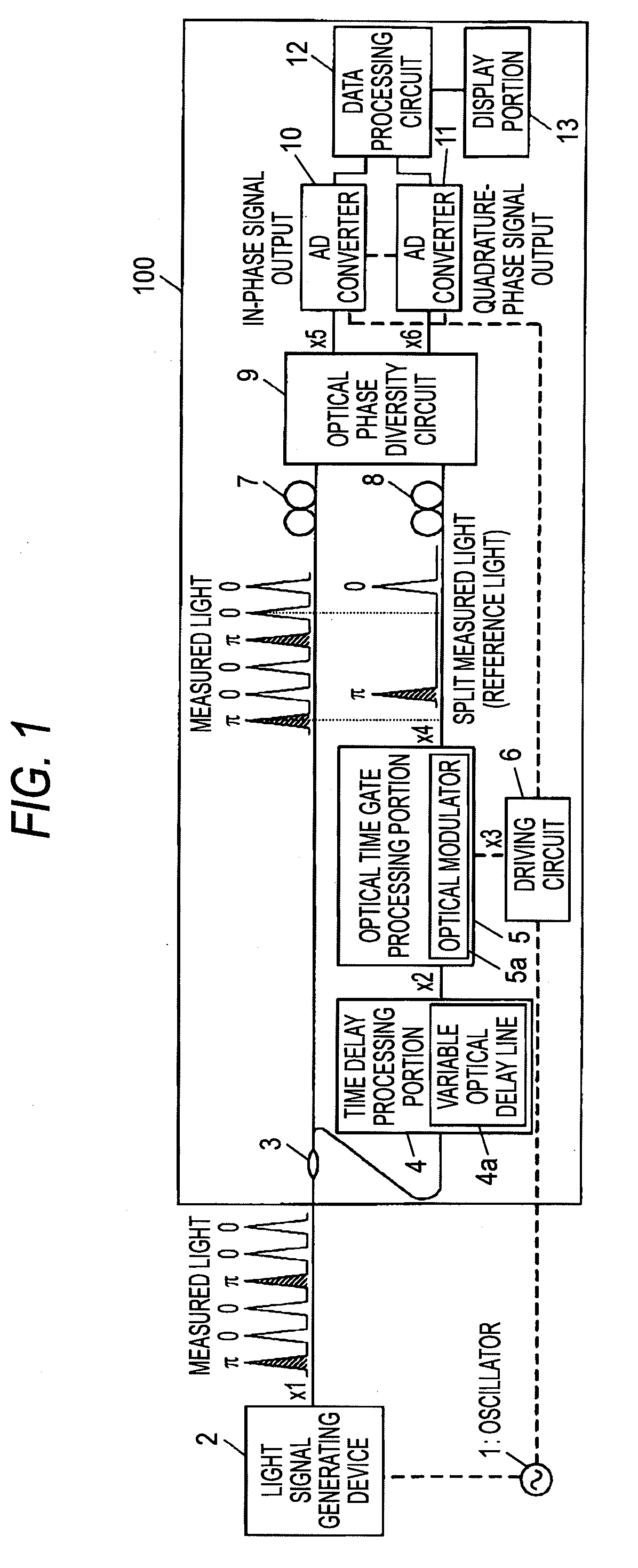
InactiveUS20090009772A1Improve performanceIncrease choiceOptical measurementsUsing optical meansTime gatingElectricity
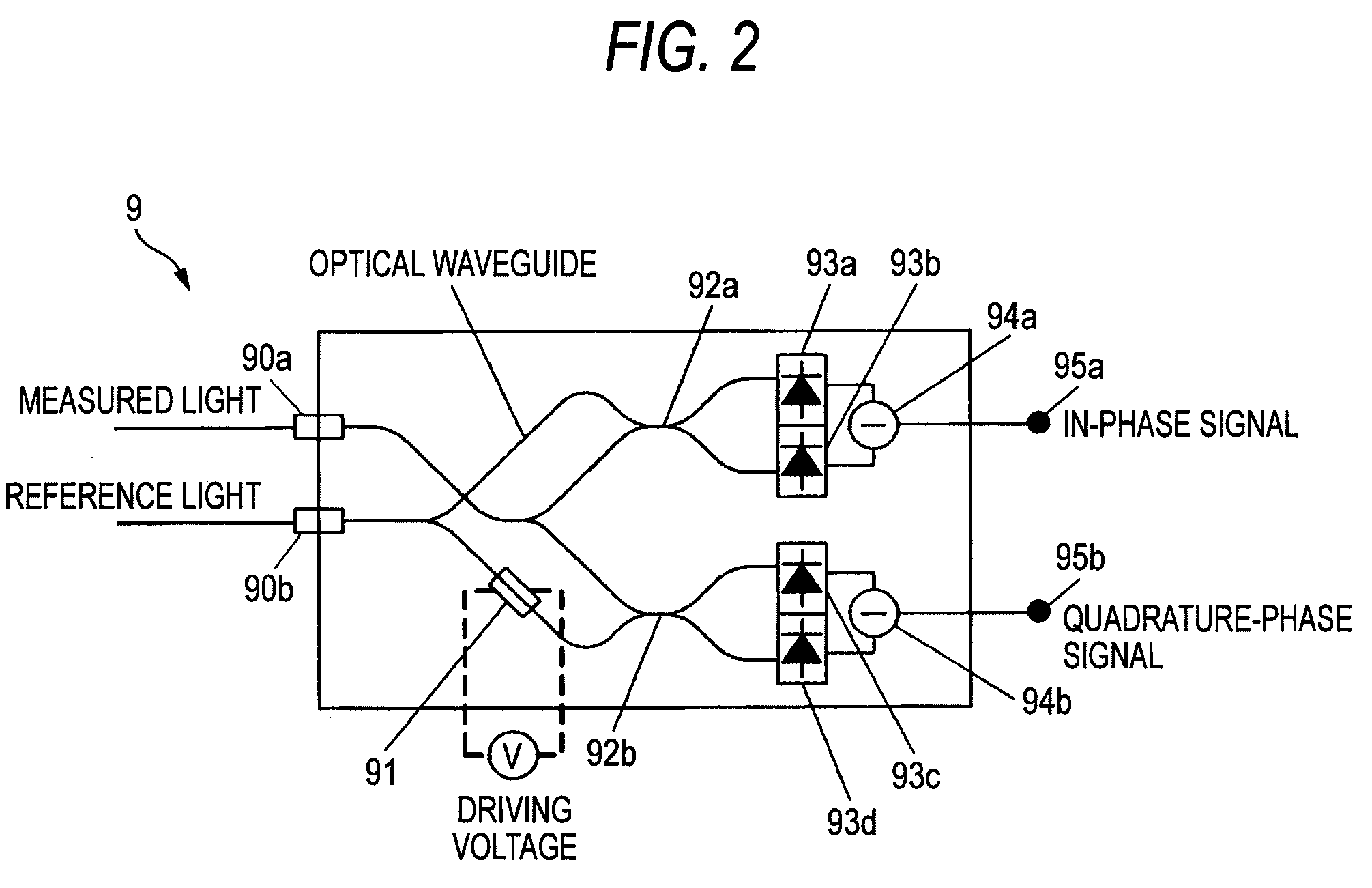
An optical measuring apparatus, includes an optical branch element for splitting a measured light into plural lights, a time delay processing portion for giving a predetermined time delay to one split light of the measured light, an optical phase diversity circuit for outputting an in-phase signal component and an quadrature-phase signal component of the measured light by virtue of an interference between the measured light and a reference light between which a relative time difference corresponds to a time give by the time delay, while using other split light of the measured light or the measured light to which a process is applied by the time delay processing portion as the reference light, a data processing circuit for calculating at least one of an amount of change of an amplitude and an amount of change of a phase of the measured light, based on the in-phase signal component and the quadrature-phase signal component, and an optical time gate processing portion or an electric time gate processing portion provided on a route extending from the optical branch element to the data processing circuit, for extracting at least one of split lights of the measured light every predetermined bit time while shifting a timing, wherein changes of amplitude / phase distributions in time are measured.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Optical path switching device
Owner:NABLESCO CORP
Optical signal receiver, optical signal receiving apparatus, and optical signal transmitting system
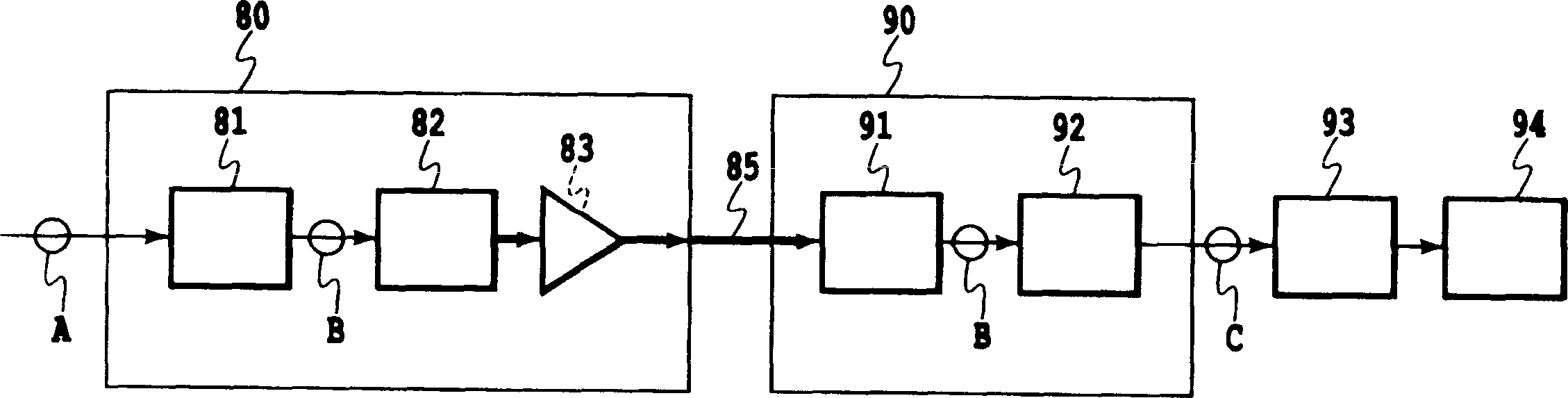
InactiveCN1706128AHigh Frequency Phase Distortion ImprovementImprove transfer characteristicsDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersWave formPhotoelectric conversion
The optical signal receiver of this invention is an optical signal receiver that receives and frequency-demodulates an optical signal, comprising: an optical branch device for splitting an input optical signal into two optical signals ( 13 ); an optical delay line for delaying one of the two branched optical signals ( 15 ); a first photoelectric conversion circuit ( 17 ) for converting the optical signal from the optical delay line into the first electrical signal ( 17 ); a second photoelectric conversion circuit ( 19 ) for converting the other optical signal of the two branched optical signals into a second electrical signal; the rectangular-wave forming circuit ( 21, 23, 25 ) for outputting a single rectangular-wave signal using the first electrical signal from the first photoelectric conversion circuit and the second electrical signal from the second photoelectric conversion circuit as inputs; and a smoothing circuit ( 12 ) for smoothing the rectangular-wave signal from the rectangular-wave forming circuit.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Apparatus and method for generating square array vector beam with invariable space diffraction by using two-dimensional grating
ActiveCN109709683AHas spatial diffraction invariant propertiesImprove energy utilizationOptical elementsGratingHigh energy
The disclosure proposes an apparatus and method for generating a square array vector beam with invariable space diffraction by using a two-dimensional grating. According to the apparatus, laser is processed by a beam expander collimating mirror to obtain a large-caliber parallel beam; the large-caliber parallel beam passes through a polarizer and then the polarized beam passes through a polarization beam splitting prism to obtain two large-caliber parallel beams in a vertical direction and a horizontal direction; the two large-caliber parallel beams in a vertical direction and a horizontal direction is reflected by a plane reflecting mirror and then the reflected beams enter two two-dimensional orthogonal gratings with the same parameters; and the two two-dimensional orthogonal gratings with the same parameters are arranged an optical branch at the right side and a lower optical branch, the relative positions of the two two-dimensional orthogonal gratings are adjusted and the optical fields of the two optical branches are superposed to generate a required periodic array square vector beam. Compared with the conventional filtering method, the provided apparatus and method has the following excellent characteristics: high energy utilization rate and invariable space diffraction and have the certain application space in fields like material processing and particle shunting.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Waveguide-type optical circuit
A waveguide-type optical circuit comprises an optical coupler being an optical branch coupler constructed from waveguide cores which are closely arranged each other, and dummy patterns that lay along sides of the waveguide cores in the optical coupler for preventing optical major axes of the waveguide cores from inclining.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method and system for fiber-optic monitoring of spatially distributed components
ActiveUS8488114B2Improve reliabilityMaterial analysis by optical meansElectrical testingUltrasound attenuationFiber
A system for monitoring a plurality of components distributed in different space locations, includes: at least one optical fiber path; an optical radiation source adapted to inject optical radiation into the at least one optical fiber path; at least one first and at least one second optical branches branching from the at least one optical fiber path and adapted to spill respective portions of the optical radiation, the first and second optical branches being adapted to be operatively associated with a respective component to be monitored. The first optical branch includes a first optical reflector and is adapted to reflect the spilled optical radiation portion unless the respective component at least partially breaks; the second optical branch includes at least one passive optical attenuator adapted to be operatively coupled to the respective component to be monitored, and having an attenuation capable of changing in response to a change in operating conditions of the respective monitored component when operatively coupled thereto, and a second optical reflector. An optical receiver is adapted to detect back-reflected optical radiation reflected by the first and second optical branches. The monitoring system is adapted to recognize a position of a component of the plurality of components based on a characteristic of the back-reflected optical radiation.
Owner:PRYSMIAN SPA
Method and system for fiber-optic monitoring of spatially distributed components
ActiveUS20100328651A1Improve reliabilityMaterial analysis by optical meansElectrical testingUltrasound attenuationOptical reflection
A system for monitoring a plurality of components distributed in different space locations, includes: at least one optical fiber path; an optical radiation source adapted to inject optical radiation into the at least one optical fiber path; at least one first and at least one second optical branches branching from the at least one optical fiber path and adapted to spill respective portions of the optical radiation, the first and second optical branches being adapted to be operatively associated with a respective component to be monitored. The first optical branch includes a first optical reflector and is adapted to reflect the spilled optical radiation portion unless the respective component at least partially breaks; the second optical branch includes at least one passive optical attenuator adapted to be operatively coupled to the respective component to be monitored, and having an attenuation capable of changing in response to a change in operating conditions of the respective monitored component when operatively coupled thereto, and a second optical reflector. An optical receiver is adapted to detect back-reflected optical radiation reflected by the first and second optical branches. The monitoring system is adapted to recognize a position of a component of the plurality of components based on a characteristic of the back-reflected optical radiation.
Owner:PRYSMIAN SPA
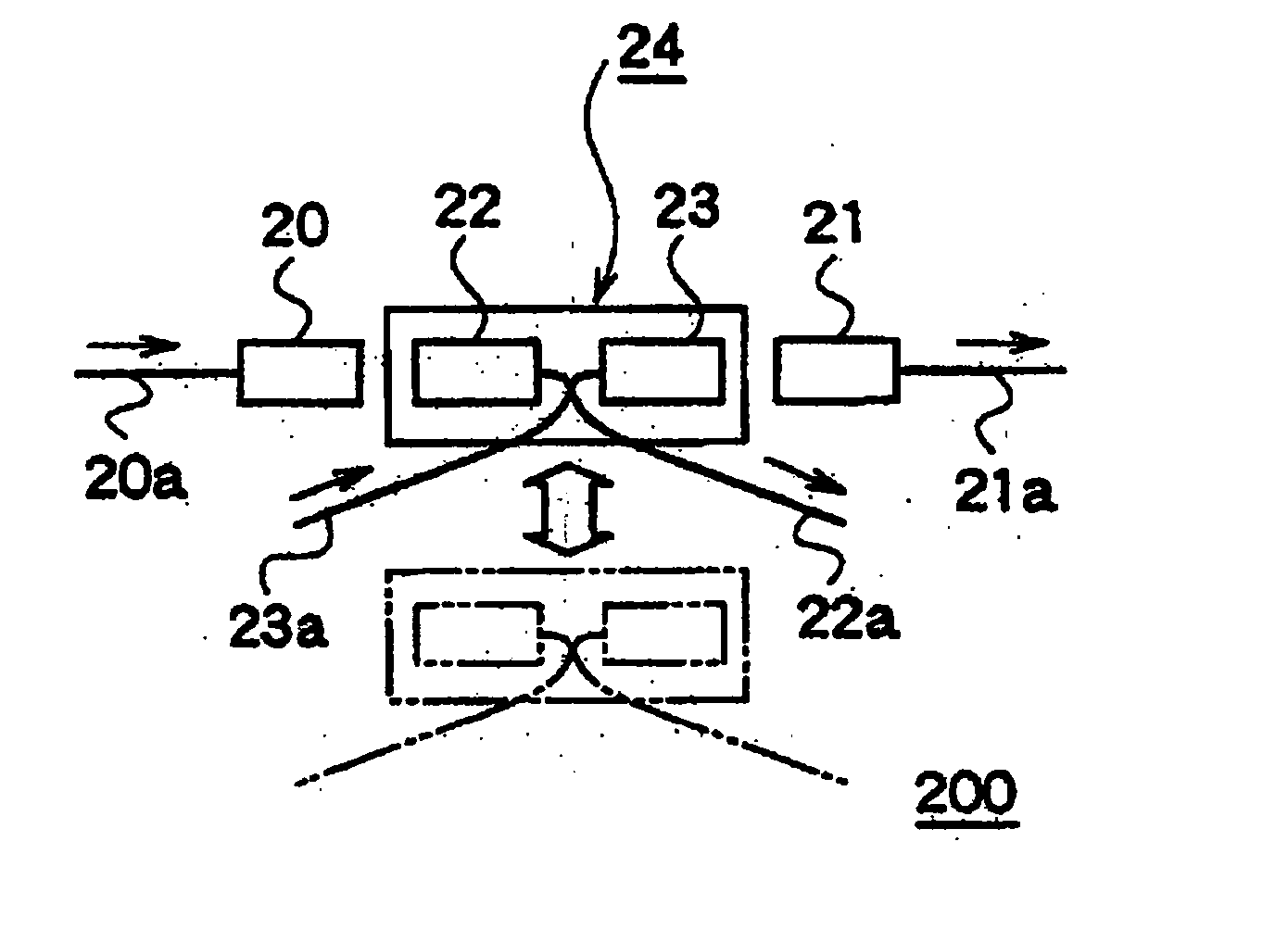
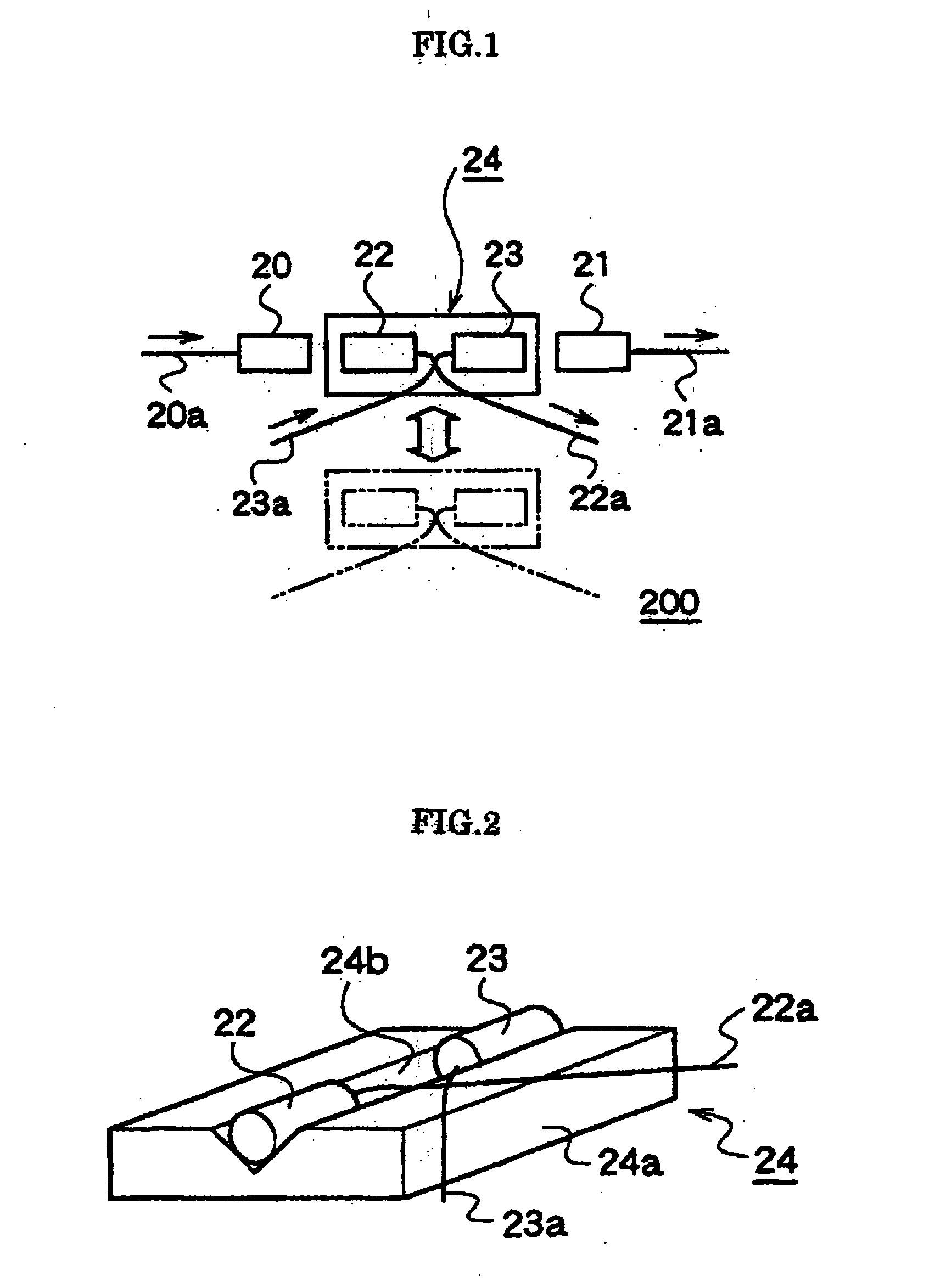
Optical switch and optical branch/insertion unit comprising it
An optical switch easy to adjust optical parts without using a catoptric system and an optical add / drop multiplexer using the optical switch are provided. Between an input light outputting collimator device 20 and an output light inputting collimator device 21 provided to face each other at a predetermined spaced interval, a drop light inputting collimator device 22 and an add light outputting collimator device 23 fixed and held on a movable holding member 24a in common are moved forward and retreated, and thereby a switching is conducted.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Optical circuit
ActiveUS20160054529A1Reduce the impactLow costCoupling light guidesSemiconductor lasersOptical reflectionPhase difference
An optical circuit, wherein the effects of reflected light generated by an optical component are reduced. The optical circuit (100) is provided with an optical branching (110) for branching light, an optical coupler (114) for coupling a first portion of branched light to an optical waveguide (118) for transmission, and an optical reflecting unit (116) for reflecting a second portion of the branched light, the phase difference between the reflected light from the optical coupler (114) and the reflected light from the optical reflecting unit (116) being (2m−1)π (where m is an integer) on an input side of the optical branching (110).
Owner:PHOTONICS ELECTRONICS TECH RES ASSOC
Optical branch device and optical coupler module
InactiveUS20060067622A1Uniform qualityImprove productivityCoupling light guidesRefractive indexWaveguide
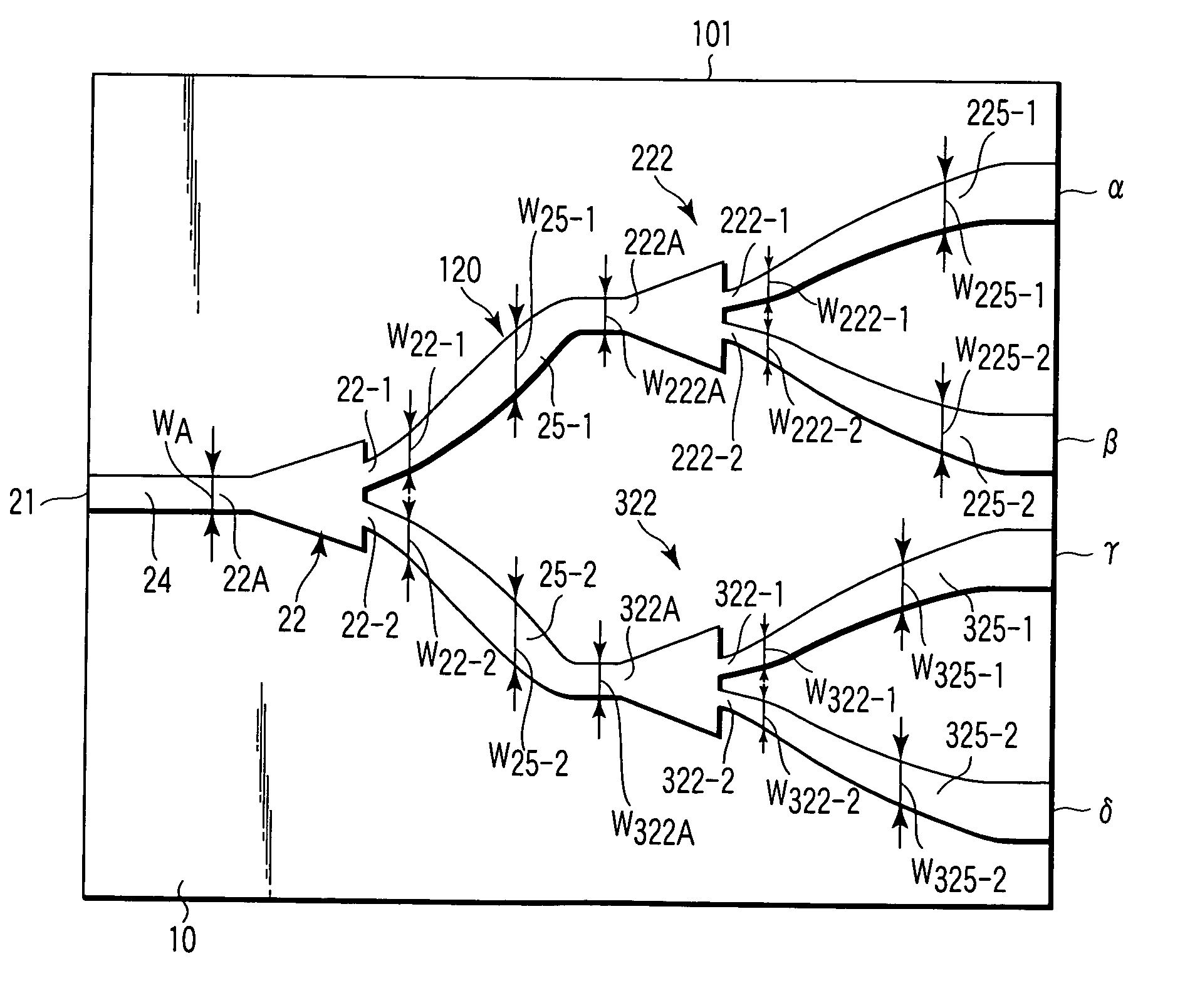
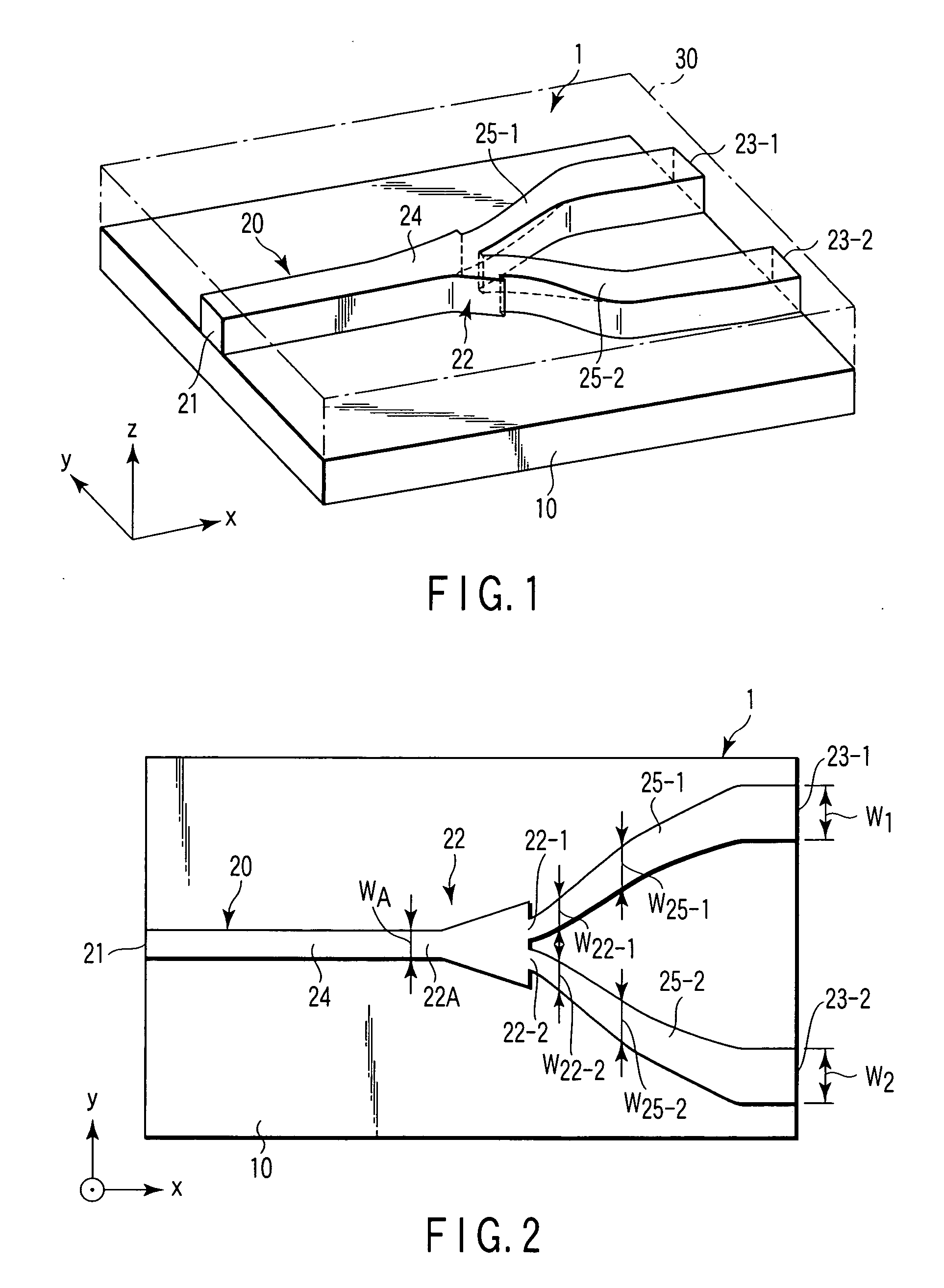
An optical branch device, comprising: a branch portion having a first branch waveguide extended linearly and continuously from a waveguide in a basis portion, and second and third branch waveguides extended in the directions farther from the first branch waveguide in such a manner that the first branch waveguide is interposed between the second and third branch waveguides; a parallel portion in which the second and third branch waveguides are positioned in parallel to the first branch waveguide; and a divergent portion in which the second and third branch waveguides are extended gradually farther from the first branch waveguide; wherein the interval pitch P (μm), in the transverse direction, between the first, second and third branch waveguides in the parallel portion and the refractive index difference (Δn) between the core and the clad are set in such a manner that C satisfies a relationship of C=0.5±0.2 wherein C is calculated by substituting P and Δn for an equation of C=Δn×P2.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Light source circuit and light source device equipped with same
ActiveUS9151894B2Effectively inhibit returning light in lightCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guidePath lengthLength wave
Owner:NEC CORP +1
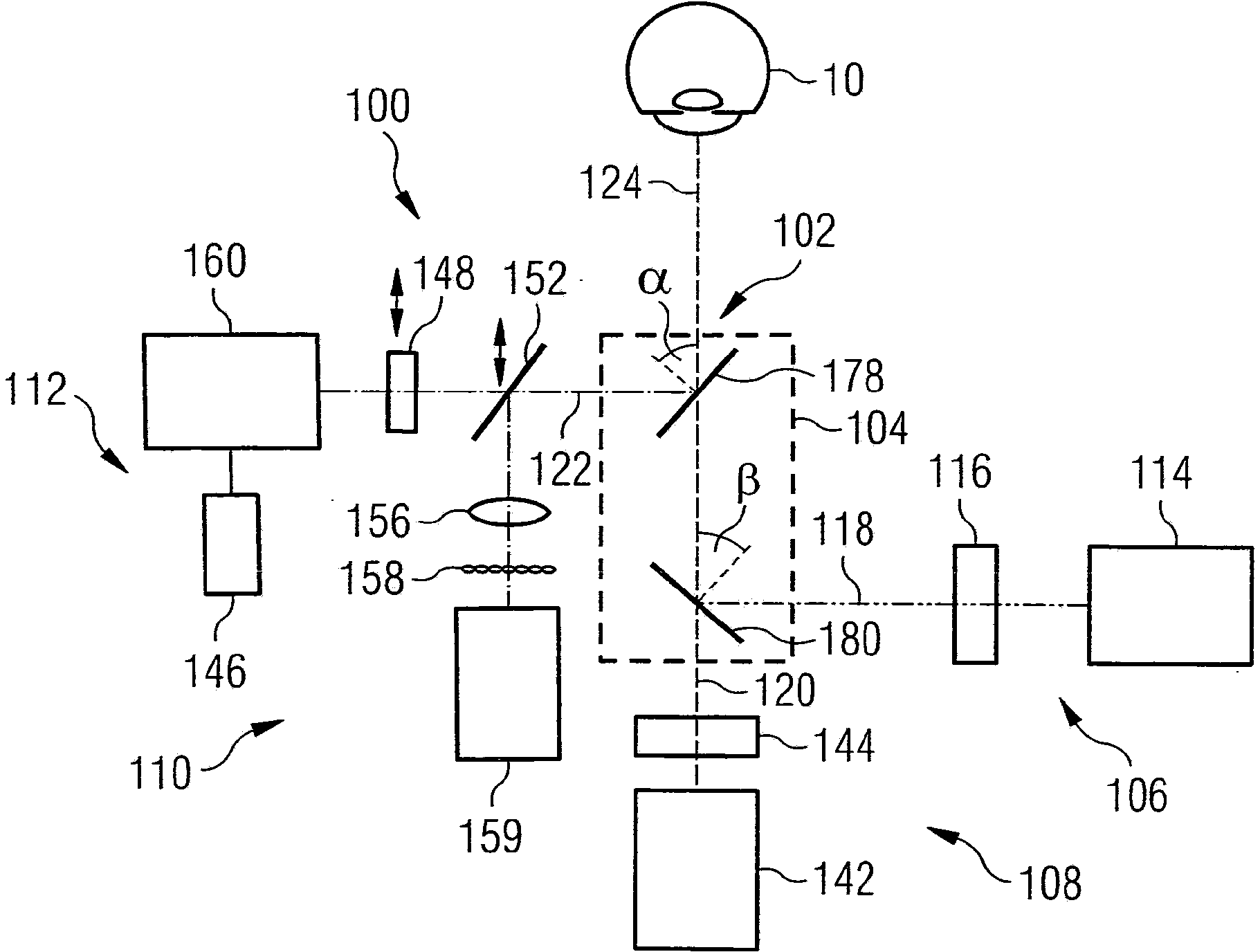
An integrated device for ophthalmology
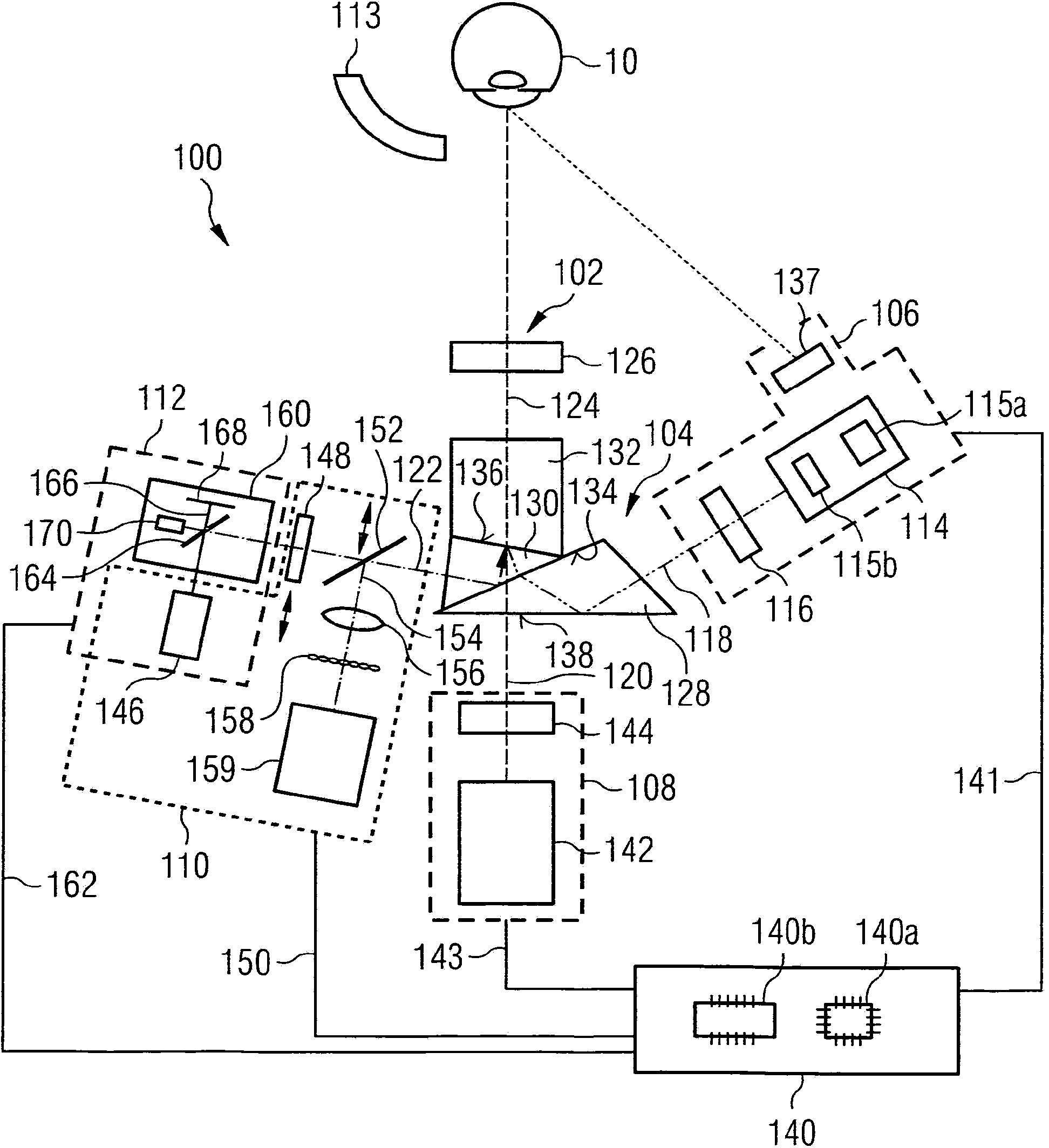
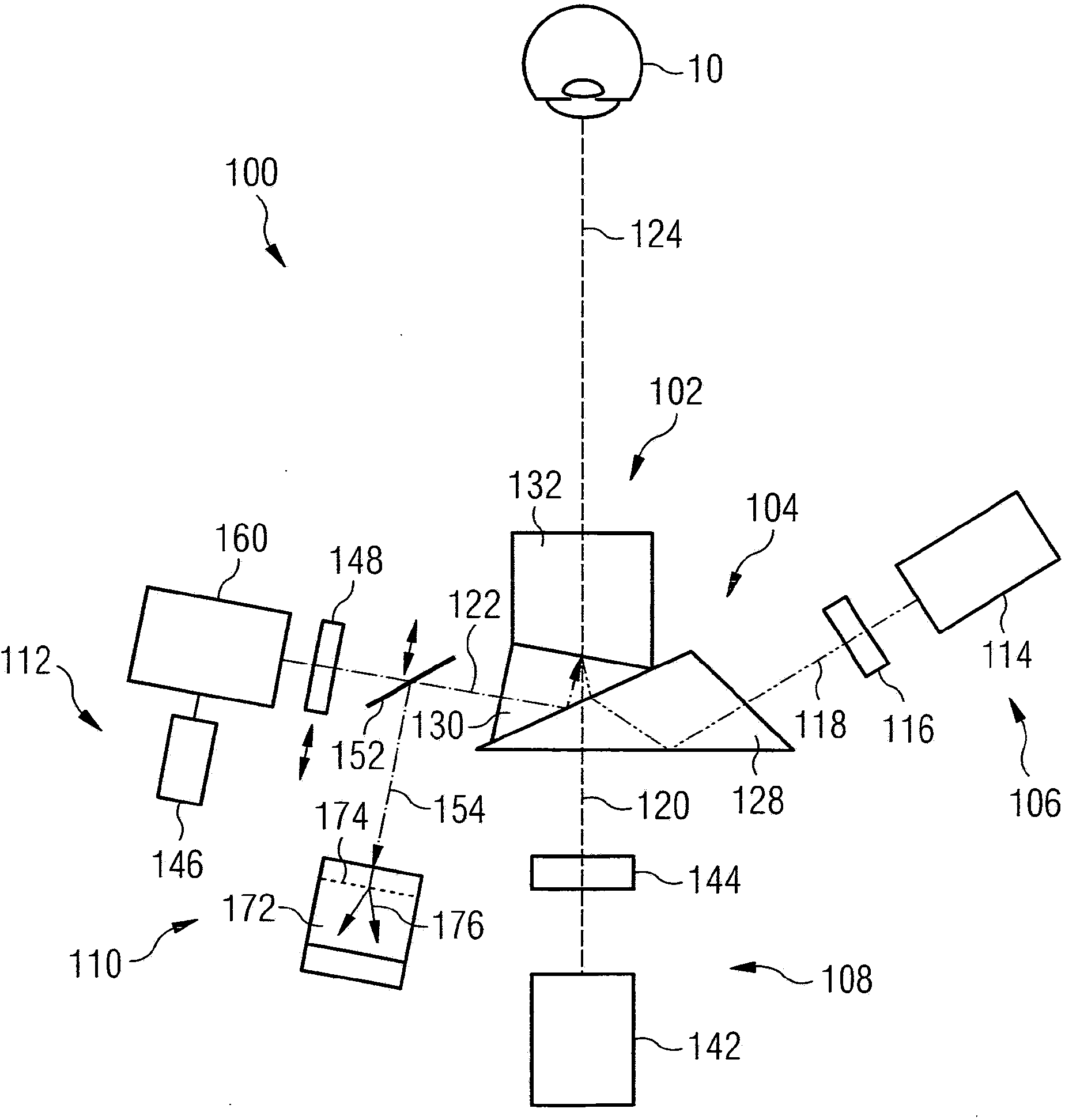
ActiveCN104066370ALow costCompact designDiagnostic recording/measuringEye treatmentIntegrated devicesRadiation
Owner:ALCON INC
Optical branching unit
InactiveUS20070053636A1Reducing light emissionImprove wavelength uniformityCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideEngineeringWaveguide
In an optical branching unit according to the invention, the cross section shape in an area of a front stage to branch to two output waveguides in the optical branch is a rectangle or a non-circle with different vertical-to-horizontal ratio, including an area that the length along the surface of the substrate is defined to be shorter than the length in the direction orthogonal to the surface of a substrate, the cross section at the output ends of the output waveguide is a rectangle or a non-circle with a different vertical-to-horizontal ratio, where the length along the surface of the substrate is defined to be longer than the length in the direction orthogonal to the surface of the substrate.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Sum frequency device and laser
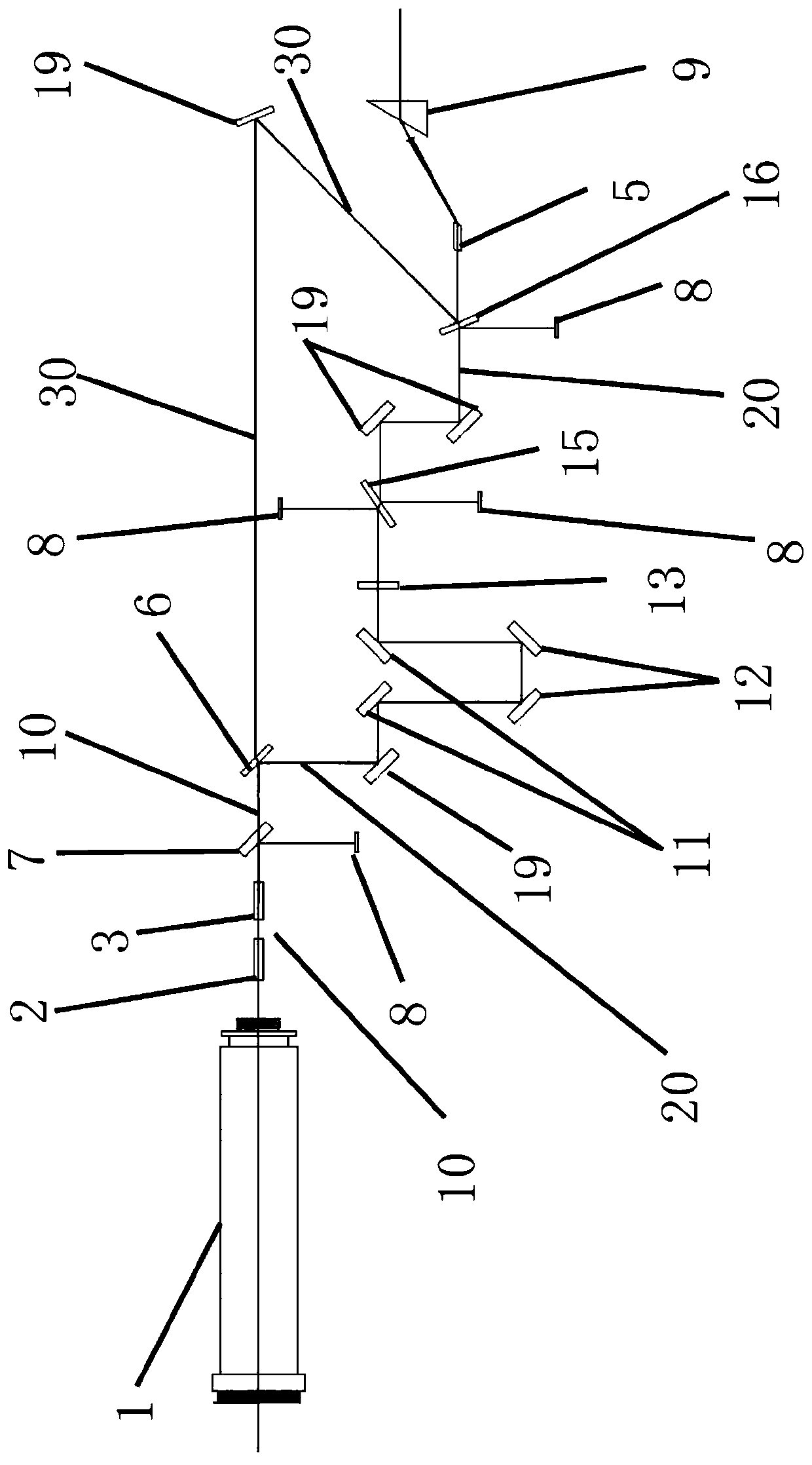
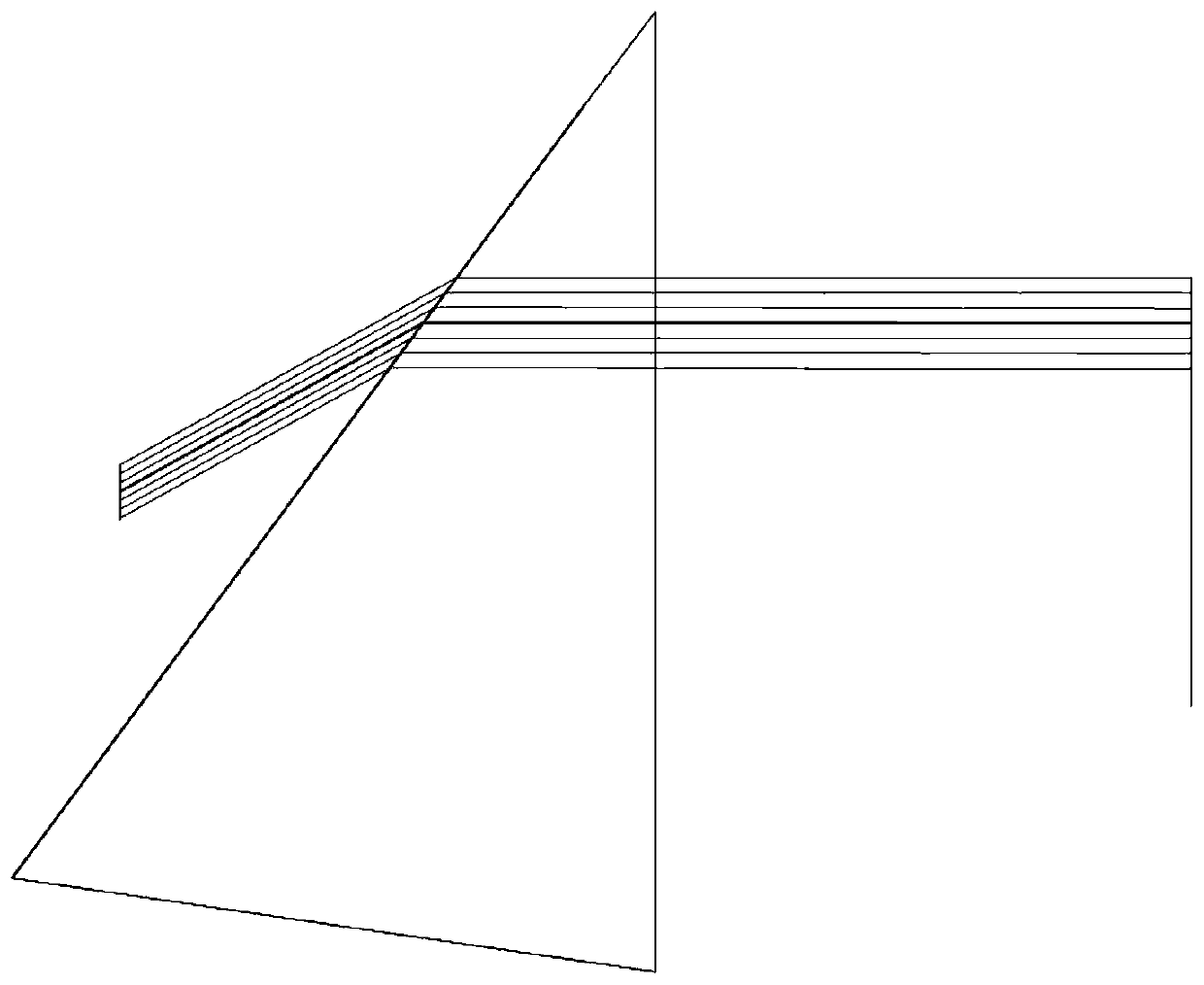
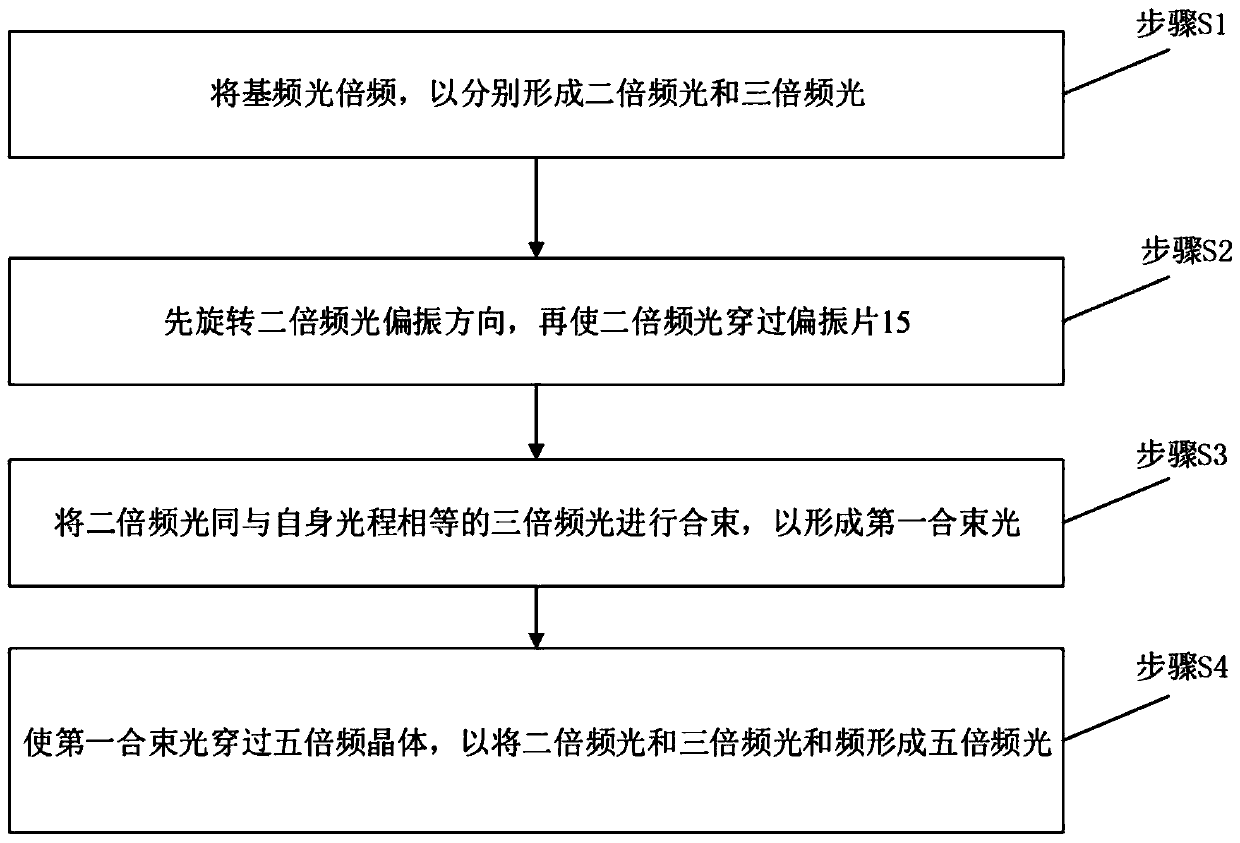
InactiveCN111106521AImprove work efficiencyQuality improvementLaser using scattering effectsBeam splittingPolarizer
The invention provides a sum frequency device which comprises a main optical path, a quintuple frequency crystal and a beam combining device. A double-frequency crystal, a triple-frequency crystal anda first beam splitting device are sequentially arranged on the main optical path. Two optical branches, namely a double-frequency optical branch and a triple-frequency optical branch, can be formed through the first beam splitting device. A wave plate and a polarizing film are sequentially arranged on the double-frequency optical branch, and the optical paths and the end points of the double-frequency optical branch and the triple-frequency optical branch are the same. The beam combining device combines the light in the double-frequency optical branch and the light in the triple-frequency optical branch. The combined light can be propagated to a quintuple-frequency crystal. The invention further provides a laser. Compared with the prior art, the device has the beneficial effects that thesum frequency working efficiency can be improved, and the quintuple-frequency laser can be efficiently obtained.
Owner:RAINBOW SOURCE LASER RSLASER
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com