Bacillus subtilis capable of producing broad spectrum and efficient antibacterial peptide and application of Bacillus subtilis
A Bacillus subtilis, antimicrobial peptide technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problem of less application of antimicrobial peptides and other problems, and achieve the effects of wide application range, broad antibacterial spectrum and short production cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Embodiment 1: Screening of BRT39 bacterial strain
[0018] (1) Take 2g soil sample from the vegetable garden rich in organic matter, add it to a small triangular flask containing 50mL of cooled sterile water, shake the table at 200r / min, shake for 20min, then place it in a water bath at 80°C for 10min, and keep Shake the Erlenmeyer flask to mix the soil sample, let it stand for 5 minutes, absorb 100 μL of the supernatant, and gradually dilute to 10 -1 ~10 -9 Concentration, select 10 -3 , 10 -4 , 10 -5 , 10 -6 Concentration coated beef extract peptone plate, cultivated at 37°C for 24h, and continued to cultivate at 30°C for 24h.
[0019] (2) According to the characteristics of the shape, size, surface structure, edge structure, texture, gloss, transparency, color and soluble pigment of the microbial colony, use the inoculation loop to pick out the isolated single colony and move it to the screening culture Base plate, and numbered, 34 ℃ for 48h.
[0020] The scree...
Embodiment 2
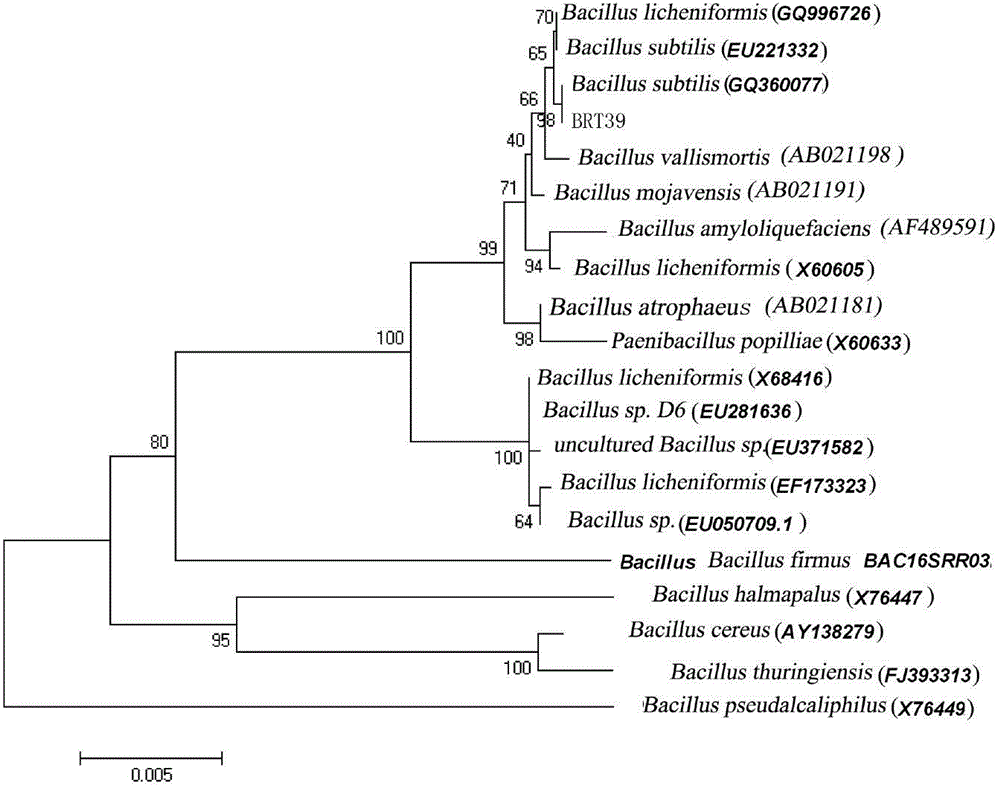
[0027] Embodiment 2: bacterial strain identification
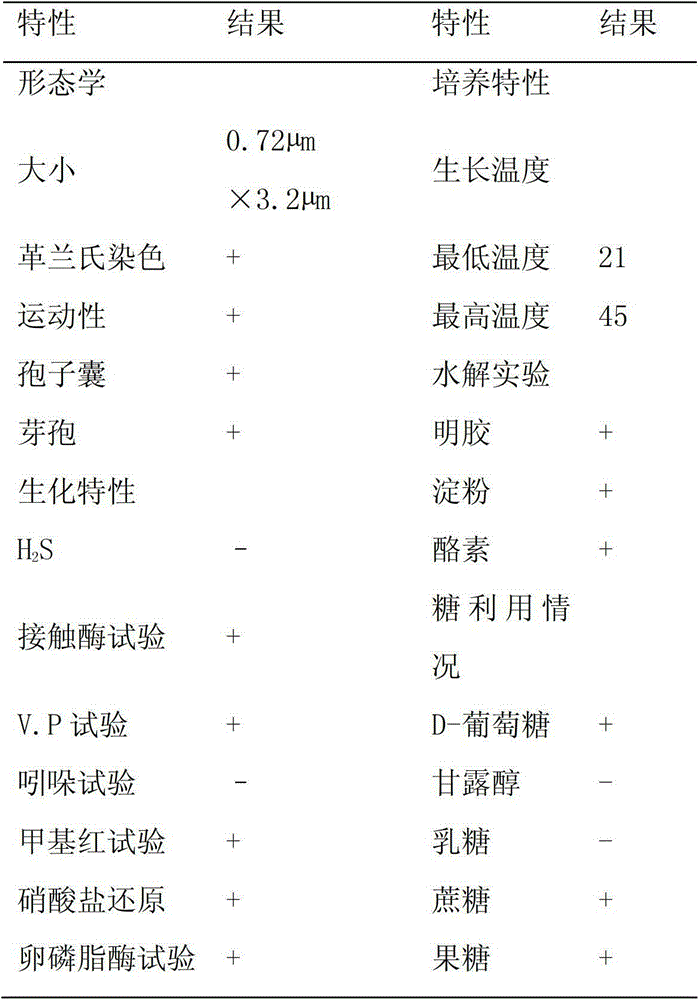
[0028] Physiological and biochemical identification of strains: Carry out carbon source utilization test, catalase test, hydrogen sulfide test, indole test, nitrate and nitrite reduction test and other tests according to the method of "Bergey's Bacteria Identification Manual" (Ninth Edition) Morphological identification: spot the strains to be identified on solid plates of beef extract peptone medium, culture at 37°C for 2 days, describe and record the characteristics of colony culture and morphological characteristics of bacteria. The physiological and biochemical identification characteristics are shown in Table 1. The results in the table are consistent with the characteristics of Bacillus subtilis species compared with "Bergey's Bacteria Identification Manual". Molecular biological identification: The extraction of bacterial genomic DNA refers to the method of "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide" (3rd edition). Prime...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Embodiment 3: Determination of antibacterial spectrum activity of bacterial strain fermented liquid
[0033] (1) The fermentation broth of strain BRT39 was centrifuged at 10,000 r / min for 5 min, and the obtained supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm microporous membrane for antibacterial activity determination.
[0034] (2) Use the nutrient agar medium to cultivate the indicator bacteria, and use the punching method to directly measure the antibacterial activity of the shake flask fermentation broth. Nutrient agar medium plates were coated with 100 μL indicator bacteria suspension (1×10 8 cfu / ml), uniformly punch holes with a hole puncher with a diameter of 6 mm, add 100 μL of the prepared fermentation broth to each hole, and use sterile water as a control. Incubate at 37°C for 16 hours, and record the size of the inhibition zone. Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureaus, Bacillus cereus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella enteritidis, Bacillus subtilis, etc. Ba...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com