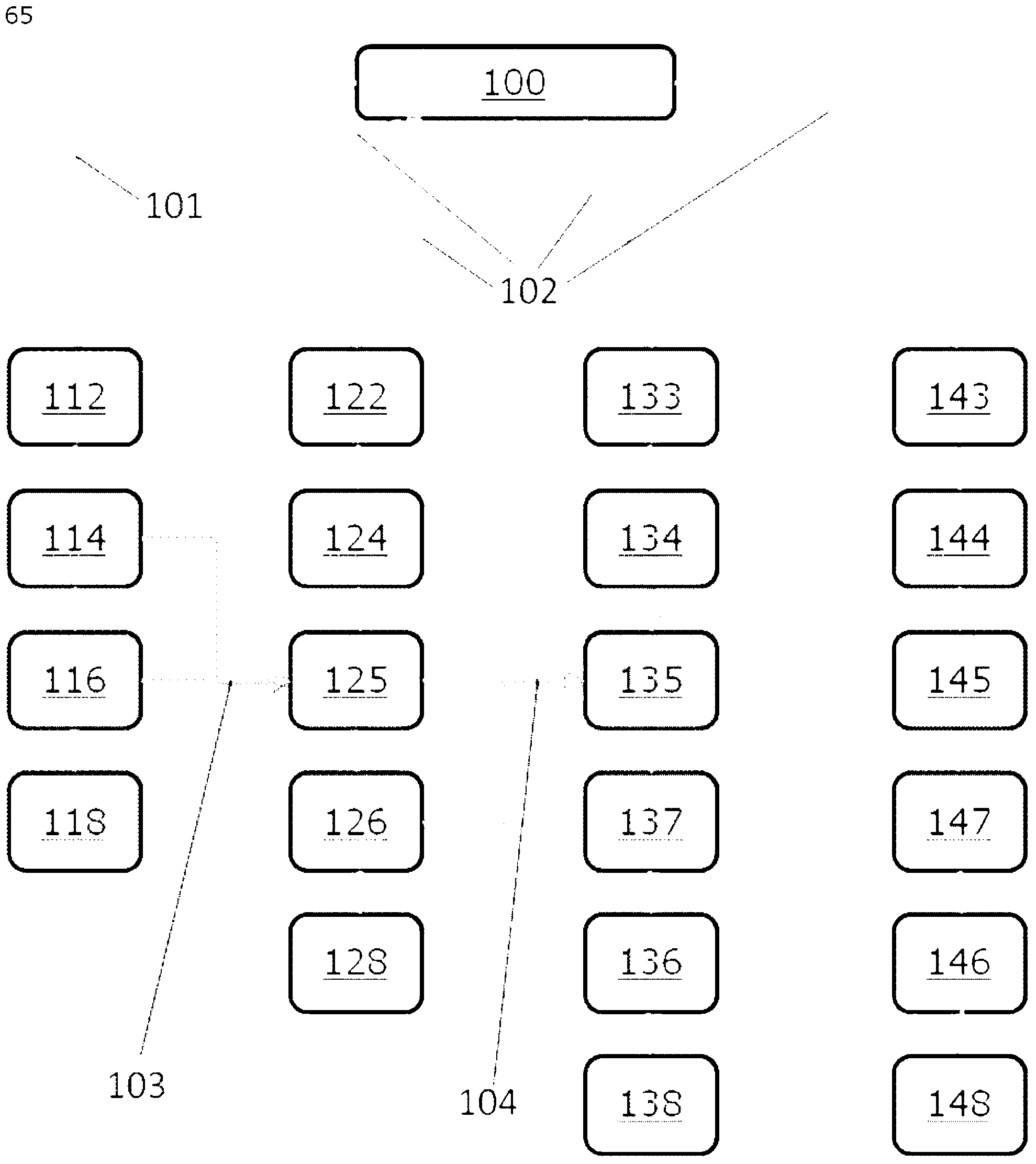
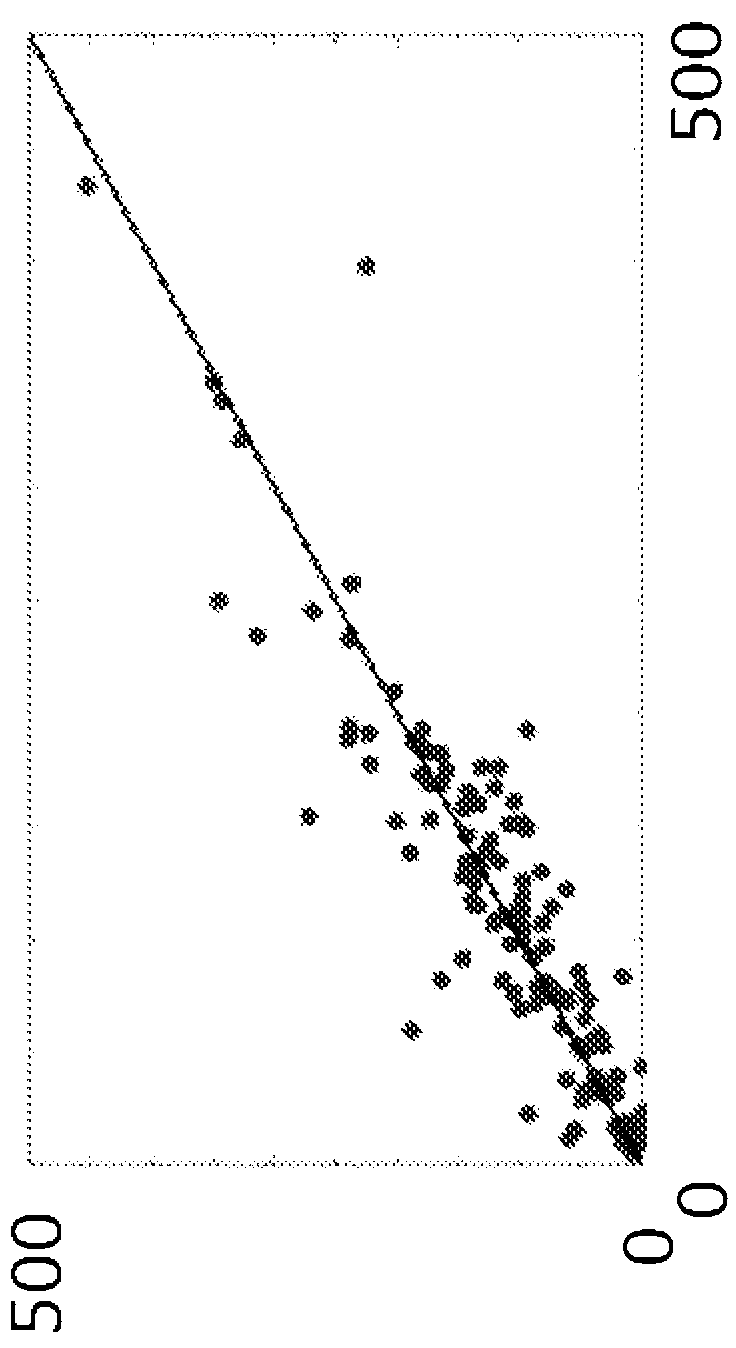
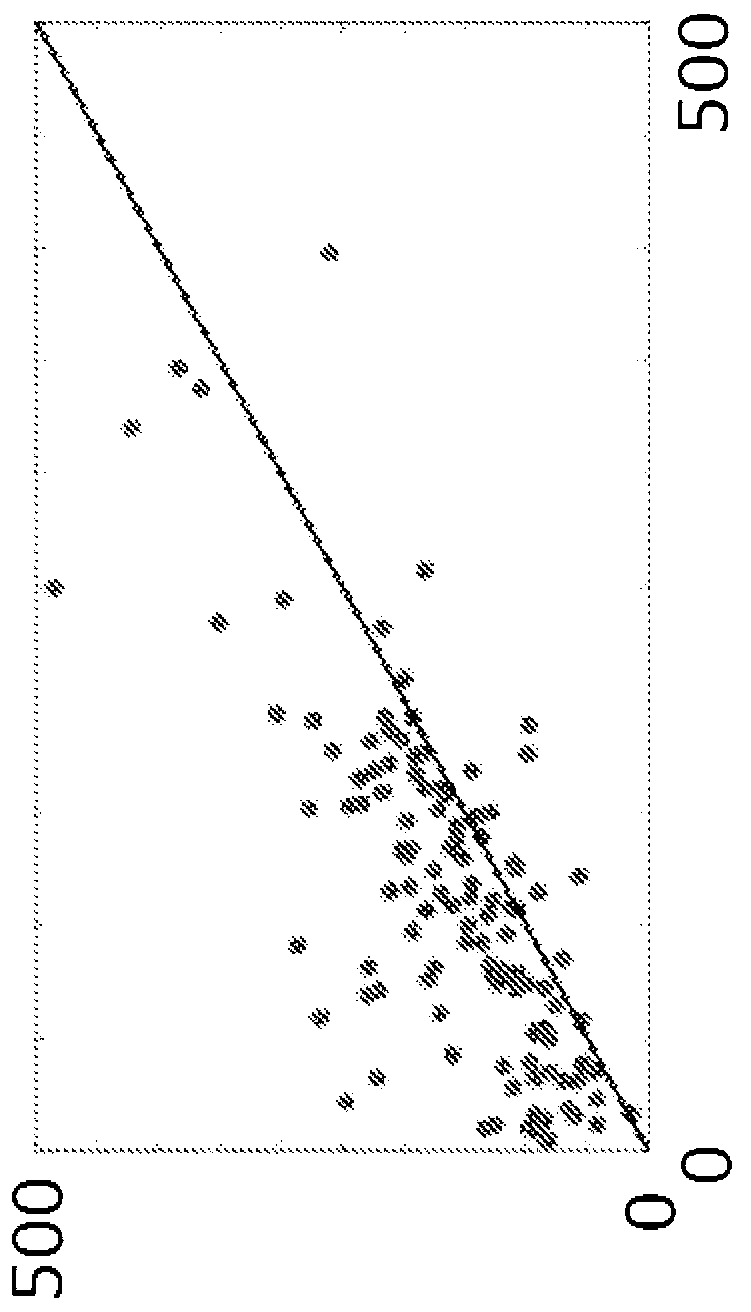
Method for delineation of tissue lesions
A biological tissue and image technology, applied in the use of computer program products and corresponding methods, computer-aided delineation of brain tissue damage in stroke patients, system field, can solve problems such as unfastness, unreliability, tissue damage, etc., and achieve improvement Speed and/or reproducibility, effect of minimizing user intervention
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0148] Example 1 - Segmentation of an image including TTP data
[0149] Materials and Methods
[0150] Morphological grayscale reconstruction
[0151] Finding a voxel within the perfusion lesion, the so-called seed point, is easily identifiable by eye; however, searching for the maximum value of the image intensity often results in false positive seed points, such as high-intensity points in image regions corresponding to unrelated regions, e.g. eyes, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), extracerebral strength, etc. To automatically detect seed points, we used morphological grayscale reconstruction to truncate small spikes while preserving the edges of TTP lesions and homogenize the background of TTP images. Compared to conventional smoothing, e.g. using a Gaussian kernel, morphological grayscale reconstruction is less sensitive to spikes and is more suitable for seed point detection for this reason. In the present context, a spike is understood as a relatively small area compared to...
example 2
[0183] Example 2 - Segmentation of images of type MTT data
[0184] Materials and methods
[0185] level set
[0186] This method emerges from the assumption that the mean MTT value, M hypo , in areas of hypoperfusion, compared to the mean M of normal MTT values norm higher. In areas of hypoperfusion, MTT values in M hypo varies around , while in normal tissues they are close to M norm . This corresponds to a low squared error between the image MTT values, MTT(x,y), and the respective mean values. Identifying damage, such as ischemic damage, can then be formulated as finding a smooth, closed curve C that minimizes the total variation (equation (1))
[0187] E=∫ Inside C (MTT(x,y)-M hypo ) 2 dxdy+∫ Outside C (MTT(x,y)-M norm ) 2 dxdy
[0188] It is important that C can represent multiple curves since ischemic regions are not necessarily contiguous, such as in the case of occlusion causing damage in the watershed region. This can be guaranteed by implicitly defi...
example 3
[0223] Example 3 - Segmentation of an image obtained by DWI
[0224] Materials and Methods
[0225] Morphological grayscale reconstruction
[0226] DWI lesions are readily recognized by the eye as areas of hyperintensity, although diffuse lesions contain artifactual hyperintensity; and due to body structure and noise artifacts, the hyperintensity spreads throughout the image. Therefore, simple thresholding of image intensities leads to high false positive and false negative rates, as Figure 11B shown. Typical image blurring, e.g. by convolution with a Gaussian kernel, is somewhat remedied to the artifact, although at the cost of potentially "moving" the lesion boundary. Morphological grayscale reconstruction uniquely truncates peaks in the image, tending to preserve the original boundaries of cohesive regions, as determined by the kernel size. We used morphological grayscale reconstruction to enhance the contrast between DWI lesions and the background. Morphological gray...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com