Method for processing degradation-resistant organic pollutants in water
A technology for organic pollutants and water treatment, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve problems such as limiting the reaction rate of the activated persulfate system, and achieve the effects of easier control of the reaction process, improved removal rate, and improved reaction rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] A method of treating refractory organic pollutants in water using a weak magnetic field / ZVI synergistically activated persulfate advanced oxidation technology in this embodiment, the specific steps are:
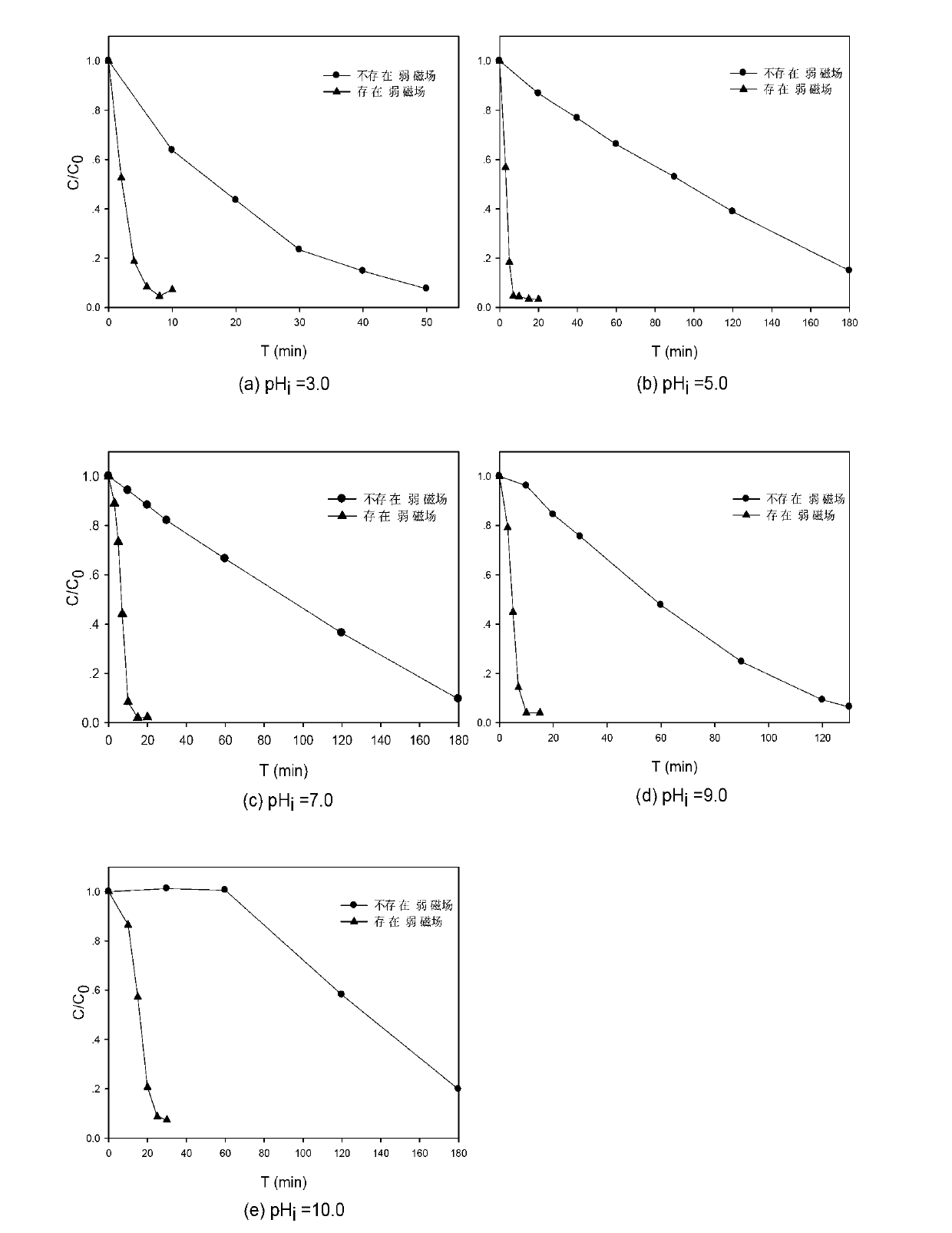
[0032] (1) Arrange a weak magnetic field around the reactor, the weak magnetic field used is a permanent magnet weak magnetic field, and the magnetic field strength is about 15-50mT. In the complete mixing reactor, the initial concentration of the printing and dyeing wastewater golden orange G is 200μM, adjust the initial pH value 3.0~10.0;
[0033] (2) First add 2mM sodium persulfate to the above printing and dyeing wastewater, and then add 2mM zero-valent iron to start the reaction. see results figure 1 . Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that in a wide pH range (3.0-10.0), the zero-valent iron / sodium persulfate system is feasible for the removal of golden orange G, and the existence of a weak magnetic field can greatly increase the reaction rate and shorten the r...
Embodiment 2
[0041] A method of treating refractory organic pollutants in water using a weak magnetic field / ZVI synergistically activated persulfate advanced oxidation technology in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
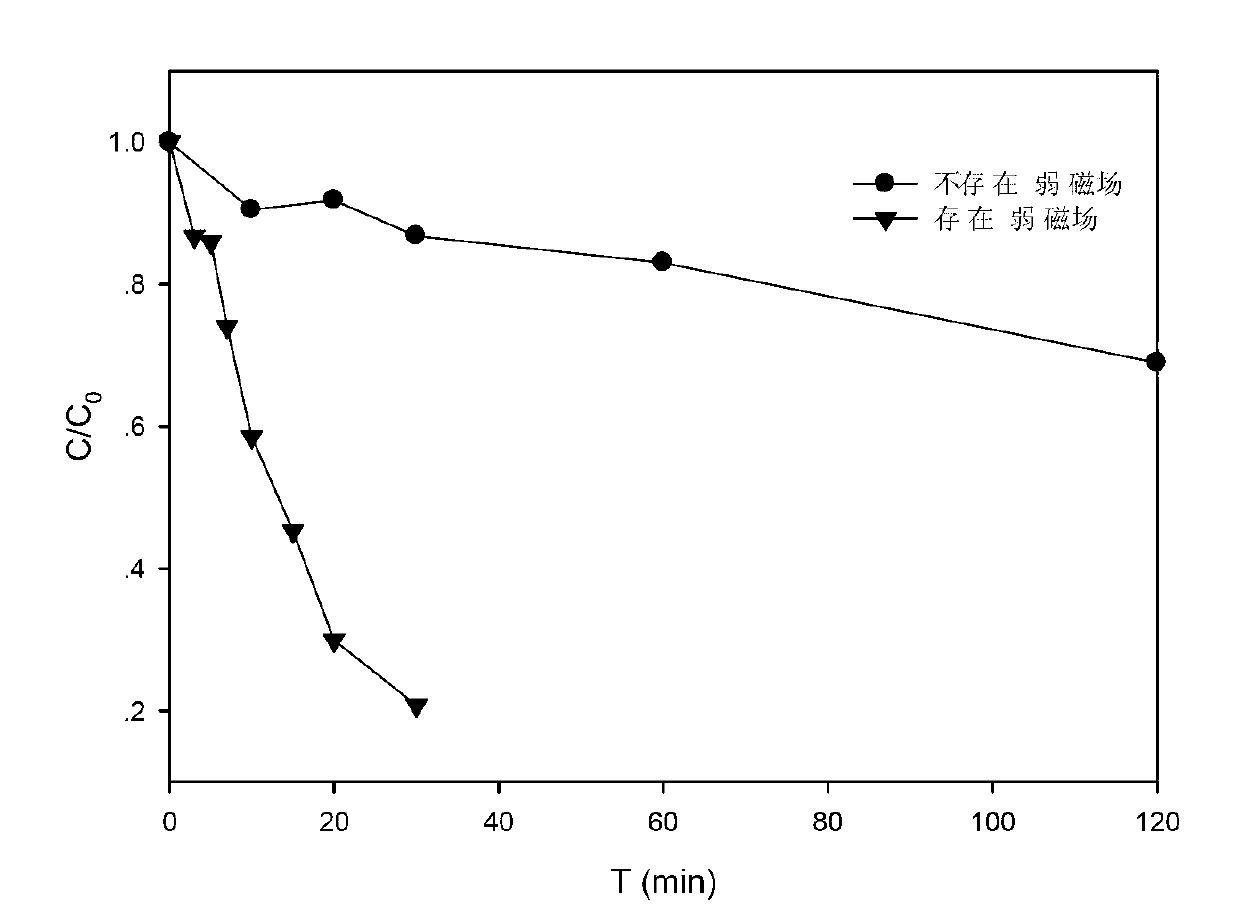
[0042] (1) A weak magnetic field is arranged around the reactor, the weak magnetic field used is a weak electromagnetic field, and the magnetic field strength is about 5-30mT; in the complete mixing reactor, the initial concentration of reactive blue 4 in printing and dyeing wastewater is 200μM, and the initial pH value is adjusted to 5.0;
[0043] (2) Simultaneously add 2mM sodium persulfate and 2mM zero-valent iron to the above printing and dyeing wastewater to start the reaction. In the presence of a weak magnetic field, the removal rate of reactive blue 4 by zero-valent iron / sodium persulfate reached 80% within 30 minutes; while in the absence of a weak magnetic field, the removal rate of reactive blue 4 was only 31% within 120 minutes. see results figure 2...
Embodiment 3
[0046] A method of treating refractory organic pollutants in water using a weak magnetic field / ZVI synergistically activated persulfate advanced oxidation technology in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
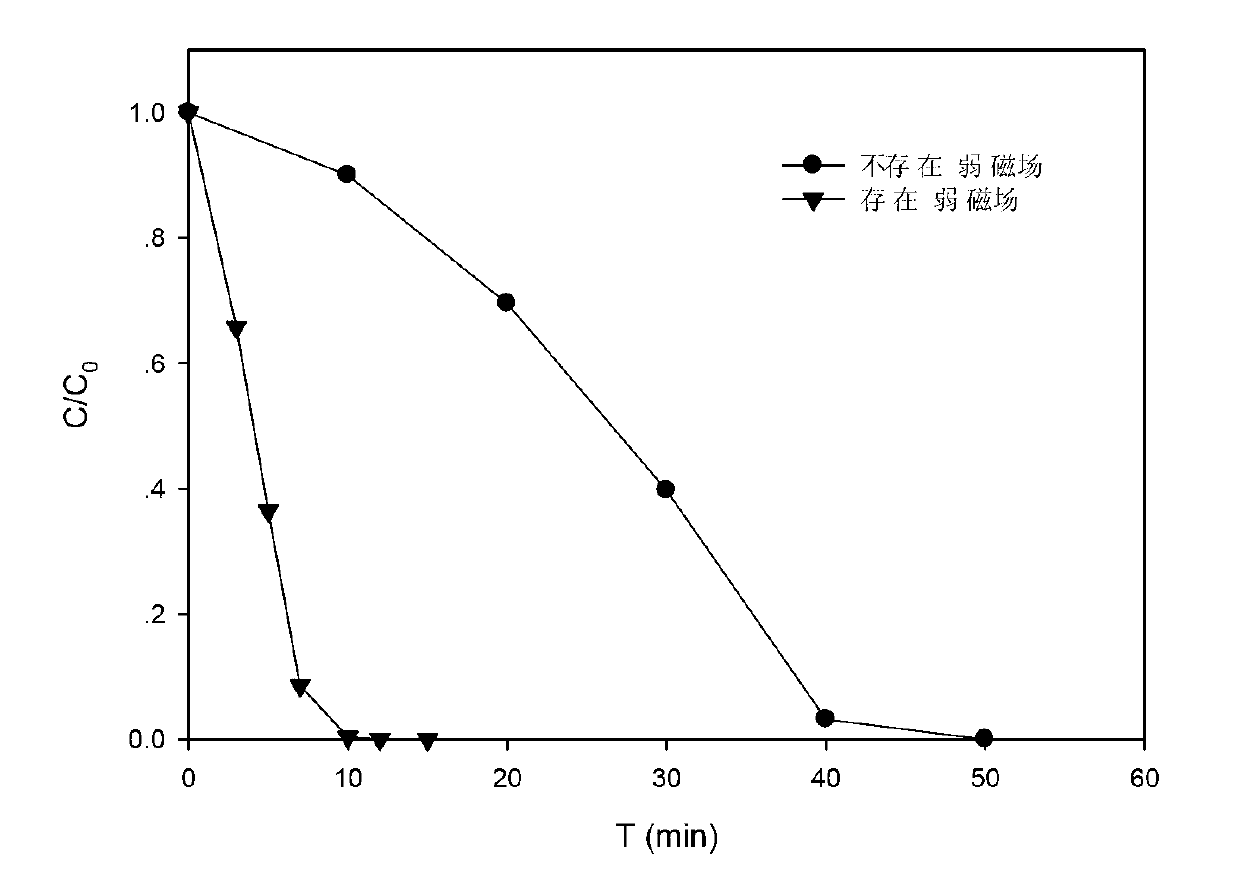
[0047] (1) A weak magnetic field is arranged around the reactor, the weak magnetic field used is a weak electromagnetic field, and the magnetic field strength is about 15-40mT; in the complete mixing reactor, the initial concentration of the refractory trace organic caffeine is 10μM, and the initial pH value is 7.0;
[0048] (2) Simultaneously add 1mM sodium persulfate and 1mM zero-valent iron to the above-mentioned treated water to start the reaction. In the presence of a weak magnetic field, the removal rate of caffeine by zero-valent iron / sodium persulfate reached 100% within 10 minutes; while in the absence of a weak magnetic field, it took 50 minutes to completely remove caffeine. see results image 3 .
[0049] Depend on image 3 It can be seen that the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com