Method for screening and correcting light intensity sampling points in alignment process
A sampling point, normal technology, applied in the direction of optics, microlithography exposure equipment, photoplate making process of pattern surface, etc., can solve the problem of affecting the precision, affecting the alignment speed of the lithography machine, the yield of the whole machine, and the light intensity The impact of radiation value and other issues, to ensure the correctness, to achieve the effect of silicon wafer alignment function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
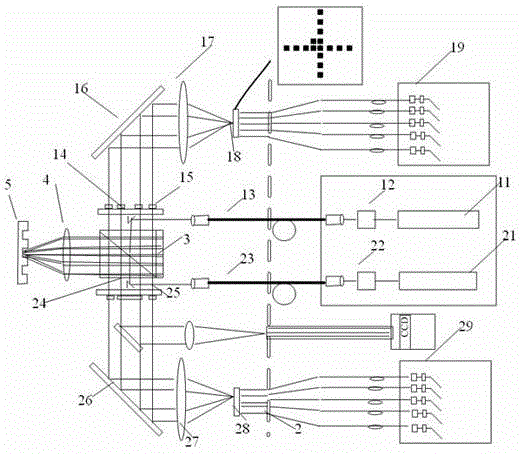
[0036] figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of a dual light source multi-level sub-alignment system of the known technology. Such as figure 1 As shown, the dual light source multi-level alignment system includes light source modules 11, 21, reference grating 2, optical fibers 13, 23, prisms 14, 24, polarizer 3, objective lens 4, marker 5, secondary wedges 15, 25, Mirrors 16 , 26 , objectives 17 , 27 , image planes 18 , 28 and detectors 19 , 29 . The specific working principle of the dual-light source multi-level alignment system is common knowledge to those skilled in the art, and will not be repeated here.
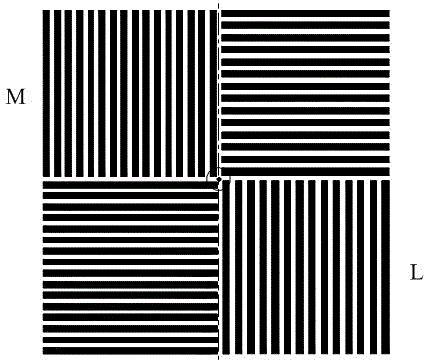
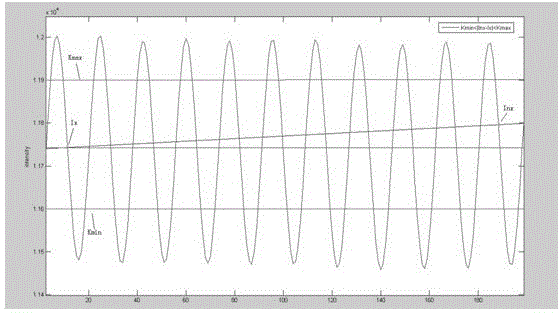
[0037] figure 2 The composition form of the alignment mark is shown, and the alignment system obtains the reflection information of various levels of light after the mark is irradiated. Issue the desired position of the mark, move the workpiece table, align the light source with the mark, and obtain the light intensity data I X (X=1, 2, 3….), calculate the alignme...
Embodiment 2
[0050] figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of a dual light source multi-level sub-alignment system of the known technology. Such as figure 1 As shown, the dual light source multi-level alignment system includes light source modules 11, 21, reference grating 2, optical fibers 13, 23, prisms 14, 24, polarizer 3, objective lens 4, marker 5, secondary wedges 15, 25, Mirrors 16 , 26 , objectives 17 , 27 , image planes 18 , 28 and detectors 19 , 29 . The specific working principle of the dual-light source multi-level alignment system is common knowledge to those skilled in the art, and will not be repeated here.
[0051] figure 2 The composition form of the alignment mark is shown, and the alignment system obtains the reflection information of various levels of light after the mark is irradiated.
[0052] Issue the desired position of the mark, move the workpiece table, align the light source with the mark, and obtain the light intensity data I X (X=1, 2, 3….), calculate the...
Embodiment 3
[0065] figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of a dual light source multi-level sub-alignment system of the known technology. Such as figure 1 As shown, the dual light source multi-level alignment system includes light source modules 11, 21, reference grating 2, optical fibers 13, 23, prisms 14, 24, polarizer 3, objective lens 4, marker 5, secondary wedges 15, 25, Mirrors 16 , 26 , objectives 17 , 27 , image planes 18 , 28 and detectors 19 , 29 . The specific working principle of the dual-light source multi-level alignment system is common knowledge to those skilled in the art, and will not be repeated here.
[0066] figure 2 The composition form of the alignment mark is shown. After the alignment system irradiates the mark, it obtains the reflection information of each level of light
[0067] Issue the desired position of the mark, move the workpiece table, align the light source with the mark, and obtain the light intensity data I X (X=1, 2, 3….), calculate the alignmen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com