Intracavitary ultrasonic lithotripsy device
A technique of intracavity ultrasound and lithotripsy, applied in the direction of internal fixator, internal bone synthesis, application, etc., can solve the problems of increasing patient trauma, pain, visual field interference, and prolonging operation time, so as to improve the operation efficiency and effect, Ease of pain and burden, and ease of crushing stones
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
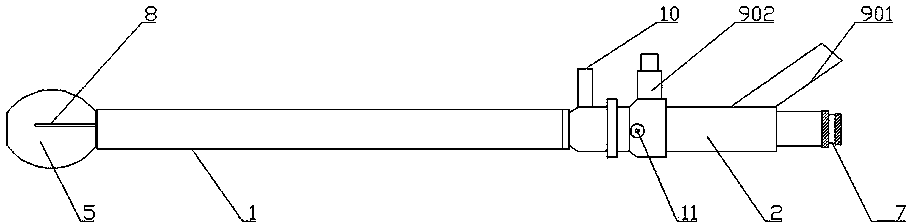
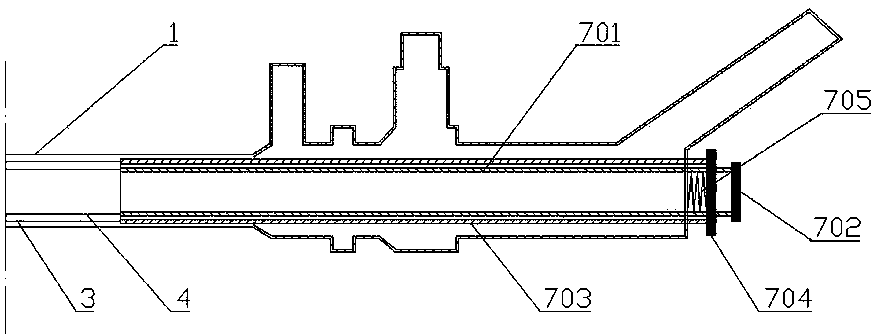
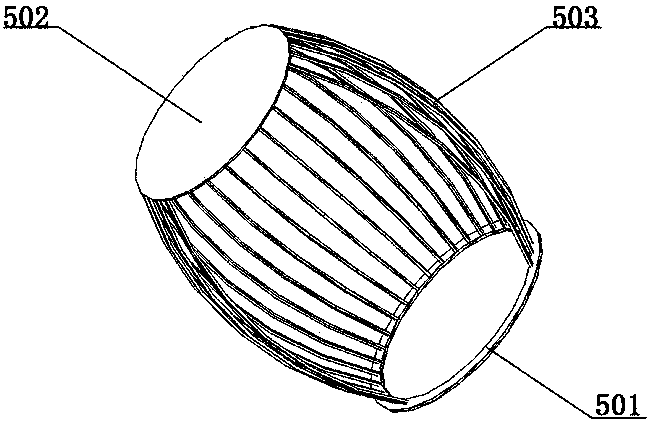
[0027] Such as figure 1 , 2 Shown in , 3: an intracavity ultrasonic lithotripsy device, comprising a straight tubular outer mirror sheath 1 open at both ends and a mirror body 2 connected to one end of the outer mirror sheath 1, the outer mirror sheath 1 is provided with a lithotripsy assembly 8 and As for the endoscopic imaging component, the lithotripsy component 8 is an ultrasonic lithotripsy component, and the lithotripsy component 8 includes an ultrasonic generator and a lithotripsy rod. The outer mirror sheath 1 is provided with a rotating sheath 3 and an endoscope sheath 4, the rotating sheath 3 and the endoscope sheath 4 are straight tubular mirror sheaths with open ends, the rotating sheath 3 can be rotatably sleeved outside the endoscope sheath 4, so The inner wall of the rotating sheath 3 is provided with an annular groove 301, and the outer wall of the endoscope sheath 4 is provided with a tab 401 that snaps into the annular groove 301, and there is no axial rela...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com