Detector array utilizing time-to-digital conversion with improved temporal precision
A detector array and detector technology, applied in the field of radiation detection, can solve the problems of fine counter output drift with time, reducing the effective temporal resolution and error of the PET detector array, and achieve the effect of improving spatial/temporal resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
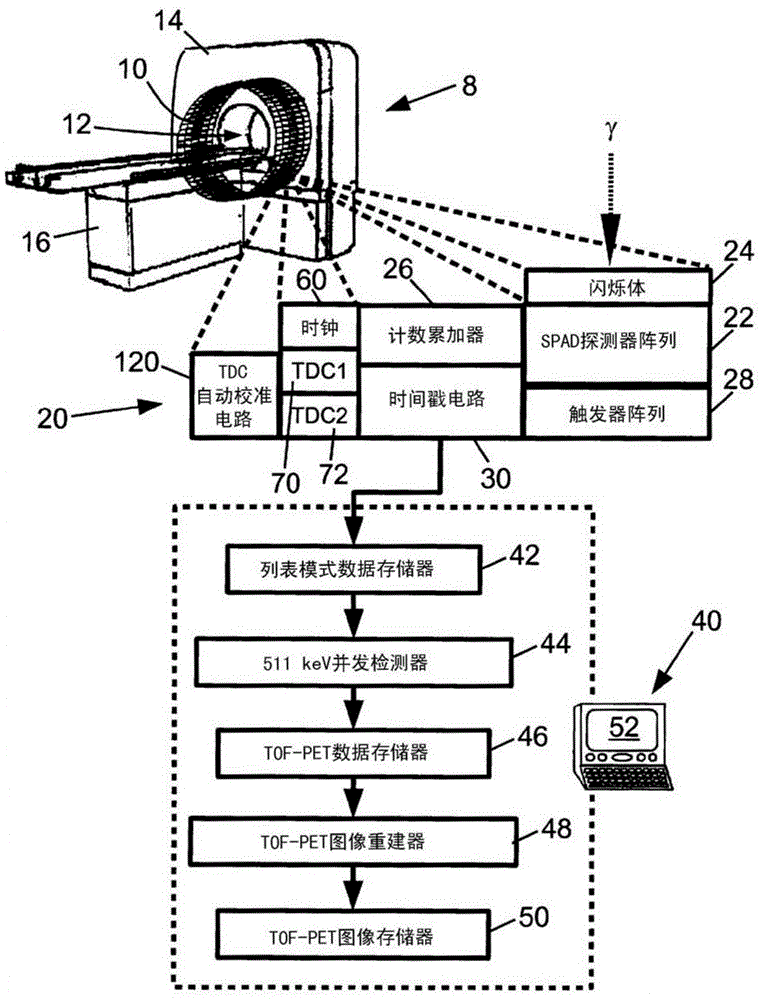
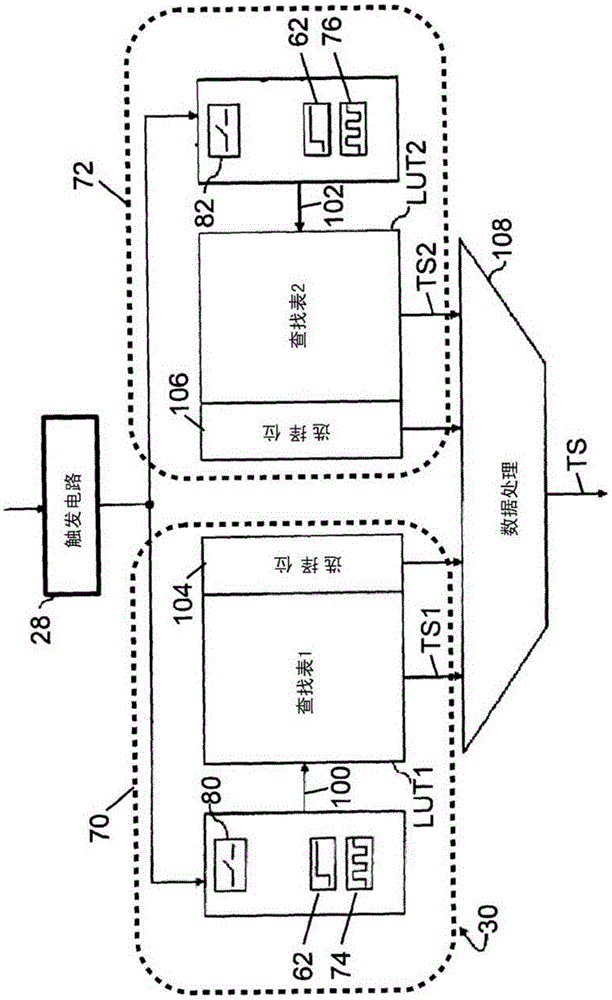
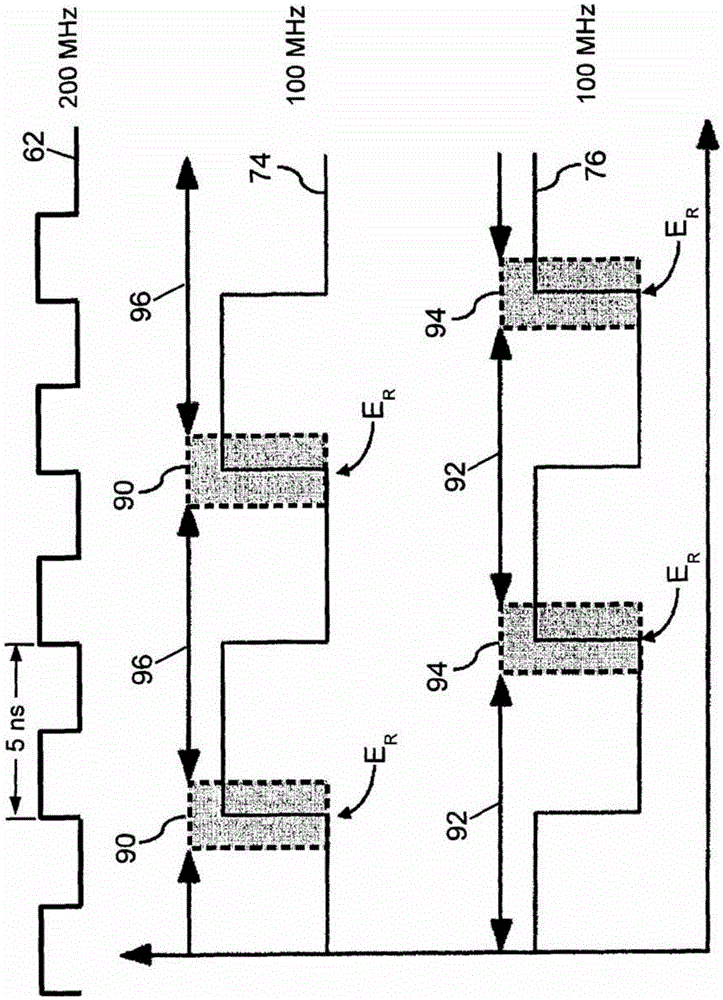
[0027] refer to figure 1 A time-of-flight positron emission tomography (TOF-PET) scanner 8 includes a plurality of radiation detectors 10 arranged to observe an imaging region 12 . exist figure 1In , a plurality of radiation detectors 10 are arranged in a circle of several detectors along the axial direction; however, other arrangements of radiation detectors can be used. Furthermore, it should be appreciated that a plurality of radiation detectors 10 are diagrammatically illustrated; typically, the radiation detectors are housed within the housing 14 of the scanner 8, and thus are not visible from the outside, and that typically, the circle of each radiation detector comprises Hundreds or thousands of radiation detectors. In some PET scanners only a single ring of radiation detectors is provided, in others two, three, four, five or more rings of radiation detectors are provided. It should be appreciated that the probe head can be substituted for the probe coil configuratio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com