A green tea bitterness and astringency discrimination method based on tea biochemical components
A discrimination method and technology for bitterness and astringency are applied in the field of green tea bitterness discrimination based on tea biochemical components, which can solve the problems of uncertainty, lack of quantitative measurement standards, and many restricted conditions.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
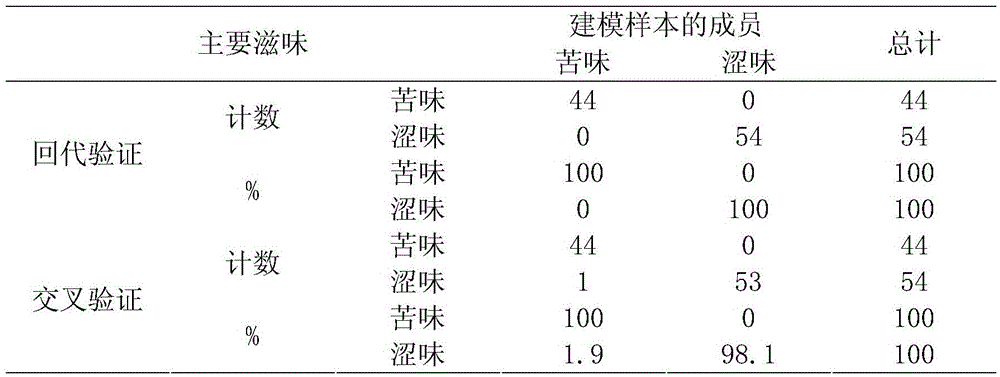
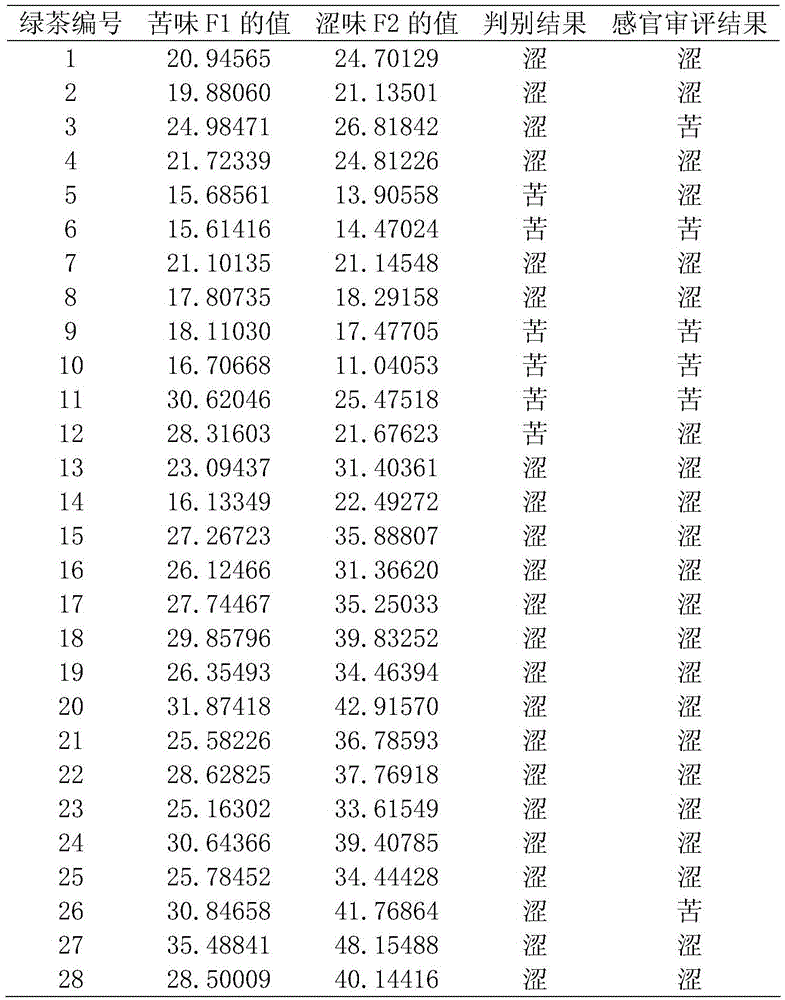
[0019] Step 1: Obtaining the Discriminant Function of Green Tea Bitterness and Astringency
[0020] 1. Acquisition of chemical information:
[0021] 1) Raw material pretreatment: Take 98 kinds of green tea samples as modeling samples, crush them to 28 meshes, accurately weigh 3.0g of the crushed tea powder, add 500ml of distilled water, extract in a water bath at 100°C for 45min, filter with filter paper, and wash the filter residue for 3 Combine the filtrate after the second time, distilled water to 500ml, after 0.45μm filter membrane filtration, obtain the test solution;
[0022] 2) Using high performance liquid chromatography to measure the content data of the biochemical components in the above-mentioned modeling samples, the chemical components are the main material components of tea, including caffeine, catechin and amino acids. Theanine, epigallocatechin, epicatechin gallate and epigallocatechin gallate, amino acids including theanine;
[0023] Among them, the chromat...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The present embodiment is a method for discriminating the bitterness and astringency of a green tea sample, comprising the following steps:
[0055] (1) Acquisition of chemical information:
[0056] Take the green tea sample to be tested, and measure the biochemical components in the green tea sample by high performance liquid chromatography, the biochemical components are caffeine, amino acid, epicatechin gallate, epigallocatechin gallate and theanine , the specific measurement steps are the same as the acquisition of chemical information in Step 1 in Example 1, and the measurement results are: caffeine is 27.649mg / g, amino acid is 11.346mg / g, epicatechin gallate is 7.534mg / g, epigallocatechin Catechin gallate is 30.969mg / g, theanine is 11.346mg / g;
[0057] (2) Bring the content data of the above-mentioned biochemical components into the discriminant function in Example 1:
[0058] F1=0.918×27.649mg / g+0.072×7.534mg / g+0.003×30.969mg / g+0.990×11.346mg / g–20.543=16.707mg / ...
Embodiment 3
[0062] This embodiment is another method for discriminating the bitterness and astringency of green tea samples, comprising the following steps:
[0063] (1) Acquisition of chemical information:
[0064] The green tea sample to be tested is taken, and the biochemical components in the green tea sample are determined by high performance liquid chromatography, and the biochemical components are caffeine, amino acid, epicatechin gallate, epigallocatechin gallate and theanine , the specific measurement steps are the same as the acquisition of chemical information in Step 1 in Example 1, and the measurement results are: caffeine is 38.597mg / g, amino acid is 29.389mg / g, epicatechin gallate is 12.019mg / g, epigallocatechin Catechin gallate is 46.444mg / g, theanine is 7.274mg / g;
[0065] (2) Bring the content data of the above-mentioned biochemical components into the discriminant function in Example 1:
[0066] F1=0.918×38.597mg / g+0.072×12.019mg / g+0.003×46.444mg / g+0.990×7.274mg / g–20....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com