Device and method for measuring relative intensity noise of laser
A technology of relative intensity noise and measurement method, which is applied in the direction of testing optical performance, etc., can solve the problems of lower measurement accuracy, large external interference, and large limitations, and achieve the effect of improving measurement accuracy and breaking through limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
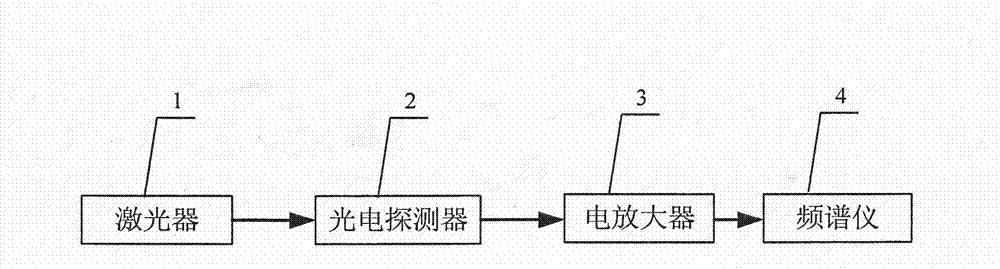
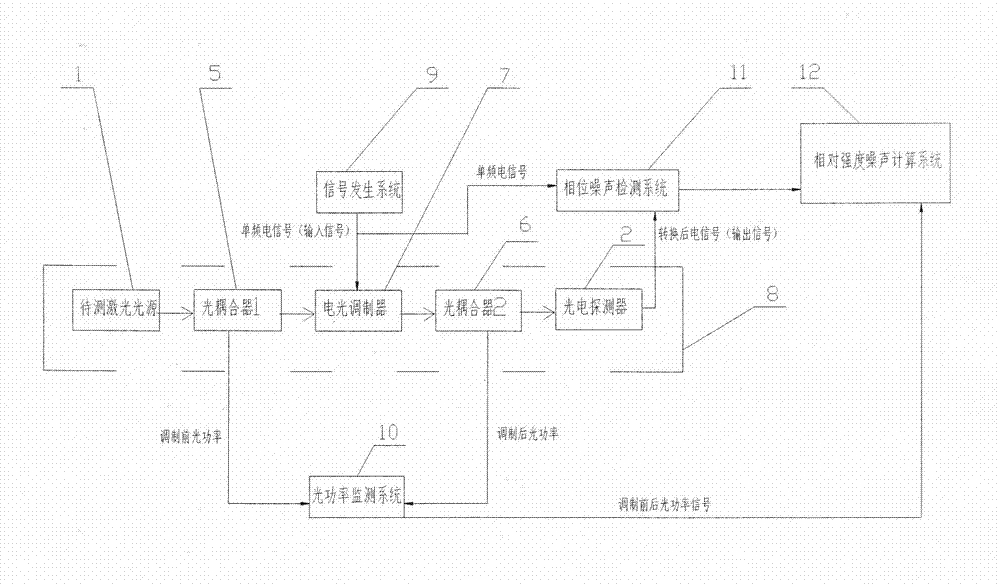
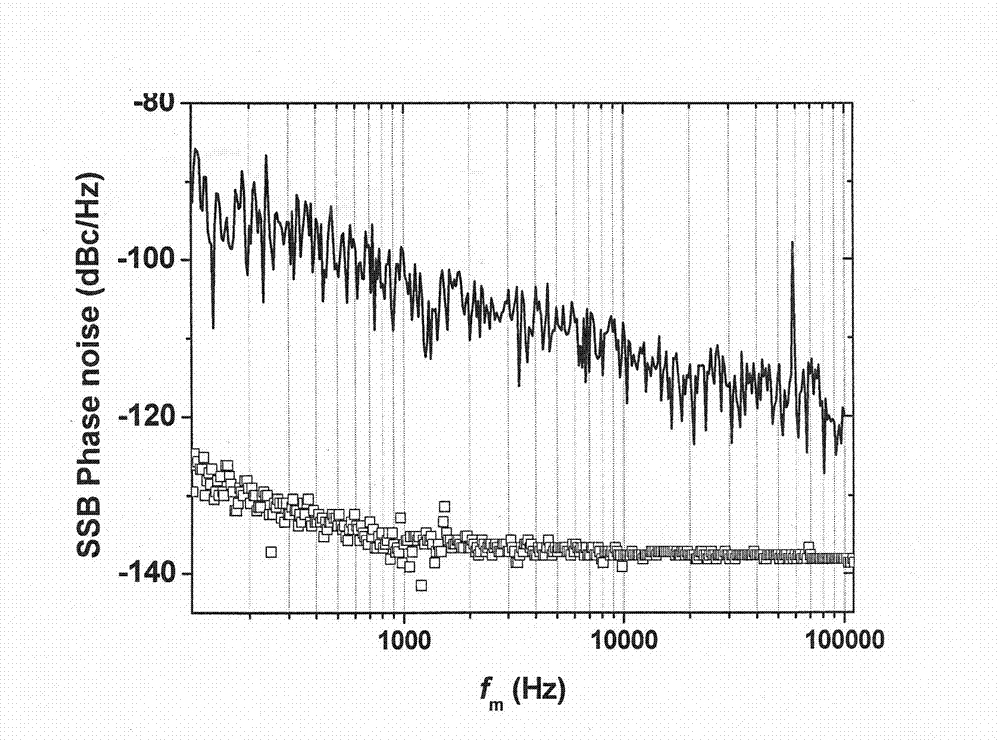
[0034] like figure 2As shown, a measurement device for relative intensity noise of a laser is composed of a microwave photon link 8, a signal generation system 9, an optical power monitoring system 10, a phase noise detection system 11, and a relative intensity noise calculation system 12. The microwave photon link Circuit 8 includes a laser to be tested 1, a photodetector 2, an optical coupler I5, an optical coupler II6, and an electro-optical modulator 7. The microwave photon link 8 is an intensity modulation-direct demodulation link, or a phase modulation-coherent link. Demodulation link; the signal generating system 9 includes a signal generating device capable of generating single-frequency electrical signals; the optical power monitoring system 10 includes an optical power device; the output optical signal of the laser to be tested 1 is input through the optical coupler I5 To the electro-optic modulator 7, the single-frequency electrical signal generated by the signal g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com