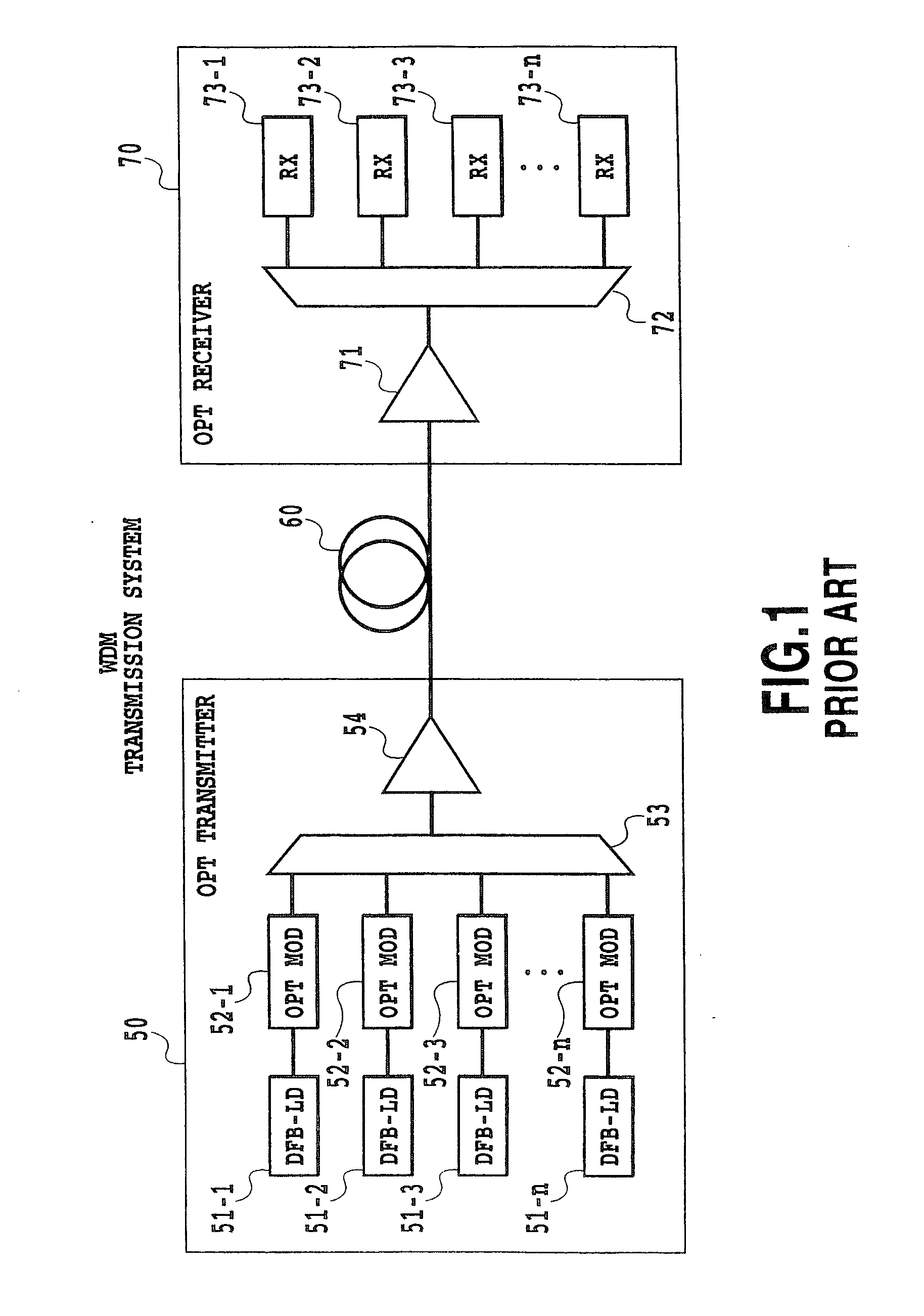
Patents
Literature
117 results about "Relative intensity noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Relative intensity noise (RIN), describes the instability in the power level of a laser. The noise term is important to describe lasers used in fiber-optic communication and LIDAR remote sensing. Relative intensity noise can be generated from cavity vibration, fluctuations in the laser gain medium or simply from transferred intensity noise from a pump source. Since intensity noise typically is proportional to the intensity, the relative intensity noise is typically independent of laser power. Hence, when the signal to noise ratio (SNR) is limited by RIN, it does not depend on laser power. In contrast, when SNR is limited by shot noise, it improves with increasing laser power. RIN typically peaks at the relaxation oscillation frequency of the laser then falls off at higher frequencies until it converges to the shot noise level. The roll off frequency sets what is specified as the RIN bandwidth. RIN is sometimes referred to as a kind of 1/f noise otherwise known as pink noise.
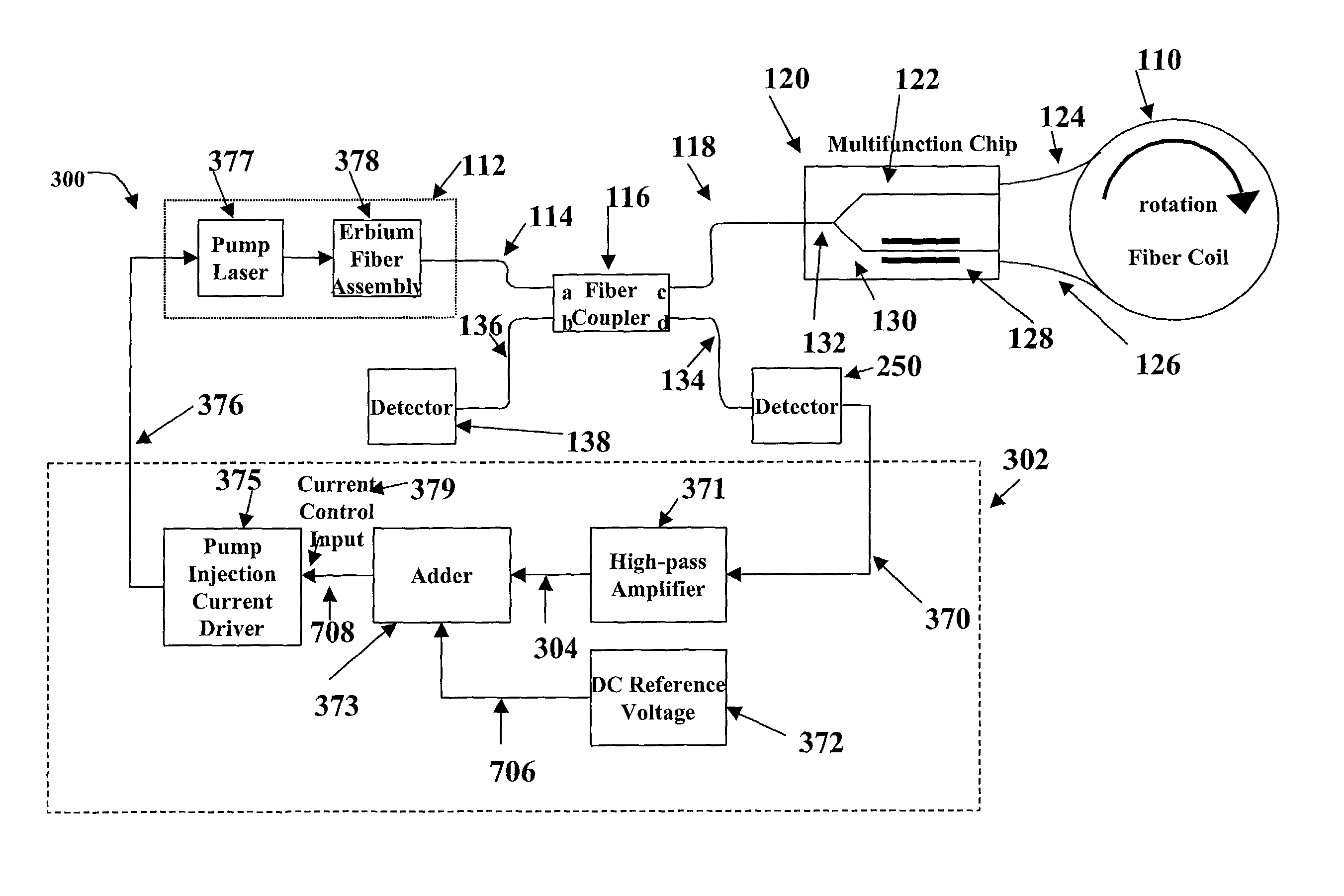
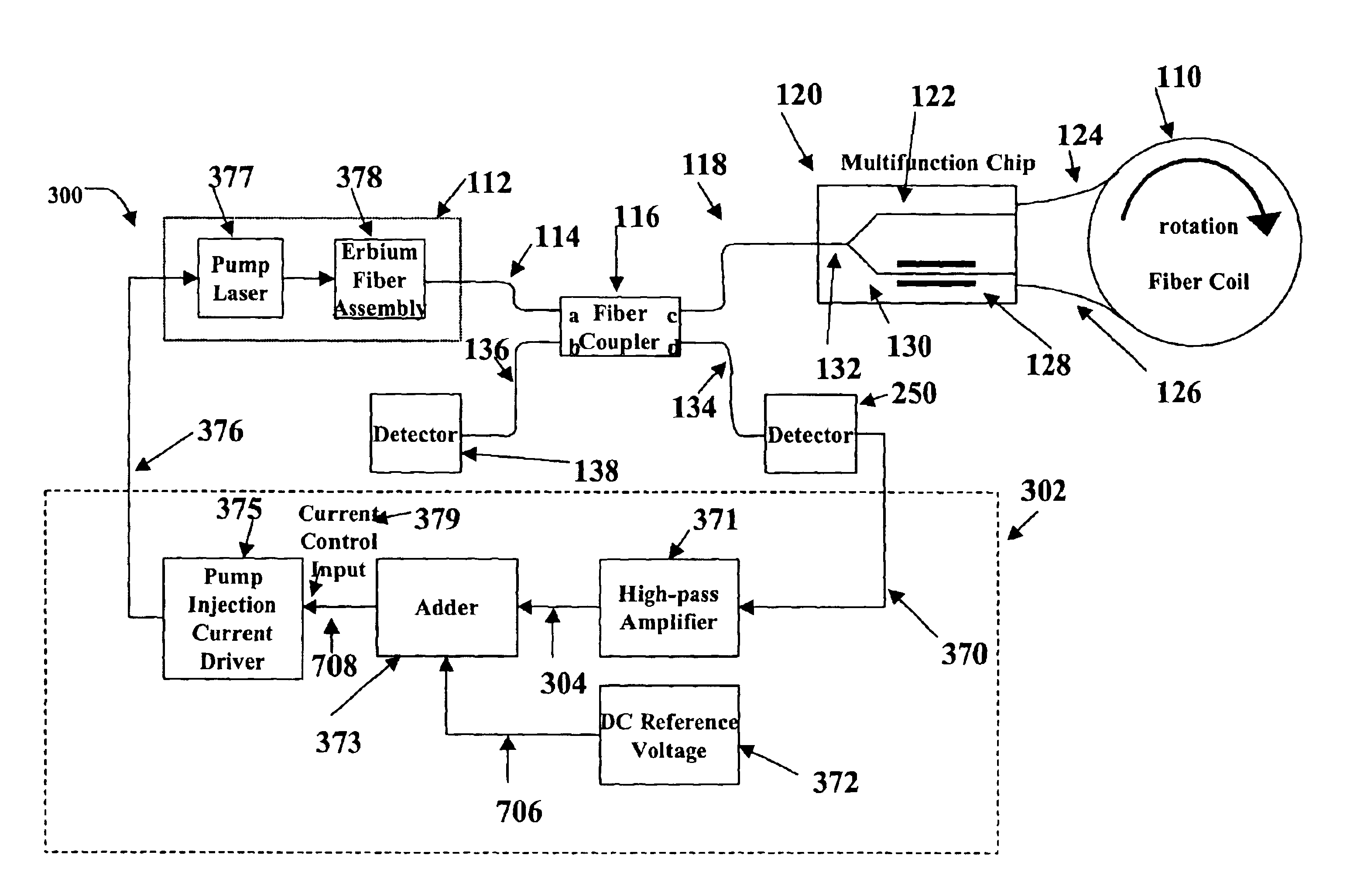
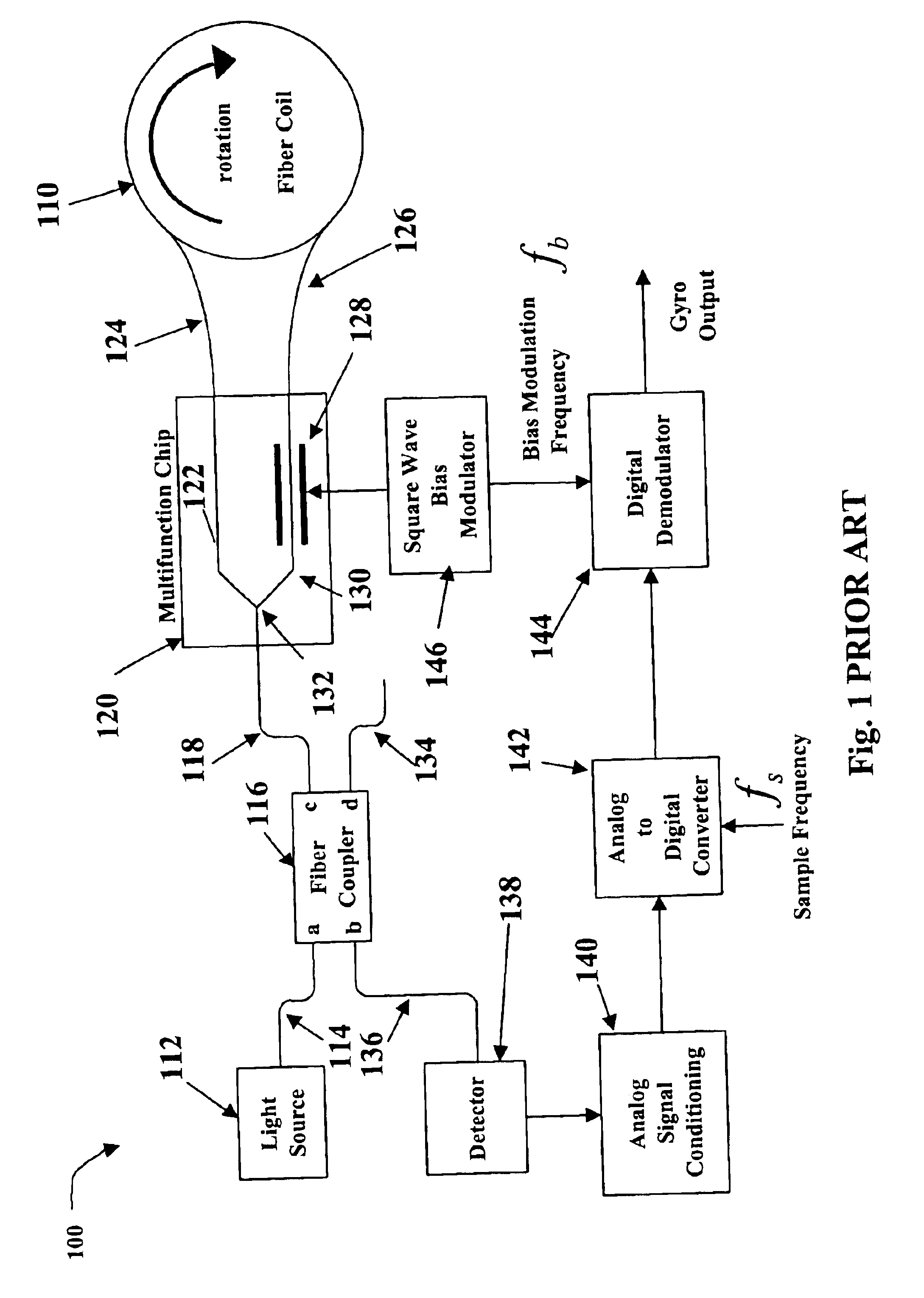
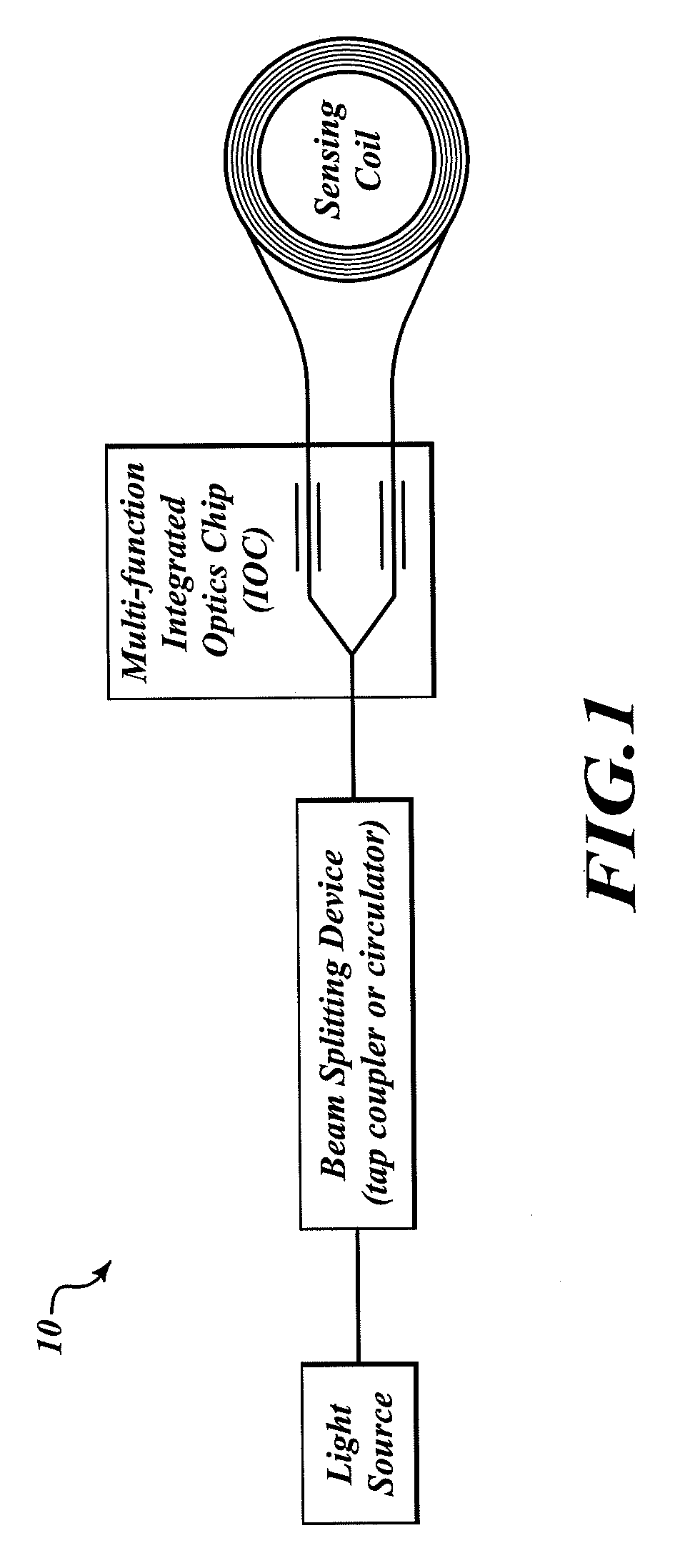
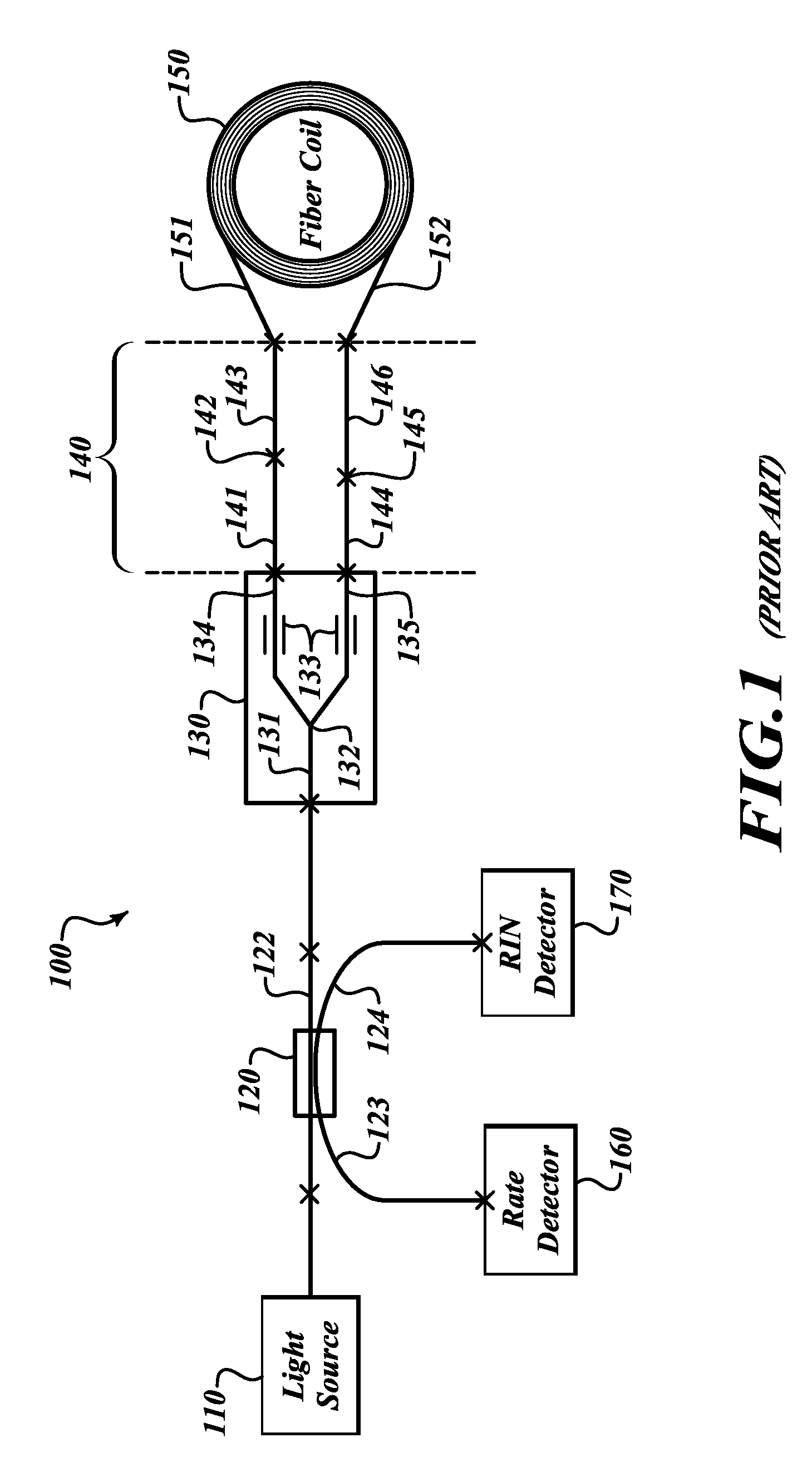
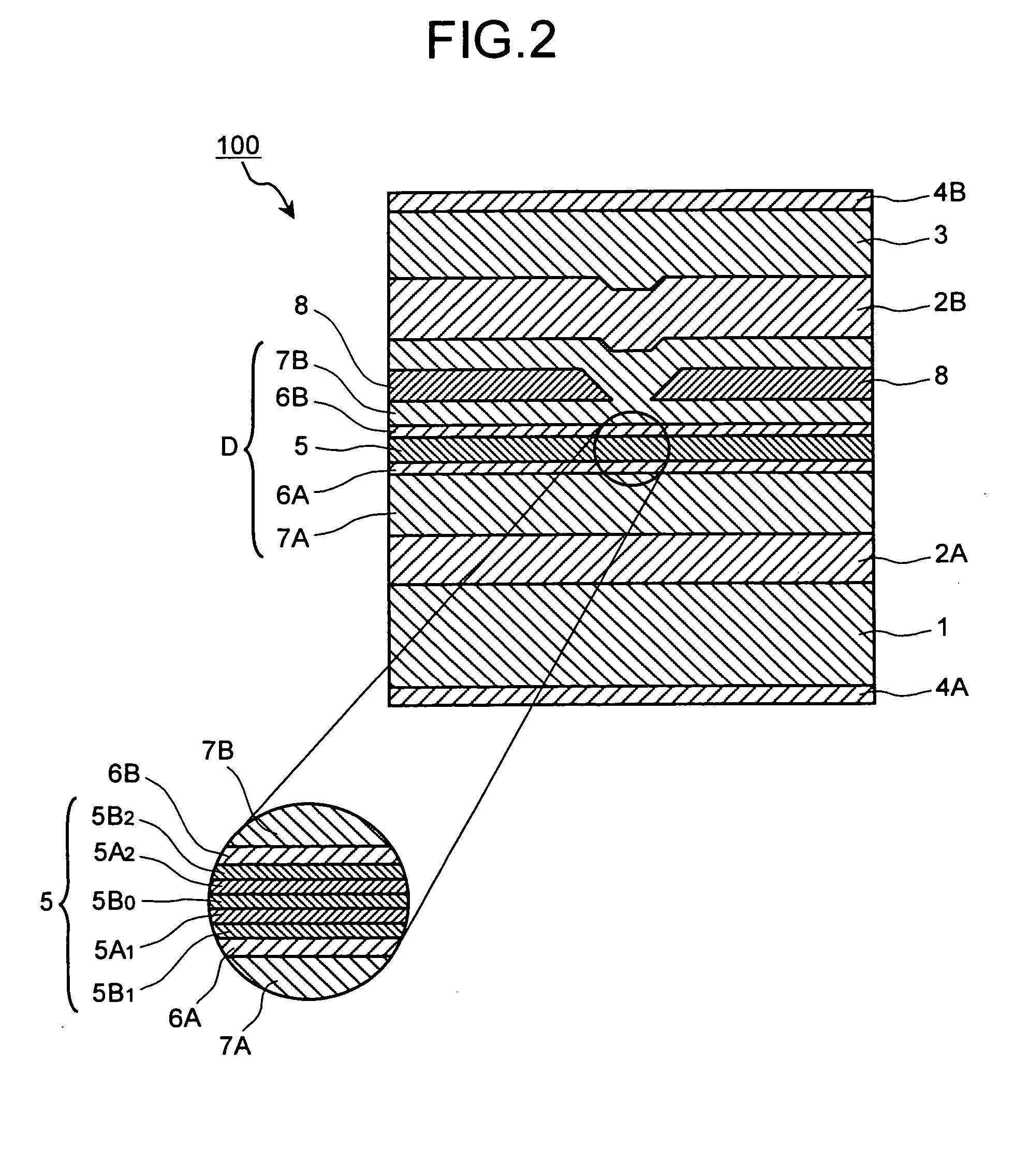
Relative intensity noise controller for fiber light sources
InactiveUS20030128365A1Sagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsFiberOctave
A system and method is provided which suppresses relative intensity noise in a fiber optic gyroscope by taking advantage of the frequency response of erbium fiber. In operation, the gain provided by the erbium fiber is added to the gain of the other components in the feedback loop to provide for stable loop performance up to about 250 kHz. The frequency response of the erbium fiber of about 3 kHz also provides a 6 db per octave roll-off, which, when used in a negative feedback control loop for controlling the current flowing to the gyroscope light source, allows for a relative intensity noise control loop with a bandwidth much greater than 3 kHz; this may be used in high performance gyroscope applications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
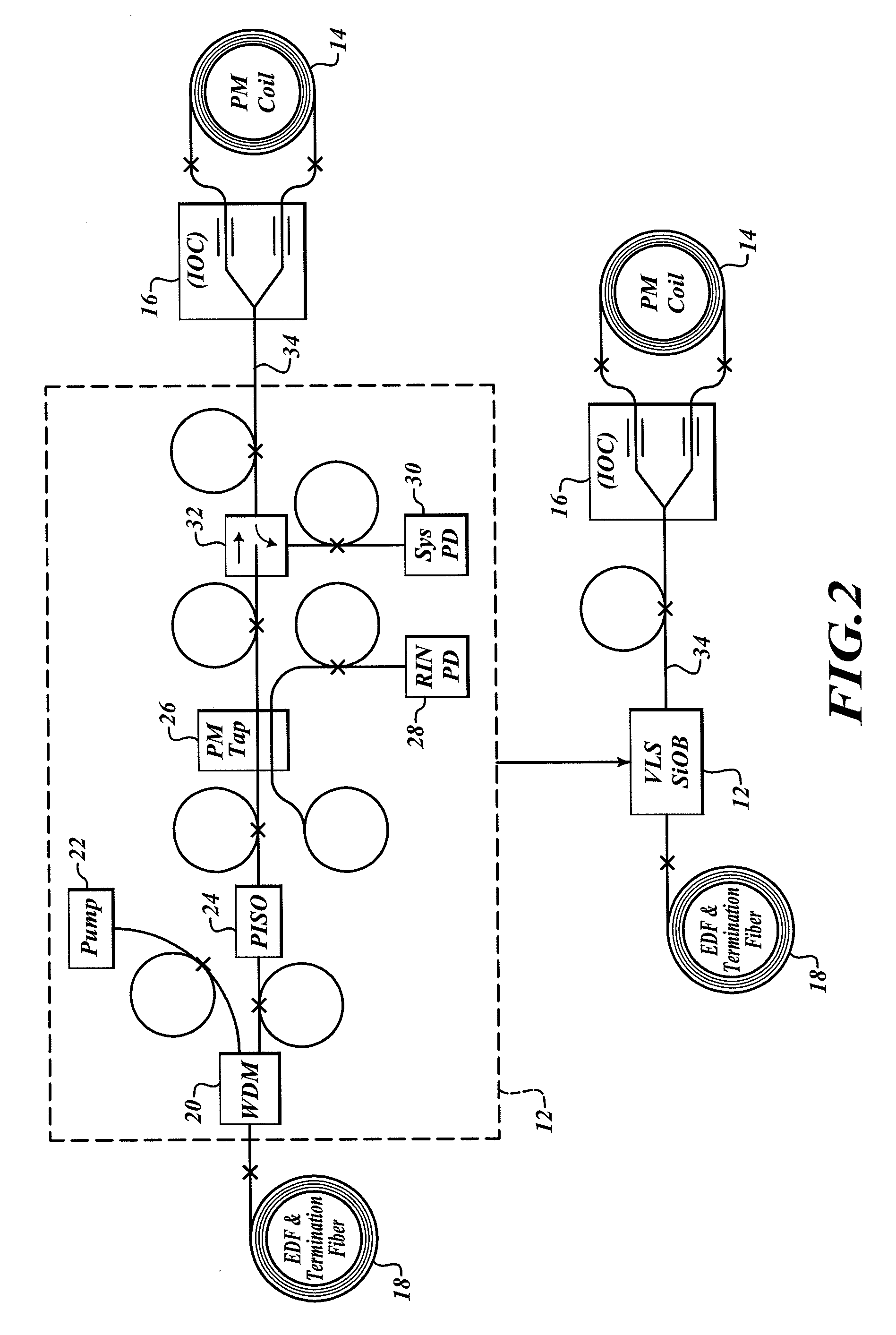
Relative intensity noise controller with maximum gain at frequencies at or above the bias modulation frequency or with second order feedback for fiber light sources
InactiveUS6765678B2Speed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersFiberNegative feedback
A system and method is provided which suppresses relative intensity noise in a fiber optic gyroscope by taking advantage of the frequency response of erbium fiber. In operation, the gain provided by the erbium fiber is added to the gain of the other components in the feedback loop to provide for stable loop performance up to about 250 kHz. The frequency response of the erbium fiber of about 3 kHz also provides a 6 db per octave roll-off, which, when used in a negative feedback control loop for controlling the current flowing to the gyroscope light source, allows for a relative intensity noise control loop with a bandwidth much greater than 3 kHz; this may be used in high performance gyroscope applications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
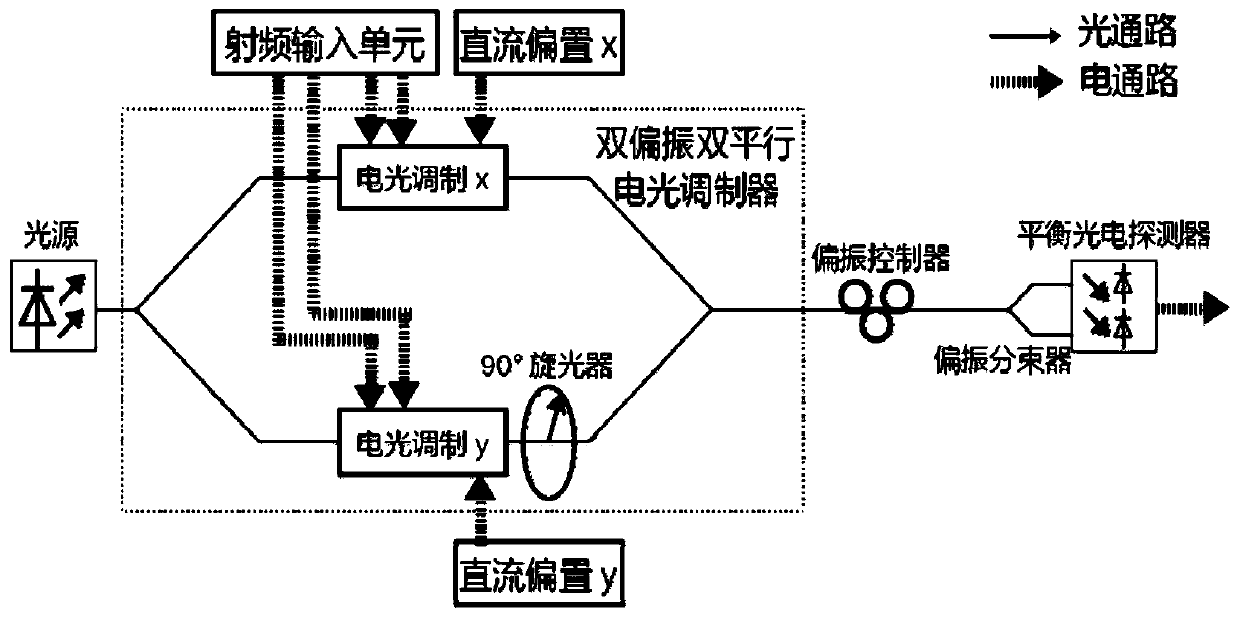
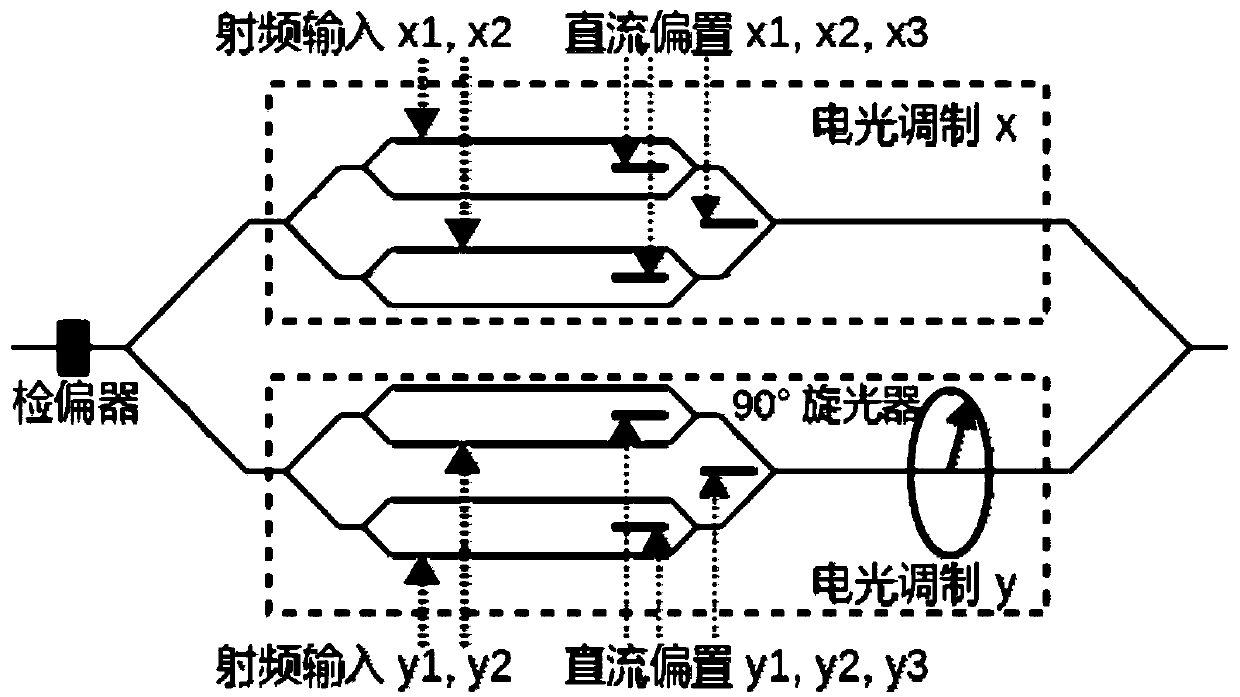
Multifunctional microwave photon module and signal processing method and device based on multifunctional microwave photon module
ActiveCN110233675ACommon Mode Noise SuppressionHigh gainElectromagnetic transmissionOptical elementsComputer moduleRelative intensity noise
The invention discloses a multifunctional microwave photon module, which comprises a dual-polarization dual-parallel Mach-Zehnder modulator, a polarization controller, a polarization beam splitter anda balance photoelectric detector. The output end of the dual-polarization dual-parallel Mach-Zehnder modulator is connected with the input end of the polarization beam splitter through the polarization controller, and the two output ends of the polarization beam splitter are connected with the two input ends of the balance photoelectric detector respectively. The invention further discloses a signal processing method and device based on the multifunctional microwave photon module. The relative intensity noise in the microwave photonic link is effectively suppressed from the outside of the laser, various kinds of processing such as frequency mixing, frequency doubling and phase shifting can be carried out on microwave signals, the structure is simple, and the implementation cost is low.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Brillouin optical time domain analyzing and sensing system based on ultra-long annular laser pumping
ActiveCN103364106AFlat distributionImprove consistencyThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansFiberRelative intensity noise
The invention discloses a Brillouin optical time domain analyzing and sensing system based on ultra-long annular laser pumping. The Brillouin optical time domain analyzing and sensing system based on the ultra-long annular laser pumping comprises first-order raman pump light (16) with the wavelength of 13 xxnm, a wavelength division multiplexer WDM pair (17) and a sensor fiber (18), wherein the wavelength division multiplexer and the sensor fiber form an ultra-long distance annular laser resonant cavity, the first-order raman pump light is fed back by the annular laser resonant cavity to generate lasing light with the wavelength of 14 XXnm. The lasing light with the wavelength of 14 XXnm performs second-order raman amplification on probe light with wavelength of 15 XXnm and Brillouin pumping. In comparison with a Brillouin sensing system based on linear cavity amplification, sensing signals are distributed more smoothly along the optical fiber, and the consistency of sensing quality in the whole process is remarkably improved; noise transfer of pumping-signal relative strength can be effectively suppressed, and temperature, spatial resolution of strain detection and measurement accuracy can be substantially improved; due to the fact that an extra second-order pump light source does not need to be added, substantial stretching of the sensing distance is obtained with low cost, and the Brillouin optical time domain analyzing and sensing system based on the ultra-long annular laser pumping has certain practicability.
Owner:饶云江
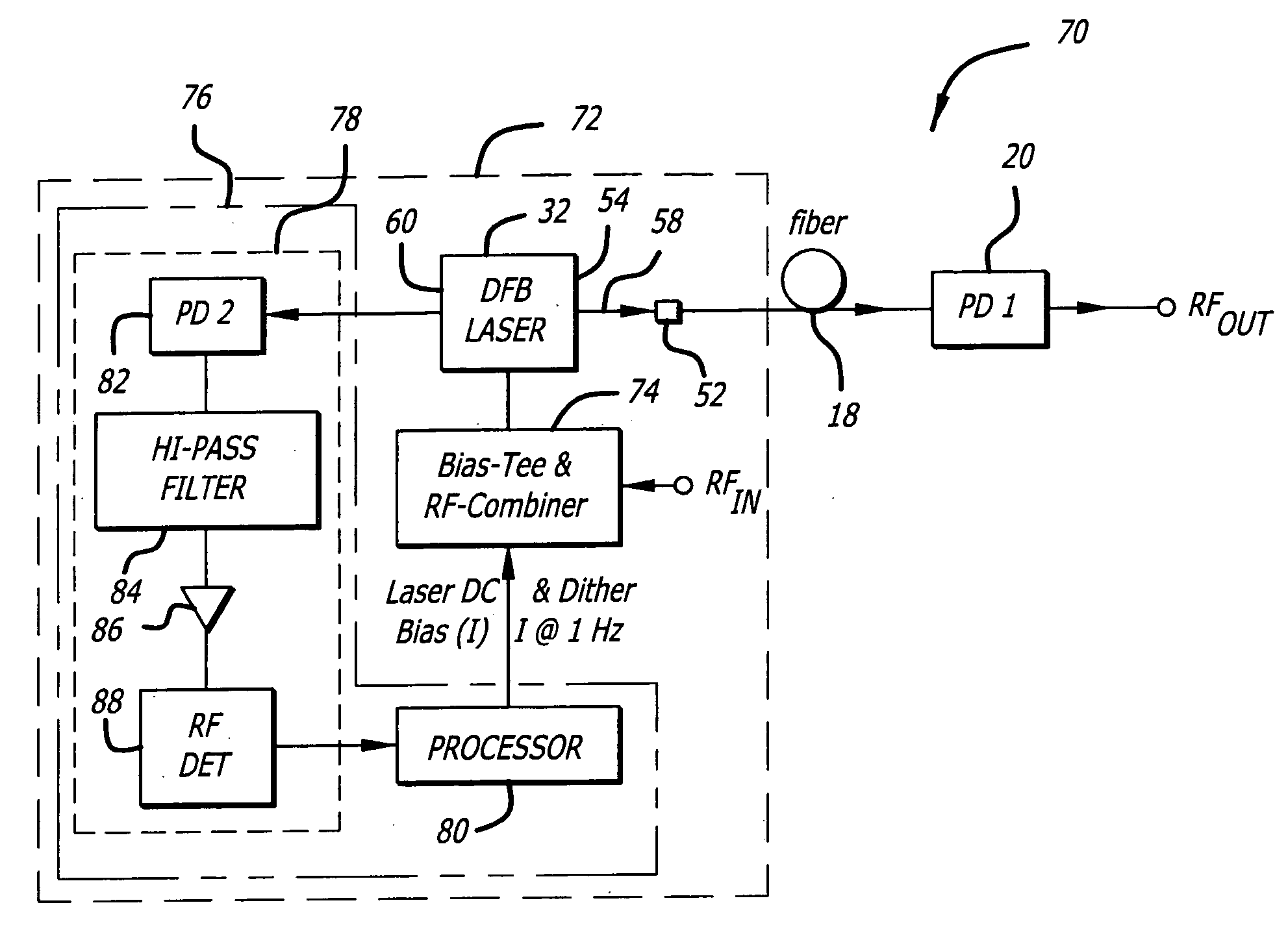
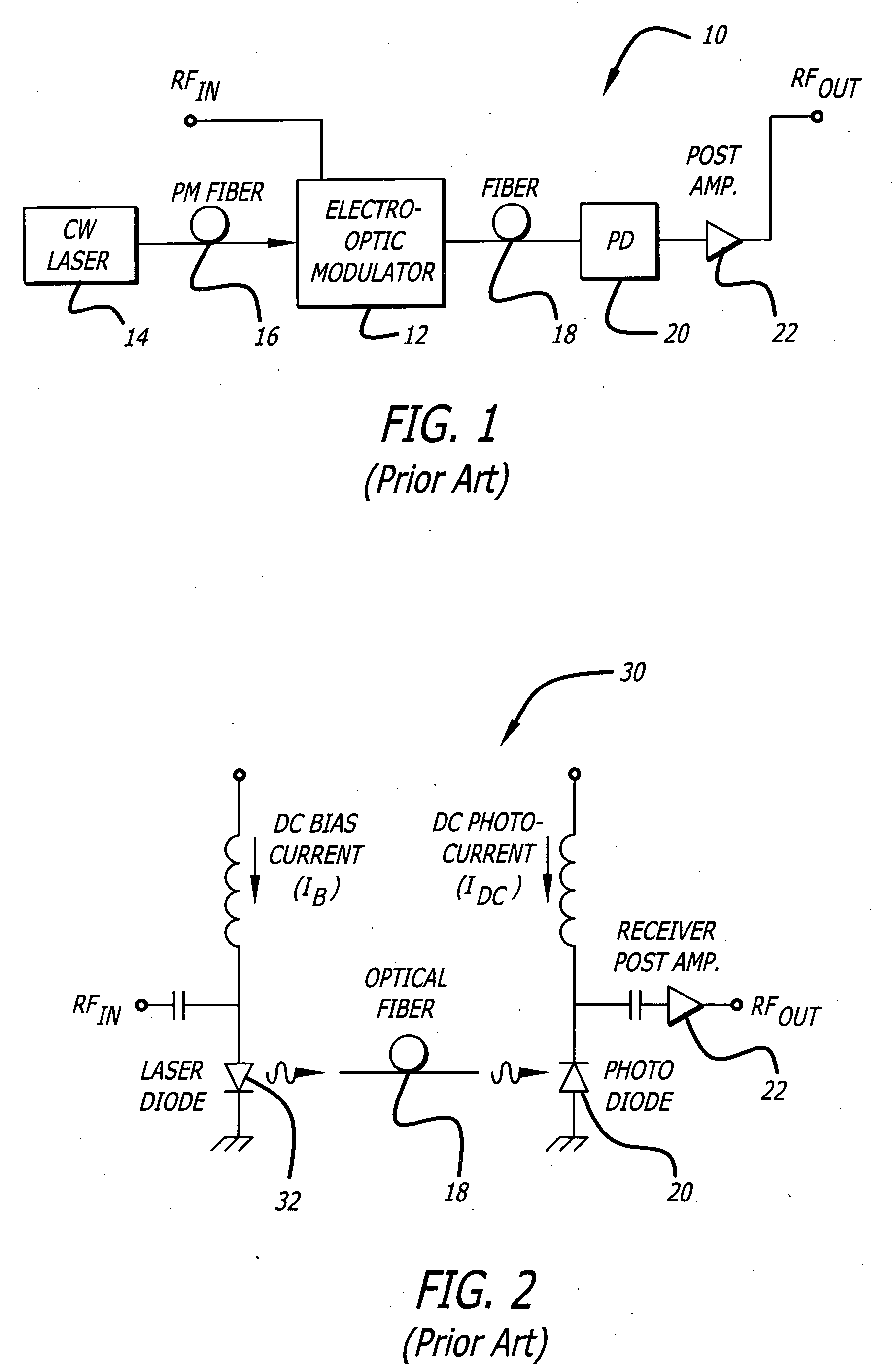
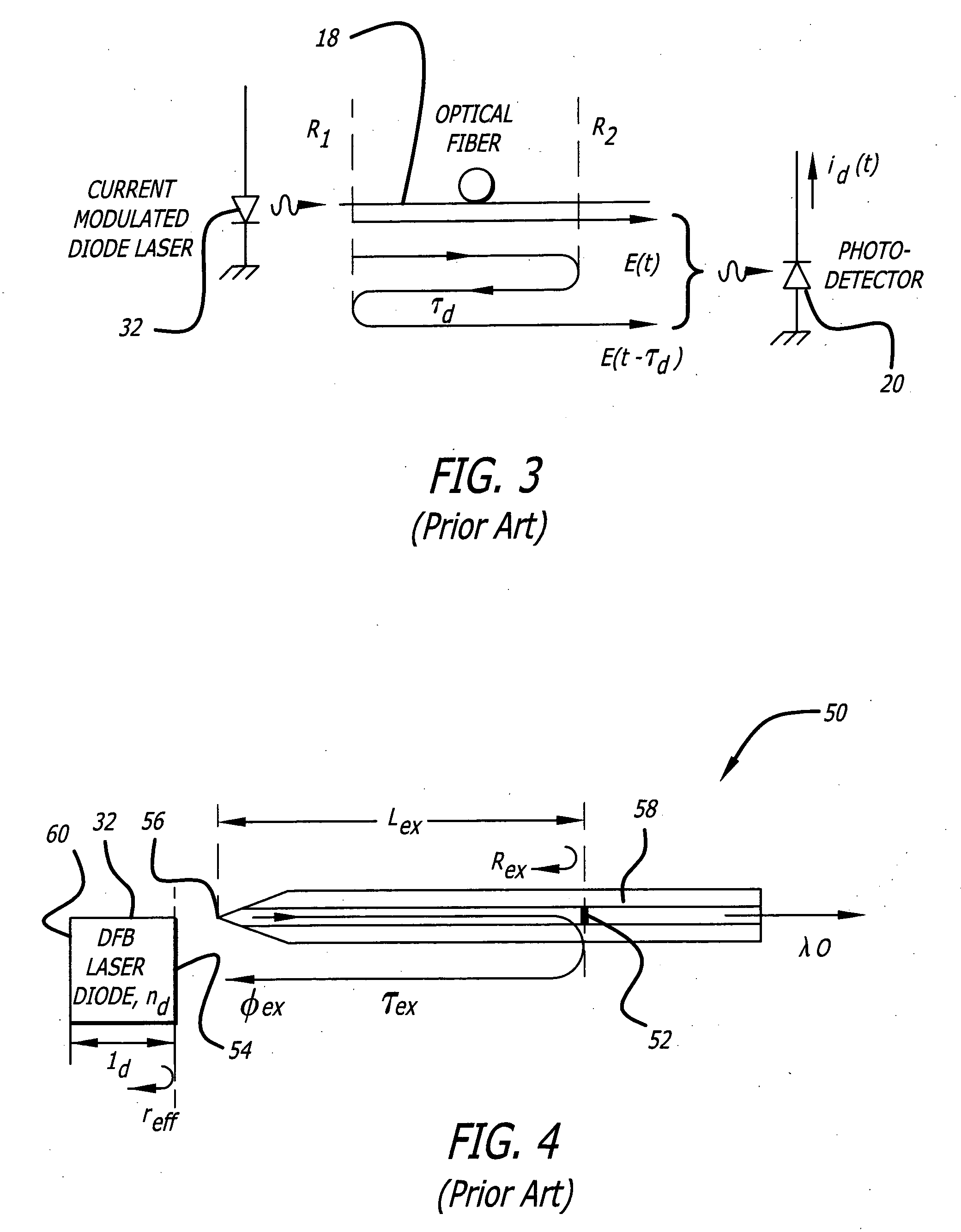
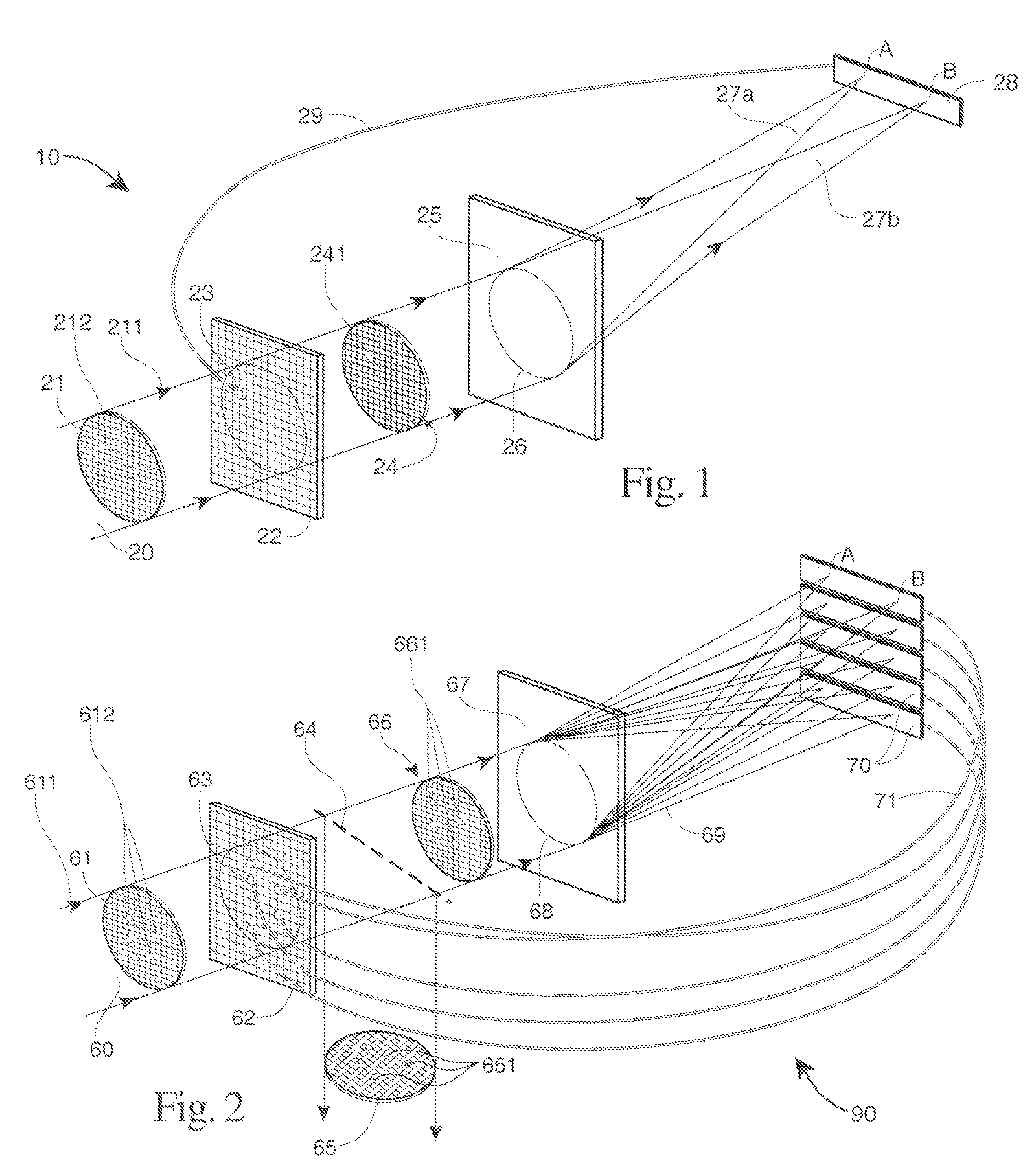
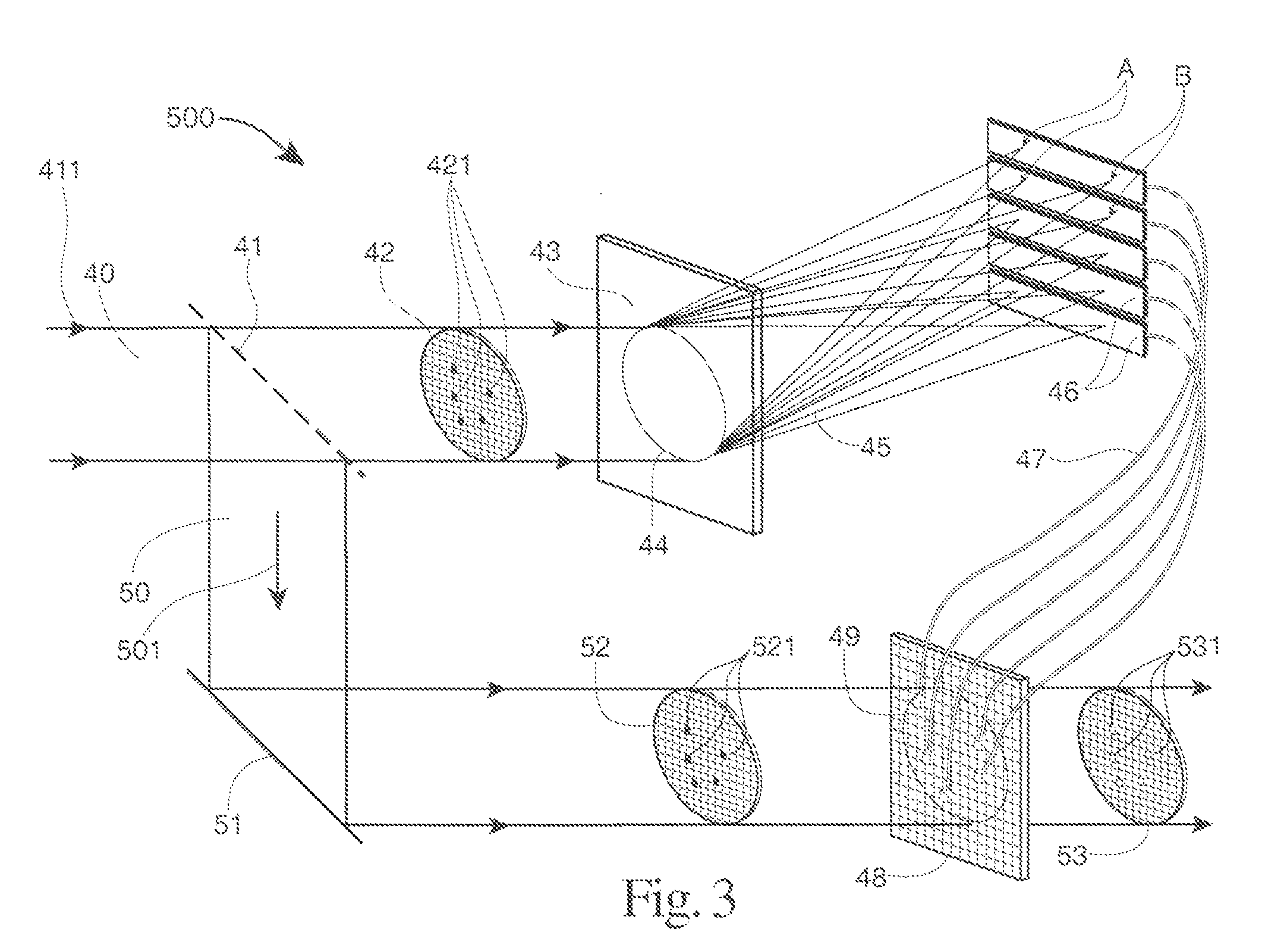
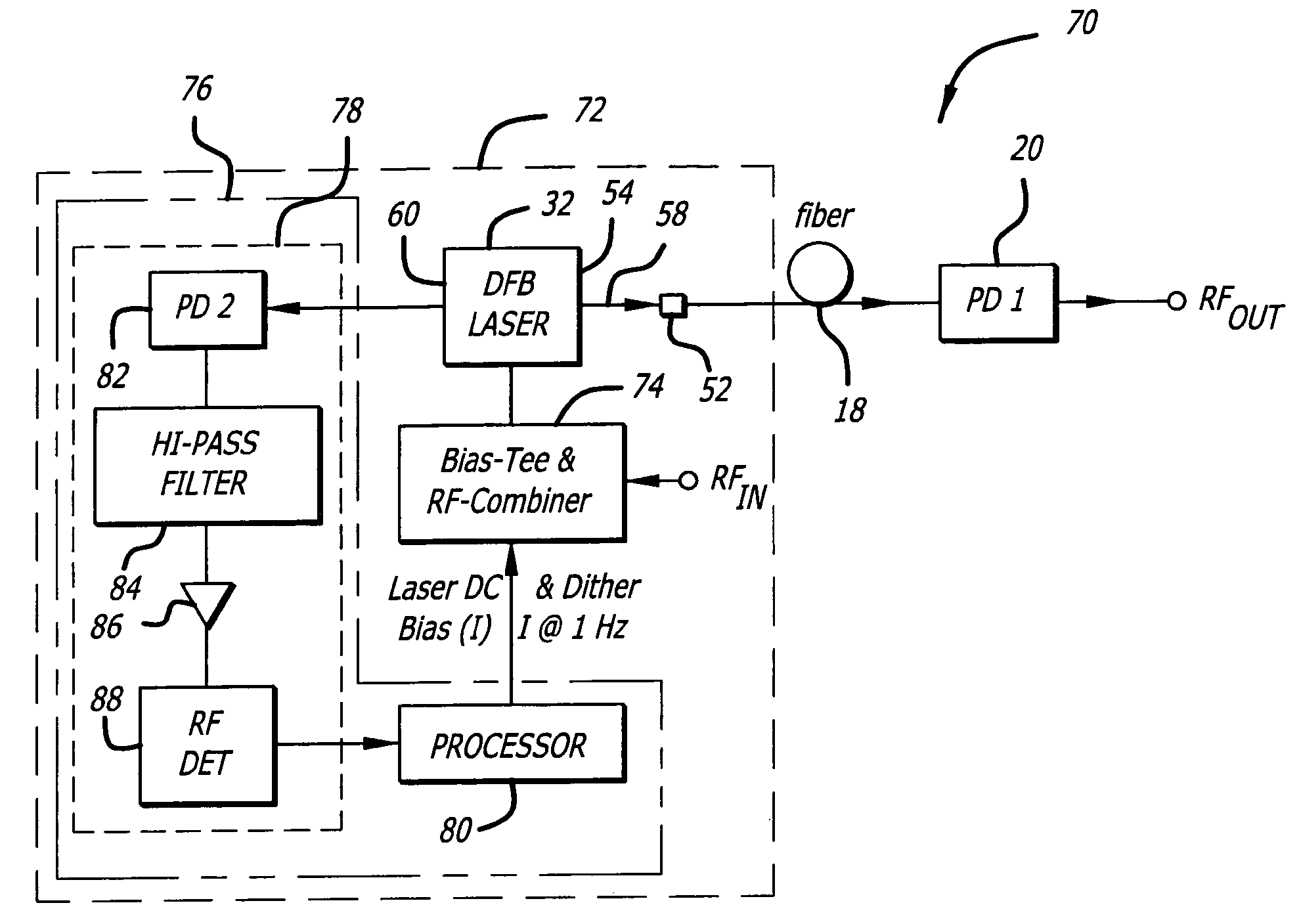
System and method for reducing interferometric distortion and relative intensity noise in directly modulated fiber optic links
A laser transmitter with a feedback control loop for minimizing noise. The novel laser transmitter includes a laser, an external reflector adapted to form an extended cavity to the laser, and a feedback control loop adapted to detect noise in the laser and in accordance therewith, adjust the optical phase of the extended cavity such that the noise is at a desired level. The optical phase of the extended cavity is adjusted by adjusting an operating parameter of the laser, such as its bias current. In an illustrative embodiment, the feedback control loop is adapted to compute the rate of change of the noise with respect to bias current and in accordance therewith, adjust the bias current of the laser such that relative intensity noise and interferometric intermodulation distortion are simultaneously minimized.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Semiconductor laser with low relative intensity noise of individual longitudinal modes and optical transmission system incorporating the laser
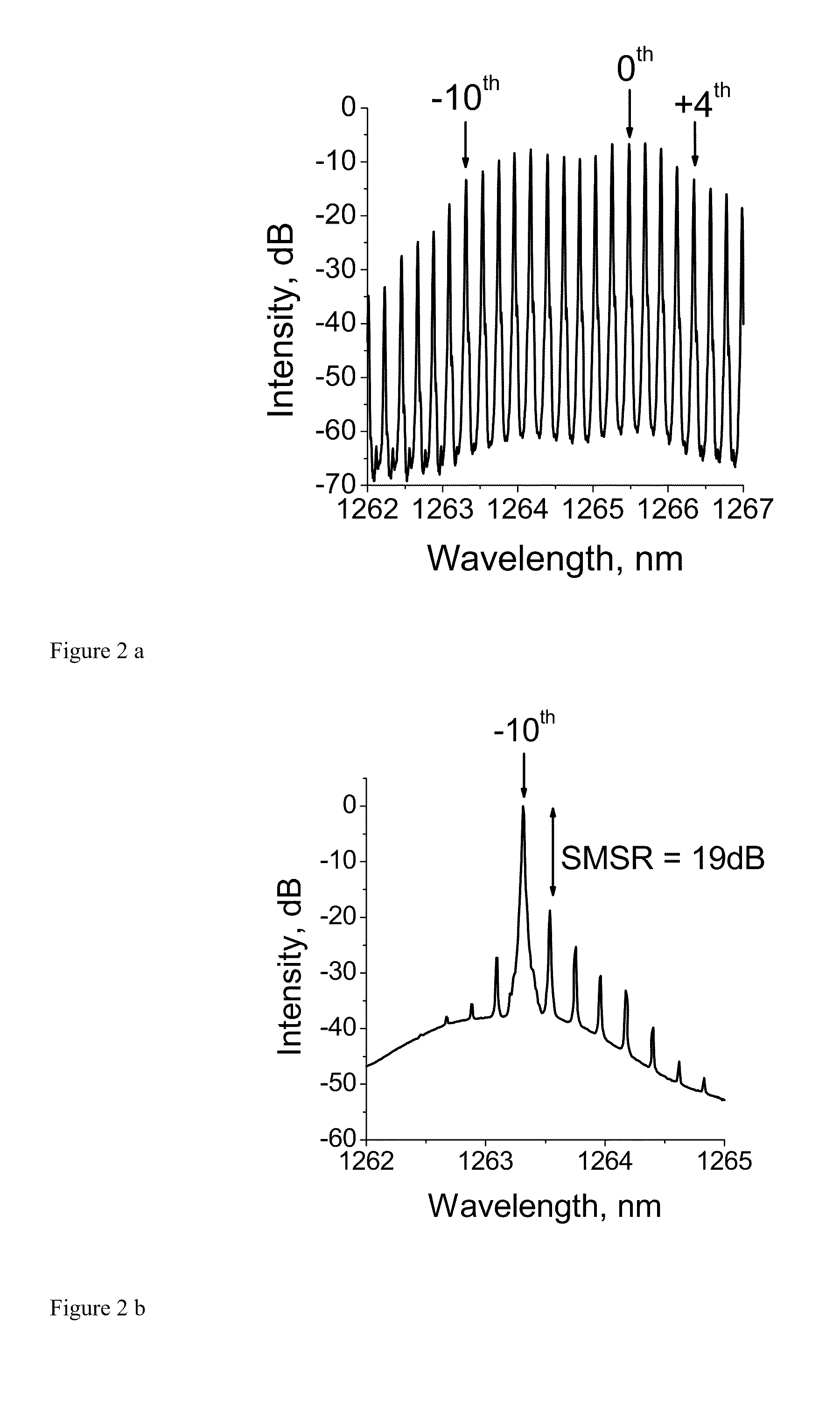
ActiveUS20100142973A1Low intensity-noiseReduce bit error rateLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionRelative intensity noiseHomogeneous broadening
A semiconductor laser comprises an electrically isolated active section and at least one noise reducing section and operates on a ground state transition of a quantum dot array having inhomogeneous broadening greater than 10 nm. The laser preferably emits more than 10 optical modes such that a total relative intensity noise of each optical mode is less than 0.2% in the 0.001 GHz to 10 GHz range. The spectral power density is preferably higher than 2 mW / nm. An optical transmission system and a method of operating a quantum dot laser with low relative intensity noise of each optical mode are also disclosed.
Owner:INNOLUME
Regenerative Mode Locked Laser Swept Source for OCT Medical Imaging
ActiveUS20130308136A1Stabilizing emission characteristicAvoids noisy disruptionMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringOptical frequenciesLaser scanning
An optical coherence analysis system uses a laser swept source that is constrained to operate in a mode locked condition using regenerative mode-locking This is accomplished by synchronously changing the laser cavity's net gain and / or phase based on time varying intensity of the swept optical signal generated by the laser. This produces a stable pulsation behavior, which is associated with smooth tuning (low optical frequency reference clock jitter) and low relative intensity noise (RIN).
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
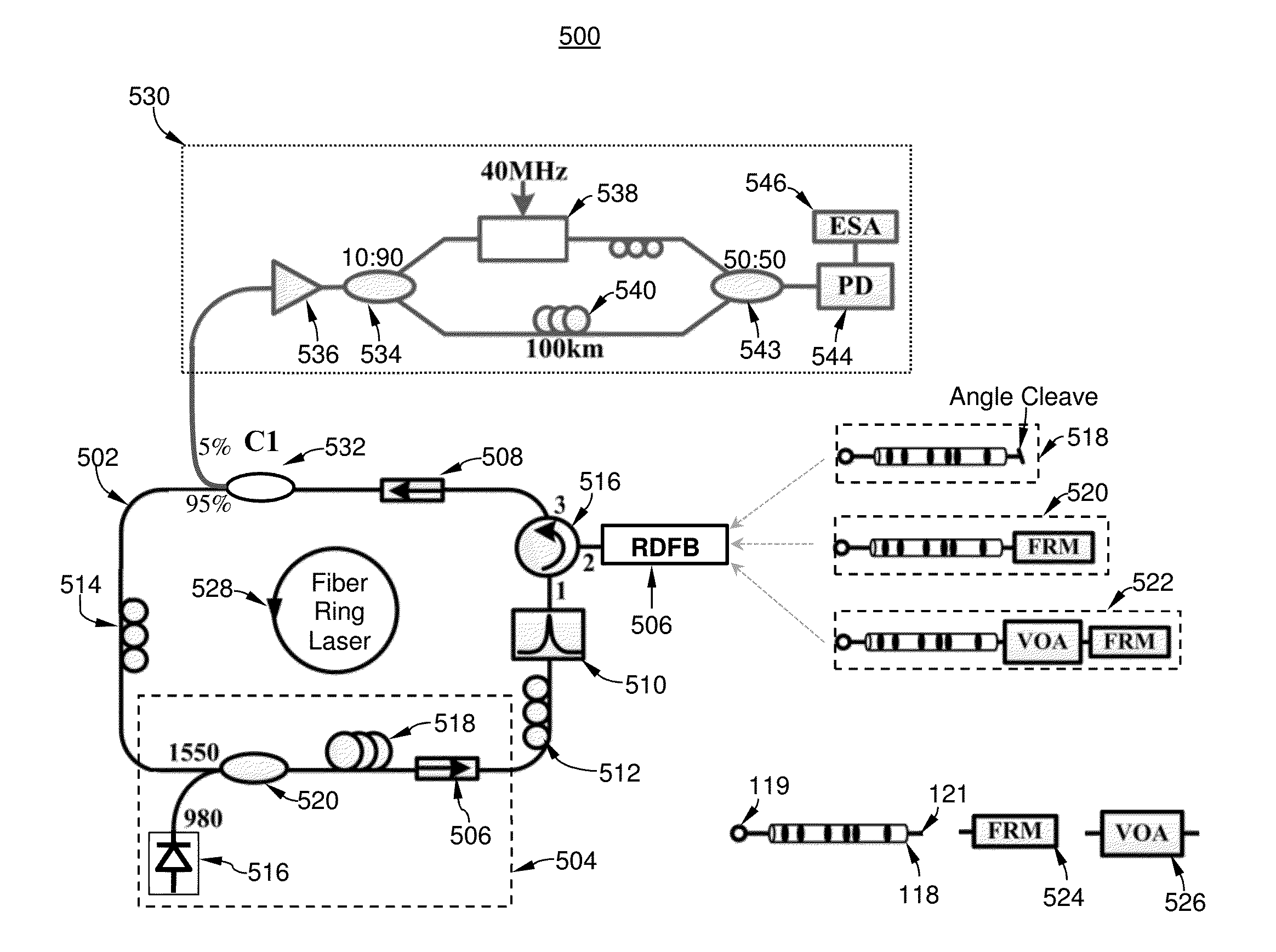
Frequency-stabilized random distributed feedback fiber ring laser with low intensity noise
ActiveUS20150255944A1Reduced frequency jitterReduce Relative Intensity NoiseLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionFrequency stabilizationRelative intensity noise
A method and apparatus for producing single mode random fiber ring laser by inducing random distributed feedback in a short section of the fiber ring to thereby enable single mode lasing while reducing frequency jitter and relative intensity noise. The random distributed feedback maybe achieved through deep refractive index modulation at a series of randomly distributed laser-irradiated points inscribed along the length of the induced random distributed feedback fiber. The laser-processed random distributed feedback fiber maybe incorporated into the fiber ring in conjunction with a variable optical attenuator and band pass optical filter for enhancing the single mode operation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA
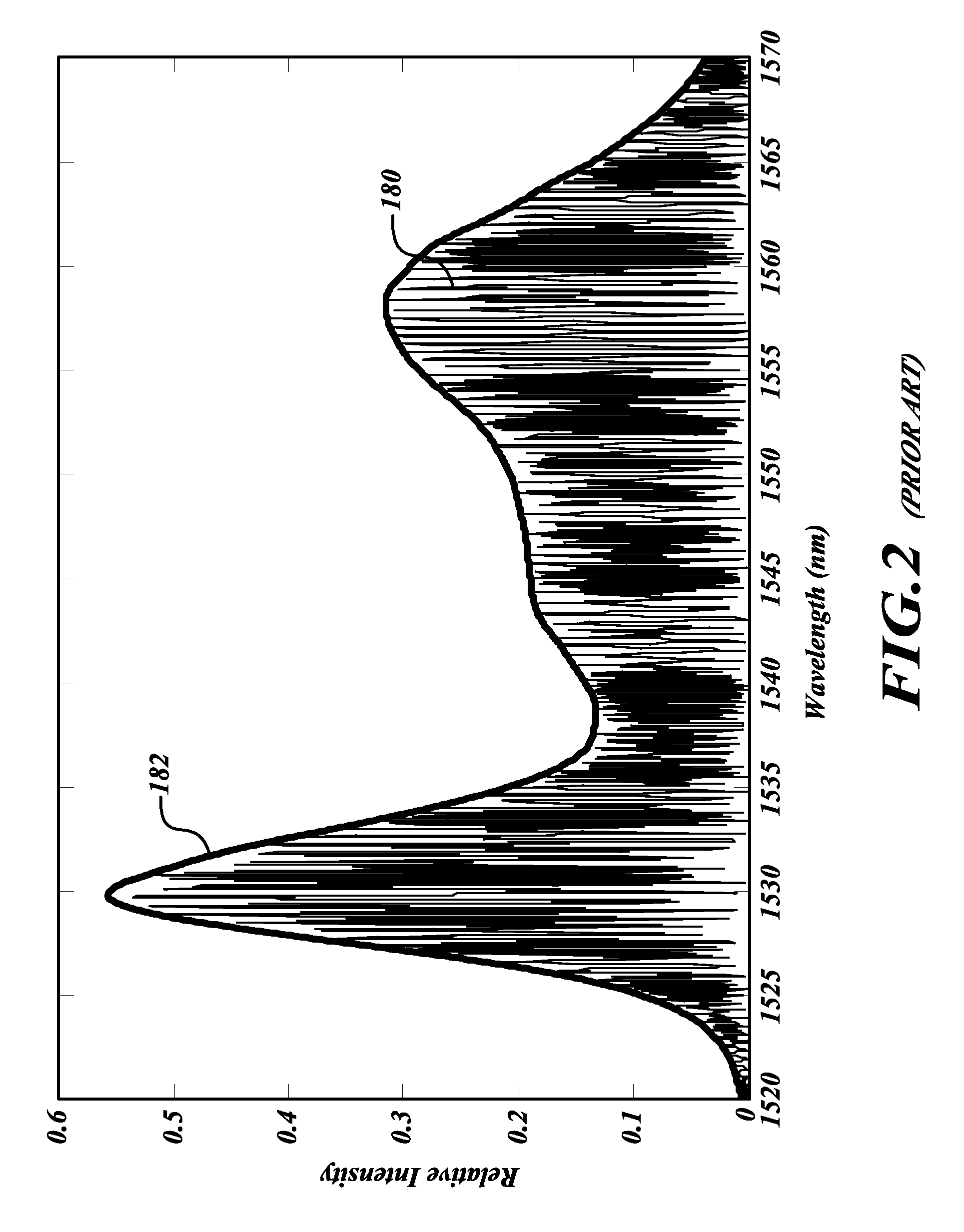
Multi-wavelength generating method and apparatus based on flattening of optical spectrum
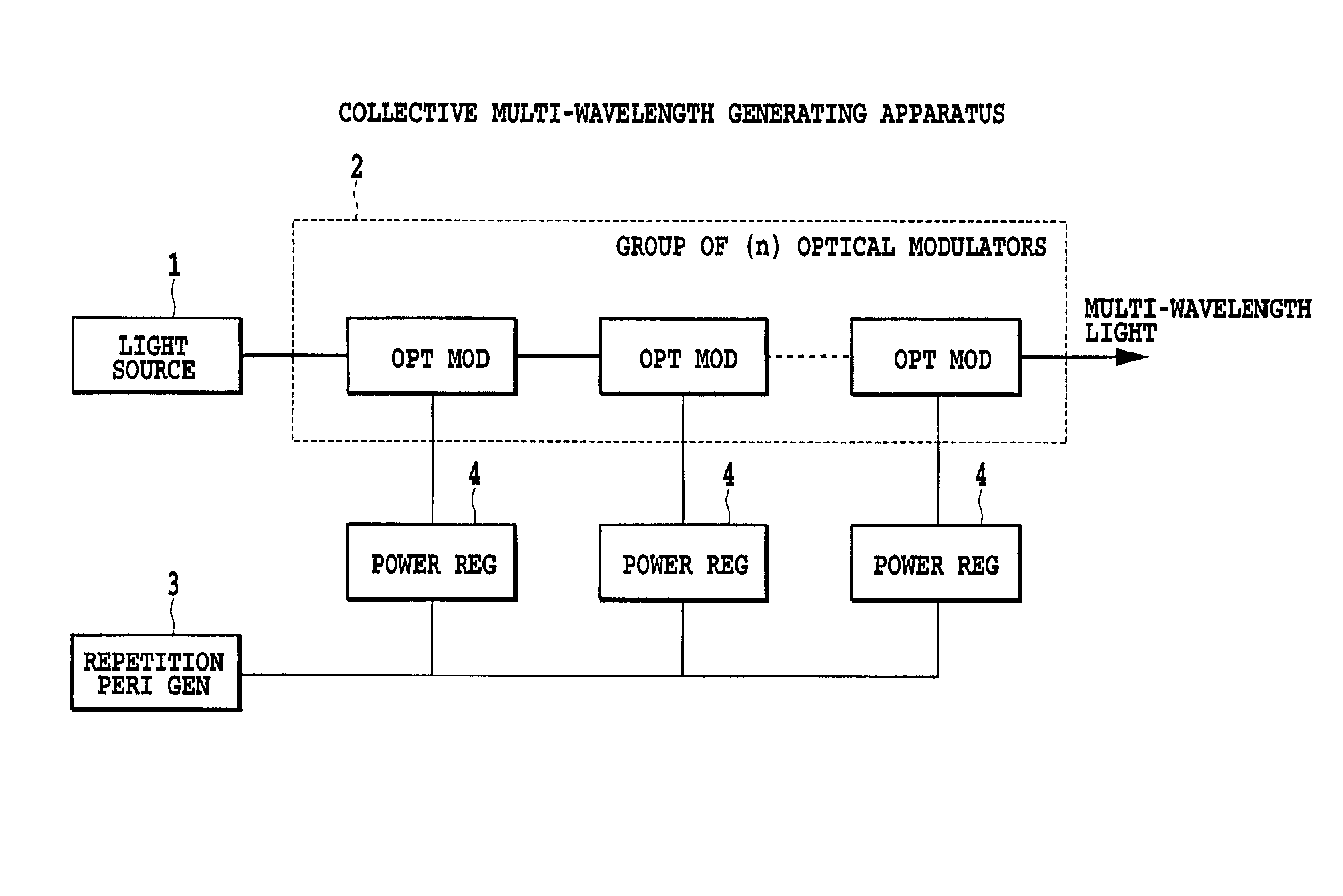
InactiveUS20040100682A1Simple and inexpensive configurationWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesMultiwavelength spectroscopySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
With respect to the relative intensity noise (RIN) for inputs to an optical modulator or the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) for outputs therefrom, the optical modulator modulating coherent lights of different wavelengths obtained by slicing a spectrum of the multi-wavelength light, the shape of a spectrum of a multi-wavelength light is controlled so that predetermined RIN and SNR can be obtained in accordance with transmission system parameters (the type and distance of optical fibers, the number of repeaters), thus enabling design meeting a performance specification for a conventional transmission section using semiconductor lasers.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Suppression method of relative intensity noise of light source of fiber-optic gyroscope
The invention discloses a suppression method of relative intensity noise of a light source of a fiber-optic gyroscope. The suppression method comprises the following steps that: reference light which is lead out from an optical fiber dead head of a fiber-optic gyroscope coupler and has light source light-intensity variation information is received by a photoelectric detector to obtain a reference signal; the reference signal is processed by a signal processing module to generate a light intensity modulation control signal; light intensity modulation is performed on a fiber-optic gyroscope signal returned from a fiber-optic ring through a light intensity modulator; light intensity variation caused by the relative intensity noise of the light source is compensated; fiber-optic gyroscope signal light modulated by the light intensity is detected through another photoelectric detector; and the fiber-optic gyroscope signal light is modulated through the signal processing module to obtain the output of the fiber-optic gyroscope of which the relative intensity noise of the light source is suppressed. With the adoption of the suppression method of the relative intensity noise of the light source of the fiber-optic gyroscope, influence of the relative intensity noise of the light source, on the output of the fiber-optic gyroscope, can be effectively suppressed, and the static property of the fiber-optic gyroscope is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
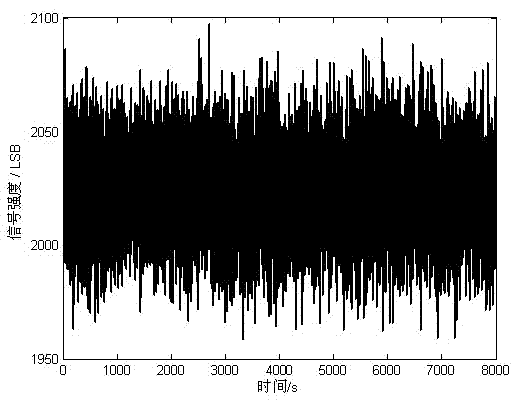
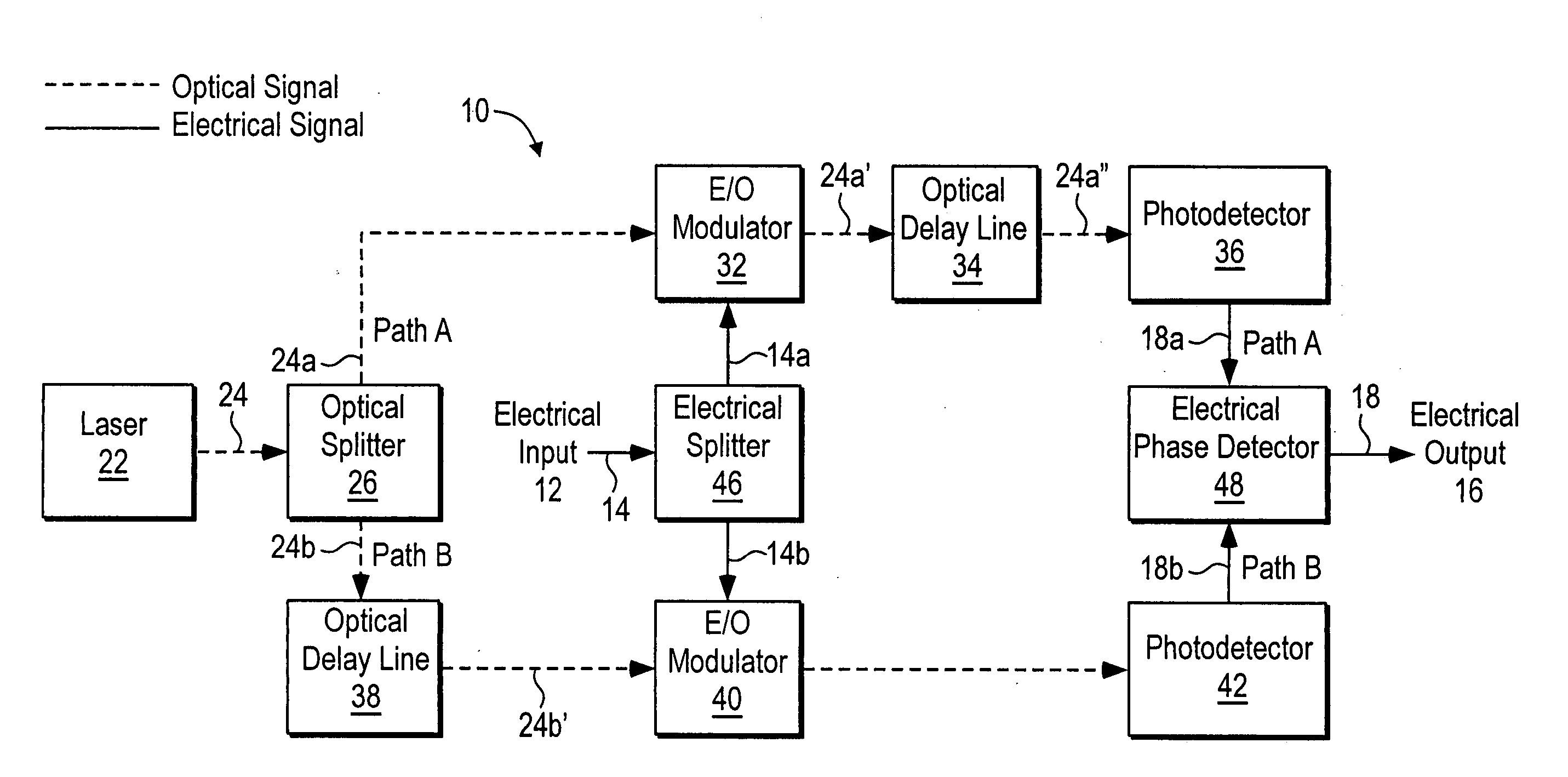
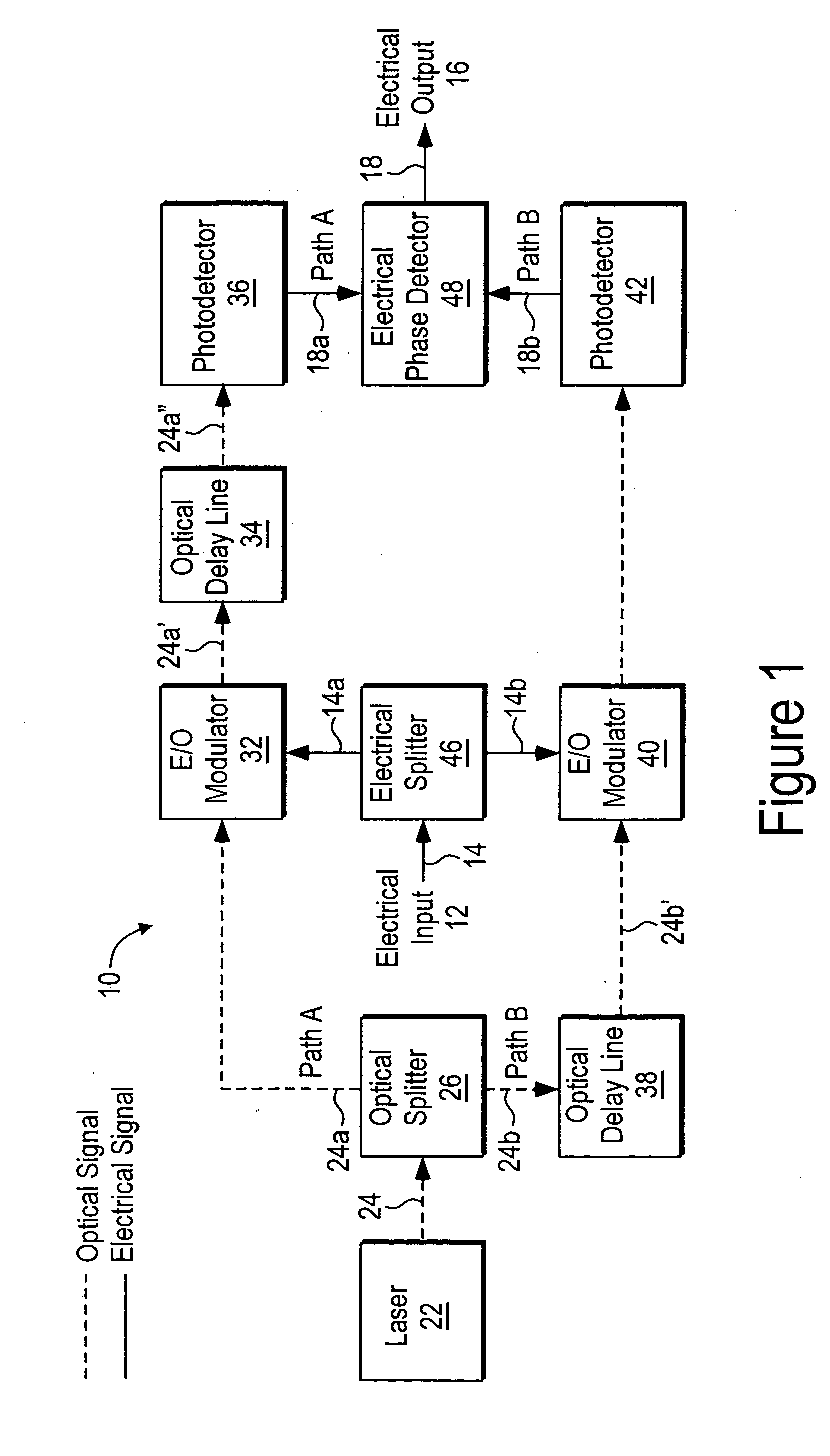
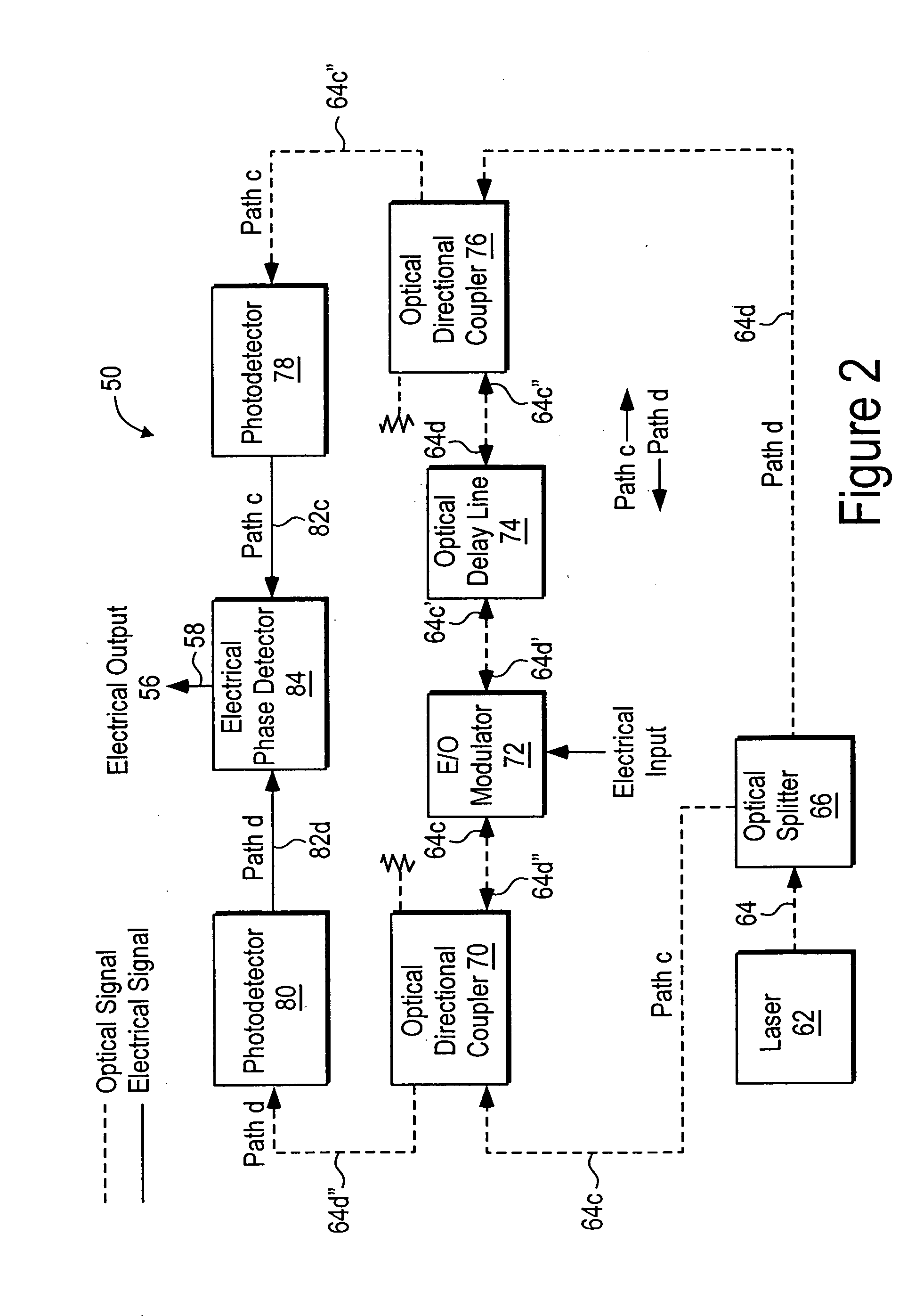
Electro-optic delay line frequency discriminator
InactiveUS20060202110A1Reduce noiseAccurate operationSpectral/fourier analysisLaser detailsDiscriminatorRelative intensity noise
An electro-optic delay line frequency discriminator has an optical signal source providing first and second optical signals that are directed along first and second paths, respectively. In the first path, the first optical signal is converted to a first corresponding optical signal that corresponds to an electrical input signal, and the first corresponding optical signal is then delayed. In the second path, the second optical signal is delayed, and the delayed second optical signal is then converted to a second corresponding optical signal that corresponds to the electrical input signal. The first and second corresponding optical signals are converted to first and second corresponding electrical signals, respectively; and a detector, responsive to the first and second corresponding electrical signals, provides an electrical output signal from the discriminator. Optical source relative intensity noise (RIN) is canceled out and does not degrade the signal-to-noise ratio of the discriminator output.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Interferometric fiber optic gyroscope with silicon optical bench front-end
ActiveUS20100301352A1Low costImprove reliabilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsSolid-state devicesFiberBeam splitting
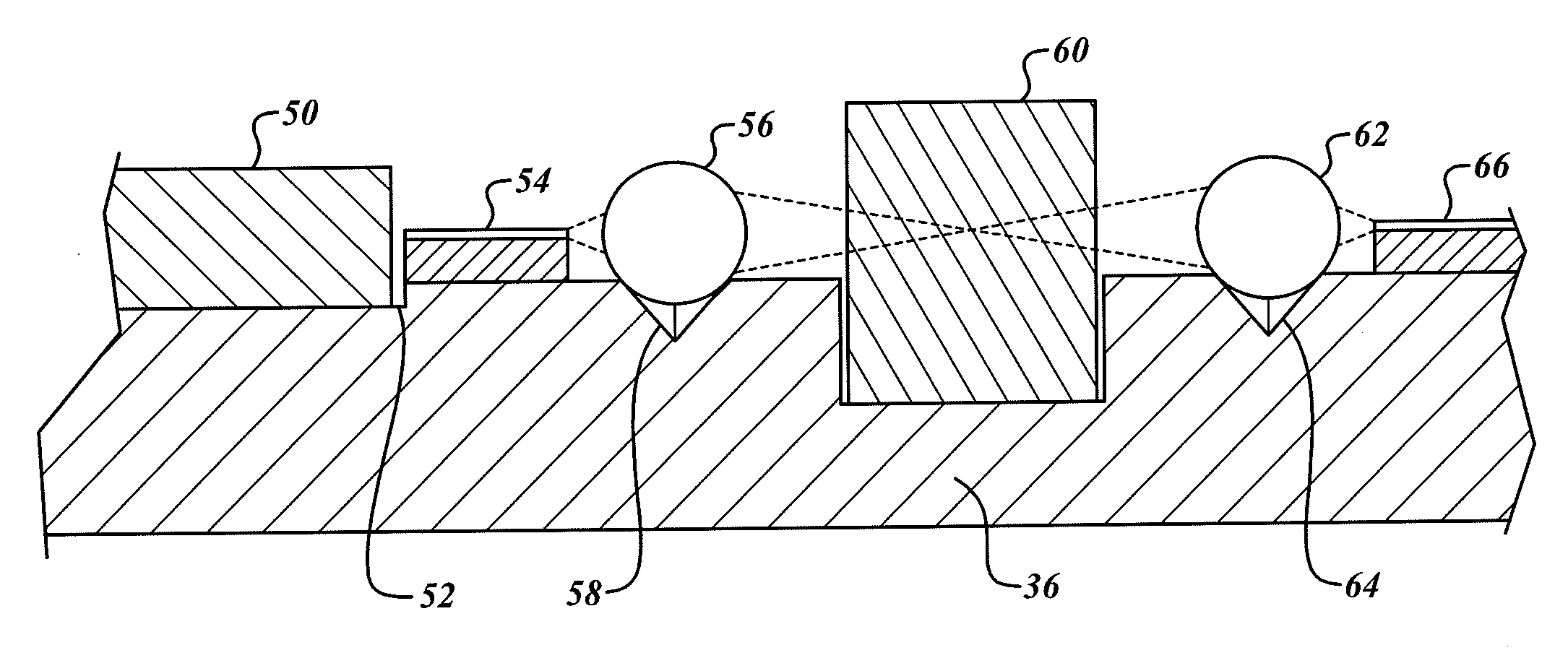
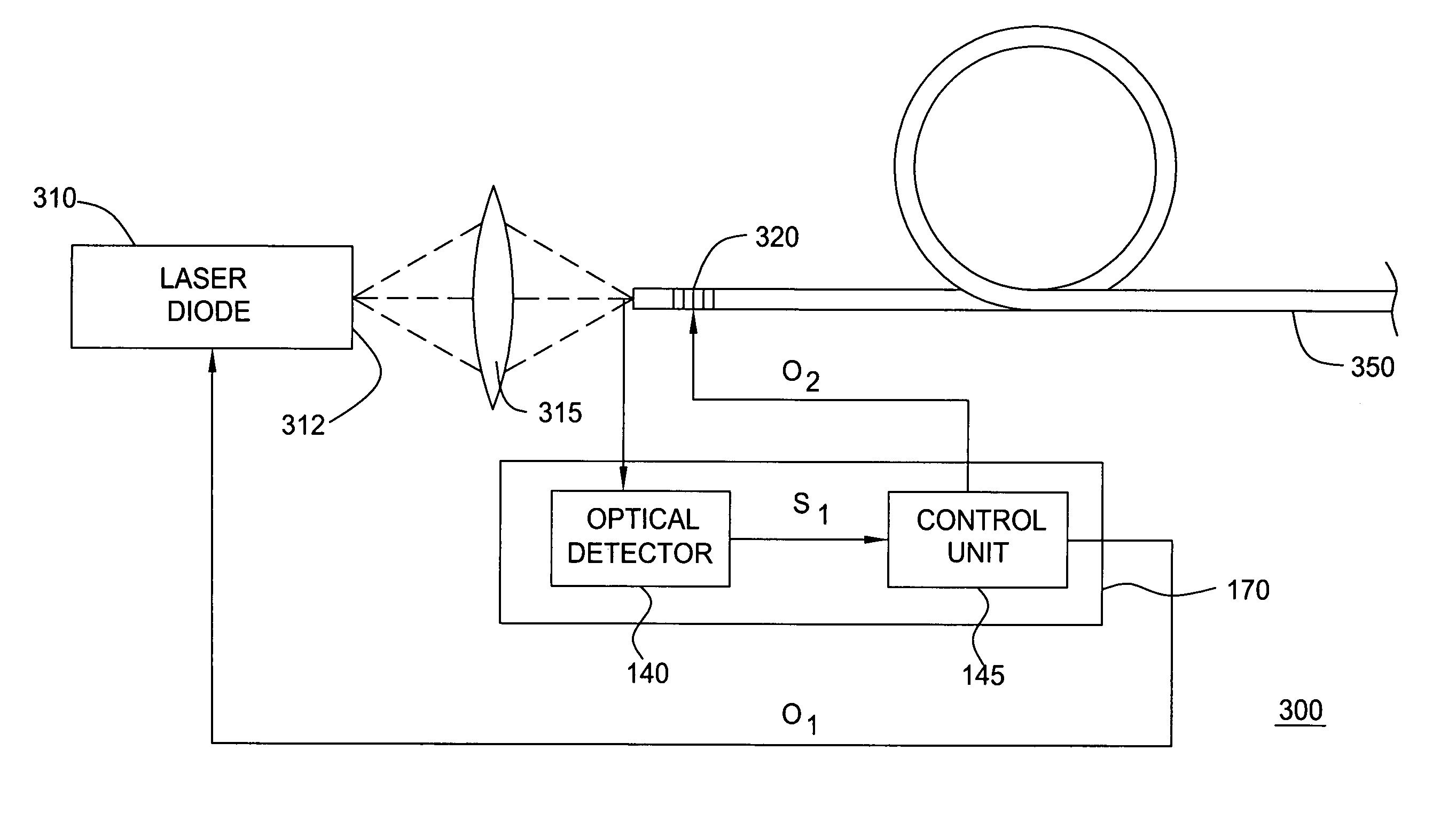
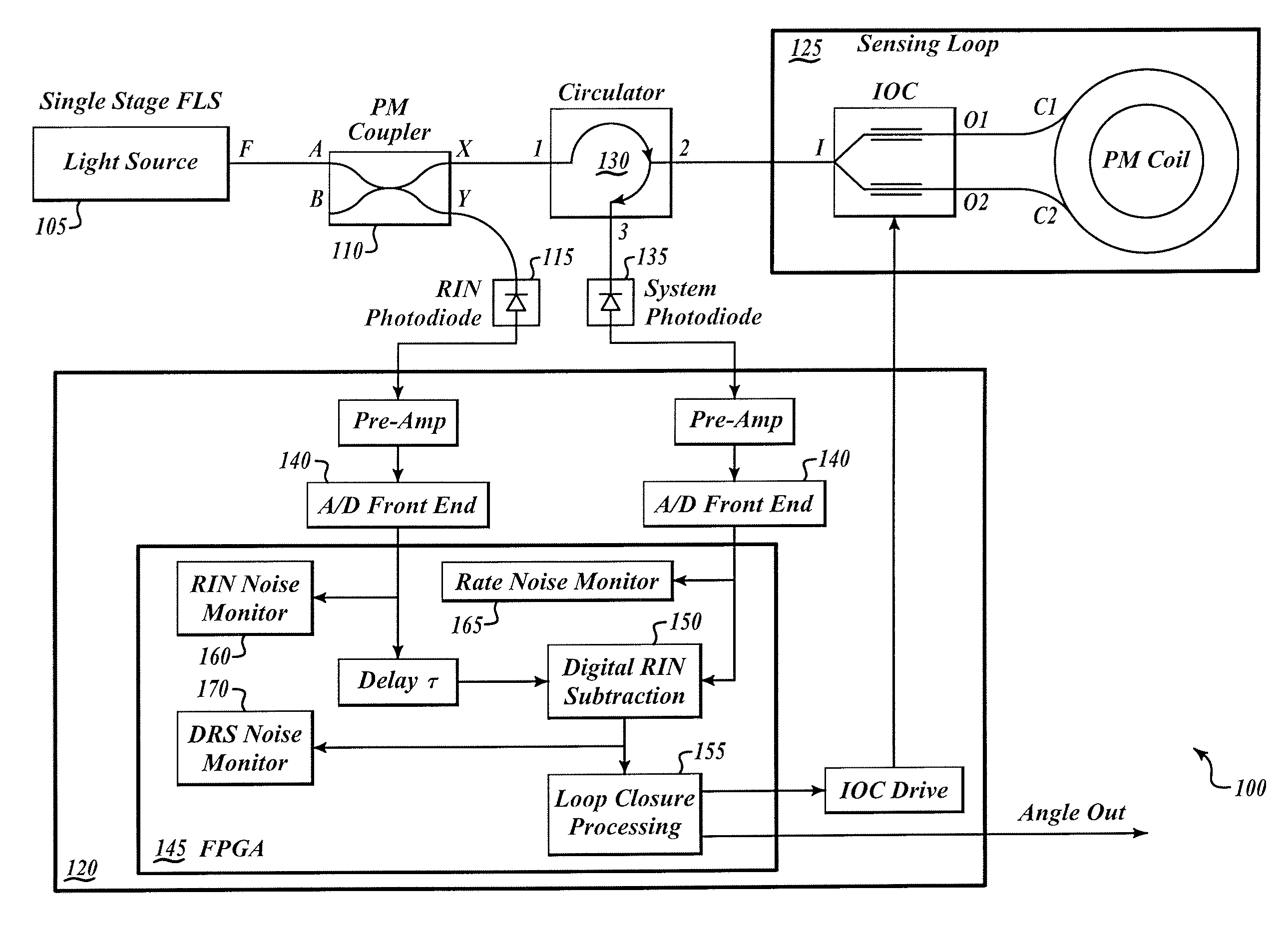
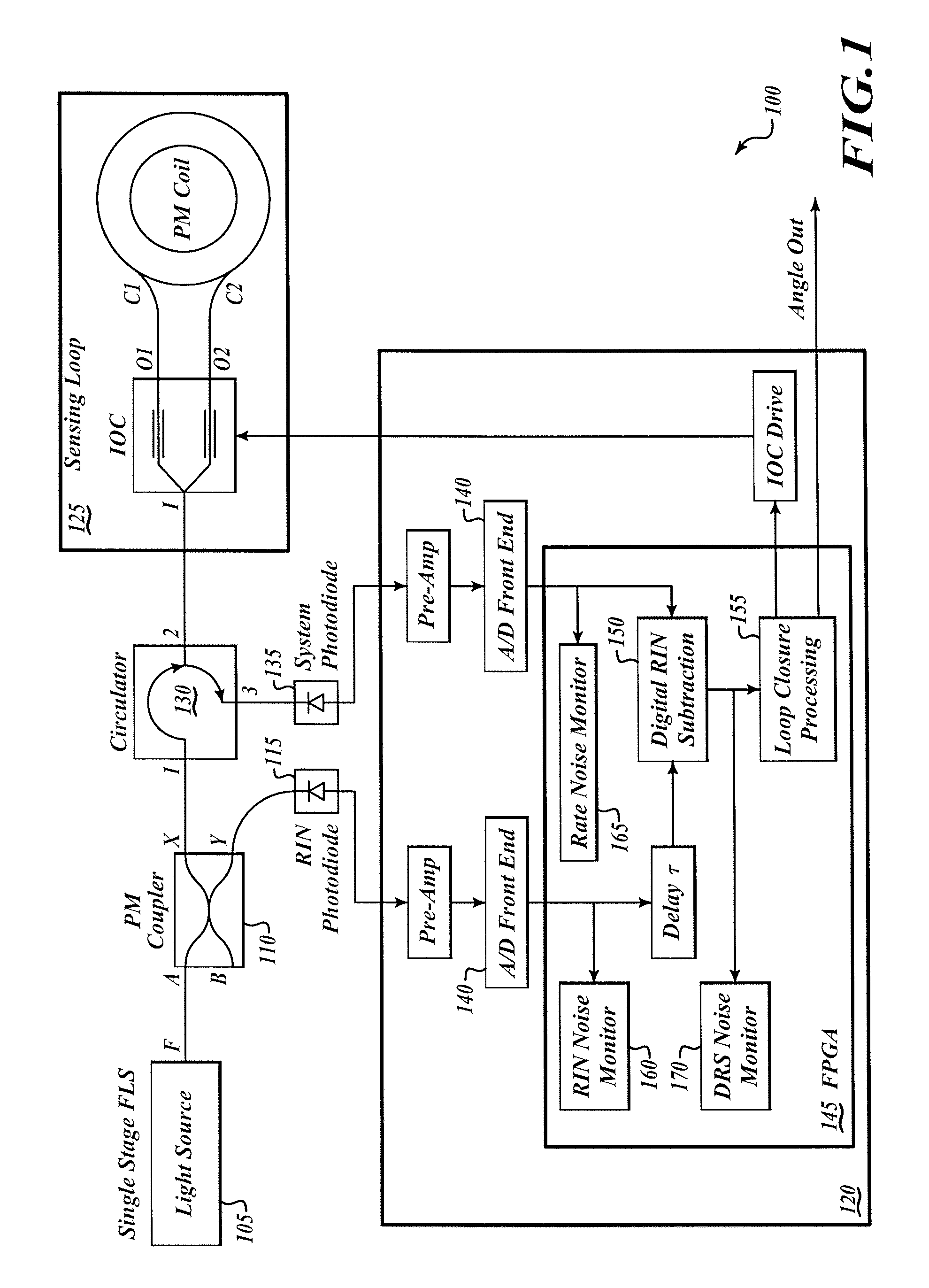
Method and apparatus are provided for a silicon substrate optical system for use in an interferometric fiber optic gyroscope (IFOG). A silicon substrate of the silicon substrate optical system is etched to receive optical components, including an input optical fiber, a pump source, a wavelength division multiplier, an isolator, a polarizing isolator, a beam splitting device, a PM tap coupler, a relative intensity noise (RIN) photodiode, a system photodiode, and an output optical fiber. The optical components are mounted on a silicon substrate to reduce the size and cost of the IFOG and increase reliability.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
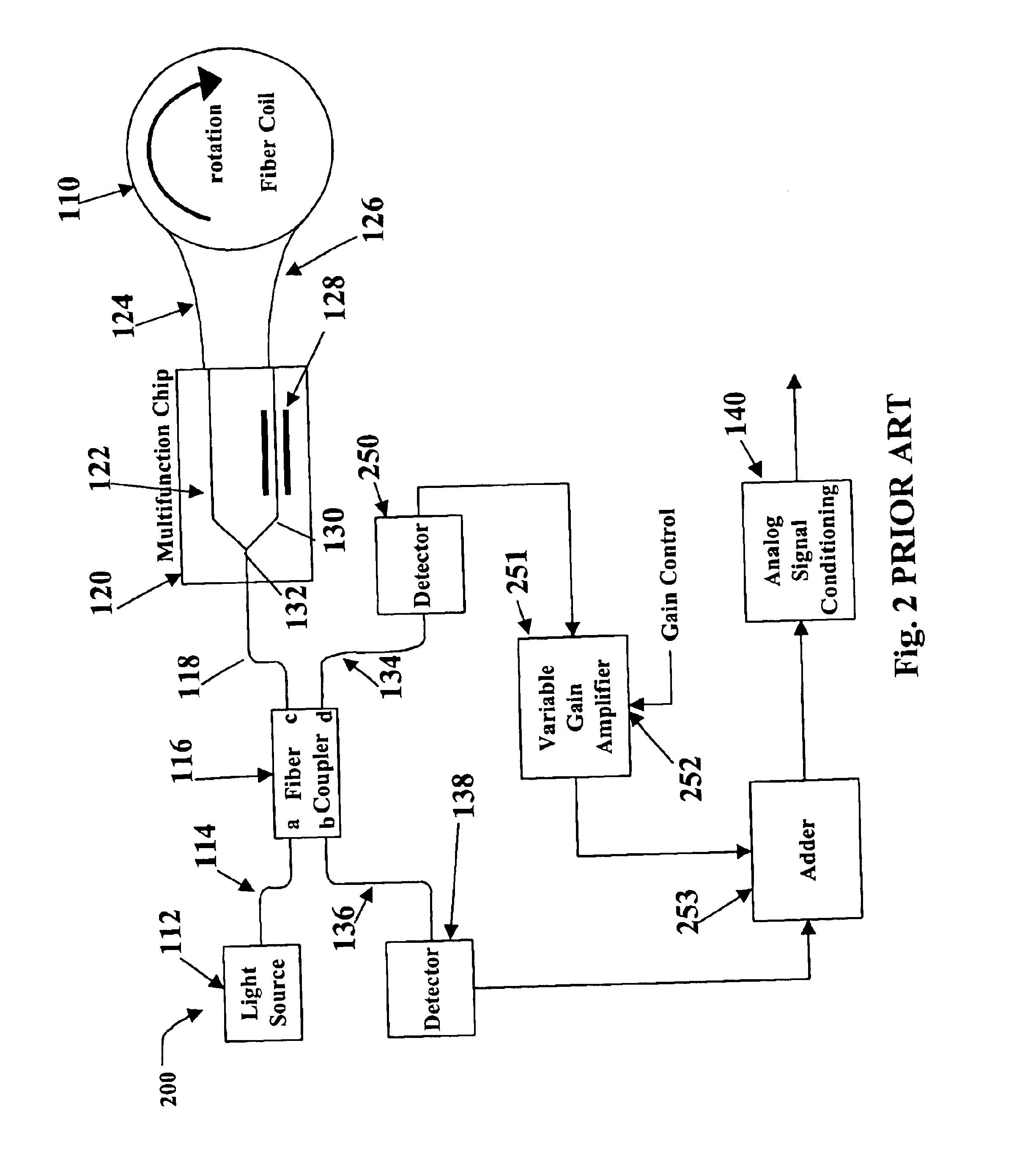
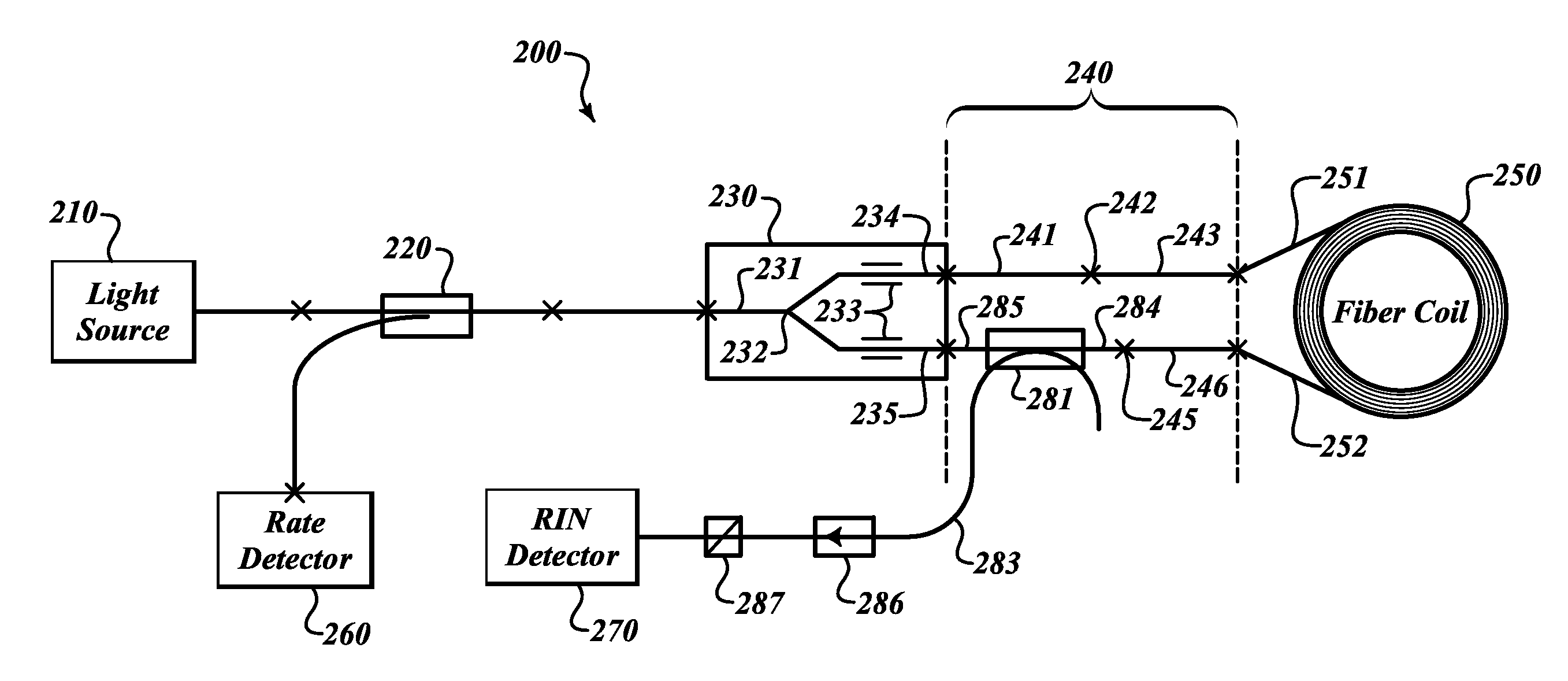
Systems and methods for effective relative intensity noise (RIN) subtraction in depolarized gyros
InactiveUS20100284018A1Improve ARW performanceEfficient noise subtractionSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersGyroscopeRelative intensity noise
Effective relative intensity noise (RIN) subtraction systems and methods for improving ARW performance of a depolarized gyros. This invention taps the RIN detector light in the sensing loop, after the light transmits through the depolarizer and the coil but before it combines with the counter propagating lightwave. The tapped RIN lightwaves are polarized with pass-axis orientated in the same direction as that of the IOC, so that the RIN detector receives lightwaves with spectrum substantially identical to that of the rate detector, leading to more effective RIN subtraction.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Laser module
ActiveUS20050123012A1Satisfactory characteristicOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionCurrent thresholdLaser light
A laser module includes a semiconductor laser element and a feedback optical component forming an external cavity with the semiconductor laser element. Even if a ratio of a current threshold of the laser module changing according to a polarized state of returned light from the feedback optical component to a current threshold of the semiconductor laser element is in an arbitrary range within a predetermined range, a total value of a relative intensity noise occurring between a first frequency determined according to a cavity length of the external cavity and at least equal to or more than a frequency band of using a laser light and a second frequency calculated by multiplying the first frequency by a predetermined number is equal to or more than −40 dB.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
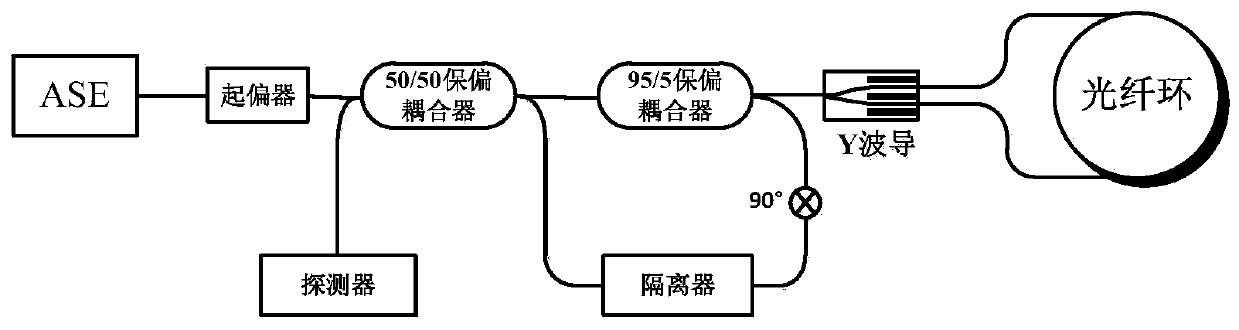
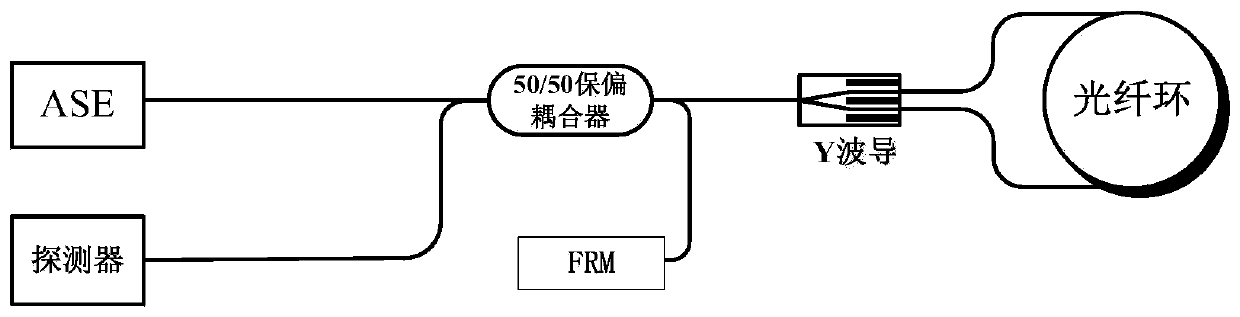
Light source relative intensity noise suppression device using double polarization maintaining coupler
InactiveCN109724585AReduce the introductionReduce lossSagnac effect gyrometersGyroscopeOptical power
The invention provides a light source relative intensity noise suppression device using a double polarization maintaining coupler, belonging to the technical field of fiber optic gyroscope. The lightsource relative intensity noise suppression device using the double polarization maintaining coupler comprises an ASE light source, a 2x2 polarization maintaining coupler, a Y-waveguide integrated optical device, a polarization maintaining fiber ring, a 95:5 polarization maintaining coupler and a detector. A 5% branch of the 95:5 polarization maintaining coupler and one branch of the 2x2 polarization maintaining coupler are welded together by a method of 90 degree melting point. The ASE light source is split into two paths of light by passing through the 2x2 polarization maintaining coupler; one path of the light is a signal light, which is divided into two paths after passing through the Y-waveguide integrated optical device and then enters into the polarization maintaining fiber ring forinterference, and the interference light is input to the 95:5 polarization maintaining coupler through the 2x2 polarization maintaining coupler; and the other path of the light is a reference light,which is input to the 95:5 polarization maintaining coupler after the 90 degree melting point. The polarization states of the interference light and the reference light are perpendicular; therefore, no interference occurs when the light is combined, and the optical power is superimposed; so that the suppression of relative intensity noise is realized; moreover, the invention has a simple structureand is easy to implement.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
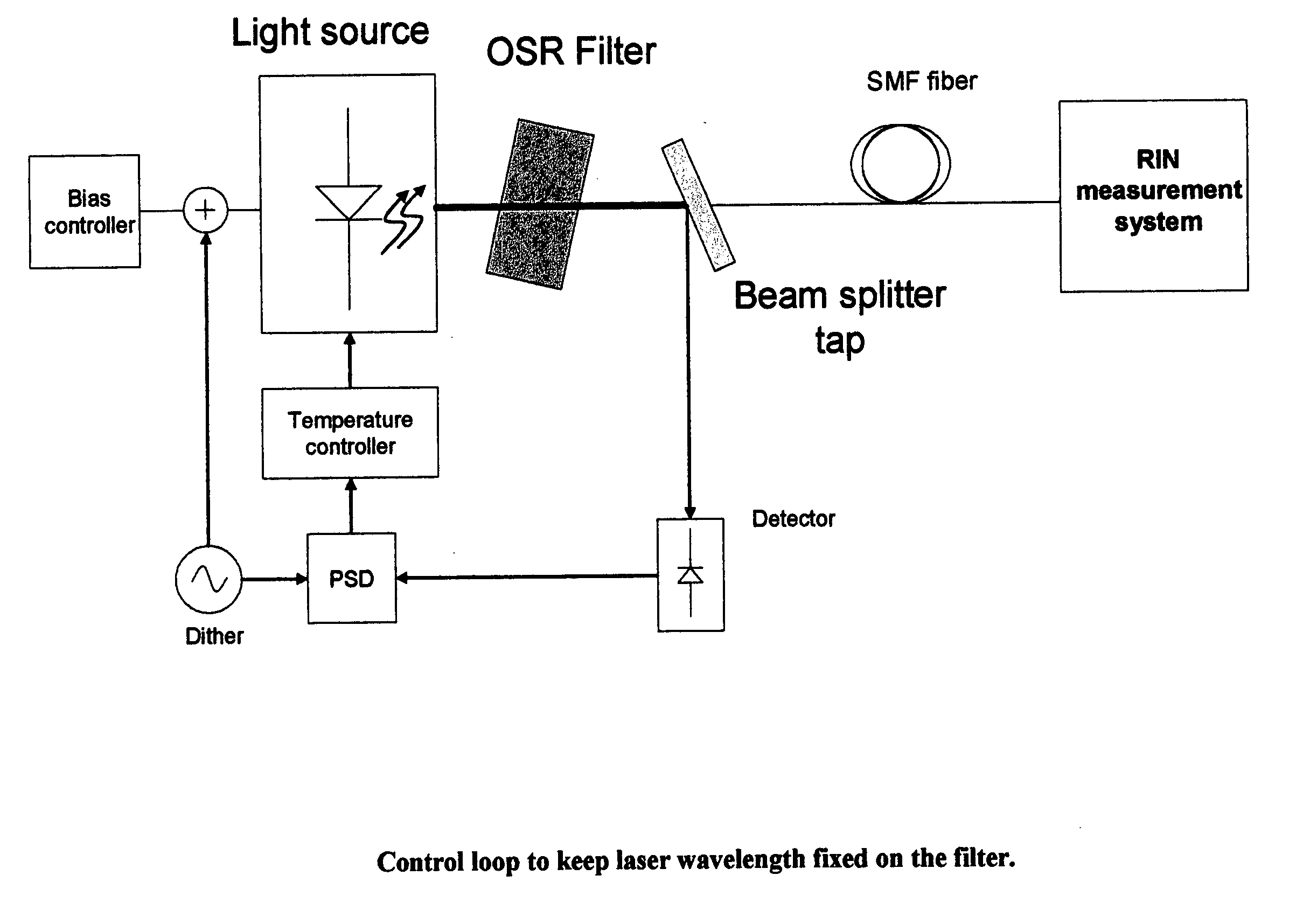
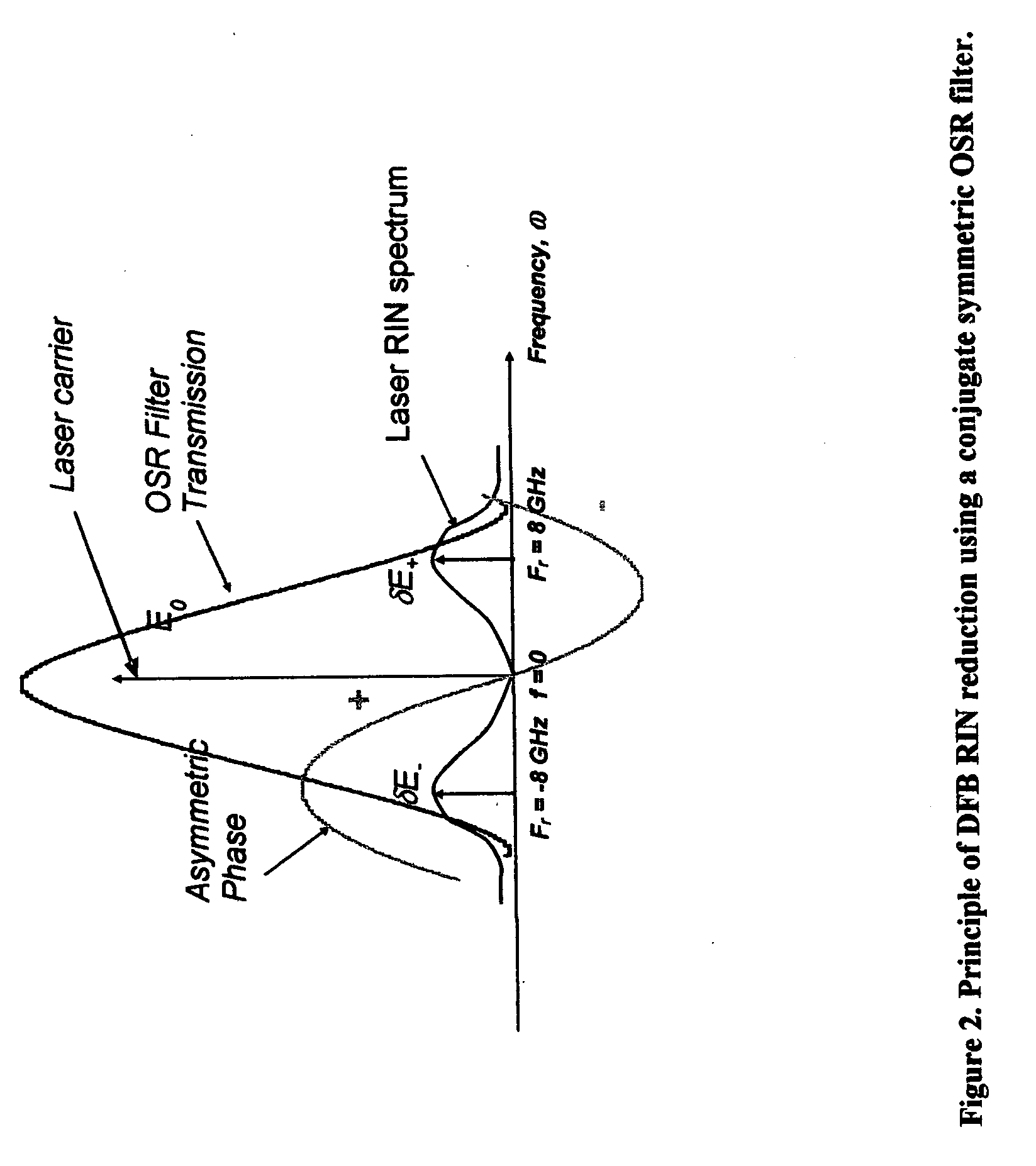
Optical source with ultra-low relative intensity noise (RIN)
InactiveUS20070012860A1Reduce resulting relative intensity noisePhotometry using reference valueLaser detailsLow noisePeak value
Apparatus for the generation of ultra-low noise light comprising: a laser generating light at a central frequency and having a frequency dependent relative intensity noise spectrum; and an optical filter having a substantially conjugate symmetric transfer function; wherein the center frequency of the light generated by the laser is substantially aligned with the peak transmission frequency of the filter; and wherein the transmission function of the filter is chosen, and the frequency dependent relative intensity noise spectrum of the laser is adjusted, to reduce the resulting relative intensity noise of the light at the output of the filter over a range of frequencies by causing the relative intensity noise spectrum of the laser to occur at frequencies for which the filter has substantial loss.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
High-precision optical fiber gyroscope
ActiveCN109459009AReduce thermal radiation interferenceReduce the impactSagnac effect gyrometersGyroscopeErbium doping
The invention relates to a high-precision optical fiber gyroscope, and belongs to the technical fields of optical fiber sensing and inertial navigation. The high-precision optical fiber gyroscope is characterized in that a circuit board comprises a main board and a light source board; a loop assembly comprises an optical fiber ring base, a polarization-maintaining optical fiber ring, a erbium-doped fiber press plate, a wavelength division multiplexer, an isolator, a reflective mirror, a wave guide plate, a coupler, a temperature sensor and a Y-shaped wave guide; the outside wall of the opticalfiber ring base is provided with an annular installation groove for accommodating the polarization-maintaining optical fiber ring; the base is positioned between an upper casing and a lower casing, and is used for separating a gyroscope body into an upper part and a lower part; the circuit board is positioned at the upper part of the gyroscope body, and the loop assembly is positioned at the lower part of the gyroscope body. The high-precision optical fiber gyroscope has the advantages that a heating device and a sensitive optical fiber ring are physically isolated by the base, so as to reduce the heat radiation interference of a transmission device to the light path part; a magnetic shielding technique is adopted for the optical fiber loop, so as to shield the geomagnetic interference and circuit electronic interference; a light source with stable wide bandwidth and high power of 1550 nm is built, so that the output wavelength is not sensitive to the temperature, and the relative intensity noise of the light source is inhibited.
Owner:HEBEI HANGUANG HEAVY IND
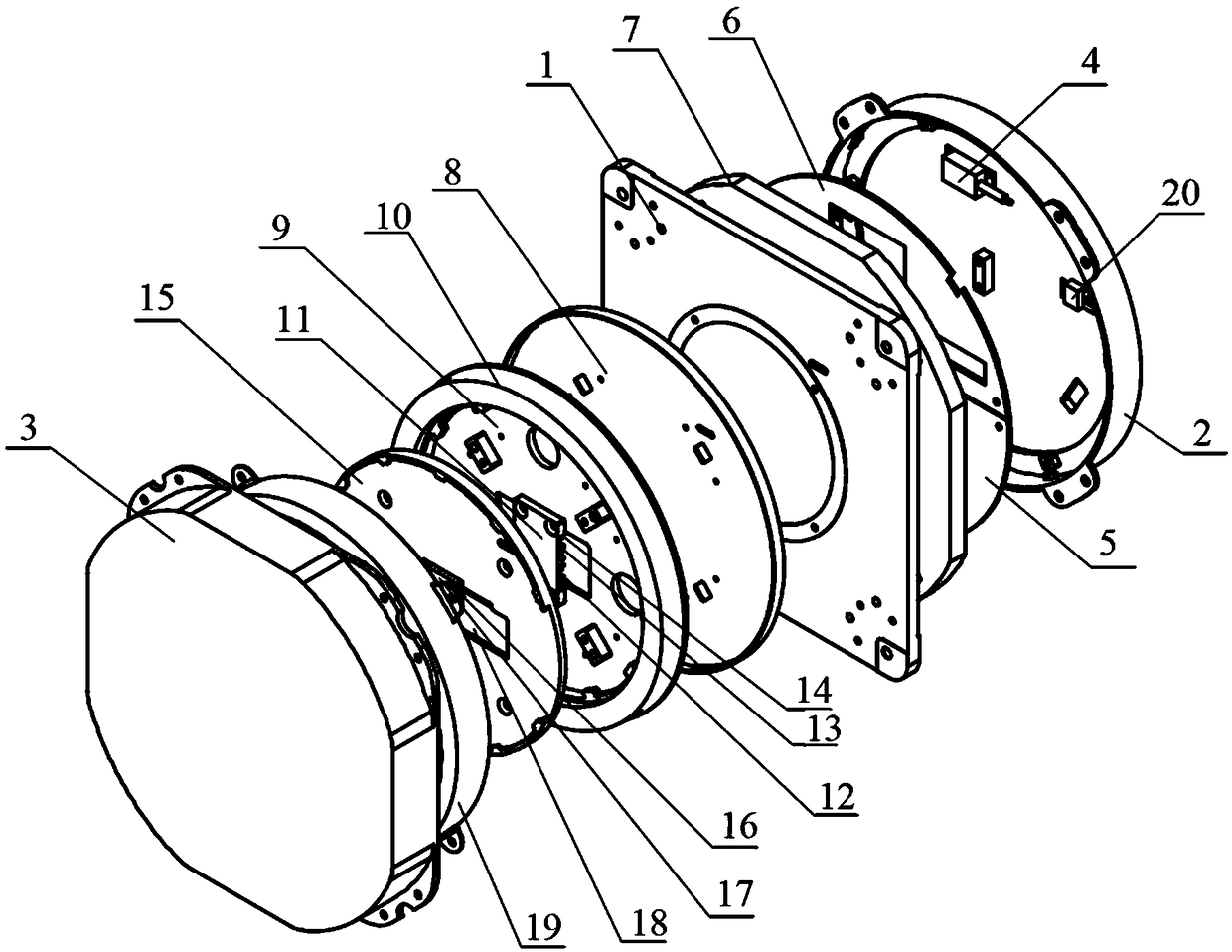
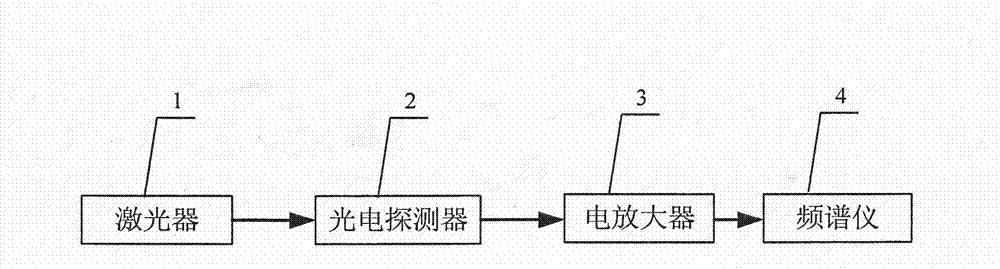
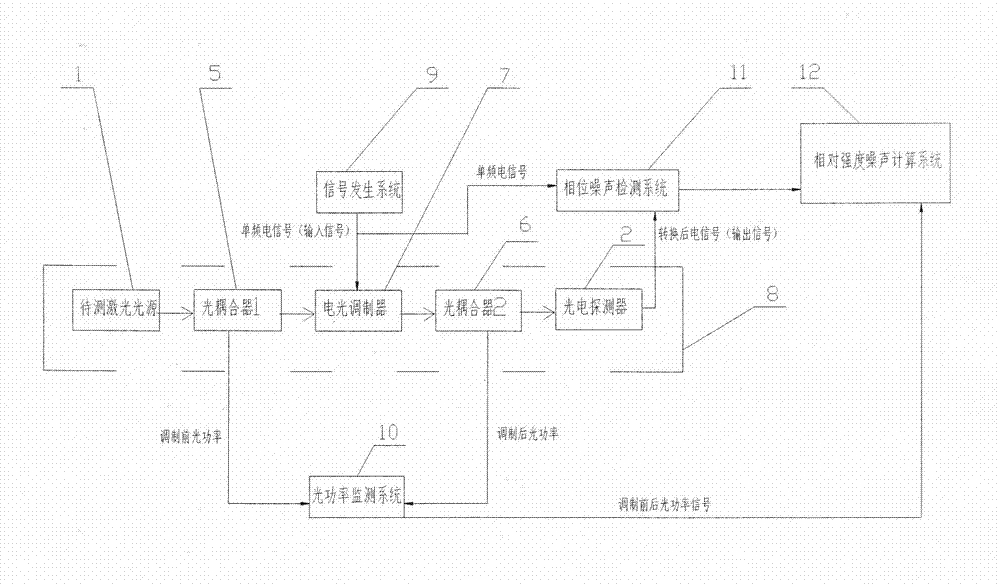
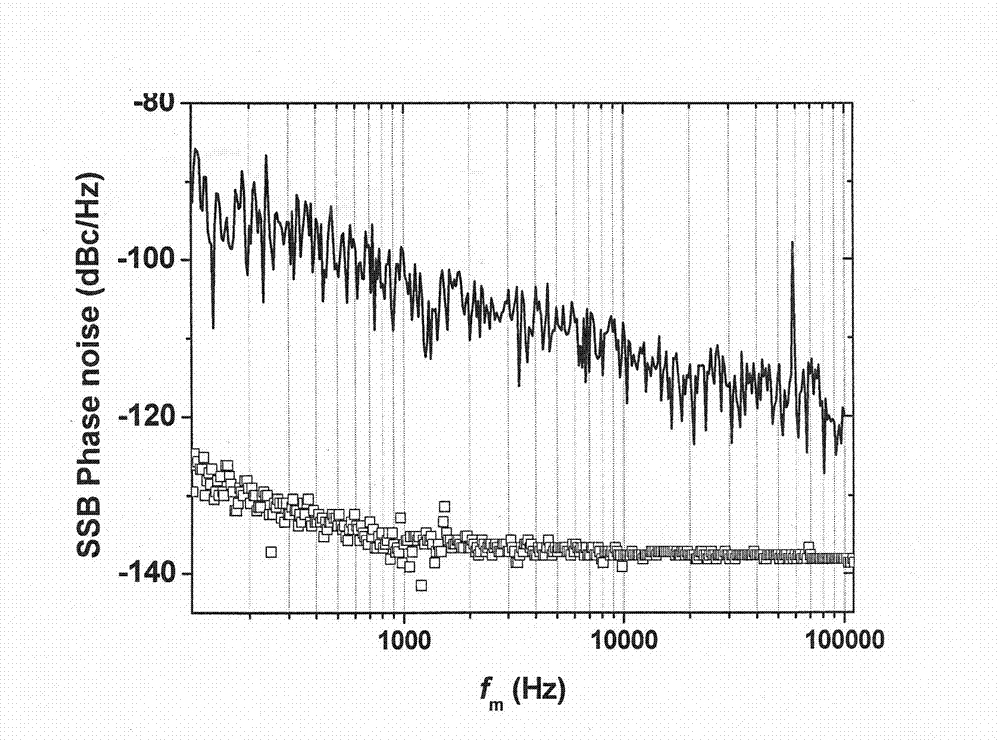
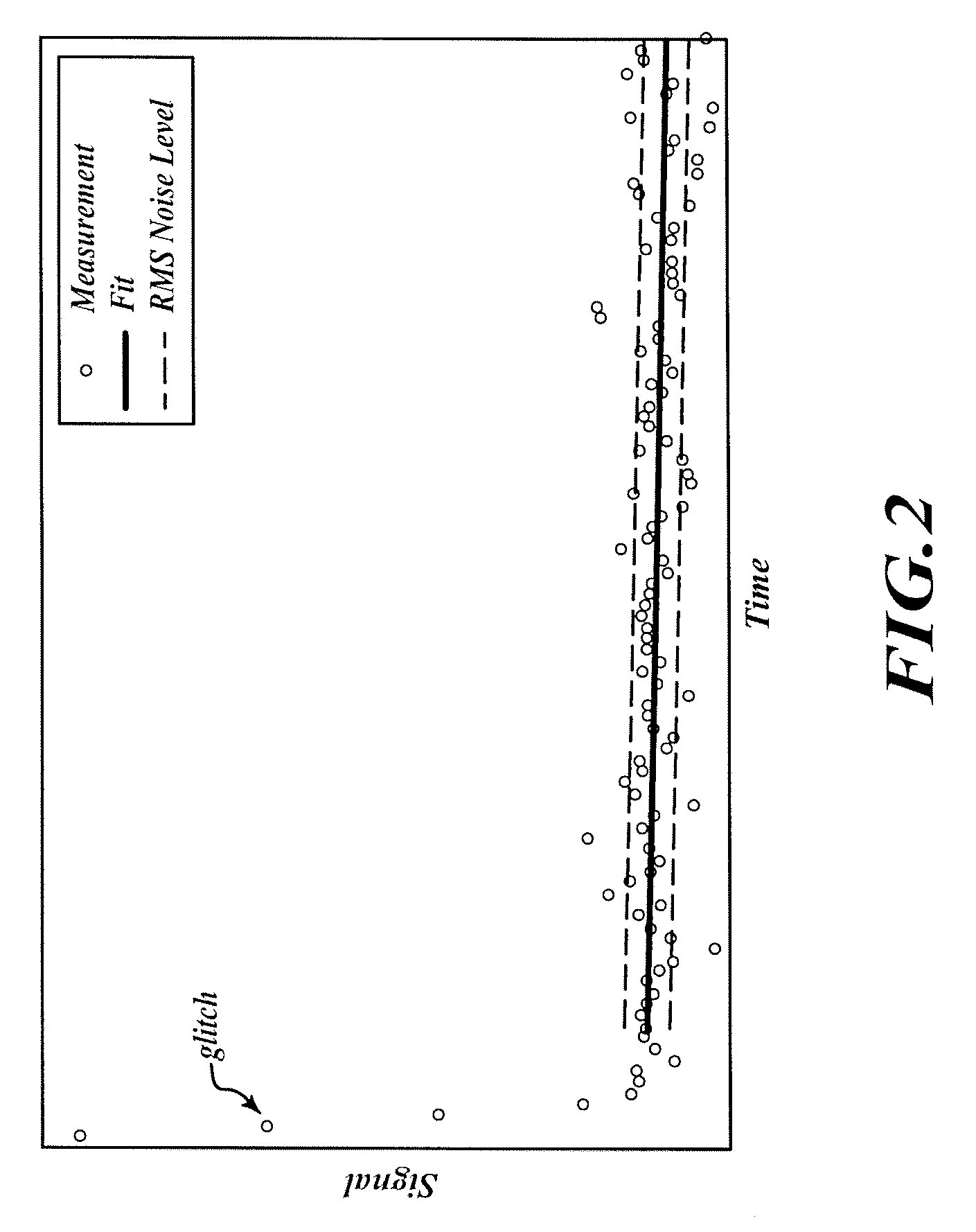
Device and method for measuring relative intensity noise of laser
ActiveCN103575511ABreak through restrictionsAvoid ambient noiseTesting optical propertiesOptical power meterEngineering
The invention discloses a device and method for measuring relative intensity noise of a laser. According to the method for measuring the relative intensity noise of the laser, the principle that after a single frequency point electric signal passes through a microwave photon link, a phase-noise index is correspondingly deteriorated is adopted and the relative intensity noise of the laser in the link is calculated through the change quantity of phase noise. The basic structure of the device for measuring the relative intensity noise of the laser comprises a single frequency point signal resource, a microwave photon link, an optical power meter and a phase-noise detector, wherein the microwave photon link is mainly composed of the laser, an electro-optical modulator, an optical coupler and a photoelectric defector. Compared with a traditional measuring method, the method for measuring the relative intensity noise of the laser has the advantages that the measuring process is conducted on the high-frequency end of an electricity domain, influence caused by various environment noises near the direct current end is avoided, the measuring accuracy is improved, the output power of the laser to be detected does not need to be considered according to the scheme, and the limitation, caused by optical output power, of a measuring system in the traditional measuring method is overcome.
Owner:广东国天时空科技有限公司
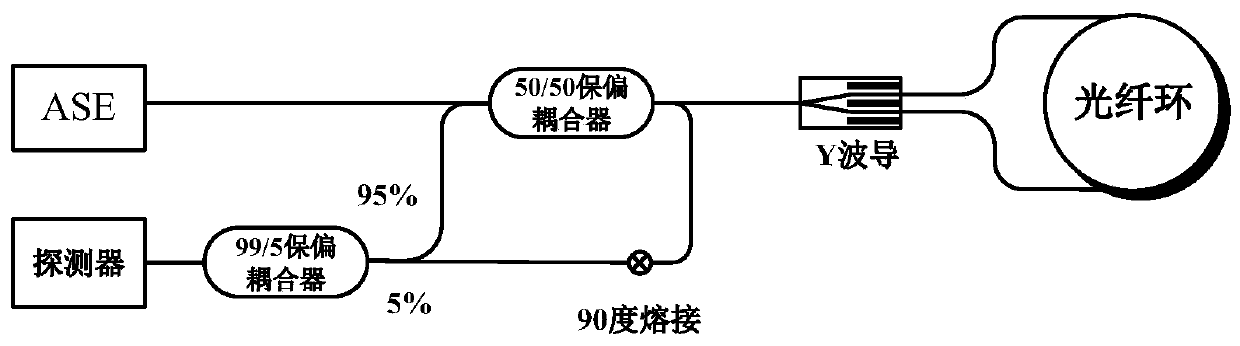
FRM-based light source relative intensity noise cancellation structure
InactiveCN109724583AReduce lossLow melting pointSagnac effect gyrometersPolarization-maintaining optical fiberOptical power
The invention provides a FRM-based light source relative intensity noise cancellation structure, and belongs to the technical field of fiber optic gyros. The structure of the invention comprises an ASE light source, a single polarization 2*2 polarization-maintaining coupler, a Faraday rotating mirror (FRM), a Y-waveguide integrated optical device, a polarization-maintaining fiber loop, and a detector, wherein the light from the ASE light source becomes a polarized light passing through the 2*2 polarization-maintaining coupler, and is then divided into two beams, of which one is used as a signal light and the other one a as reference light; the signal light is divided into two beams through the Y-waveguide integrated optical device into the fiber loop for interference, the reference light passes through the FRM such that the polarization state is rotated by 90 degrees and reflected, and the reference light and the reflected light combine to enter the detector. The reference light and the interference light of the invention have a certain time difference, and the polarization states are perpendicular to each other with no interference occurring when the lights are combined, so that the optical power is increased, and the suppression of the relative intensity noise is completed.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Multi-wavelength generating method and apparatus based on flattening of optical spectrum
InactiveUS20050008373A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersMultiwavelength spectroscopySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
With respect to the relative intensity noise (RIN) for inputs to an optical modulator or the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) for outputs therefrom, the optical modulator modulating coherent lights of different wavelengths obtained by slicing a spectrum of the multi-wavelength light, the shape of a spectrum of a multi-wavelength light is controlled so that predetermined RIN and SNR can be obtained in accordance with transmission system parameters (the type and distance of optical fibers, the number of repeaters), thus enabling design meeting a performance specification for a conventional transmission section using semiconductor lasers.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
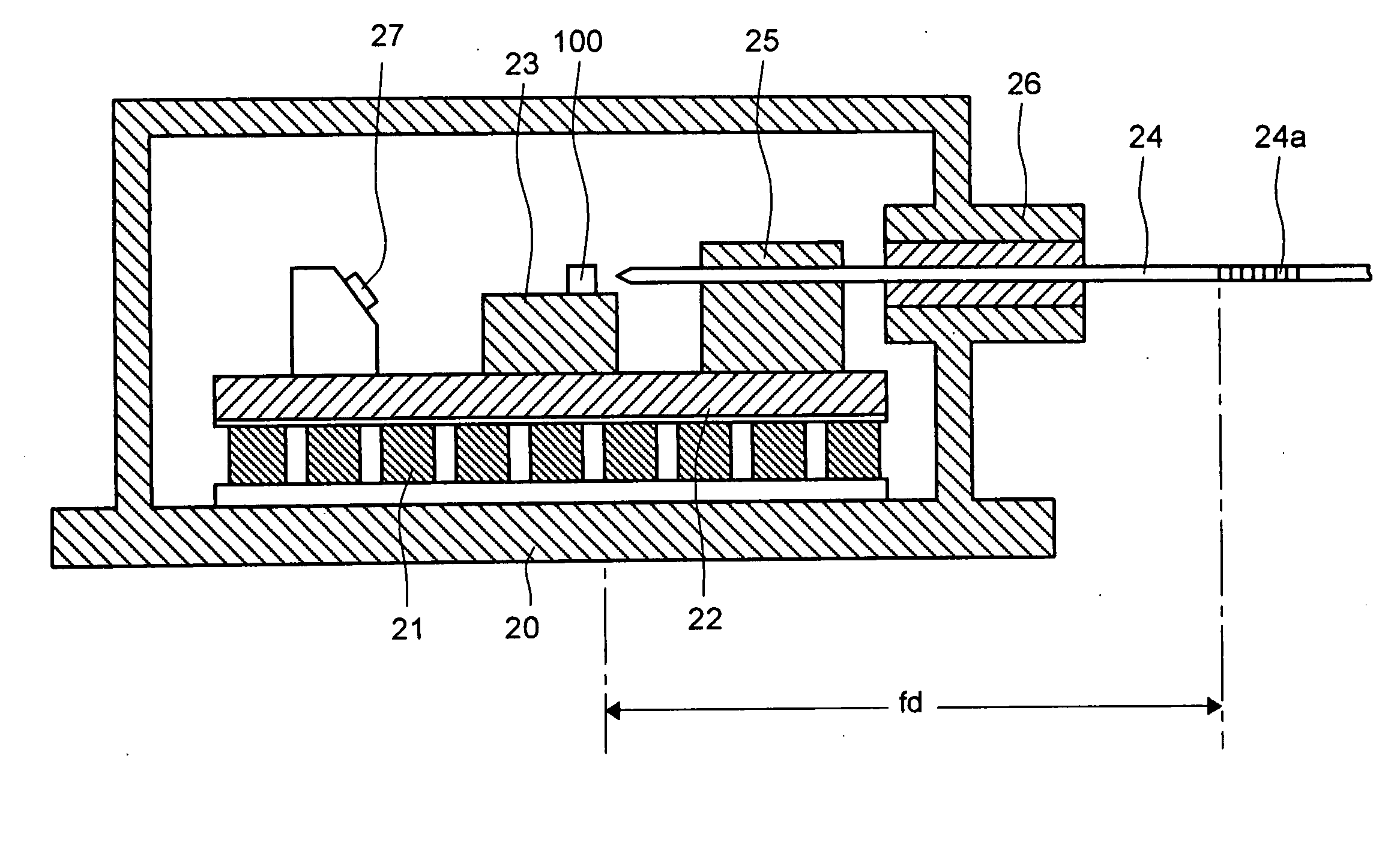
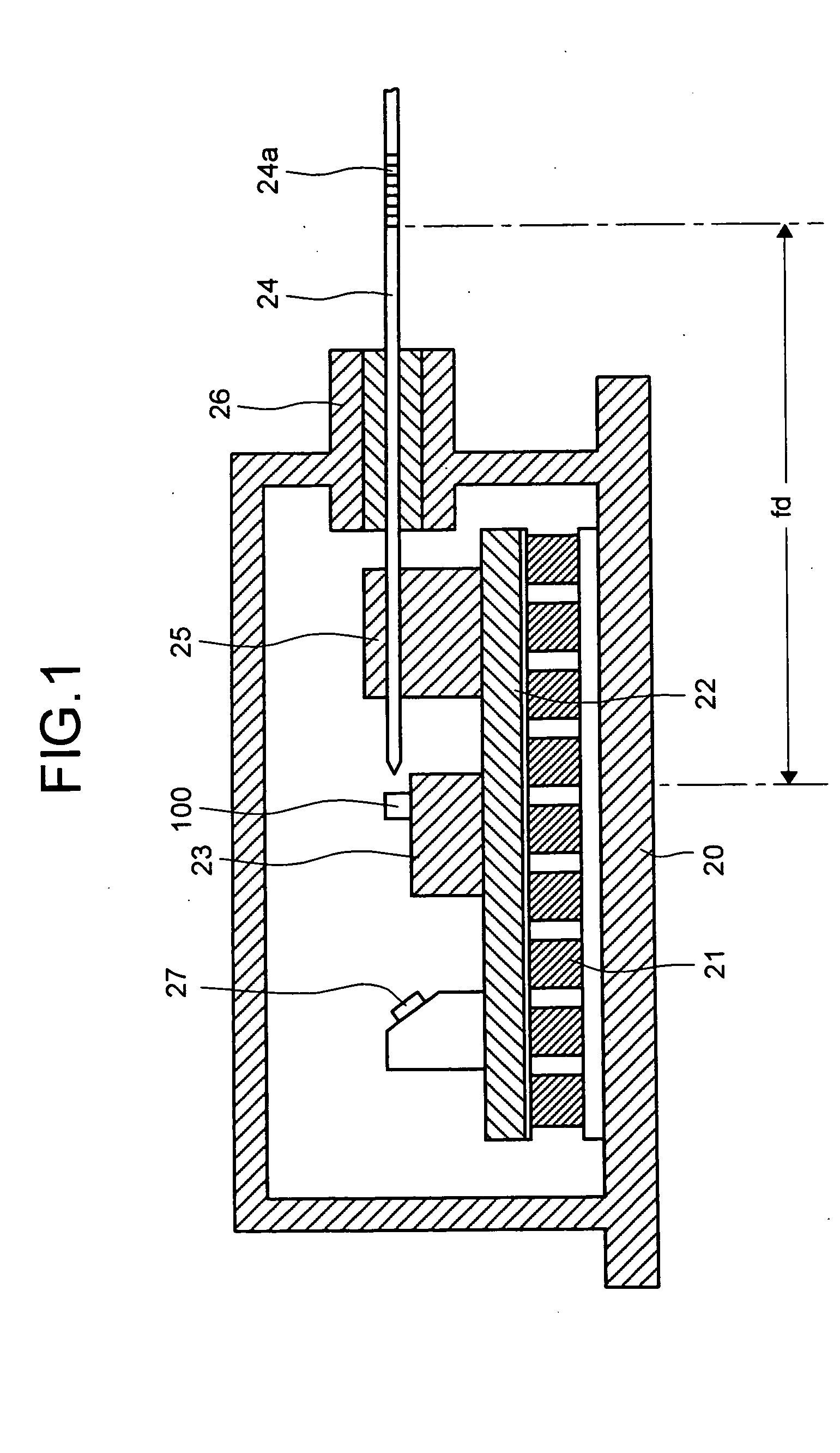
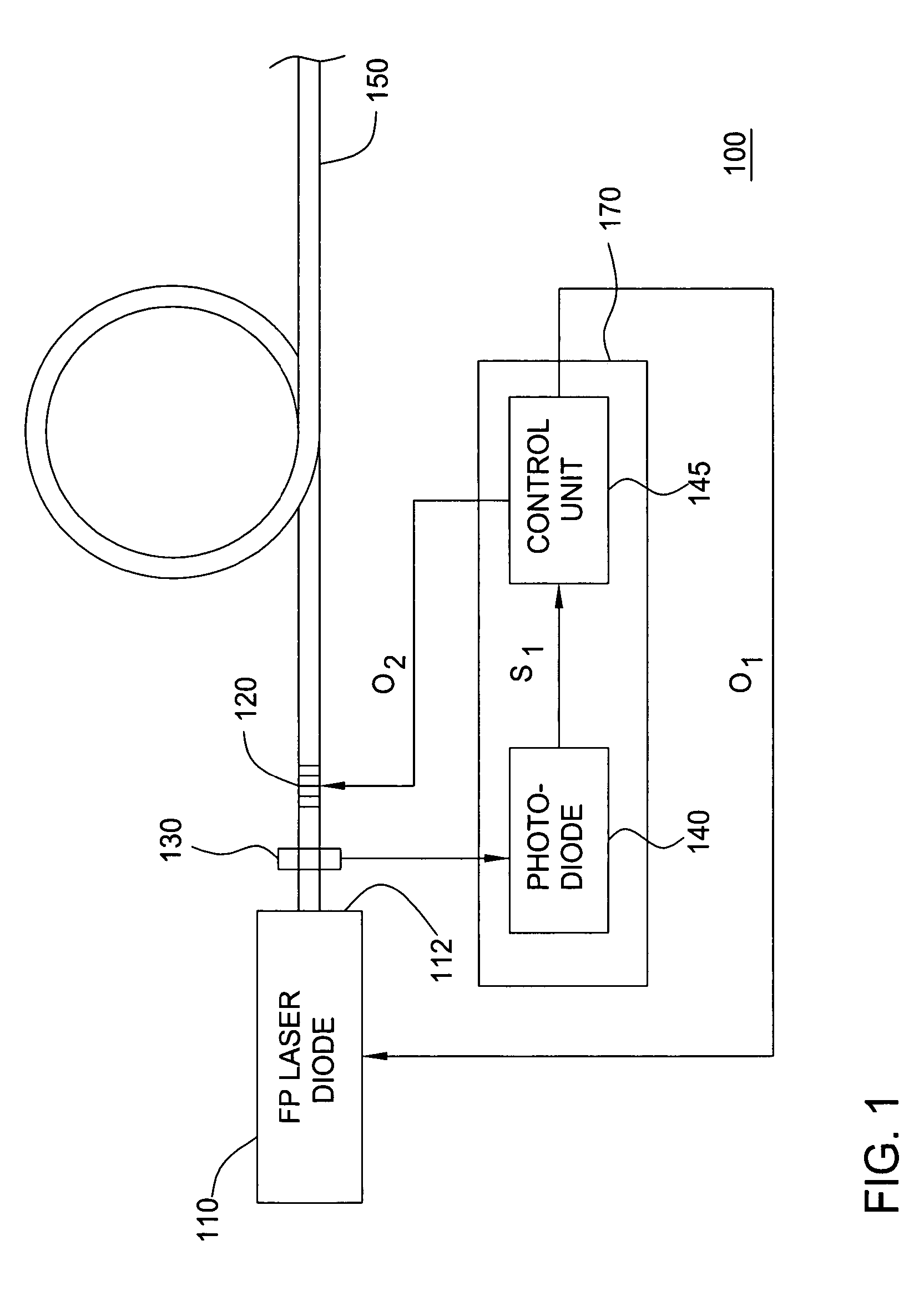
Low relative intensity noise fiber grating type laser diode
ActiveUS7158552B2Reduce Relative Intensity NoiseLaser using scattering effectsLaser optical resonator constructionFiberGrating
The dependency of intensity noise is used to determine the wavelength difference between a laser diode gain peak and a reflection peak of a fiber grating in a fiber grating type laser diode. Monitoring and determining the relative noise intensity of such a laser enables the control of the laser diode or the fiber grating such that the intensity noise is as low as possible. Such an approach enables the use of a fiber grating type laser diode as Raman pumps in high-speed transmission systems where low intensity noise is a requirement, especially when the Raman pump power propagates in the same direction as the transmission signals (known as Raman co-pumps).
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Multi-wavelength generating method and apparatus based on flattening of optical spectrum
InactiveUS6831774B2Simple and inexpensive configurationWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionRelative intensity noiseSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
Amulti-wavelength generating apparatus generates a wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) signal by modulating light with a single central frequency and an electric signal having a particular pulse repetition frequency. The resulting optical spectrum configuration is conntrollable so that a Relative Intensity Noise (RIN) or Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) requirement may be achieved. A modulated or pulsed light source in used to obtain a descrete spectrum with particular mode spacing, which is then modulated to permit dynamic power control for specific modes of the discrete spectrum.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Holographic adaptive optic system
InactiveUS7495200B1Optical measurementsPhotometry using reference valuePhase correctionWavefront sensor
A holographic adaptive optic system for correcting the wavefront of a light. A phase correction device with a plurality of pixels in the path of the light. A holographic wavefront sensor in the path providing a pair of reconstruction beams for each phase correction device pixel. The relative intensity of the two beams being proportional to the amount of aberration present in the initial beam. A detector that measures the relative intensity of the pair of reconstructed beams. The detector connected by at least one individual control connector to the relevant pixel in the phase correction device. The individual control connectors controlling the phase correction device based upon the relative intensity between the two reconstruction beams to reduce the wavefront aberration.
Owner:AIR FORCE US SEC THE THE
System and method for reducing interferometric distortion and relative intensity noise in directly modulated fiber optic links
A laser transmitter with a feedback control loop for minimizing noise. The novel laser transmitter includes a laser, an external reflector adapted to form an extended cavity to the laser, and a feedback control loop adapted to detect noise in the laser and in accordance therewith, adjust the optical phase of the extended cavity such that the noise is at a desired level. The optical phase of the extended cavity is adjusted by adjusting an operating parameter of the laser, such as its bias current. In an illustrative embodiment, the feedback control loop is adapted to compute the rate of change of the noise with respect to bias current and in accordance therewith, adjust the bias current of the laser such that relative intensity noise and interferometric intermodulation distortion are simultaneously minimized.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
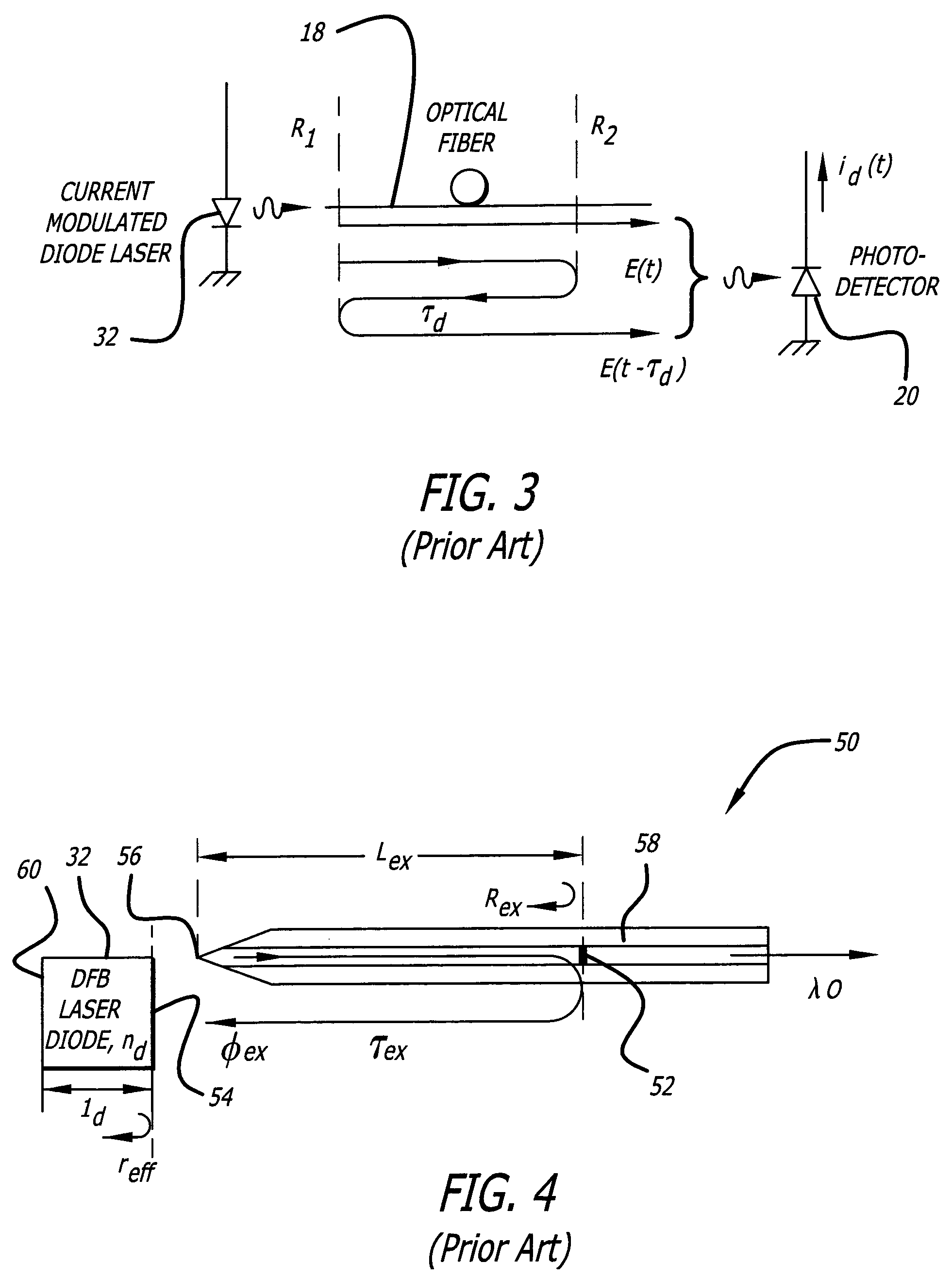
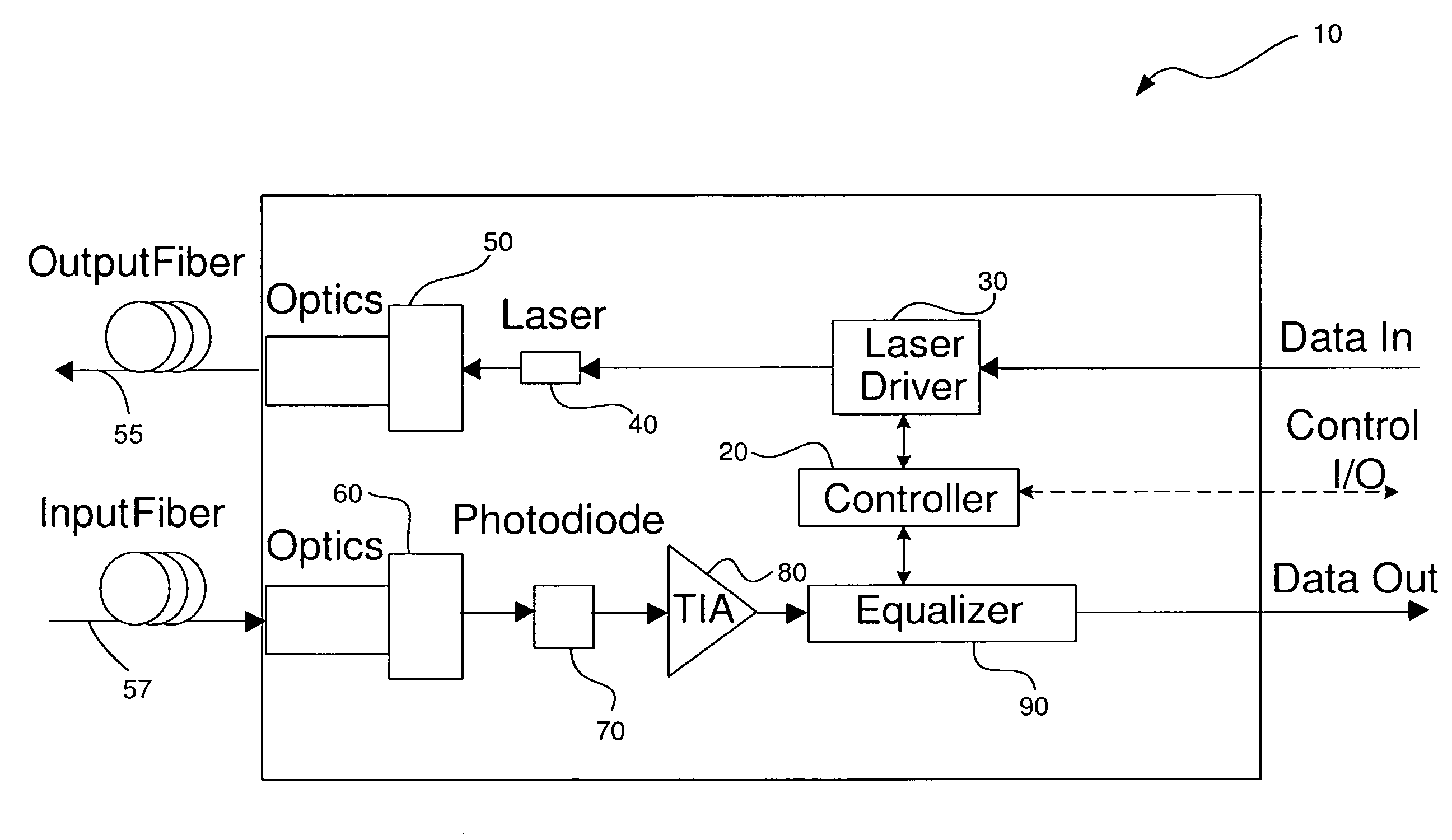
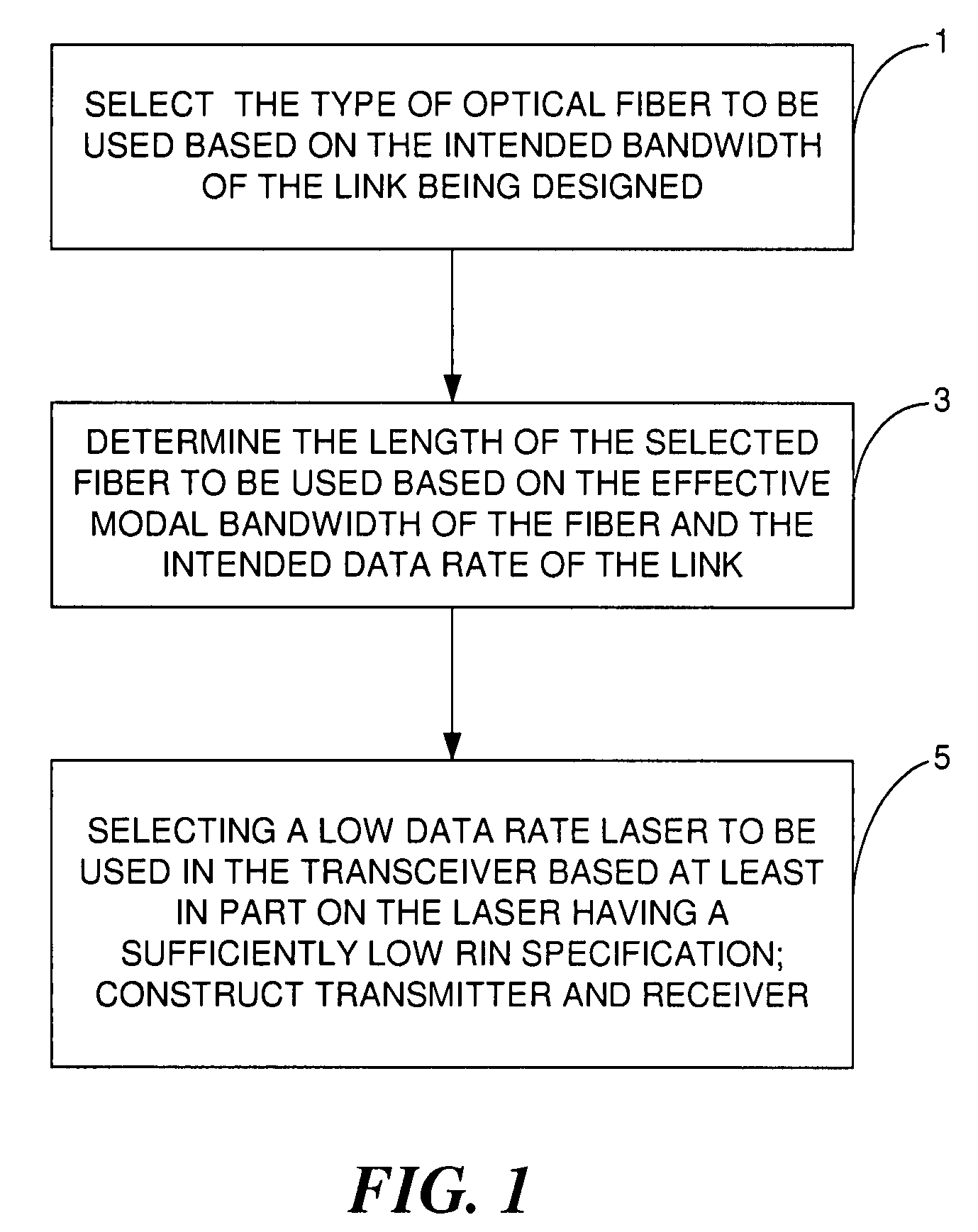
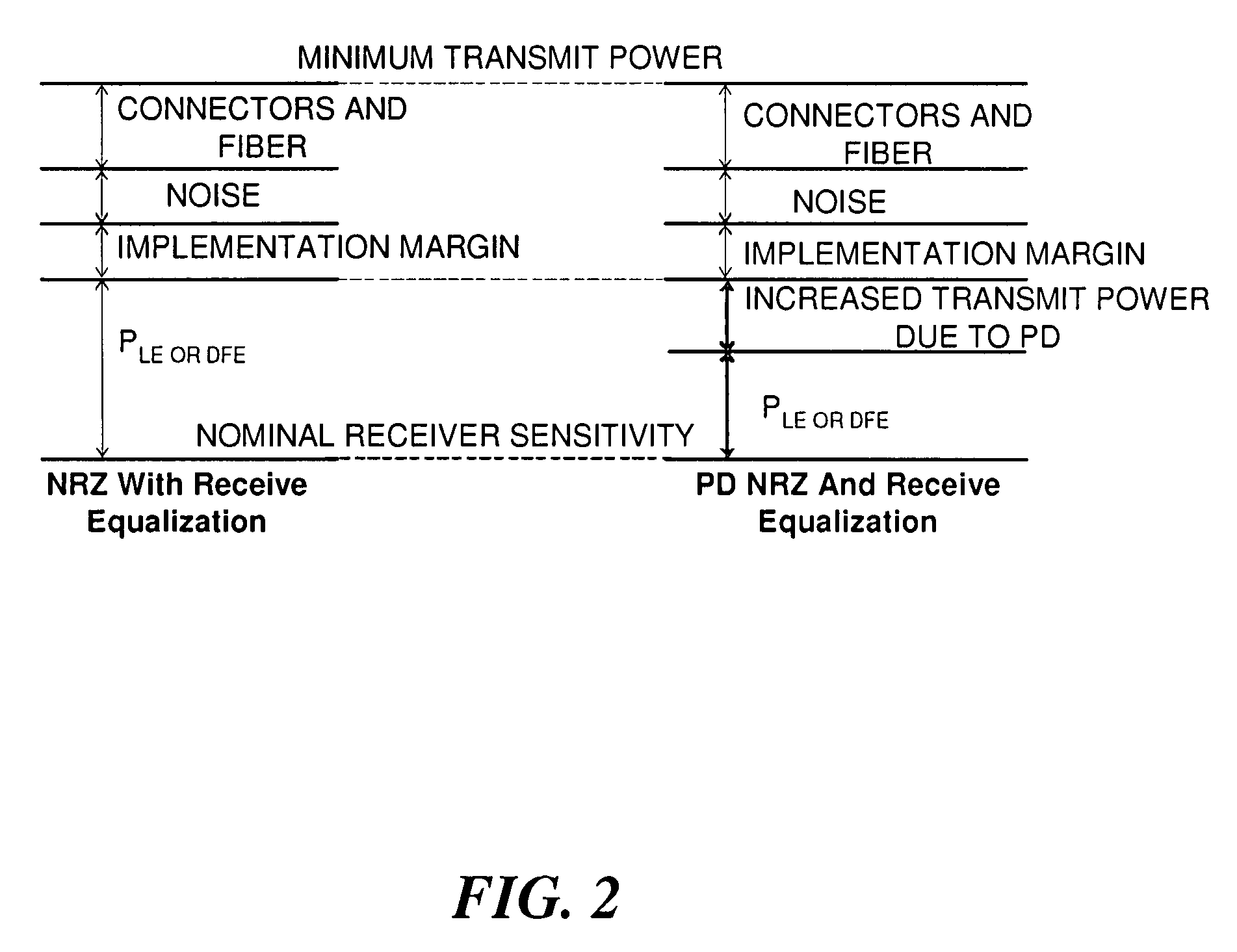
Fiber optic link, a transceiver for use in the link, and methods for designing and constructing fiber optic links and transceivers
A fiber optic link is provided that uses a relatively low-cost transceiver that incorporates relatively inexpensive low bandwidth optical and electrical components to achieve high data rate operations. The data rate of the fiber optic link can be greater than the data rate of the laser of the transceiver provided the laser meets certain noise requirements; in particular, the relative intensity noise (RIN) of the laser must be low enough to ensure low bit error rate (BER) operation of the link.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
Laser Swept Source with Controlled Mode Locking for OCT Medical Imaging
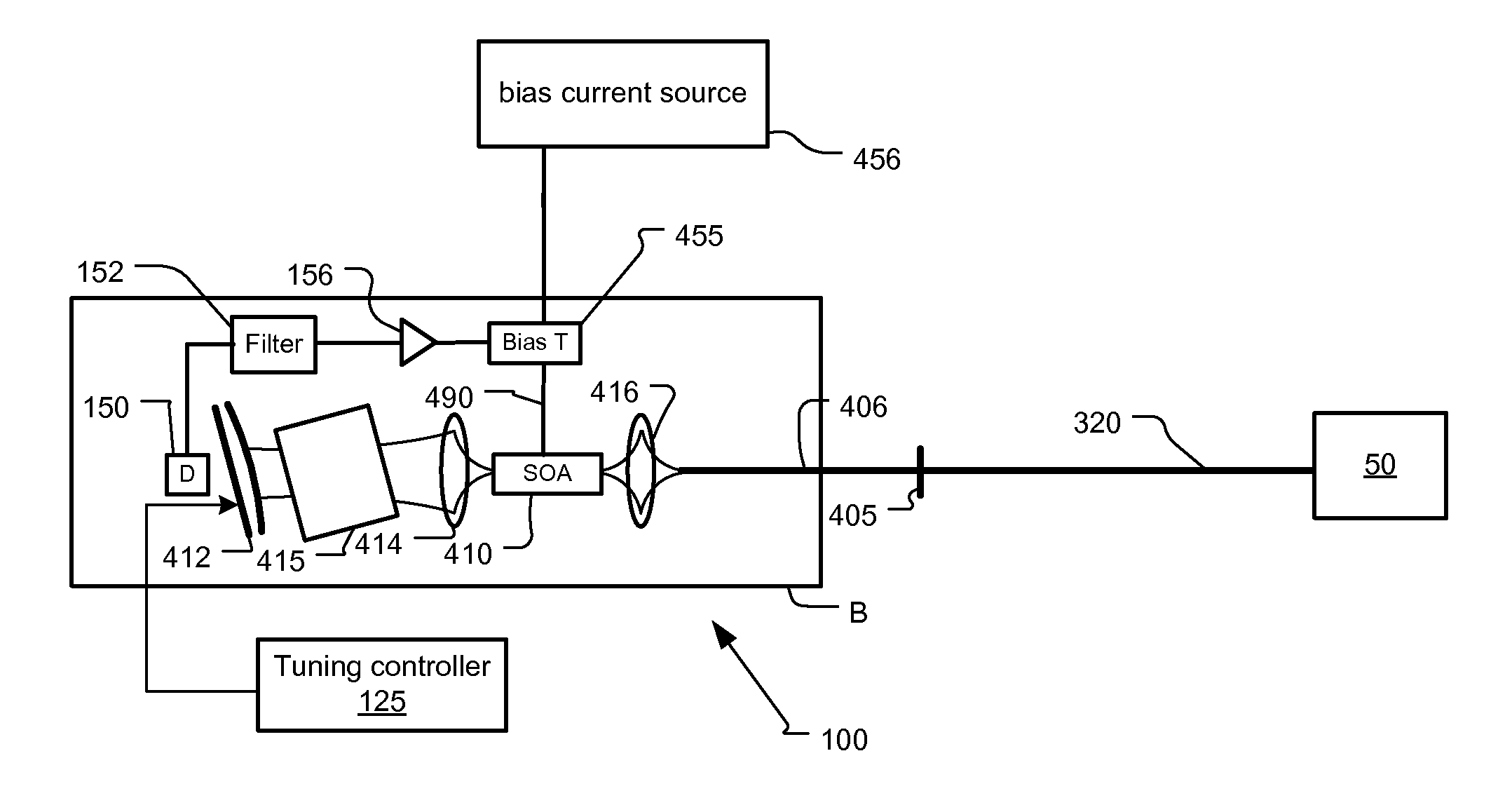
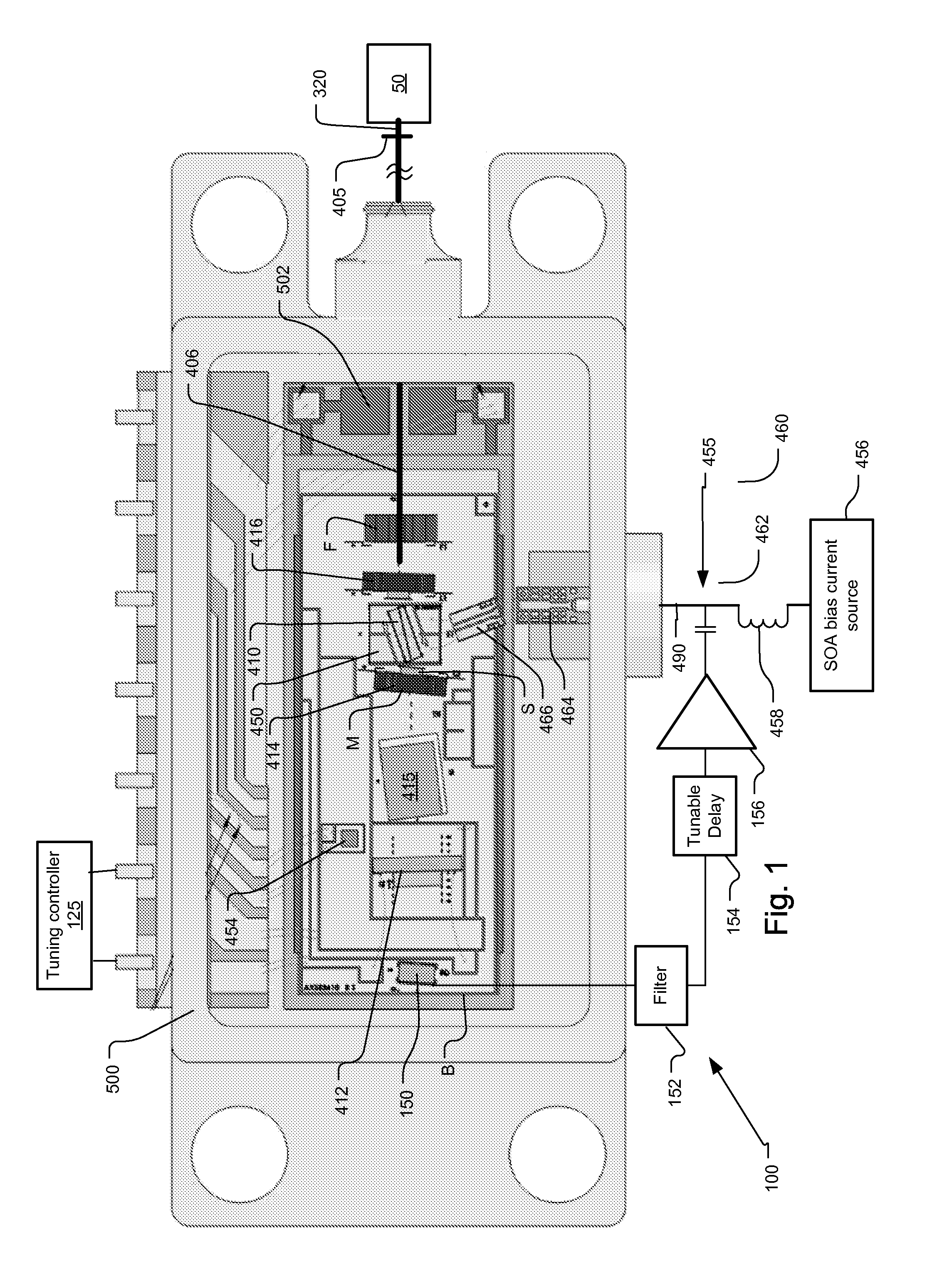
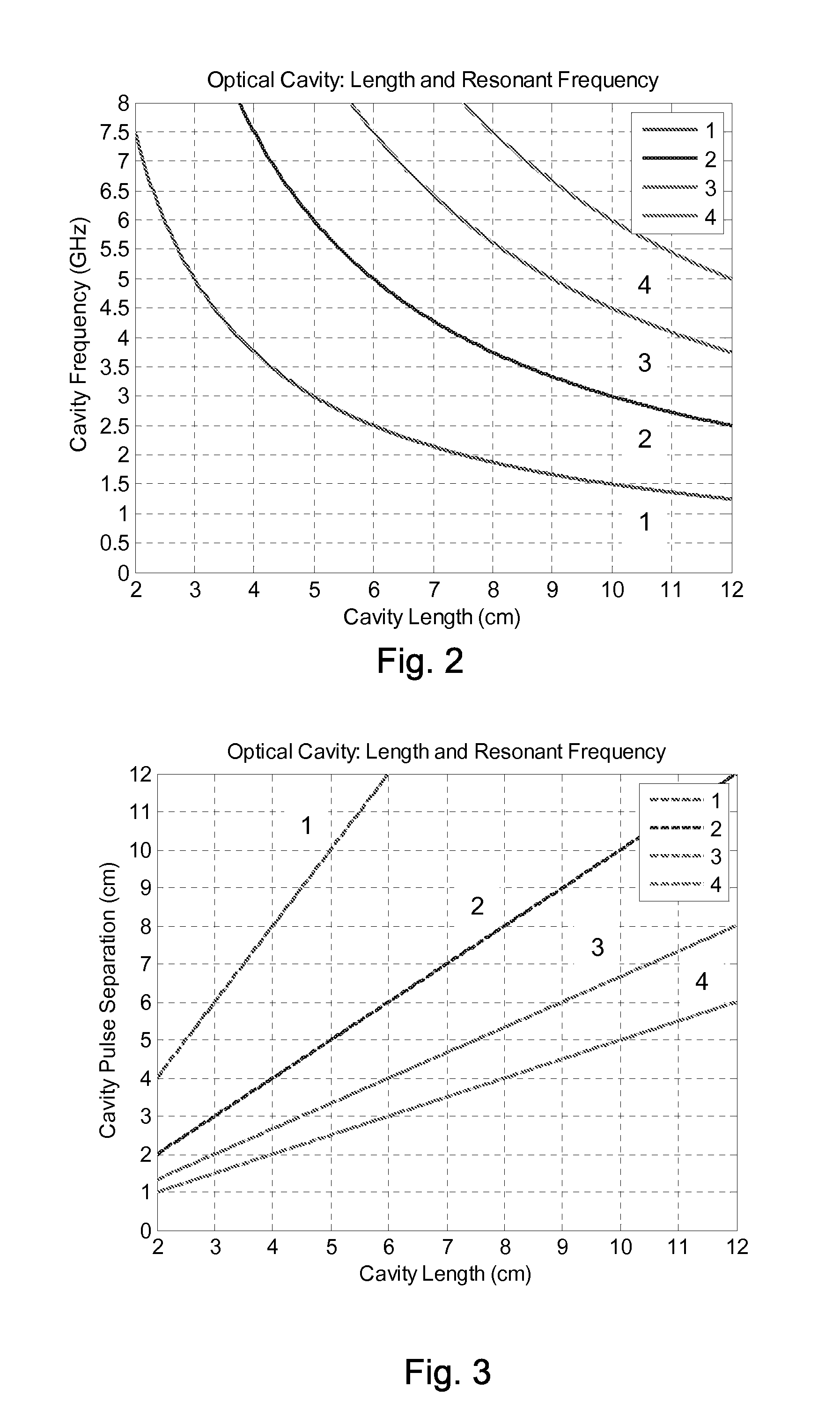
ActiveUS20140085639A1Facilitating high-speed tuningEasy to adjustLaser detailsSolid-state devicesRound-trip gainLaser scanning
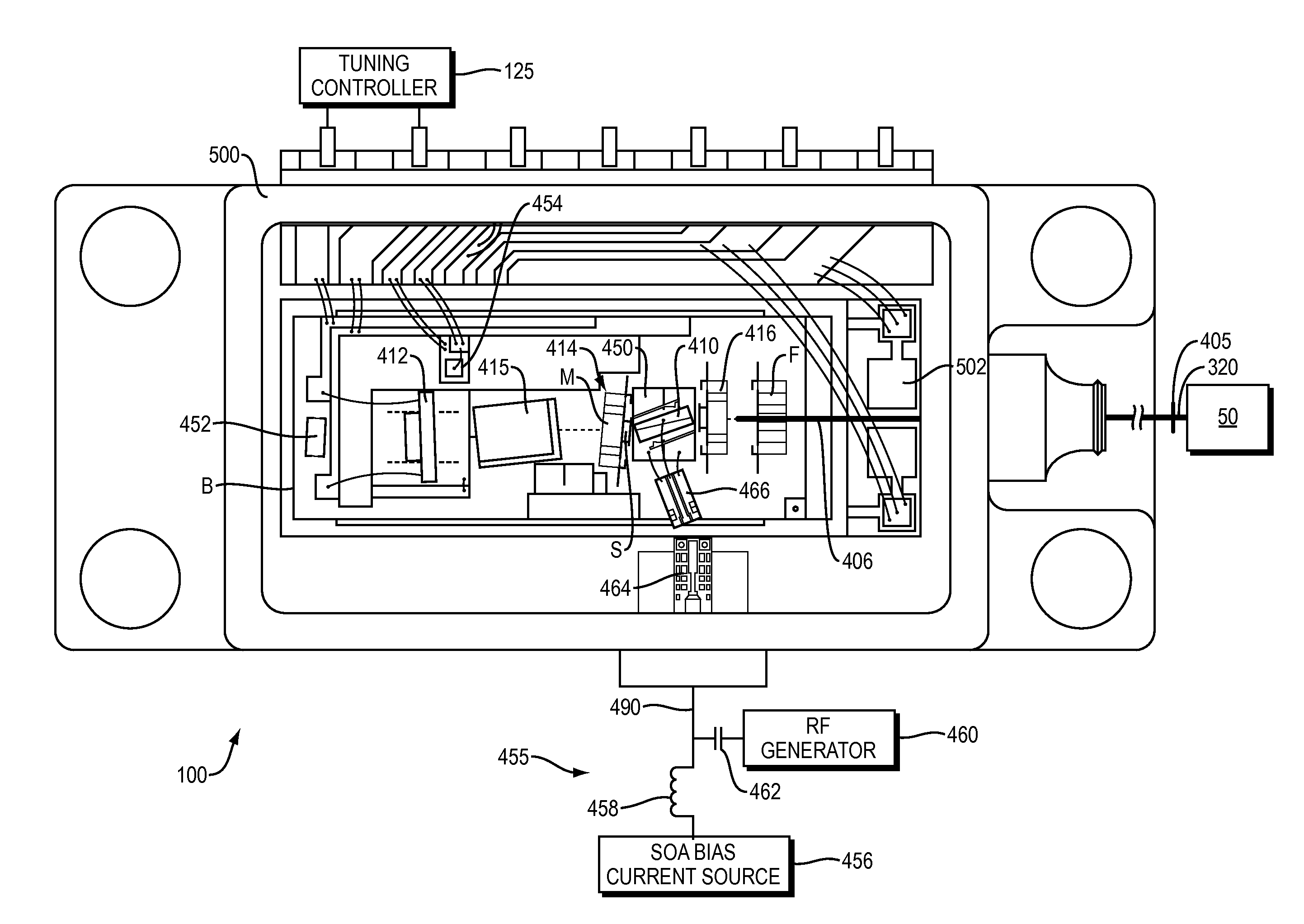
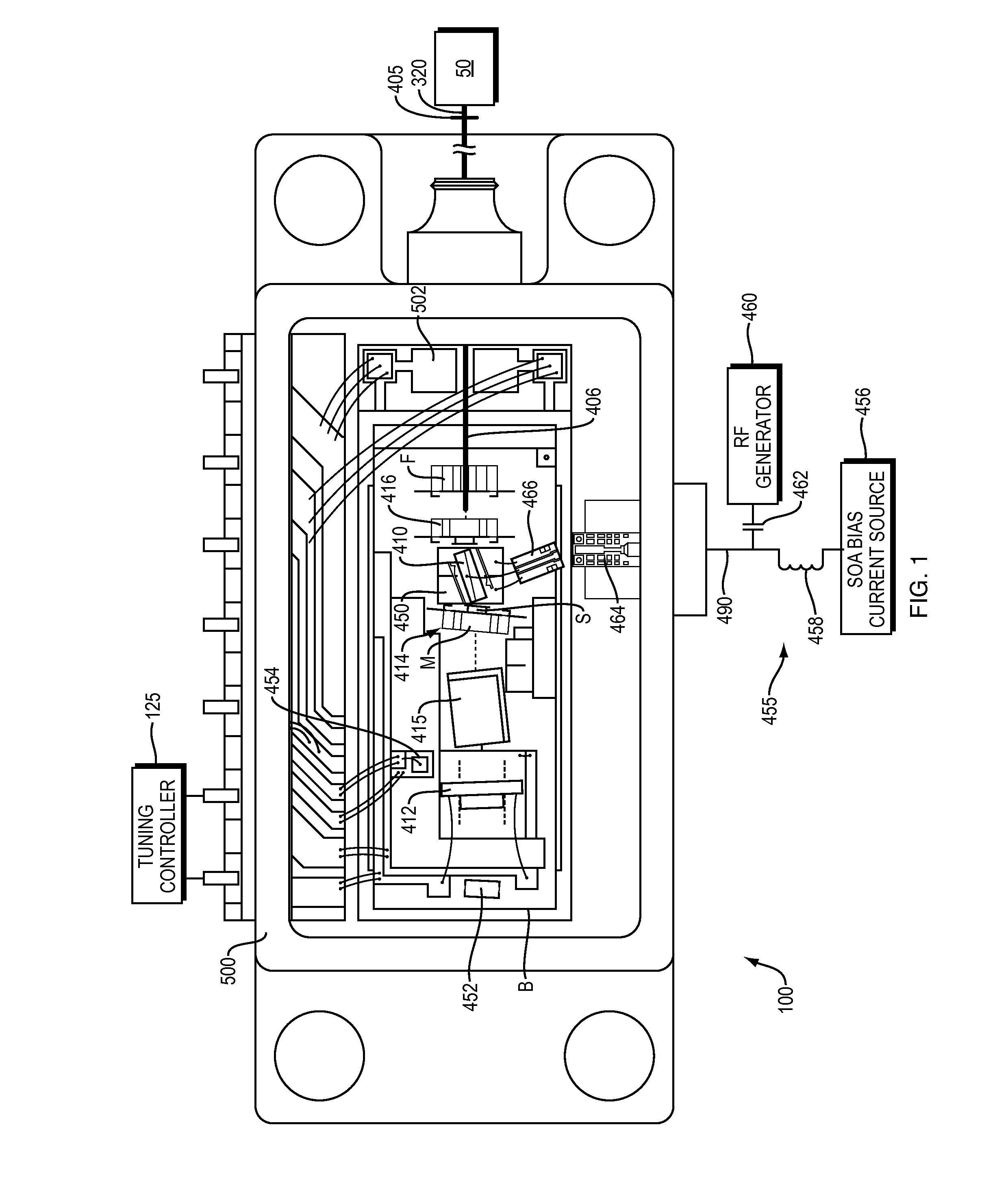
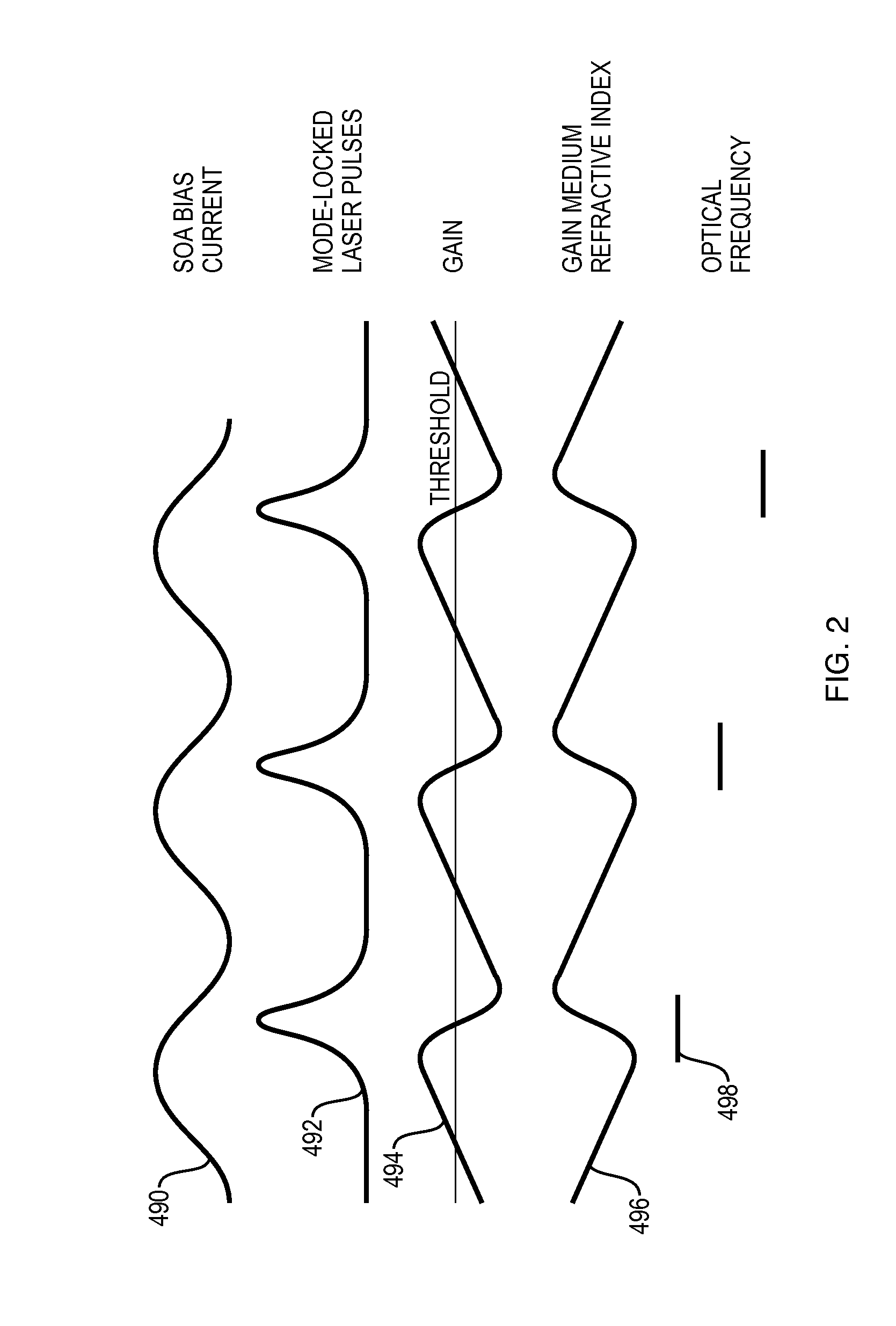
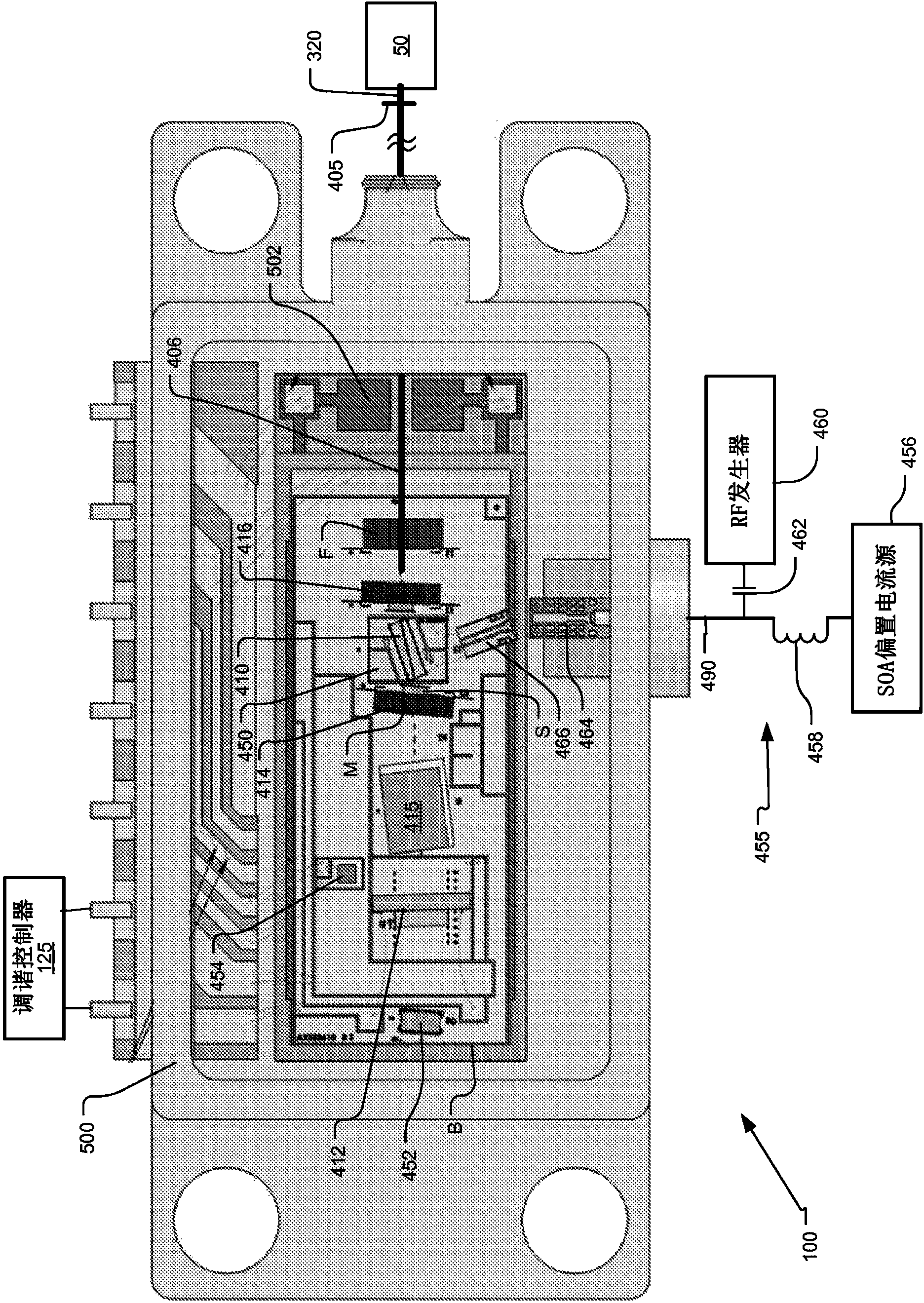
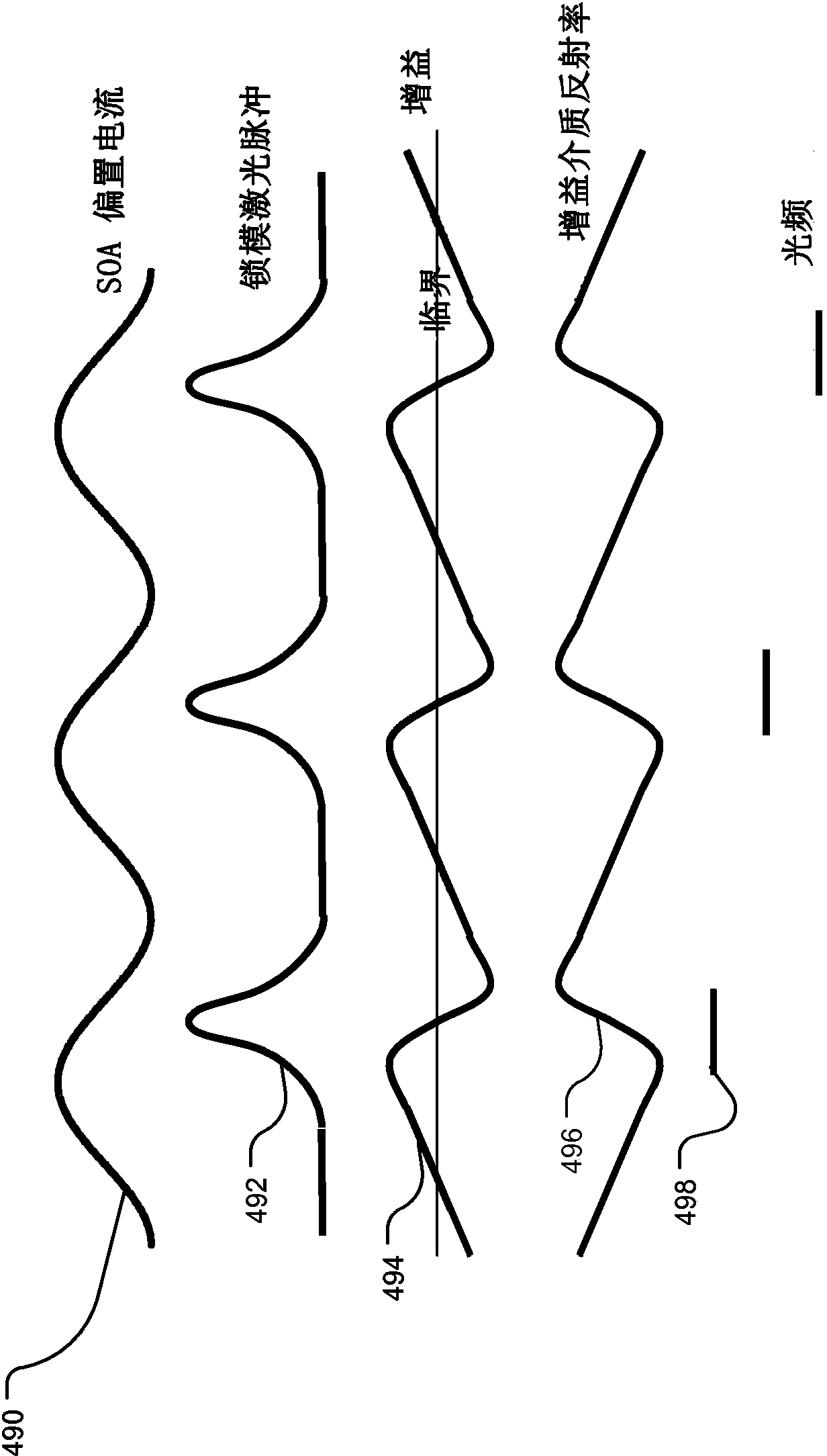
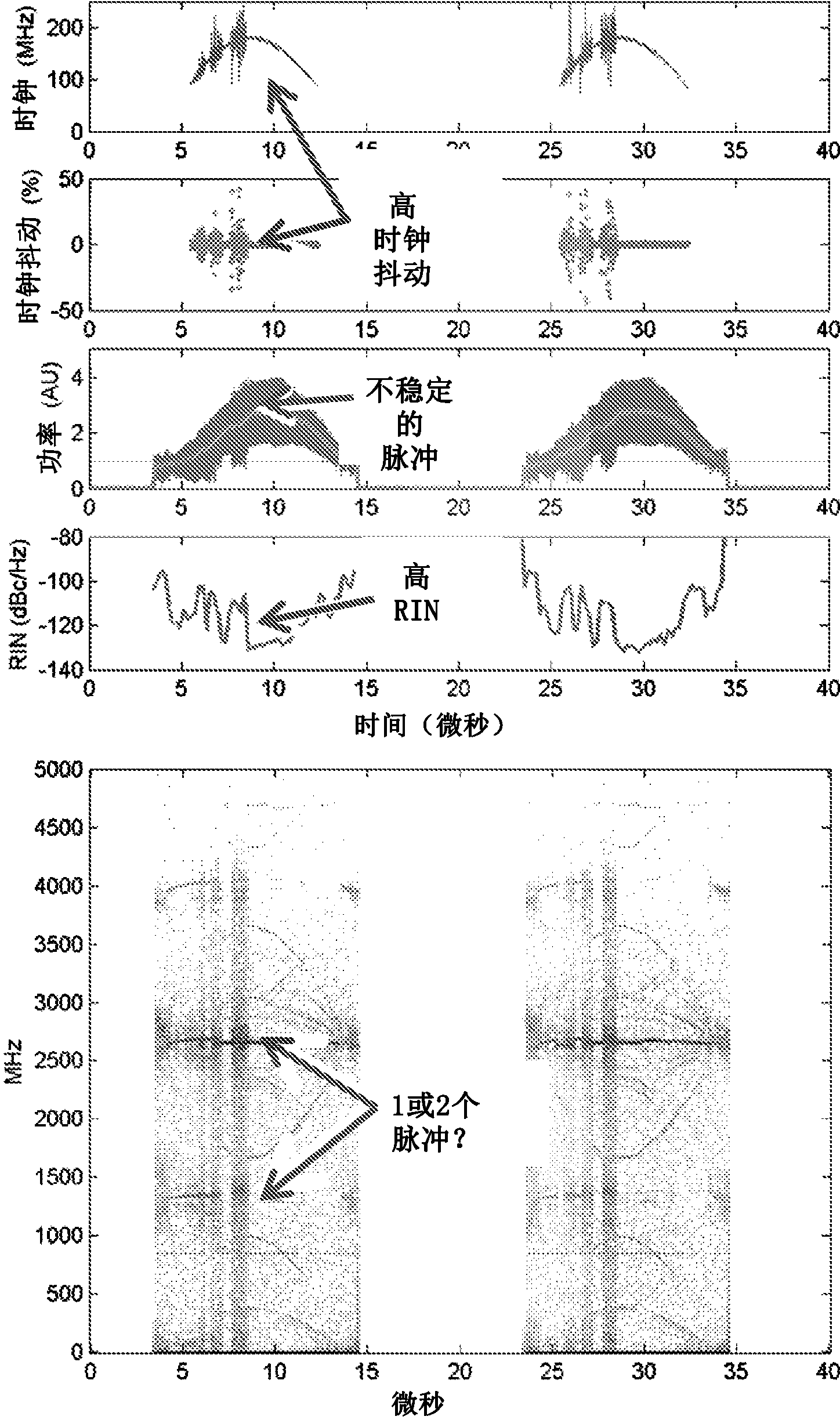
An optical coherence analysis system uses a laser swept source that is constrained to operate in a mode locked condition. This is accomplished by synchronously changing the laser cavity's gain and / or phase based on the round trip travel time of light in the cavity. Many high-speed wavelength swept laser sources emit pulses synchronized with the round trip time of the cavity as part of a nonlinear optical frequency red shifting process. Stable pulsation is associated with smooth tuning and low relative intensity noise. Addition of mode-locking methods to this class of lasers can control and stabilize these lasers to a low clock jitter and RIN state, and in specific cases allow long-to-short wavelength tuning in addition to the usual short-to-long (red shifting). The laser may comprise a SOA (410), a tunable Fabry-Perot-Filter (412) as one reflector and an Output coupler (405) in an optical fiber (406) to adjust the cavity length.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Laser swept source with controlled mode locking for OCT medical imaging
InactiveCN103444020ALaser optical resonator constructionMaterial analysis by optical meansMode-lockingRelative intensity noise
An optical coherence analysis system uses a laser swept source that is constrained to operate in a mode locked condition, which is accomplished by synchronously changing the gain and / or phase of a laser cavity based on the round trip travel time of light in the cavity. A plurality of high-speed wavelength swept laser sources emit pulses synchronized with the round trip time of the cavity as part of a nonlinear optical frequency red shifting process. Stable pulsation is associated with smooth tuning and low relative intensity noise. Addition of mode-locking methods to the class of lasers can control and stabilize the lasers to a low clock jitter and RIN state, and in specific cases allow long-to-short wavelength tuning in addition to the usual short-to-long (red shifting). The laser may comprise a SOA (410), a tunable Fabry-Perot -filter (412) as one reflector and an output coupler (405) in an optical fiber (406) to adjust the cavity length.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Method and apparatus for monitoring angle random walk of a fiber optic gyroscope
ActiveUS20090225323A1Reduce noiseSagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsFiberNoise level
A system for determining a level of angle random walk (ARW) associated with a fiber optic gyroscope (FOG) includes first and second photodiodes. The first photodiode is configured to receive a first light signal from a light source associated with the FOG. The second photodiode is configured to receive a second light signal from a fiber optic coil associated with the FOG. First and second analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) are operable to respectively convert the first and second light signals into corresponding respective first and second digital signals. A digital relative-intensity-noise (RIN) subtraction element is configured to receive the first and second digital signals and output a third signal based on the first and second digital signals. An electronic device is configured to determine a first noise level associated with the third signal, and determine the ARW level from the first noise level.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
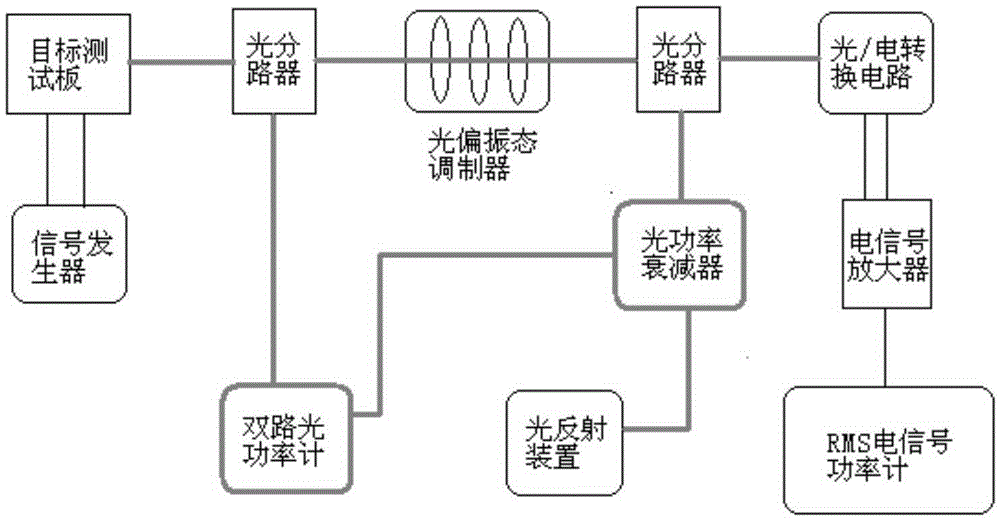
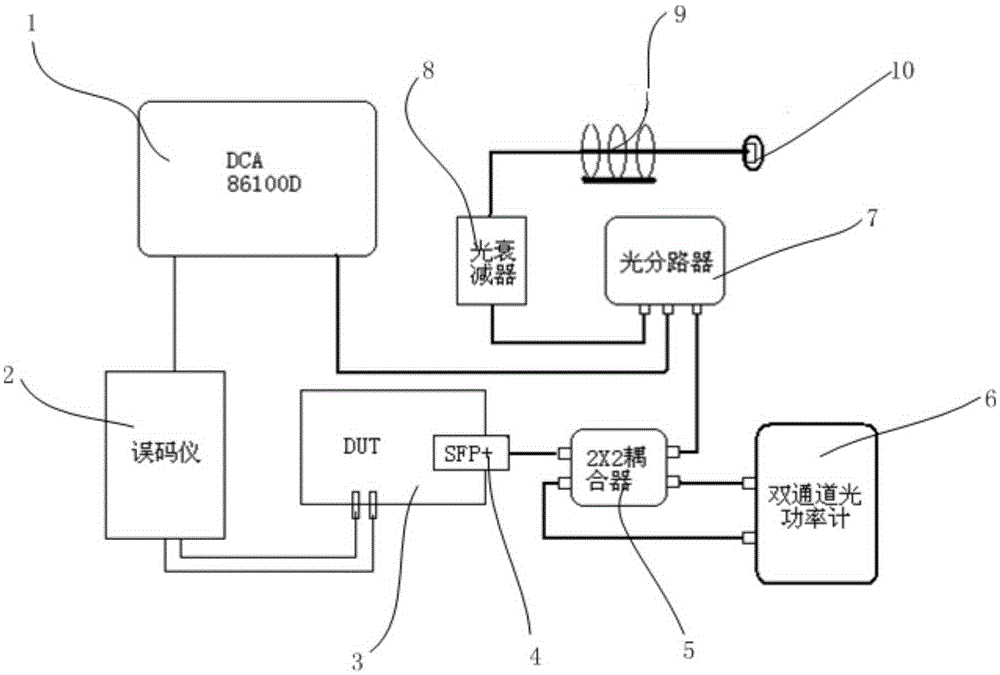
Photoelectric conversion module relative intensity noise test device and test method
ActiveCN105262536AIncrease production capacityRealize inspection batch controlElectromagnetic transmissionOptical power meterRelative intensity noise
The invention discloses a photoelectric conversion module relative intensity noise (RIN) test device and test method, comprising employing an electric signal supply module to supply high speed signals for a photoelectric conversion module to be detected; utilizing a reflection module to form reflected light to interfere the photoelectric conversion module to be detected; utilizing an optical power calculation and display module to control reflected light signal attenuation according to the power difference standard between the emission light and the reflected light of the photoelectric conversion module to be detected; providing required reflection interference light signals for the photoelectric conversion module to be detected; utilizing an optical eye pattern display module to display the emission light eye pattern of the photoelectric conversion module after reflected light interference; and selecting a worst value among the jitter values of the eye patterns in the eye pattern display module as a sampling eye pattern to calculate an RIN index. The test device and test method solve the problems of inconvenient wiring and complex data analysis of a current photoelectric conversion module RIN test method, thereby conveniently and visually obtaining the RIN index of the photoelectric conversion module to be detected.
Owner:JIANGSU ALLRAY
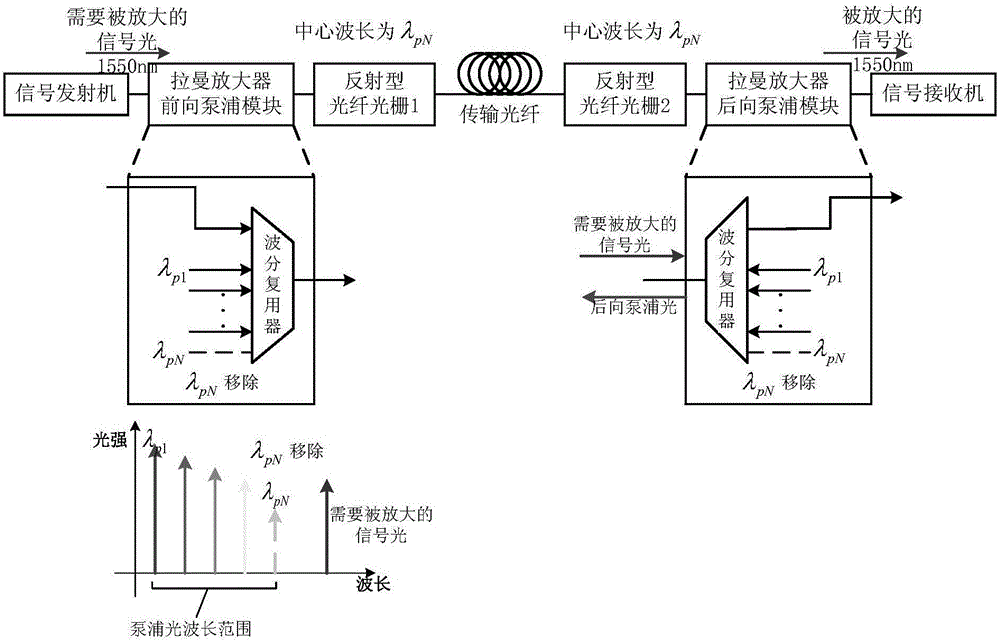
Optical fiber communication transmission system and method applied to multi-wavelength bidirectional pumping high-order bidirectional Raman amplification
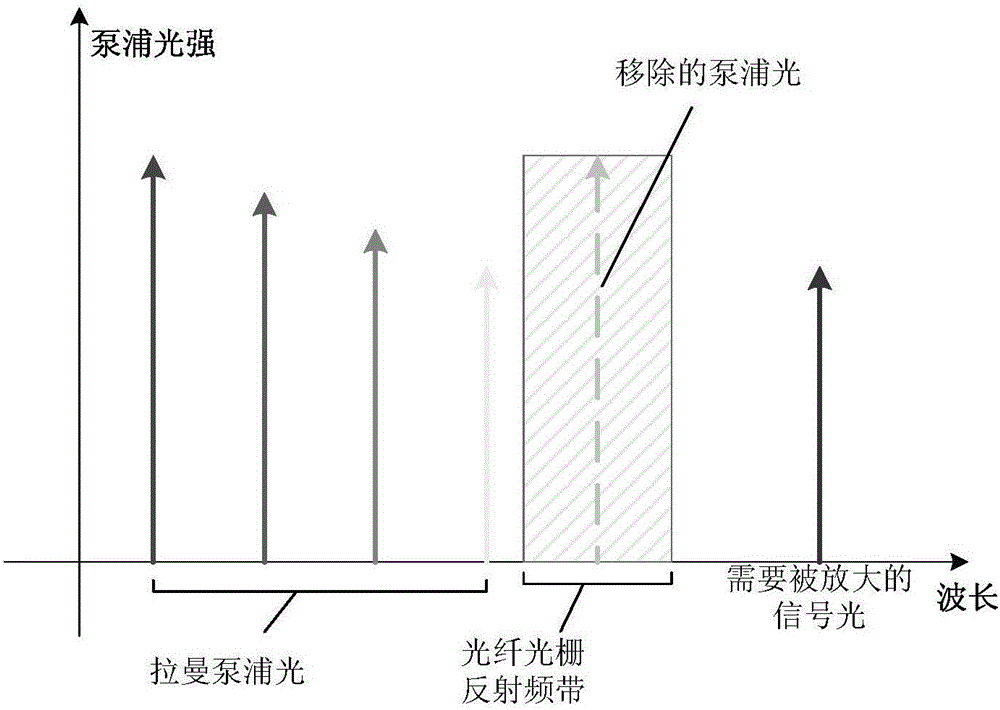
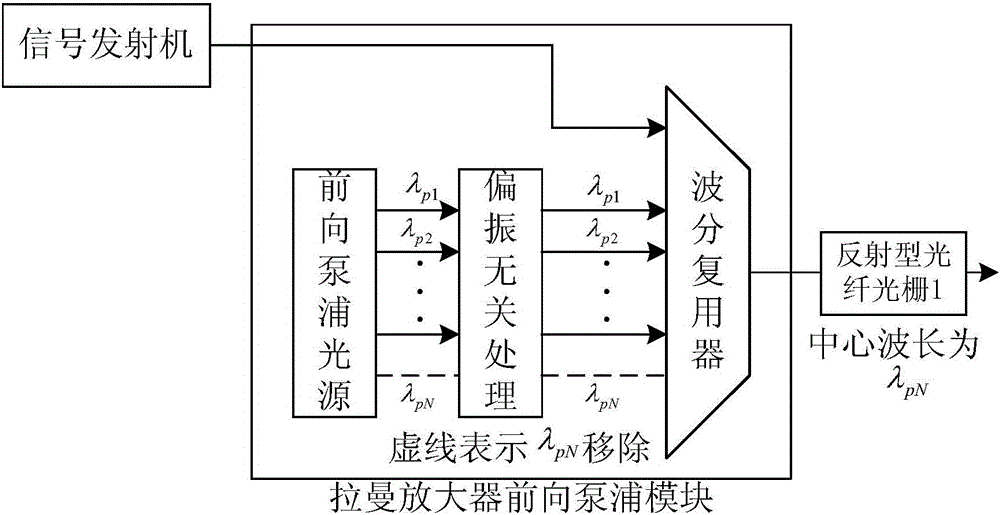
InactiveCN106788751ASuppress intensity noiseIncrease walk awayElectromagnetic transmissionGratingRaman amplifiers
The invention discloses an optical fiber communication transmission system and method applied to multi-wavelength pumping high-order bidirectional Raman amplification, which are applied to an ultra-long span optical fiber communication system and a common optical fiber communication system, can reduce one pump light in a multi-wavelength pumped bidirectional high-order Raman amplifier, and solve the problems of high relative intensity noise and low gain efficiency in a current multi-wavelength pumped high-order Raman amplification process and meanwhile reduce the system cost. A pump light closest to a signal light wavelength is reduced on a forward high-order Raman amplifier; and a reflection-type fiber grating filter is inserted respectively at an output end of the forward high-order Raman amplifier and an input end of a backward high-order Raman amplifier, and the central wavelength of the fiber grating is the wavelength of the pump light that has been reduced. The method of the invention can reduce the number of pump lights of the high-order Raman amplifier and reduce cost, and at the same time, reduce the relative intensity noise of the high-order Raman amplifier, greatly improve the backward gain and forward gain efficiency of the high-order Raman amplifier, and extend the transmission distance of a bidirectional high-order Raman fiber communication system.
Owner:STATE GRID INFORMATION & TELECOMM BRANCH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com