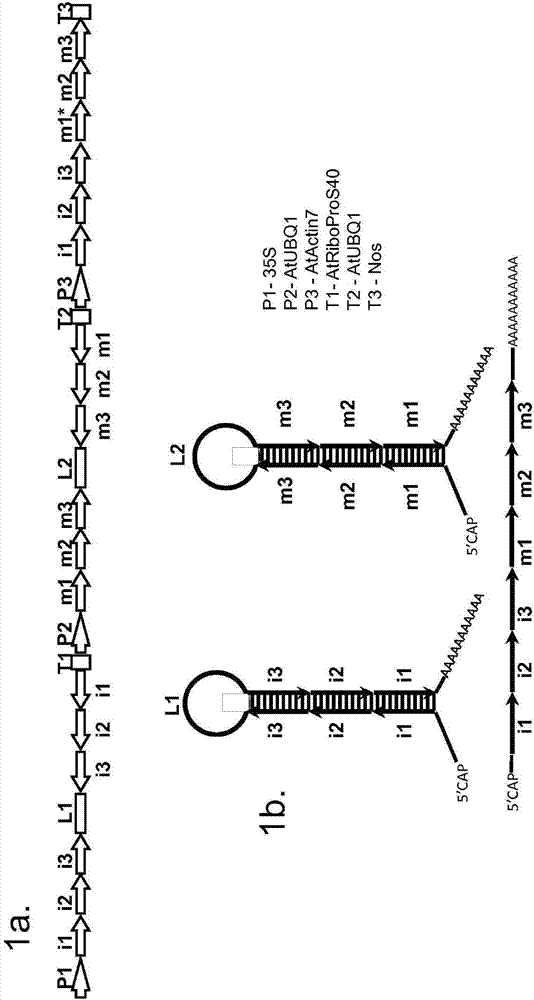
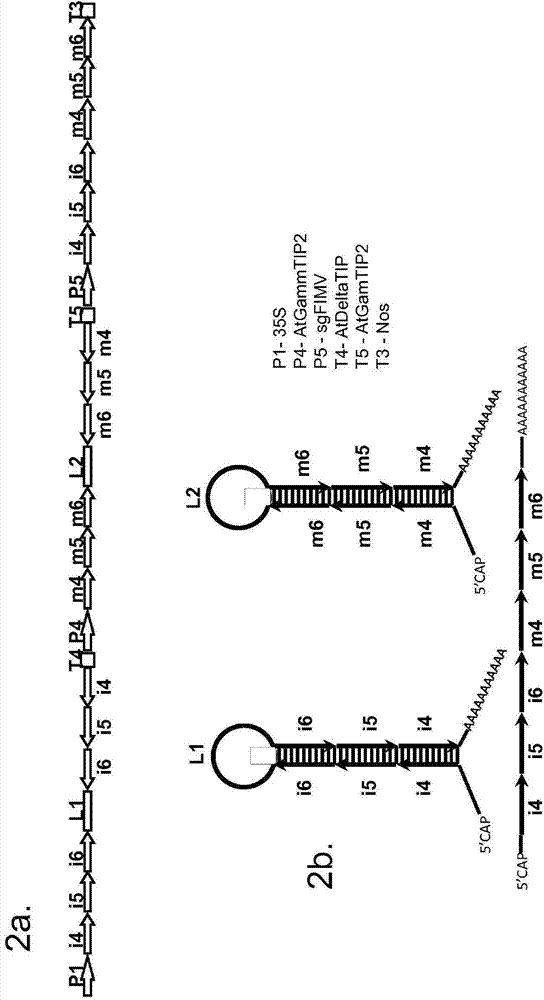
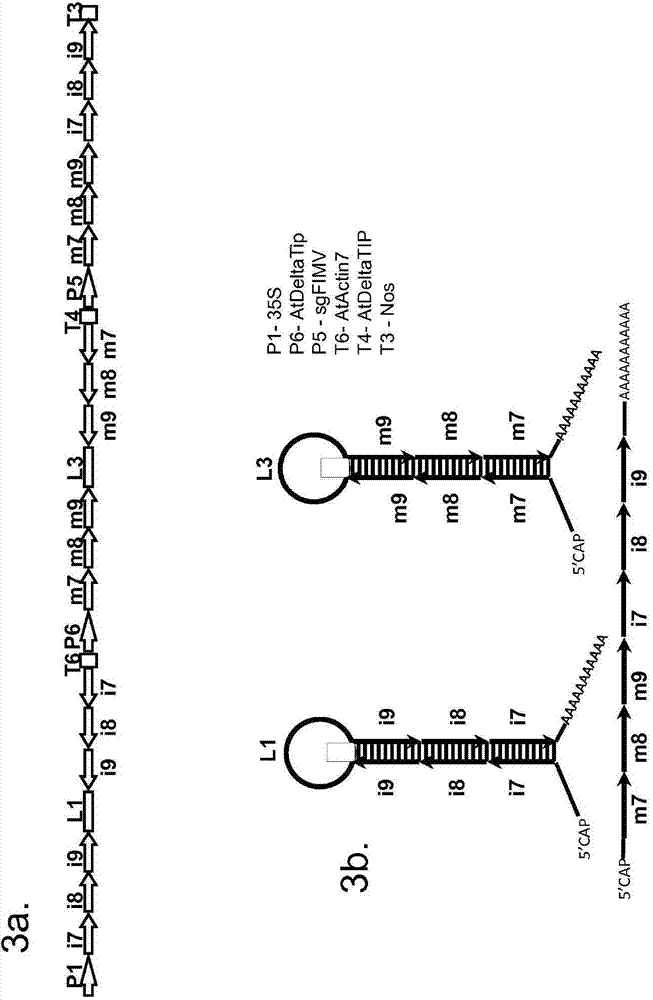
Gall wasp control agents
A nucleic acid and nucleotide technology, applied in the field of gene silencing, which can solve the problems of chemical pesticides that are unfavorable to the environment, harmful to non-target crops and fauna, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0163] gall bee transcriptome sequencing
[0164] Gall wasp-infected leaves were collected from infected red gum from Emek, Israel. Gall wasp larvae were removed from galls found in leaves and / or petioles by cutting and opening the galls with a sharp knife under a binocular microscope. Use a mixture of larvae from various larval developmental stages. Place batches of 100 larvae in microtubes on ice. The tubes were then sealed and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80°C until further processing. Total RNA was isolated using the MasterPure RNA purification kit and manual (MRC85102 - Epicentere Biotechnologies). The total RNA volume was 50 μl. Total RNA was then treated with DNAse to remove any remaining residual DNA, followed by isolation of poly A mRNA (MicroPoly(A) Purist, Small Scale mRNA Purification Kit, AM1919Ambion). The final volume of mRNA was 20 μl. Purified mRNA was stored at -80°C until 454 sequencing. 454 sequencing was performed according...
Embodiment 2
[0166] Identification of Li and Om target genes and sequences
[0167]Unique viable Li and Om genes that are critical for cellular processes or proper developmental progression in specific tissues or whole organisms are selected as targets for gene silencing. First, standard procedures based on degenerate primers of known homologous Hymenopteran sequences will be used to identify fragments of the target gene. Thereafter, the respective transcriptomes of Li and Om gall wasp larvae were sequenced using the 454 Sequencer deep sequencing platform (454 Life Sciences; Branford, CT, USA; now Roche, Basel). Using the Roche software package and annotated using the Blast2Go program (available at http: / / www.blast2go.org / ), sequences were assembled and the results annotated based on sequence alignments with known published Hymenopteran transcriptomes.
[0168] Table 1 gives SEQ ID NO: Complete or partial gene sequences of the identified genes 1-9 from Li and Om.
[0169] Table 1. Li...
Embodiment 3
[0184] Identification of Li and Om target genes and sequences
[0185] A BLAST (NCBI) comparison (15,16) using 141 genes that are lethal when expressed as RNAi in Drosophila was used to identify 127 direct to homologous sequences. The identified Nv sequences were further used to screen the lethal genes of the Om and Li transcriptome libraries prepared in Example 1. The screen identified 39 potential target sequences from the Om transcriptome library and 48 potential targets from the Li transcriptome library comprising a contiguous reading frame of at least 500 nucleotides, and 1 sequence comprising a 309 nucleotide Potential Li-derived target genes (SEQ ID NO:76) of contiguous open reading frames, or at least 50% of each predicted full-length gene. In one example, a BLAST (NCBI) comparison using the Drosophila melanogaster gene ADV37321 (CG18740) (15), which has been identified as an RNAi-lethal factor, was used to identify the Nv homolog gene XP_001605573. The Nv homolog...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com