A bio-based thermoplastic elastomer material and a preparation method thereof
A thermoplastic elastomer and bio-based technology, applied in the field of bio-based thermoplastic elastomer materials and their preparation, can solve the problems of low strength and difficulty in continuous production, and achieve high strength, low cost and good resilience
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
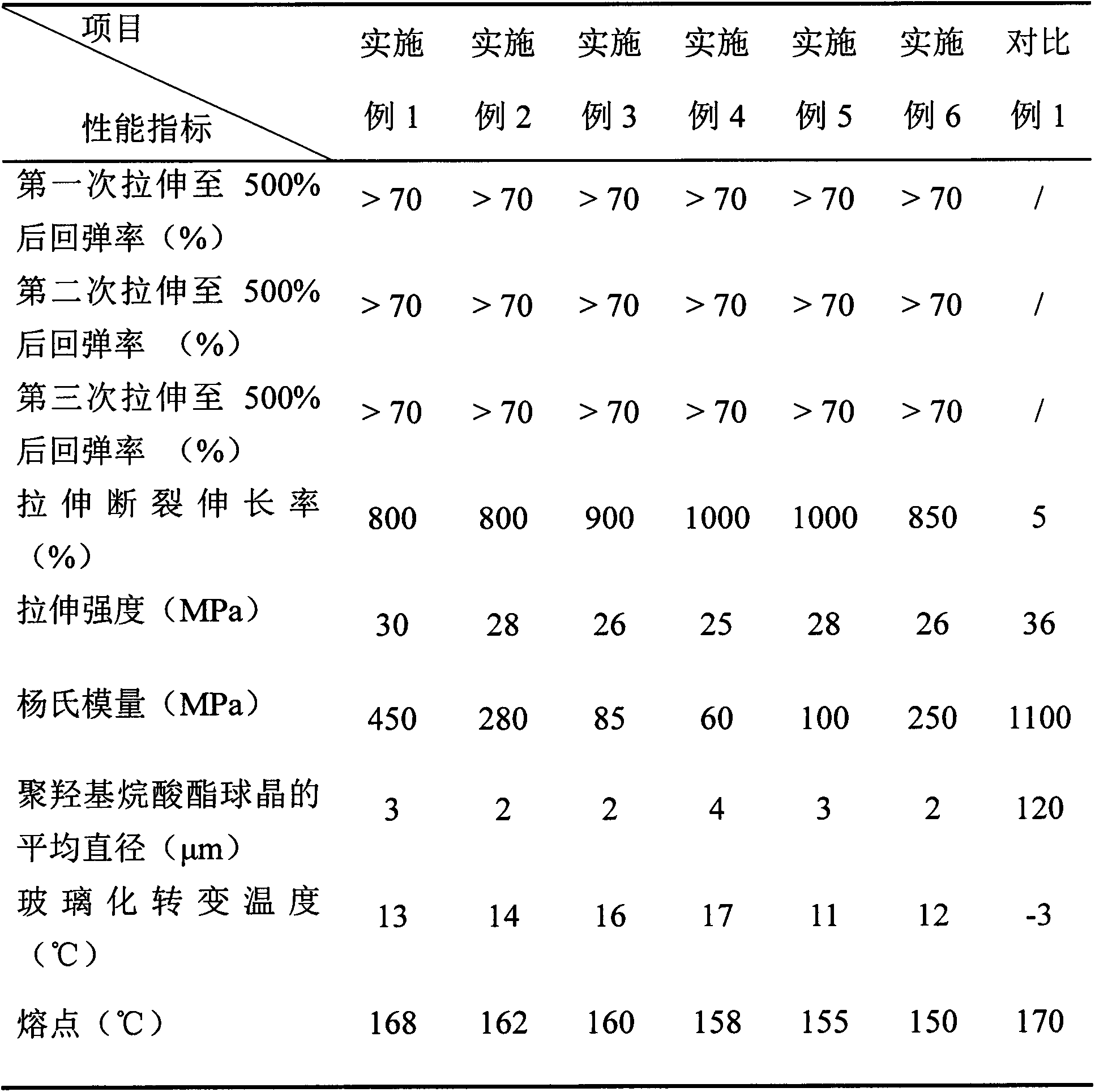
[0021] 42kg of 3-hydroxybutyrate homopolymer, 28kg of 3-hydroxybutyrate-4-hydroxybutyrate copolymer with 4-hydroxybutyrate monomer molar content of 28%, and 90% of vinyl acetate monomer by weight Ethylene-vinyl acetate random copolymer 30kg, behenic acid amide 0.35kg are premixed uniformly in a high-speed mixer (720 rev / min, 5 minutes), and then the above-mentioned premix is added to a parallel twin-screw extruder to melt Blend extrusion to obtain bio-based thermoplastic elastomer material. The temperatures of the twin-screw extruder from the feeding section to the die section were 30°C, 150°C, 155°C, 160°C, and 165°C, respectively, and the screw speed was 100 rpm. The bio-based thermoplastic elastomer material was pressed into a sheet by a flat vulcanizer for testing of tensile properties, resilience, spherulite morphology and thermal properties. The test results are listed in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0023] 30kg of 3-hydroxybutyrate homopolymer, 20kg of 3-hydroxybutyrate-4-hydroxybutyrate copolymer with 28% molar content of 4-hydroxybutyrate monomer, and 90% of vinyl acetate monomer by weight Ethylene-vinyl acetate random copolymer 50kg, behenic acid amide 0.25kg are premixed uniformly in a high-speed mixer (720 rev / min, 5 minutes), then the above-mentioned premix is added to a parallel twin-screw extruder to melt Blend extrusion to obtain bio-based thermoplastic elastomer material. The temperatures of the twin-screw extruder from the feeding section to the die section were 30°C, 150°C, 155°C, 160°C, and 165°C, respectively, and the screw speed was 120 rpm. The bio-based thermoplastic elastomer material was pressed into a sheet by a flat vulcanizer for testing of tensile properties, resilience, spherulite morphology and thermal properties. The test results are listed in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0025] 28kg of 3-hydroxybutyrate homopolymer, 20kg of 3-hydroxybutyrate-4-hydroxybutyrate copolymer with 28% molar content of 4-hydroxybutyrate monomer, and 90% of vinyl acetate monomer by weight Ethylene-vinyl acetate random copolymer 110kg, behenic acid amide 0.25kg are premixed uniformly in a high-speed mixer (720 rev / min, 5 minutes), then the above-mentioned premix is added to a parallel twin-screw extruder to melt Blend extrusion to obtain bio-based thermoplastic elastomer material. The temperatures of the twin-screw extruder from the feeding section to the die section were 30°C, 150°C, 155°C, 160°C, and 165°C, respectively, and the screw speed was 150 rpm. The bio-based thermoplastic elastomer material was pressed into a sheet by a flat vulcanizer for testing of tensile properties, resilience, spherulite morphology and thermal properties. The test results are listed in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com