Multi-module DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) library and method for constructing transcription activator like effector nuclease plasmid
A transcription activation and effector technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of material cost, time cost, high sequencing cost, unfavorable TALEN specificity, cumbersome operation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
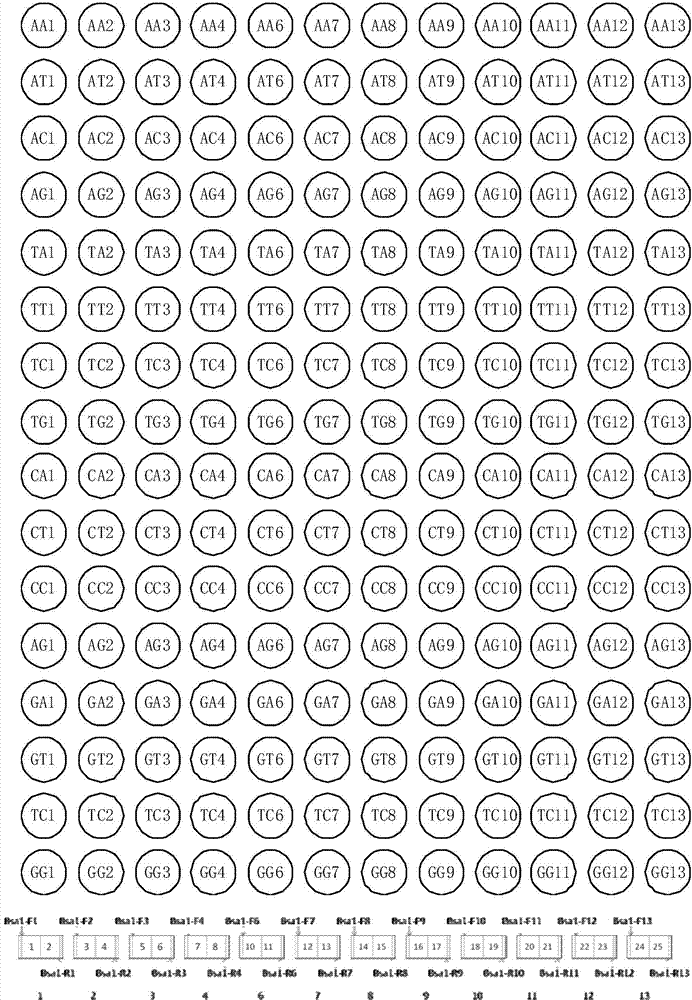
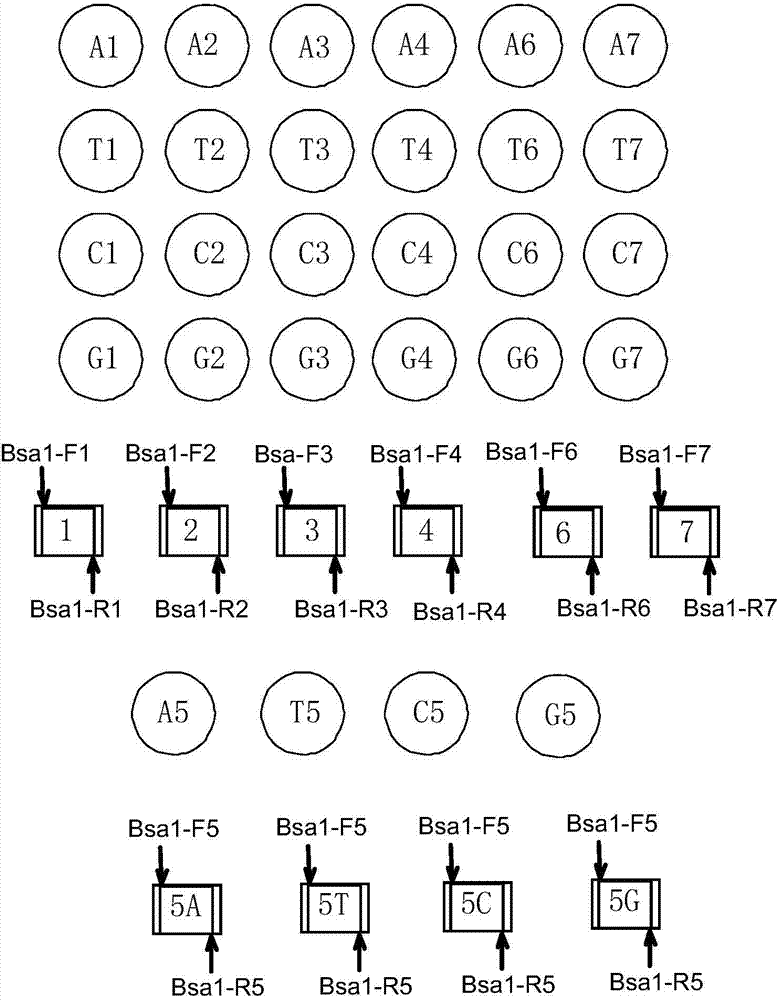
[0071] Example 1 Connection between TALENs recognition modules and construction of recombinant vector
[0072] In a preferred mode of the present invention, n=12, m=7, p=4; in the multi-module unit library, the number of double-base linking units is 12, which are divided into two groups, numbered 1-4 and 6-13 , the base sequences of the first cohesive end and the second cohesive end are respectively shown in the 9th-12th bases of SEQ ID No.45-52 and SEQ ID No.55-70. There are 7 single-base linking units in each group, and the coded amino acid sequences are, for example, the base sequences of the first sticky end and the second sticky end of the single-base linking units numbered 1 to 7, respectively, such as SEQ ID No.45-58 Bases 9-12 are indicated. The first sticky end of the single-base linking unit numbered 5 is complementary to the second sticky end of the double-base linking unit numbered 4, and the second sticky end is complementary to the first sticky end of the double...
Embodiment 2
[0143] Ligate TALENs that recognize the following bases.
[0144] Fragment 1: CGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCT,
[0145] Fragment 2: CGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCT,
[0146] Fragment 3: CCCACTCGTCCCATCCAGTA;
[0147] (1) First select the required recognition module from the PCR library:
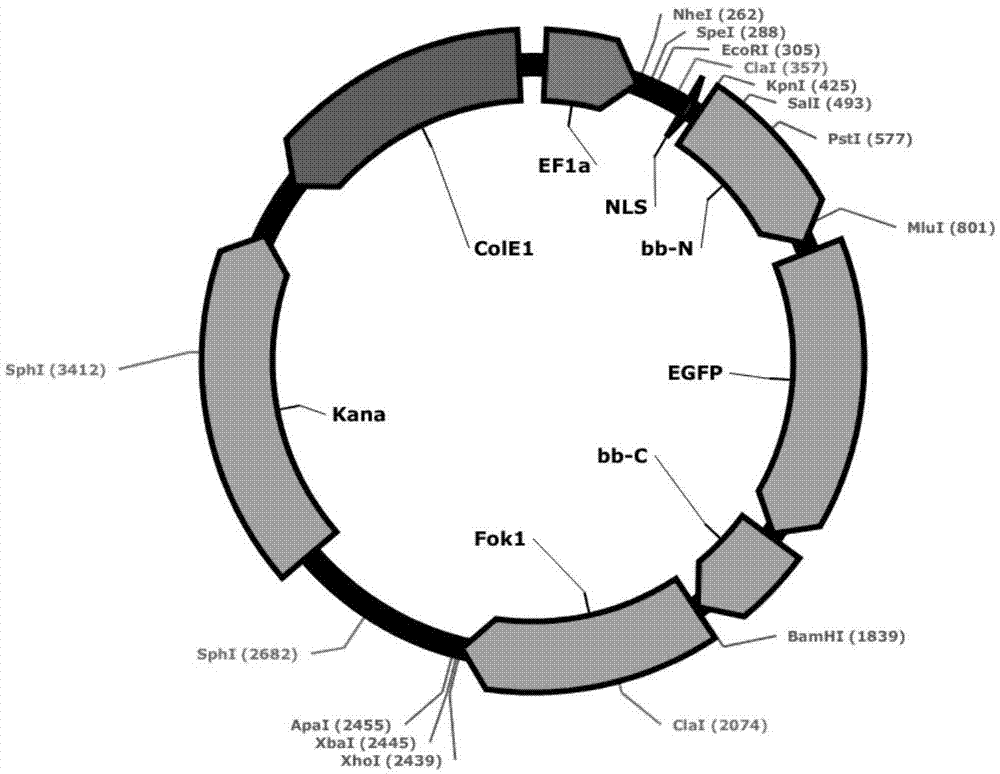
[0148] CGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCT selection modules CG-1, CG-2, CG-3, CG-4, C-5, GC-6, GC-7, GC-8, GC-9, GC-10, GC-11, GC-12 , GC-13; the connection vector is pEF1a-NLS-TALE backbone-Fok1(R)–pA (with a T recognition module on the vector).
[0149] CGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCGCT selection modules C-1, G-2, C-3, G-4, C-5, GC-6, GC-7, GC-8, GC-9, GC-10, GC-11, GC-12 , GC-13. The connection vector is pEF1a-NLS-TALE backbone-Fok1(R)-pA (with a T recognition module on the vector).
[0150] CCCACTCGTCCCATCCAGTA select modules C-1, C-2, C-3, A-4, C-5, T-6, C-7, GT-8, CC-9, CA-10, TC-11, CA-12 , GT-13. The connection vector is pEF1a-NLS-TALE backbone-Fok1(R)-pA (with an A recognition module on the vector).
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com