A microcavity interference flow velocity pressure difference sensitive structure and a microcavity interference fiber optic velocity flow sensor
A flow sensor and sensitive structure technology, applied in fluid velocity measurement, velocity/acceleration/shock measurement, measurement flow/mass flow, etc., can solve the problems of measurement sensitivity drop, polarization signal fading, signal temperature drift, etc., to eliminate polarization The effect of signal fading, interference elimination, and high measurement sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
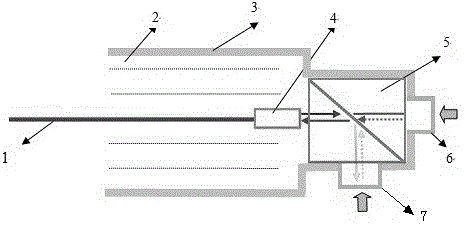
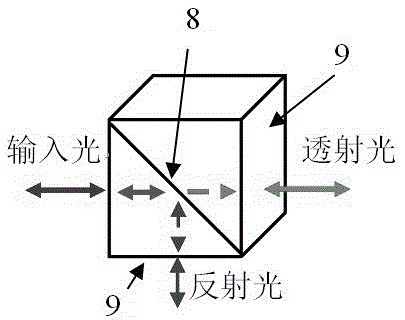
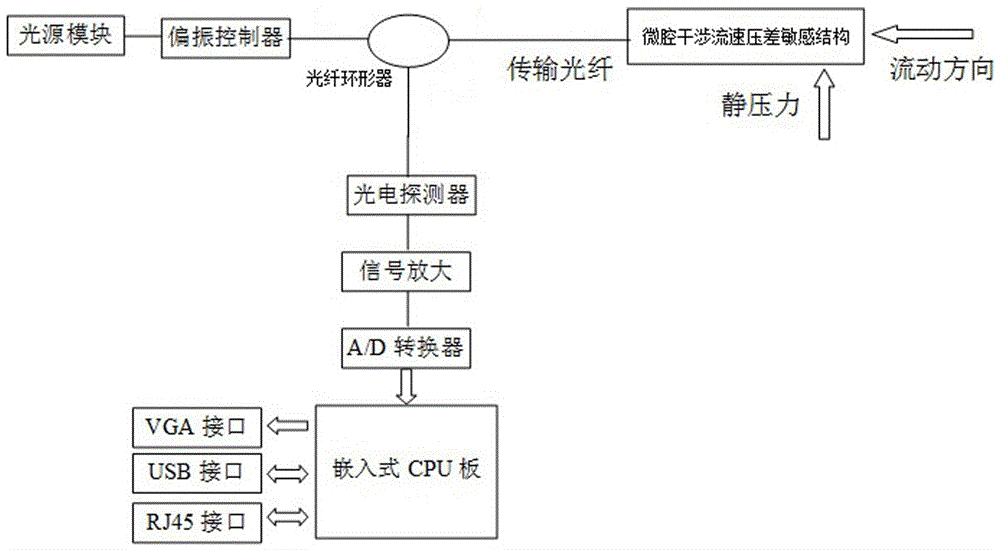
[0051] The microcavity interference flow rate pressure difference sensitive structure of this embodiment includes a transmission optical fiber, a housing, an optical fiber collimator disposed in the housing, and a light beam splitting cube; the light beam splitting cube is connected to and sleeved on the housing The first pressure-sensitive diaphragm for sensing hydrostatic pressure and the second pressure-sensitive diaphragm for sensing fluid velocity pressure; the optical fiber collimator collimates the light wave signal in the transmission fiber and outputs it to the optical beam splitting cube , and the interference light wave signal generated by the reflection of the first and second pressure-sensitive diaphragms is coupled into the transmission fiber; The reflected light of the sensitive diaphragm interferes to form an interference light wave signal carrying flow velocity and pressure difference information.
Embodiment 2
[0053] The microcavity interference flow rate pressure difference sensitive structure of this embodiment includes a transmission optical fiber, a housing, an optical fiber collimator disposed in the housing, and a light beam splitting cube; the light beam splitting cube is connected to and sleeved on the housing The first pressure-sensitive diaphragm for sensing hydrostatic pressure and the second pressure-sensitive diaphragm for sensing fluid velocity pressure; the optical fiber collimator collimates the light wave signal in the transmission fiber and outputs it to the optical beam splitting cube , and the interference light wave signal generated by the reflection of the first and second pressure-sensitive diaphragms is coupled into the transmission fiber; The reflected light of the sensitive diaphragm interferes to form an interference light wave signal carrying flow velocity and pressure difference information; the housing is filled with packaging filling materials for stabl...
Embodiment 3
[0055]The microcavity interference flow velocity and pressure difference sensitive structure of this embodiment includes a transmission optical fiber, a housing, a self-focusing lens arranged in the housing, and a light beam splitting cube; the light beam splitting cube is connected to and sleeved on the housing. The first pressure-sensitive diaphragm for sensing hydrostatic pressure and the second pressure-sensitive diaphragm for sensing fluid velocity pressure; the self-focusing lens collimates the light wave signal in the transmission fiber and outputs it to the light beam splitting cube, And the interference light wave signal generated by reflecting back the first and second pressure-sensitive diaphragms is coupled into the transmission fiber; the light beam splitting cube divides the output light of the self-focusing lens into two beams, and makes the first and second pressure-sensitive diaphragms The reflected light of the sheet interferes to form an interference light wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com